تشمل تنسيقات عرض التطبيق التي تتيح التمرير القوائم (TransformingLazyColumn) ومربّعات الحوار.
تشكّل هذه التنسيقات معظم شاشات التطبيقات، وهي تمثّل
مجموعة من المكوّنات التي يجب أن تتوافق مع أحجام الشاشات الأكبر. تأكَّد من
أنّ المكوّنات متجاوبة، أي أنّها تملأ العرض المتاح وتتحكّم في تعديلات TransformingLazyColumn عندما يكون هناك المزيد من ارتفاع الشاشة
متاحًا. تم تصميم هذه التنسيقات بحيث تتلاءم مع مختلف الأجهزة، ولدينا بعض الاقتراحات إضافية للاستفادة بشكل أكبر من المساحة الموسّعة.
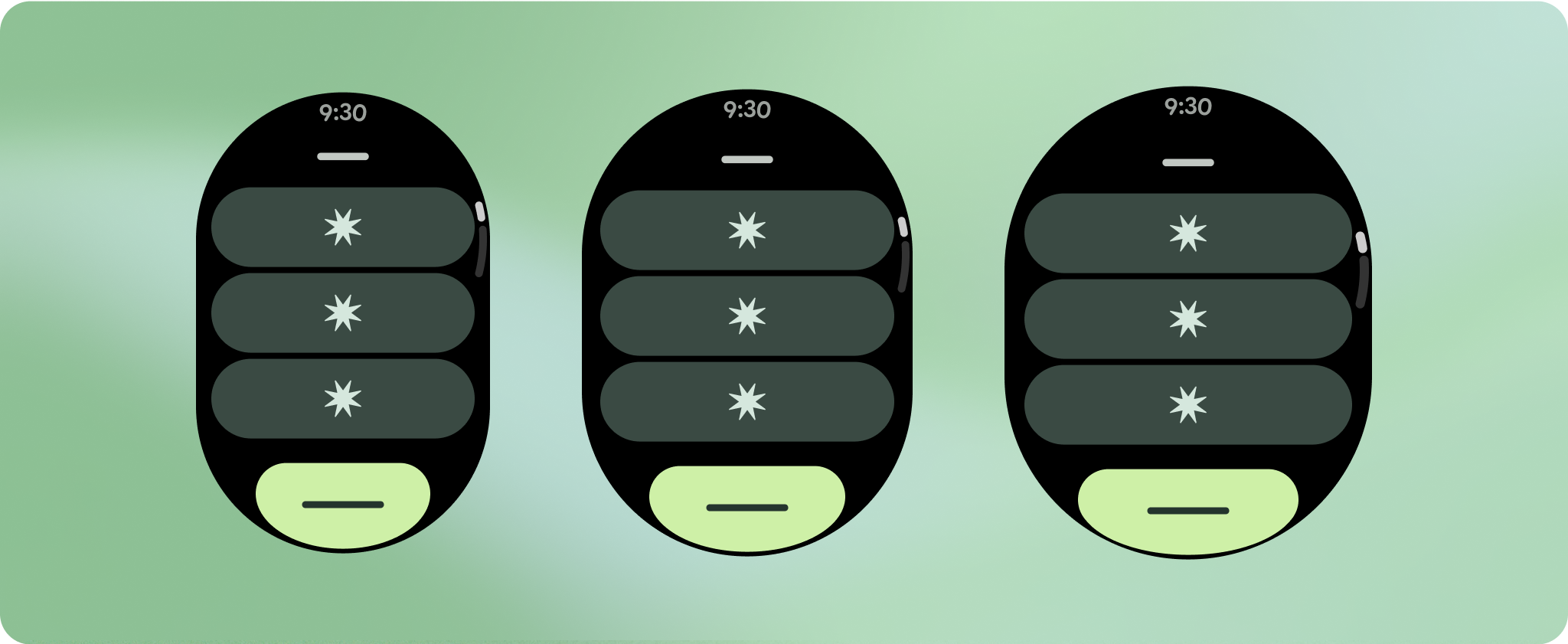
إنشاء تصاميم سريعة الاستجابة ومحسّنة
لمساعدة تصاميمك على التكيّف مع أحجام الشاشات الأكبر، عدّلنا سلوك التنسيقات والمكونات ليكون سلوكًا مضمّنًا سريع الاستجابة، بما في ذلك الهوامش والوسائد المستندة إلى النسبة المئوية. لحلّ هذه المشكلة، عدّلنا تنسيقات مكتبة واجهة المستخدم في Android ومكوناتها لتتضمّن سلوكًا متجاوبًا مضمّنًا، بما في ذلك الهوامش والوسائد المستندة إلى النسبة المئوية. إذا كنت تستخدِم مكونات Compose ، يمكنك اكتساب ميزة الاستجابة هذه تلقائيًا.
