Wear OS के लिए ऐप्लिकेशन डिज़ाइन करते समय, सोच-समझकर लेआउट चुनें अनुभव प्राप्त करें. ऐसा इसलिए, क्योंकि Wear OS स्मार्ट डिसप्ले पर काम करता है और क्लिपिंग भी बेहतर तरीके से काम करती है आम तौर पर, हैंडहेल्ड डिवाइसों की तुलना में दो तरह के कैननिकल लेआउट होते हैं आपको अपना ऐप्लिकेशन डिज़ाइन करते समय इन बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए.
ऐसे ऐप्लिकेशन लेआउट जिन्हें स्क्रोल नहीं किया जा सकता
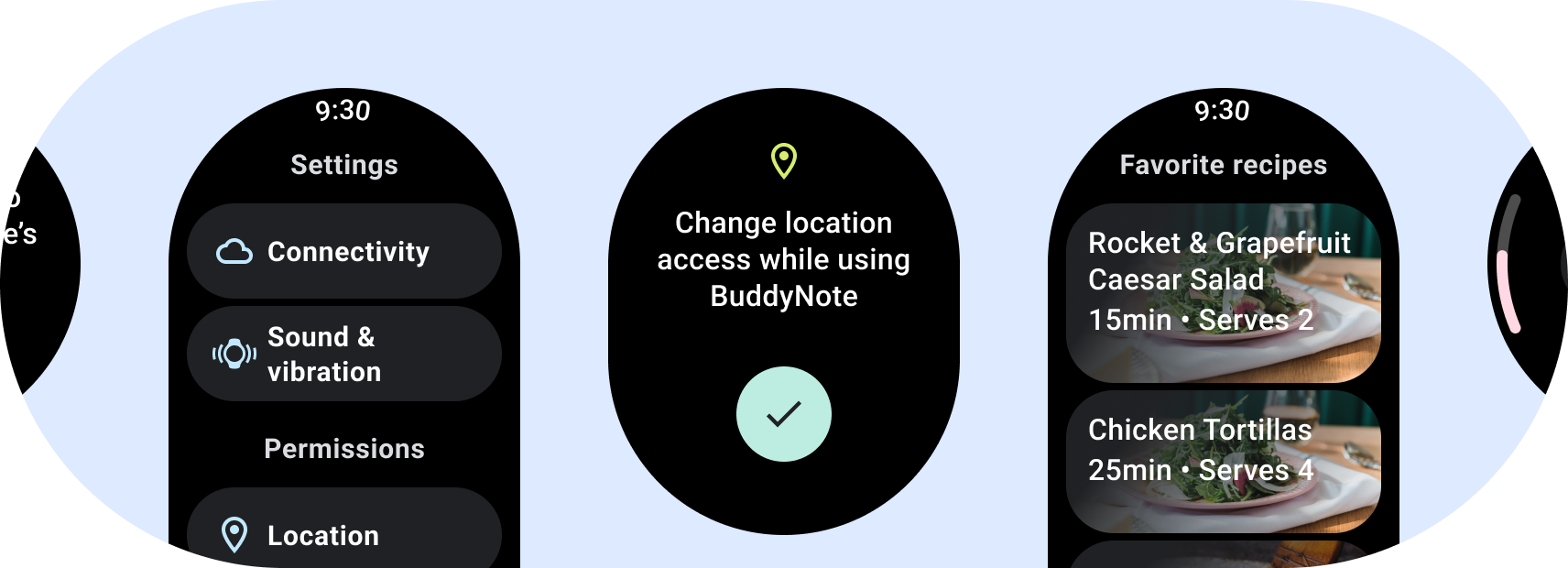
स्क्रोल न होने वाले लेआउट, जानकारी पर फ़ोकस करते हैं और उपयोगकर्ताओं को उनके काम के बहुत कम या कोई इंटरैक्शन नहीं. इस वजह से, इसे बनाना चुनौती भरा हो सकता है इन लेआउट का रिस्पॉन्सिव व्यवहार:
बिना स्क्रोल वाले रिस्पॉन्सिव व्यू के लिए बनाया गया
- भाषाओं, फ़ॉन्ट स्केलिंग, डिवाइसों, और वैरिएबल के कॉम्बिनेशन पर जांच करें कॉन्टेंट.
- स्क्रोल न किए जा सकने वाले लेआउट का इस्तेमाल सिर्फ़ तब करें, जब कॉन्टेंट के बारे में जानकारी हो या उसे कंट्रोल किया गया हो से पहले या किसी खास डिज़ाइन का इस्तेमाल करना पड़ सकता है.
- लेआउट पर सुझाए गए ऊपर, नीचे, और किनारे के मार्जिन लागू करें.
