The Navigation component includes a NavigationUI
class. This class contains static methods that manage navigation with the top
app bar, the navigation drawer, and bottom navigation.
Top app bar
The top app bar provides a consistent place along the top of your app for displaying information and actions from the current screen.
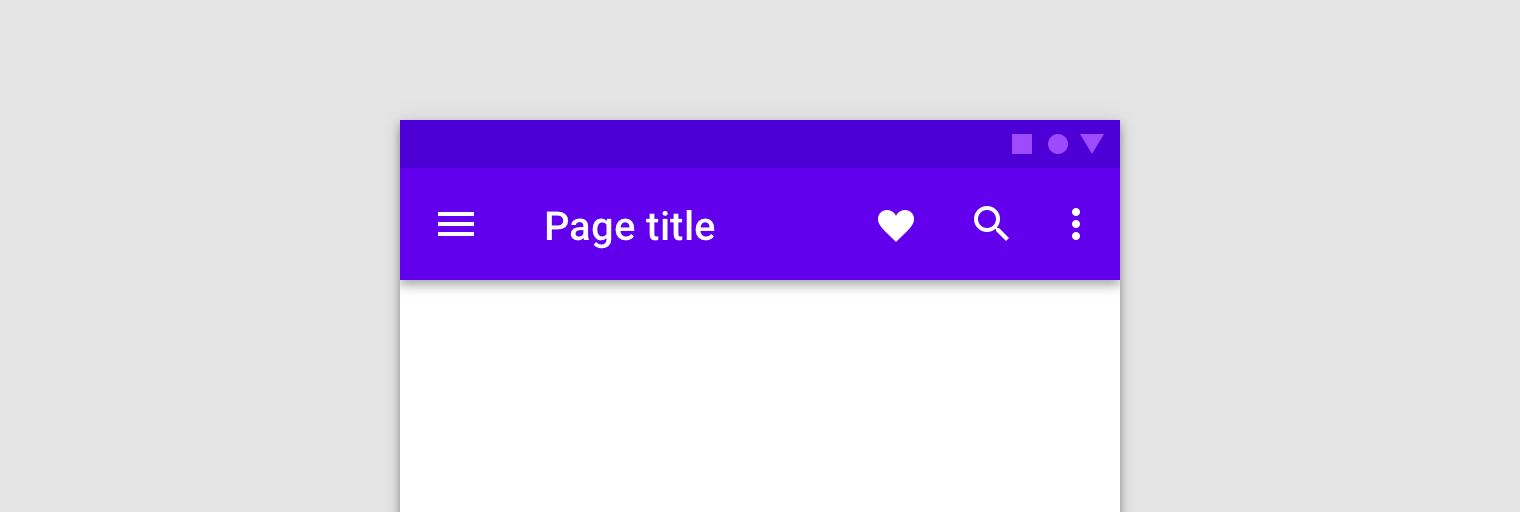
NavigationUI contains methods that automatically update content in your top
app bar as users navigate through your app. For example, NavigationUI uses the
destination labels from your navigation graph to keep the title of the top app
bar up-to-date.
<navigation> <fragment ... android:label="Page title"> ... </fragment> </navigation>
When using NavigationUI with the top app bar implementations discussed below,
the label you attach to destinations can be automatically populated from the
arguments provided to the destination by using the format of {argName} in your
label.
NavigationUI provides support for the following top app bar types:
For more information on app bars, see Set up the app bar.
AppBarConfiguration
NavigationUI uses an AppBarConfiguration
object to manage the behavior of the Navigation button in the upper-left corner
of your app's display area. The Navigation button’s behavior changes depending
on whether the user is at a top-level destination.
A top-level destination is the root, or highest level destination, in a set of hierarchically-related destinations. Top-level destinations do not display an Up button in the top app bar because there is no higher level destination. By default, the start destination of your app is the only top-level destination.
When the user is at a top-level destination, the Navigation button becomes a
drawer icon
![]() if the destination uses a
if the destination uses a DrawerLayout. If the destination doesn't use a
DrawerLayout, the Navigation button is hidden. When the user is on any other destination, the Navigation button appears as an Up button
 .
To configure the Navigation button using only the start destination as the
top-level destination, create an
.