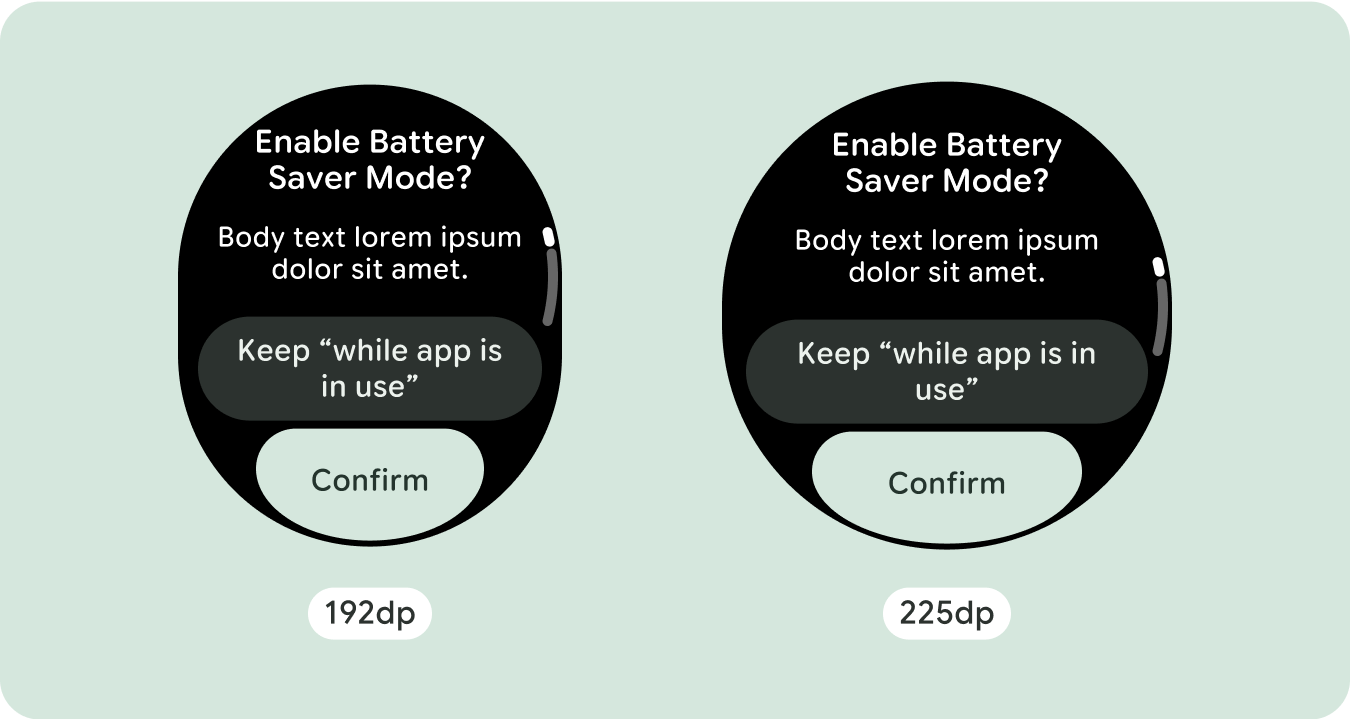
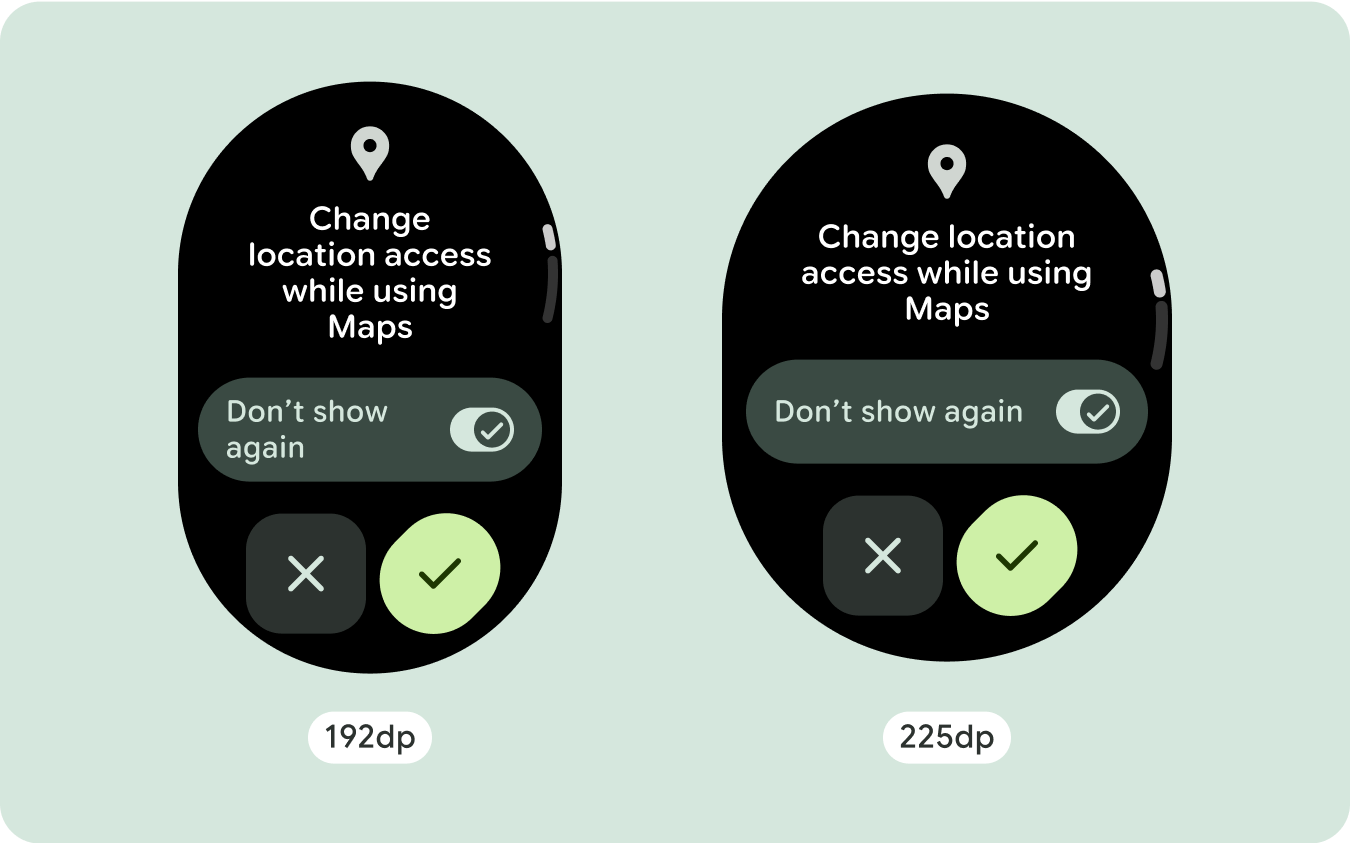
