تتميز الساعات الذكية بأحجام شاشة أصغر من الأجهزة المحمولة باليد، لذلك من المهم ترتيب العناصر وعرضها بطريقة يمكن للمستخدمين الوصول إليها وتستخدم مساحة الشاشة المتاحة بكفاءة. للمساعدة في ملاءمة العناصر للشاشة، استخدِم القدر الصحيح من المساحة المتروكة والهوامش على النحو المحدّد في إرشادات المواد.
حتى عندما يناسب تصميمك الشاشة، قد يتم اقتطاع عناصر واجهتك أو اقتصاصها عندما يقوم المستخدم بأحد الإجراءات التالية:
- يغيّر هذا الزر لغة العرض.
- لتغيير حجم النص
- تُفعِّل هذه السياسة إعداد النظام تغميق النص.
من الأهمية بمكان اختبار تصميماتك مع وضع هذه الاعتبارات في الاعتبار للتأكد من أنها تتكيّف بسلاسة مع بيئات المستخدمين المختلفة.
إبقاء العناصر التفاعلية مرئية بالكامل
إذا كانت واجهتك تحتوي على عناصر تفاعلية، فتحقق من أنه يمكن للمستخدمين تمرير هذه العناصر بالكامل في العرض، خاصةً إذا كانت هذه العناصر موضوعة على
حافة الصفحة. إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم مكتبة Horology، يمكنك استخدام مصنع تصميم responsive(). بخلاف ذلك، يمكنك استخدام الفواصل وإضافة الهوامش إلى أعلى وأسفل العنصر ScalingLazyColumn لمنع اقتصاص عناصر القائمة الأولى
والأخيرة بشكل دائم.
استخدام الشرائح بدلاً من البطاقات للحصول على تخطيطات كثيفة
إذا كنت بحاجة إلى تنسيق أكثر كثافة، استخدِم CompactChip بدلاً من البطاقات. تجعل المساحة السطحية الأكبر للبطاقات من الصعب جدًا منع اقتطاع النص واقتصاص المحتوى.
مراعاة تأثيرات حجم الشاشة عند الاقتطاع والاقتصاص
بناءً على حجم شاشة جهاز Wear OS، تتوفّر لك مساحة أصغر أو أكبر لإظهار المزيد من النصوص والأزرار:
تصميم للهوامش المئوية، وليس هوامش ثابتة
لإنشاء محتوى يتكيّف مع حجم شاشة جهاز Wear OS، عليك تطبيق هوامش النسبة المئوية، حيث يكون حجم كل هامش متناسبًا مع حجم الشاشة. في الحالات التي تظهر فيها العناصر على الجزء العلوي أو السفلي من الشاشة، يجب تطبيق مساحة داخلية إضافية لتقليل اقتصاص المحتوى من حافة الشاشة المنحنية. في المقابل، تزداد المساحة في الجزء العلوي والسفلي عندما تكون مجموعة من المحتوى صغيرة بما يكفي لتلائم شاشة واحدة.