To configure the Navigation button using only the start destination as the
top-level destination, create an AppBarConfiguration object, and pass in the corresponding navigation graph, as shown below:
Kotlin
val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph)
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build();
In some cases, you might need to define multiple top-level destinations instead
of using the default start destination. Using a BottomNavigationView is a
common use case for this, where you may have sibling screens that are not
hierarchically related to each other and may each have their own set of related
destinations. For cases like these, you can instead pass a set of destination
IDs to the constructor, as shown below:
Kotlin
val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(setOf(R.id.main, R.id.profile))
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(R.id.main, R.id.profile).build();
Create a Toolbar
To create a Toolbar with NavigationUI, first define the bar in your main
activity, as shown:
<LinearLayout> <androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar android:id="@+id/toolbar" /> <androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment" ... /> ... </LinearLayout>
Next, call setupWithNavController()
from your main activity's onCreate() method, as shown in the following
example:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment) val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) .setupWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(this, R.id.nav_host_fragment); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController( toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
To configure the Navigation button to appear as an Up button for all
destinations, pass an empty set of destination IDs for your top-level
destinations when building your AppBarConfiguration. This can be useful
if, for example, you have a second activity that should display an Up button
in the Toolbar on all destinations. This allows the user to navigate back
to the parent activity when there are no other destinations on the back
stack. You can use
setFallbackOnNavigateUpListener()
to control the fallback behavior for when navigateUp() would otherwise
do nothing, as shown in the following example:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration( topLevelDestinationIds = setOf(), fallbackOnNavigateUpListener = ::onSupportNavigateUp ) findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) .setupWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = (NavHostFragment) supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder() .setFallbackOnNavigateUpListener(::onSupportNavigateUp) .build(); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController( toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
Include CollapsingToolbarLayout
To include a CollapsingToolbarLayout with your Toolbar, first define the
Toolbar and surrounding layout in your activity, as shown below:
<LinearLayout> <com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="@dimen/tall_toolbar_height"> <com.google.android.material.appbar.CollapsingToolbarLayout android:id="@+id/collapsing_toolbar_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" app:contentScrim="?attr/colorPrimary" app:expandedTitleGravity="top" app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed|snap"> <androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar android:id="@+id/toolbar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize" app:layout_collapseMode="pin"/> </com.google.android.material.appbar.CollapsingToolbarLayout> </com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout> <androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment" ... /> ... </LinearLayout>
Next, call setupWithNavController()
from your main activity's onCreate method, as shown below:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val layout = findViewById<CollapsingToolbarLayout>(R.id.collapsing_toolbar_layout) val toolbar = findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) layout.setupWithNavController(toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... CollapsingToolbarLayout layout = findViewById(R.id.collapsing_toolbar_layout); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(layout, toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
Action bar
To add navigation support to the default action bar, call
setupActionBarWithNavController()
from your main activity's onCreate() method, as shown below. Note that you
need to declare your AppBarConfiguration outside of onCreate(), since you
also use it when overriding onSupportNavigateUp():
Kotlin
private lateinit var appBarConfiguration: AppBarConfiguration ... override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) setupActionBarWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration; ... @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); NavigationUI.setupActionBarWithNavController(this, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
Next, override onSupportNavigateUp() to handle Up navigation:
Kotlin
override fun onSupportNavigateUp(): Boolean { val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment) return navController.navigateUp(appBarConfiguration) || super.onSupportNavigateUp() }
Java
@Override public boolean onSupportNavigateUp() { NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(this, R.id.nav_host_fragment); return NavigationUI.navigateUp(navController, appBarConfiguration) || super.onSupportNavigateUp(); }
Support app bar variations
Adding the top app bar to your activity works well when the app bar’s layout is similar for each destination in your app. If, however, your top app bar changes substantially across destinations, then consider removing the top app bar from your activity and defining it in each destination fragment, instead.
As an example, one of your destinations may use a standard Toolbar, while
another uses an AppBarLayout to create a more complex app bar with tabs, as
shown in figure 2.