- उन जगहों के लिए प्रतिशत वैल्यू में मार्जिन तय करें जहां कॉन्टेंट की अनुमति नहीं है क्लिप बनाई जानी चाहिए.
- टेक्स्ट के अंदर मौजूद स्पेस का सबसे अच्छा इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, एलिमेंट को व्यवस्थित करें स्क्रीन करने और डिवाइस के अलग-अलग साइज़ के हिसाब से बैलेंस बनाए रखने में मदद करता है.
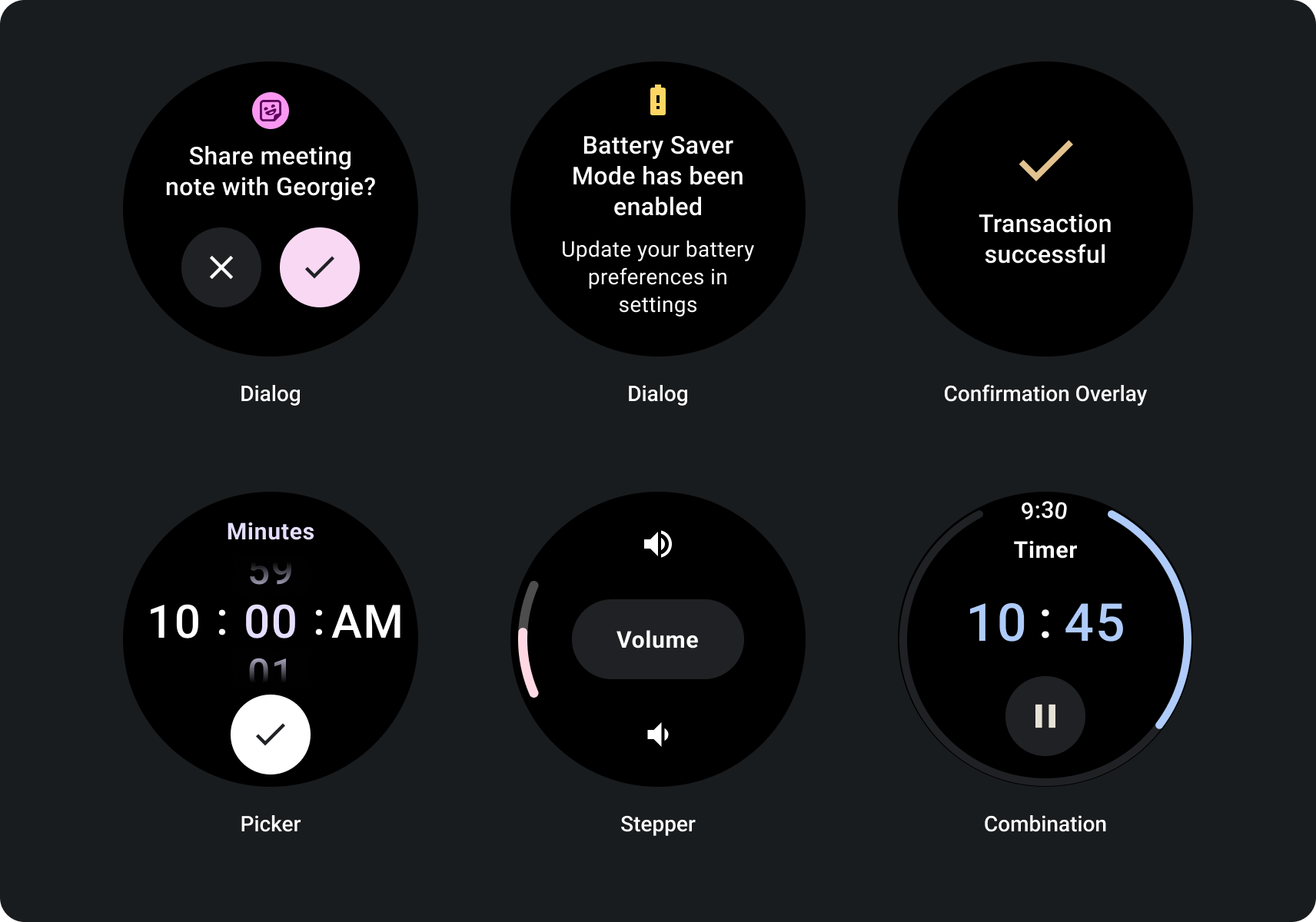
स्क्रोल होने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लेआउट
ऐसे पेज जिनमें मौजूद जानकारी, एक स्क्रीन में फ़िट होने के लिए तय की गई सीमा से ज़्यादा होती है या ऐसा करना इसलिए ज़रूरी है, ताकि लंबे सफ़र में मदद मिले. इसके लिए, स्क्रोल करके व्यू.
रिस्पॉन्सिव स्क्रोल व्यू के लिए बनाया गया
- सबसे ऊपर, नीचे, और किनारे के सुझाए गए मार्जिन लागू करें.