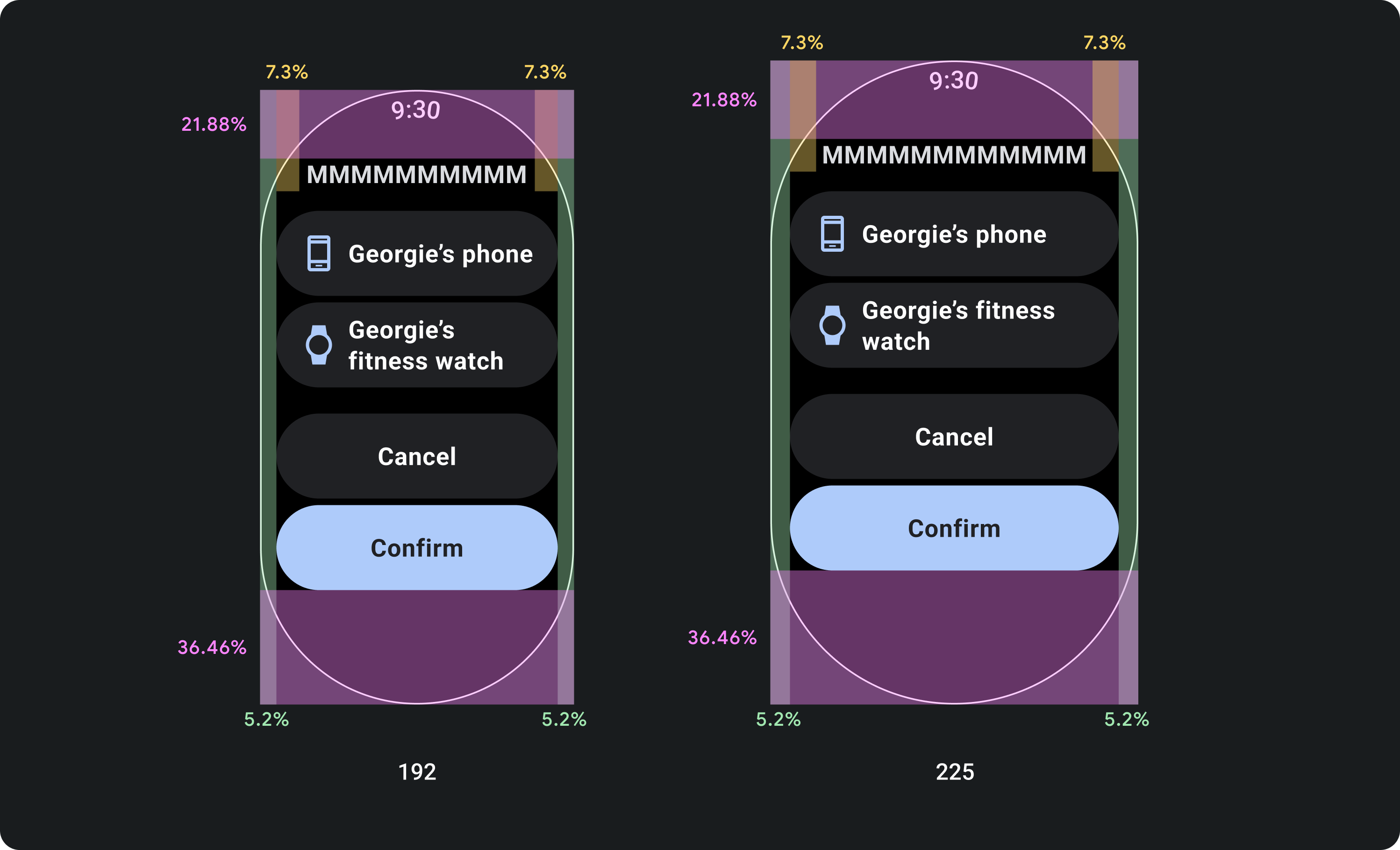
الإجراءات التي يُنصح بها
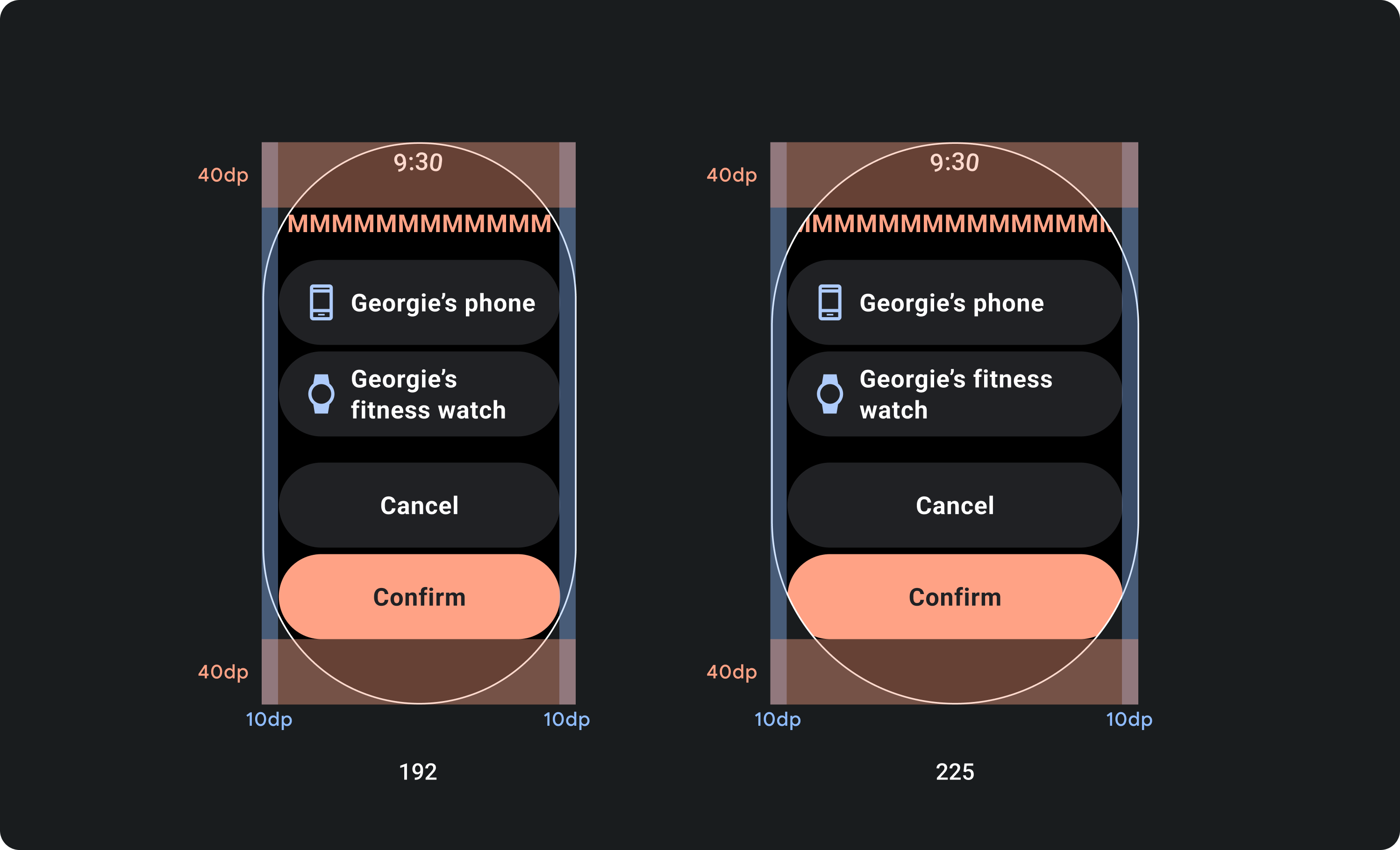
الإجراءات غير المُوصى بها
استخدِم عدد الأحرف المسموح به الذي تطلبه الشاشات الأصغر حجمًا
في معظم الحالات، يمكن أن تعرض الشاشات الأكبر حجمًا مزيدًا من النص والمحتوى قبل الاقتطاع. على الرغم من أنه قد تتوفر مساحة أفقية أكبر، ومع ذلك، صمِّم دائمًا لأصغر حجم شاشة لإنشاء تجربة متسقة عبر الأجهزة.
على سبيل المثال، قد يحتوي أحد الأزرار على مساحة لمزيد من الأحرف على شاشة أكبر قبل الاقتطاع، ولكن إذا كانت عبارة مهمة تحث المستخدم على اتخاذ إجراء ضرورية لتجربة المستخدم، فاستخدم نصًا قصيرًا بما يكفي ليظهر بالكامل، بدون اقتطاع، على شاشة جهاز صغير.
بدلاً من ذلك، إذا كان المربّع يعرض محتوى متغيّرًا، مثل النص الذي يتم استرجاعه من خادم، ننصحك بالتخطيط لاحتمالية اقتطاع هذا النص على شاشات أصغر حجمًا.

الإجراءات التي يُنصح بها