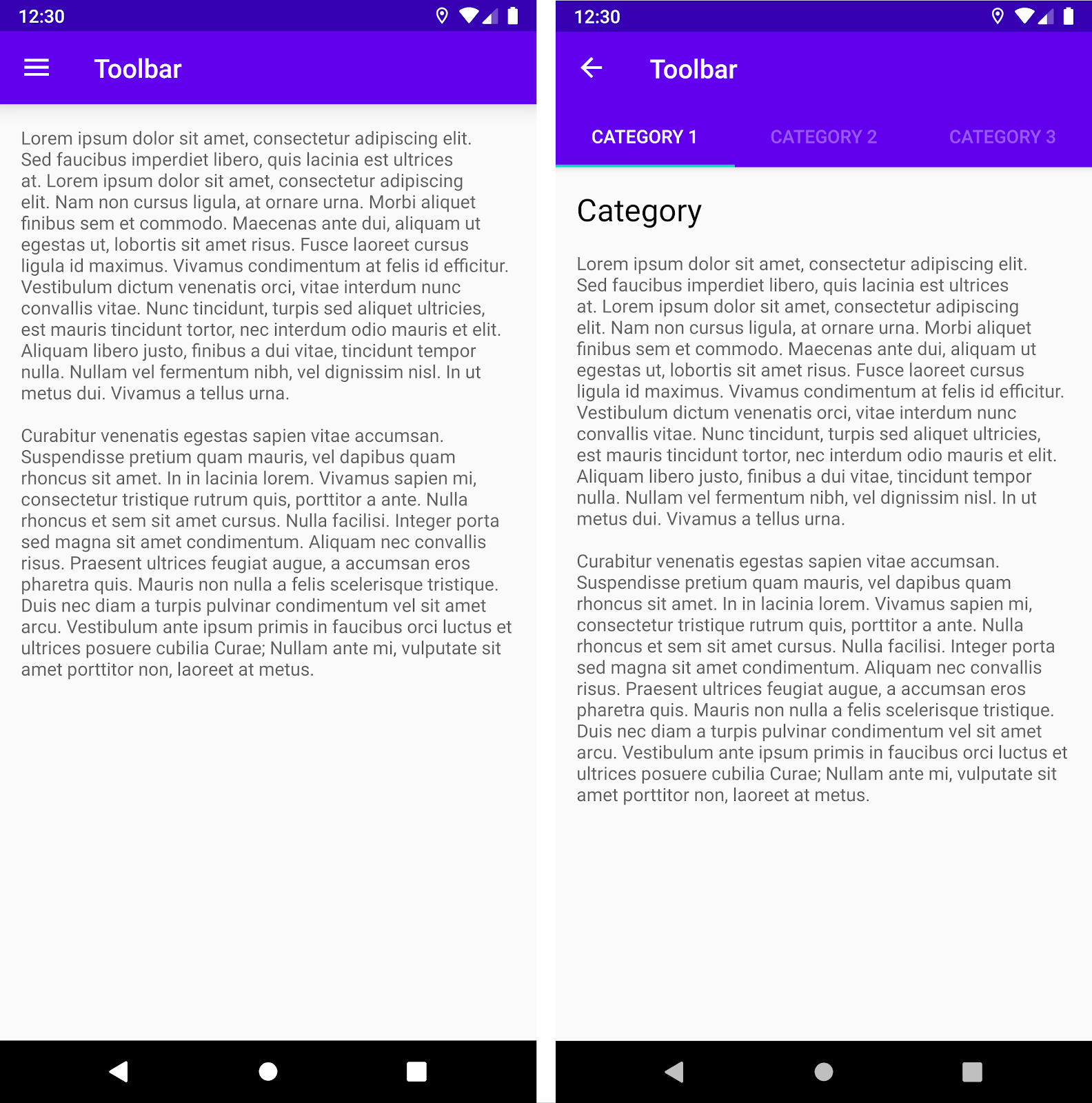
Toolbar. On the right, an AppBarLayout with a
Toolbar and tabs.To implement this example within your destination fragments using
NavigationUI, first define the app bar in each of your fragment layouts,
beginning with the destination fragment that uses a standard toolbar:
<LinearLayout>
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
... />
...
</LinearLayout>
Next, define the destination fragment that uses an app bar with tabs:
<LinearLayout>
<com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout
... />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
... />
<com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout
... />
</com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout>
...