- क्लिप बनाने से रोकने के लिए प्रतिशत मानों में बाहरी मार्जिन को स्क्रोल किए जा सकने वाले कंटेनर की शुरुआत और आखिर में शामिल होता है.
- यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) एलिमेंट के बीच, तय डीपी वैल्यू में मार्जिन लागू करें.
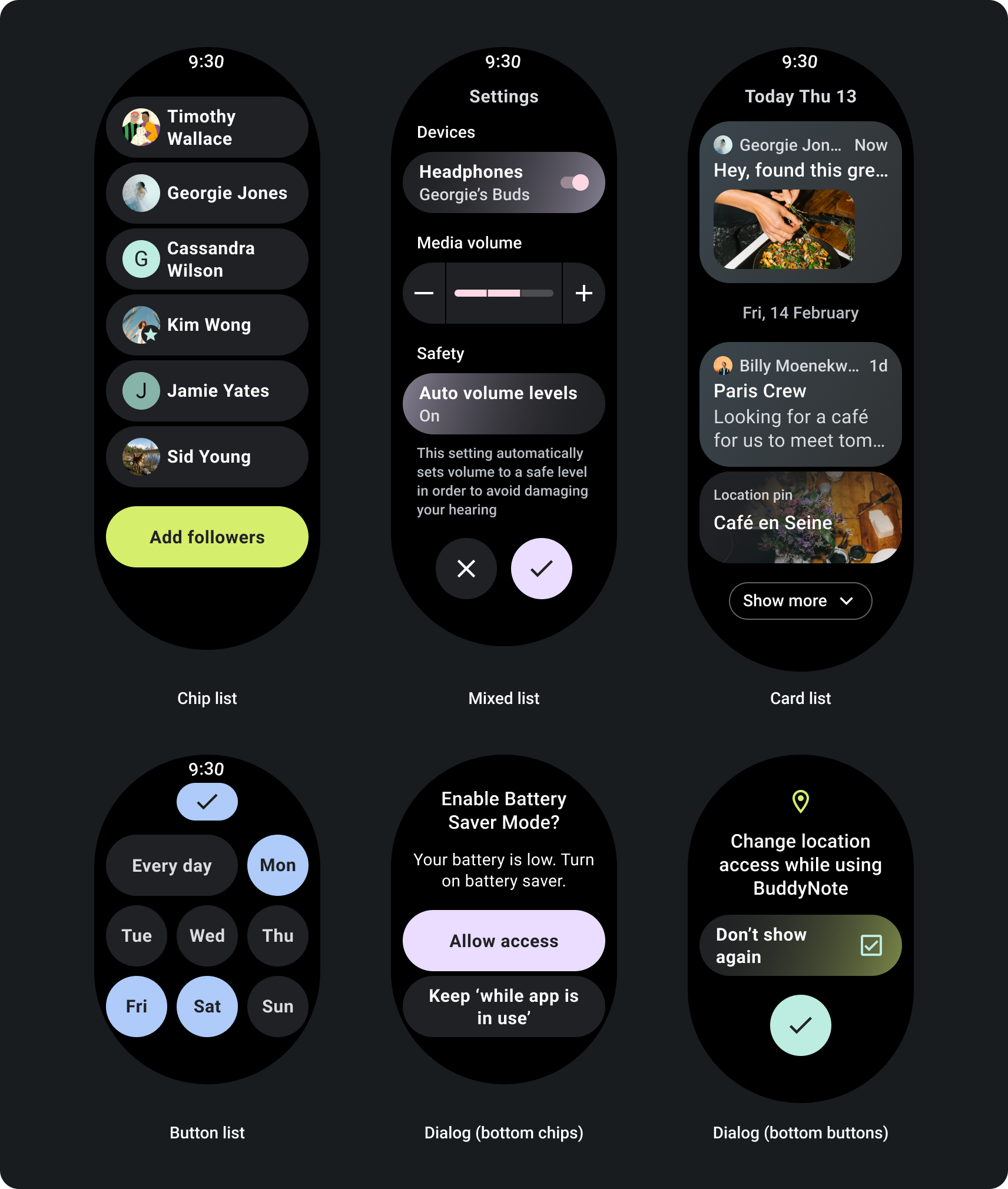
स्क्रीन साइज़ ब्रेकपॉइंट का इस्तेमाल करके, अडैप्टिव स्क्रोल व्यू बनाने का तरीका
रिस्पॉन्सिव डिज़ाइन इस्तेमाल करने वाले स्क्रोल व्यू, आम तौर पर कई तरह के स्क्रीन साइज़. हालांकि, कुछ खास मामलों में ब्रेकपॉइंट का इस्तेमाल