</LinearLayout>
The navigation configuration logic is the same for both of these fragments,
except that you should call
setupWithNavController()
from within each fragment's onViewCreated() method, instead of initializing
them from the activity:
Kotlin
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { val navController = findNavController() val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph) view.findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) .setupWithNavController(navController, appBarConfiguration) }
Java
@Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(view); AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()).build(); Toolbar toolbar = view.findViewById(R.id.toolbar); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController( toolbar, navController, appBarConfiguration); }
Tie destinations to menu items
NavigationUI also provides helpers for tying destinations to menu-driven UI
components. NavigationUI contains a helper method,
onNavDestinationSelected(),
which takes a MenuItem along with the
NavController that hosts the
associated destination. If the id of the MenuItem matches the id of
the destination, the NavController can then navigate to that destination.
As an example, the XML snippets below define a menu item and a destination with
a common id, details_page_fragment:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <navigation xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" ... > ... <fragment android:id="@+id/details_page_fragment" android:label="@string/details" android:name="com.example.android.myapp.DetailsFragment" /> </navigation>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> ... <item android:id="@+id/details_page_fragment" android:icon="@drawable/ic_details" android:title="@string/details" /> </menu>
If your menu was added via the Activity's onCreateOptionsMenu(), for example,
you can associate the menu items with destinations by overriding the Activity's
onOptionsItemSelected() to call onNavDestinationSelected(), as shown in
the following example:
Kotlin
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean { val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment) return item.onNavDestinationSelected(navController) || super.onOptionsItemSelected(item) }
Java
@Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { NavController navController = Navigation.findNavController(this, R.id.nav_host_fragment); return NavigationUI.onNavDestinationSelected(item, navController) || super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); }
Now, when a user clicks the details_page_fragment menu item, the app
automatically navigates to the corresponding destination with the same id.
Add a navigation drawer
The navigation drawer is a UI panel that shows your app's main navigation menu.
The drawer appears when the user touches the drawer icon
![]() in the app bar or when the user swipes a finger from the left edge of the
screen.
in the app bar or when the user swipes a finger from the left edge of the
screen.
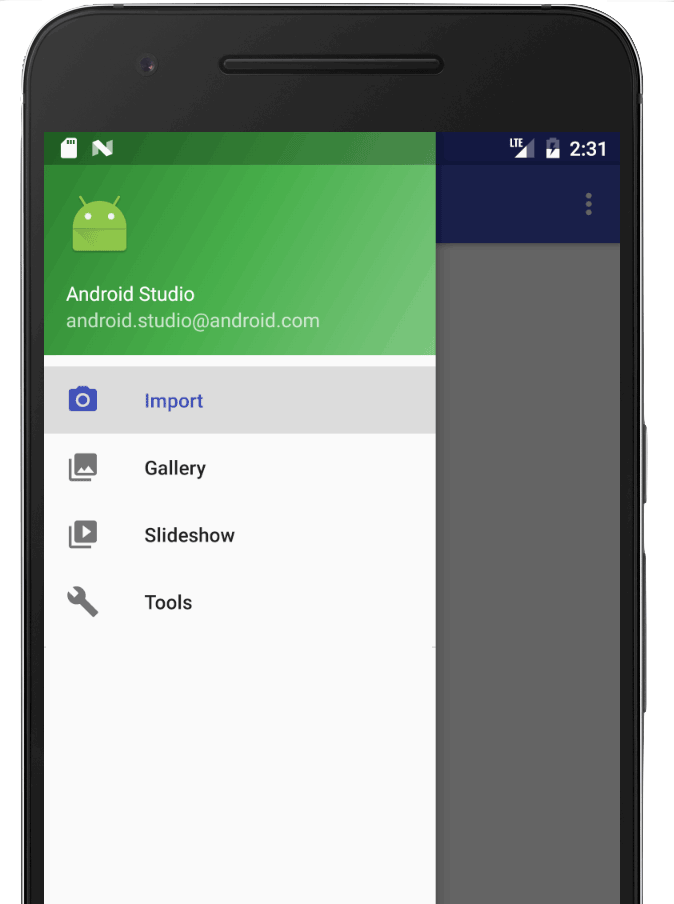
The drawer icon is displayed on all
top-level destinations that use a DrawerLayout.
To add a navigation drawer, first declare a
DrawerLayout as the root
view. Inside the DrawerLayout, add a layout for the main UI content and
another view that contains the contents of the navigation drawer.