करके, डाइमेंशन बदलें और अतिरिक्त विकल्प दिखाने वाले लेआउट को बेहतर बनाएं, बेहतर बनाएं कॉन्टेंट को एक नज़र में देखना या स्क्रीन पर बेहतर तरीके से फ़िट करना. यह उदाहरण दिखाता है कि बड़ी स्क्रीन पर, नीचे के दो बटन कैसे चौड़ा किए जाते हैं:
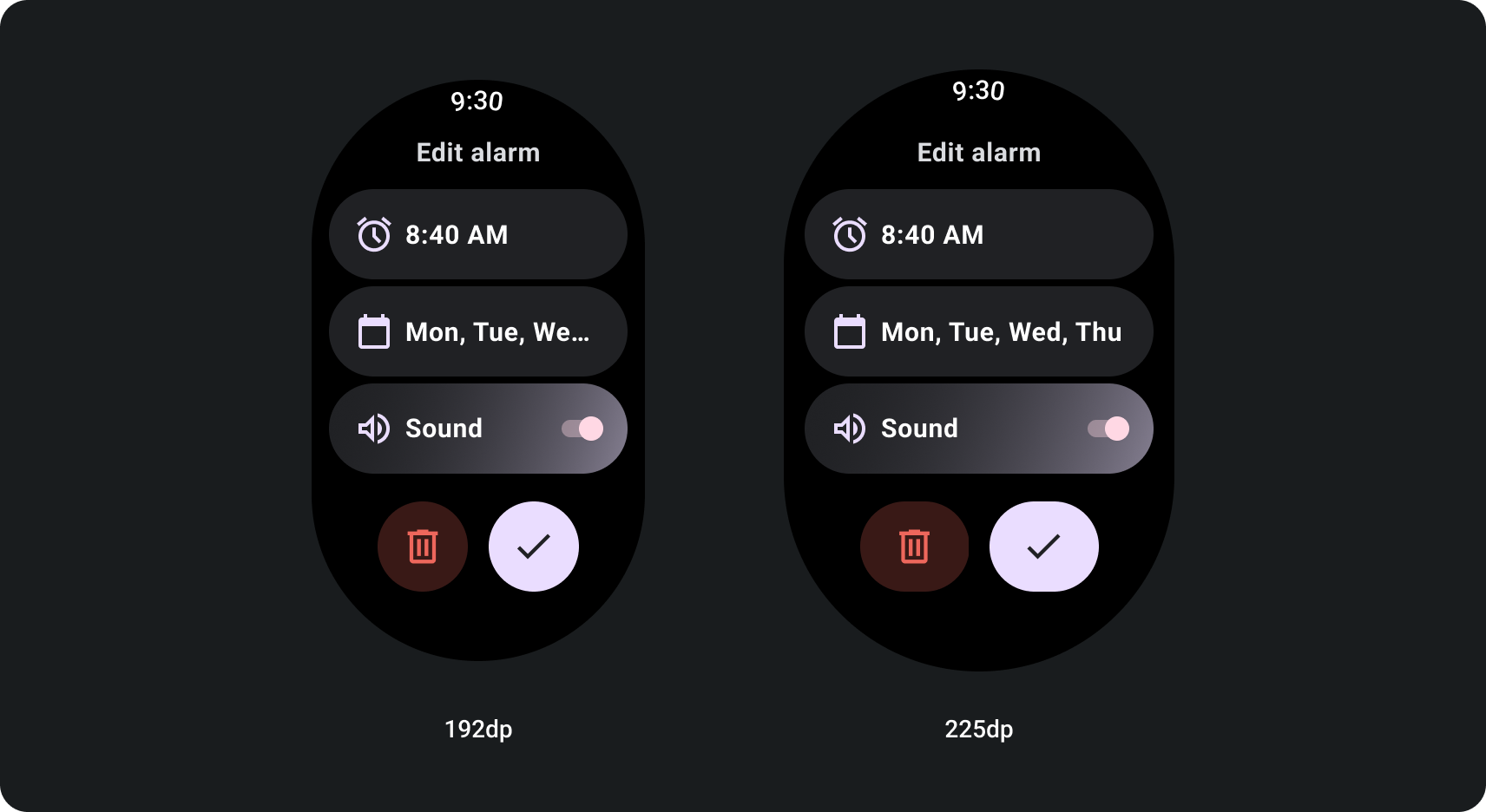
Figma के डिज़ाइन की किट
पहले से मौजूद ऐप्लिकेशन के डिज़ाइन लेआउट देखने के लिए, डिज़ाइन किट डाउनलोड करने वाले पेज पर जाएं अलग-अलग ऐप्लिकेशन और टाइल बनाने के लिए कॉम्पोनेंट, विकल्प, और सुझाव सबसे सही तरीकों का पालन करने वाले डिज़ाइन.