For example, the following layout uses a DrawerLayout with two child views: a
NavHostFragment to
contain the main content and a
NavigationView
for the contents of the navigation drawer.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Use DrawerLayout as root container for activity -->
<androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/drawer_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<!-- Layout to contain contents of main body of screen (drawer will slide over this) -->
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
app:navGraph="@navigation/nav_graph" />
<!-- Container for contents of drawer - use NavigationView to make configuration easier -->
<com.google.android.material.navigation.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/nav_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="start"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true" />
</androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout>
Next, connect the DrawerLayout
to your navigation graph by passing it to AppBarConfiguration, as shown in
the following example:
Kotlin
val appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration(navController.graph, drawerLayout)
Java
AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder(navController.getGraph()) .setDrawerLayout(drawerLayout) .build();
Next, in your main activity class, call
setupWithNavController()
from your main activity's onCreate() method, as shown below:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController findViewById<NavigationView>(R.id.nav_view) .setupWithNavController(navController) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); NavigationView navView = findViewById(R.id.nav_view); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(navView, navController); }
Starting in
Navigation 2.4.0-alpha01,
the state of each menu item is saved and restored when you use
setupWithNavController.
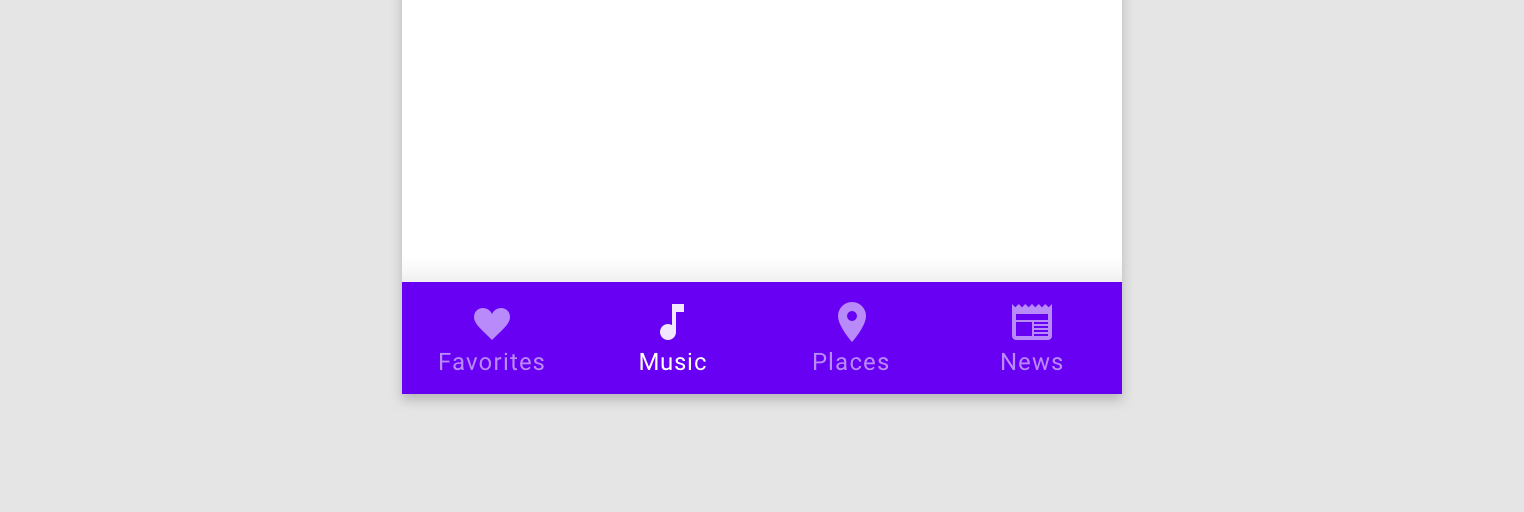
Bottom navigation
NavigationUI can also handle bottom navigation. When a user selects a menu
item, the NavController calls
onNavDestinationSelected()
and automatically updates the selected item in the bottom navigation bar.
To create a bottom navigation bar in your app, first define the bar in your main activity, as shown below:
<LinearLayout> ... <androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView android:id="@+id/nav_host_fragment" ... /> <com.google.android.material.bottomnavigation.BottomNavigationView android:id="@+id/bottom_nav" app:menu="@menu/menu_bottom_nav" /> </LinearLayout>
Next, in your main activity class, call
setupWithNavController()
from your main activity's onCreate() method, as shown below:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) ... val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController findViewById<BottomNavigationView>(R.id.bottom_nav) .setupWithNavController(navController) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ... NavHostFragment navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); BottomNavigationView bottomNav = findViewById(R.id.bottom_nav); NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(bottomNav, navController); }
Starting in
Navigation 2.4.0-alpha01,
the state of each menu item is saved and restored when you use
setupWithNavController.
Listen for navigation events
Interacting with the NavController
is the primary method for navigating between destinations. The NavController
is responsible for replacing the contents of the NavHost
with the new destination. In many cases, UI elements—such as a top app bar or
other persistent navigation controls like a BottomNavigationBar—live outside
of the NavHost and need to be updated as you navigate between destinations.
NavController offers an OnDestinationChangedListener interface that is
called when the NavController's current destination
or its arguments change. A new listener can be registered via the
addOnDestinationChangedListener()
method. Note that when calling addOnDestinationChangedListener(), if the
current destination exists, it's immediately sent to your listener.
NavigationUI uses OnDestinationChangedListener to make these common UI
components navigation-aware. Note, however, that you can also use
OnDestinationChangedListener on its own to make any custom UI or business
logic aware of navigation events.
As an example, you might have common UI elements that you intend to show in
some areas of your app while hiding them in others. Using your own
OnDestinationChangedListener, you can selectively show or hide these UI
elements based on the target destination, as shown in the following example:
Kotlin
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener { _, destination, _ -> if(destination.id == R.id.full_screen_destination) { toolbar.visibility = View.GONE bottomNavigationView.visibility = View.GONE } else { toolbar.visibility = View.VISIBLE bottomNavigationView.visibility = View.VISIBLE } }
Java
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener(new NavController.OnDestinationChangedListener() { @Override public void onDestinationChanged(@NonNull NavController controller, @NonNull NavDestination destination, @Nullable Bundle arguments) { if(destination.getId() == R.id.full_screen_destination) { toolbar.setVisibility(View.GONE); bottomNavigationView.setVisibility(View.GONE); } else { toolbar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); bottomNavigationView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } } });
Argument-based listeners
As an alternative, you can also use arguments with default values within
the navigation graph, which can be used by the appropriate UI controller
to update its state. For example, rather than base the logic in the
OnDestinationChangedListener on the destination ID as per the previous
example, we can create an argument in the NavGraph:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:id="@+id/navigation\_graph" app:startDestination="@id/fragmentOne"> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentOne" android:name="com.example.android.navigation.FragmentOne" android:label="FragmentOne"> <action android:id="@+id/action\_fragmentOne\_to\_fragmentTwo" app:destination="@id/fragmentTwo" /> </fragment> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentTwo" android:name="com.example.android.navigation.FragmentTwo" android:label="FragmentTwo"> <argument android:name="ShowAppBar" android:defaultValue="true" /> </fragment> </navigation>
This argument isn't used when
navigating to the destination, but
rather as a way to attach additional information to the destination by using
the defaultValue. In this case, the value indicates whether the app bar
should be shown when on this destination.
We can now add an OnDestinationChangedListener in the Activity:
Kotlin
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener { _, _, arguments -> appBar.isVisible = arguments?.getBoolean("ShowAppBar", false) == true }
Java
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener( new NavController.OnDestinationChangedListener() { @Override public void onDestinationChanged( @NonNull NavController controller, @NonNull NavDestination destination, @Nullable Bundle arguments ) { boolean showAppBar = false; if (arguments != null) { showAppBar = arguments.getBoolean("ShowAppBar", false); } if(showAppBar) { appBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } else { appBar.setVisibility(View.GONE); } } } );
The NavController
invokes this callback whenever the navigation destination changes. The
Activity can now update the state or visibility of the UI components
that it owns based upon the arguments received in the callback.
One advantage of this approach is that the Activity sees only the
arguments in the navigation graph and doesn't know individual Fragment
roles and responsibilities. Similarly, the individual fragments do not know
about the containing Activity and the UI components that it owns.
Additional resources
To learn more about navigation, see the following additional resources.
Samples
- Android Architecture Components Basic Navigation Sample
- Android Architecture Components Advanced Navigation Sample
Codelabs
Blog posts
Videos
- 10 Best Practices for Moving to a Single Activity
- Single Activity: Why, When, and How (Android Dev Summit '18)
- Android Jetpack: manage UI navigation with Navigation Controller (Google I/O '18)