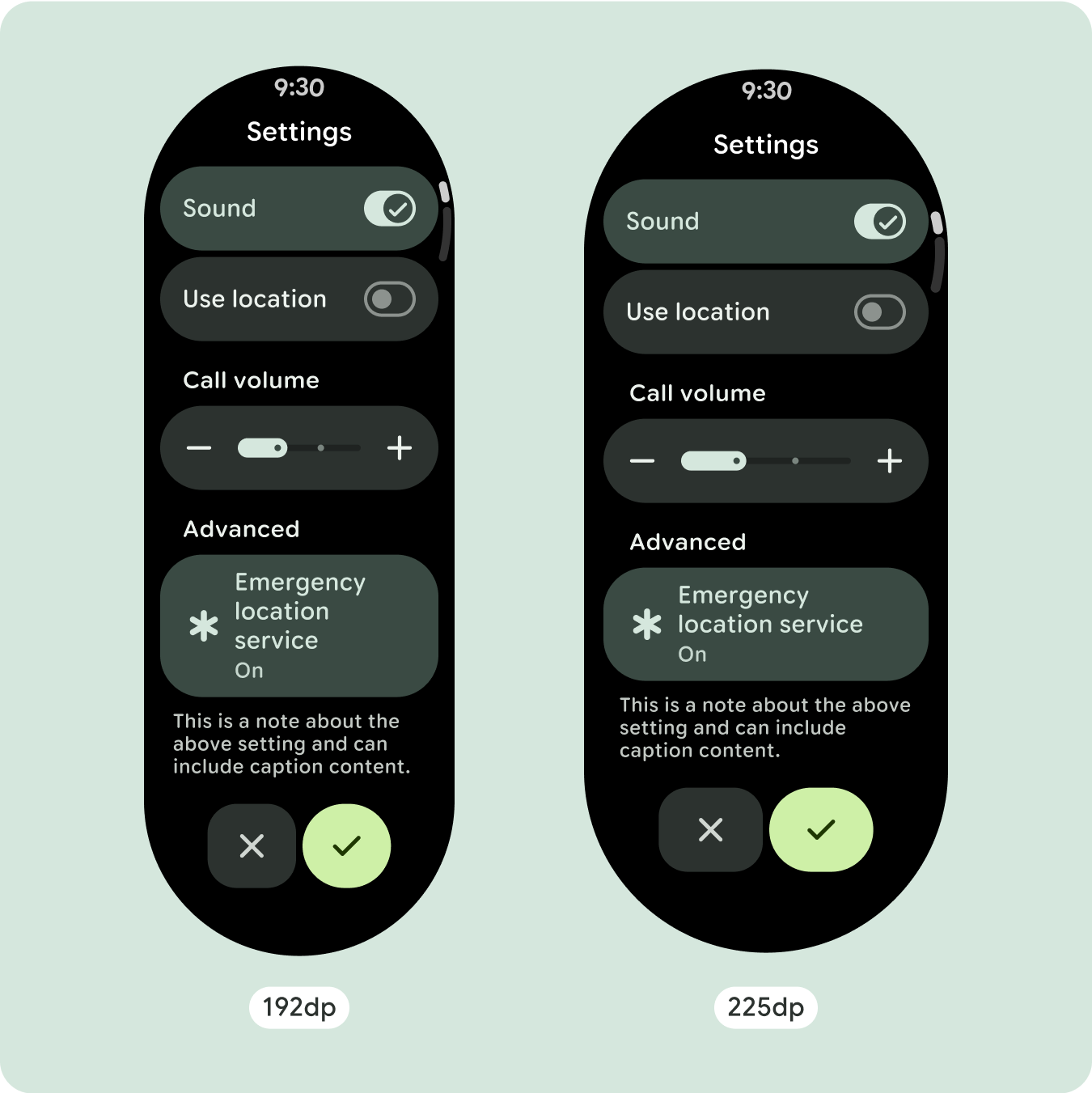
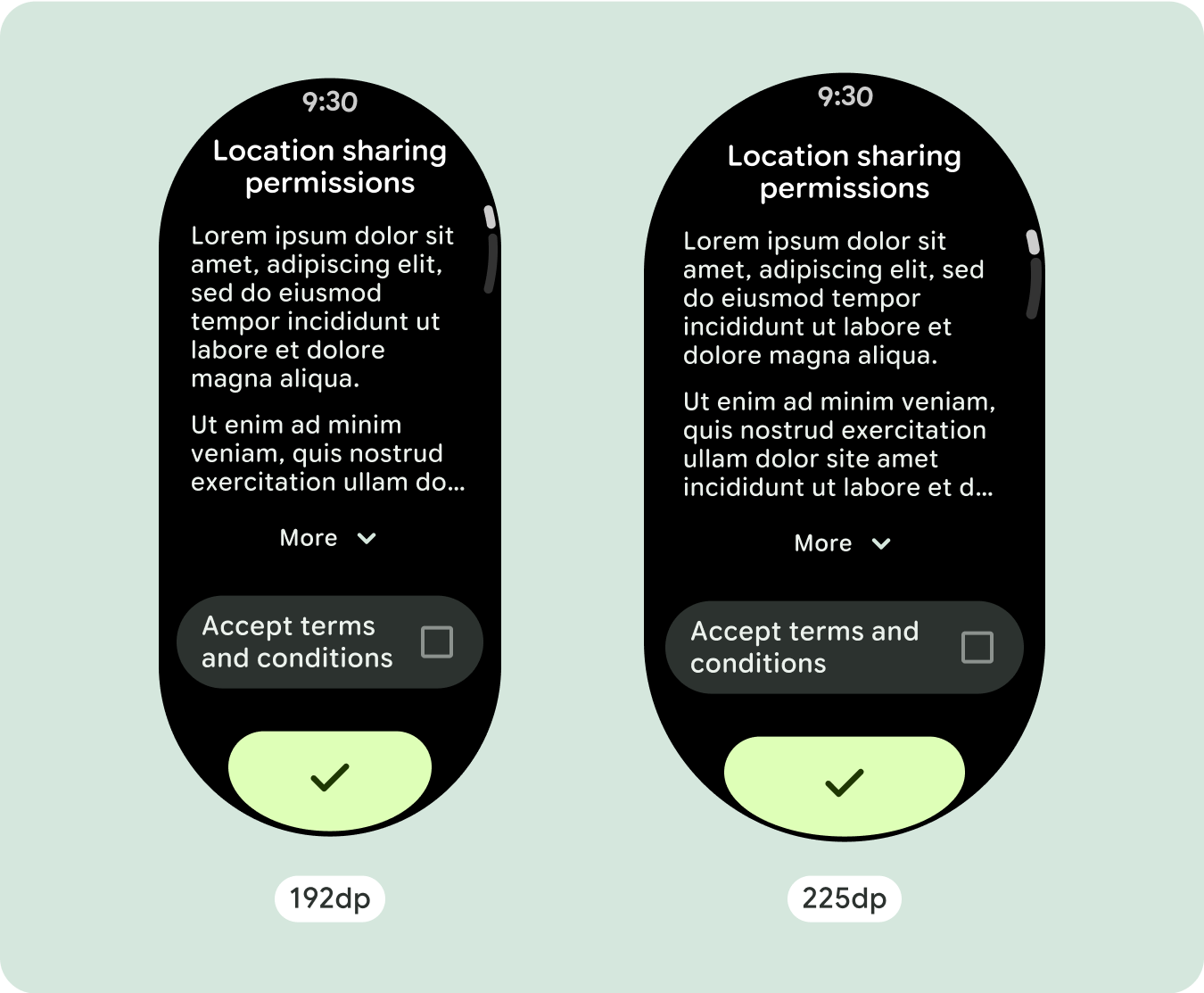
بالنسبة إلى تصميمات الشاشة الفريدة، يجب إجراء اختبار شامل على مجموعة متنوعة من أحجام الشاشة، لضمان توافق المكونات والعناصر بسلاسة وتجنُّب اقتصاص المحتوى. تساعد علامتا النسبة المئوية في زيادة حجم الفواصل بفعالية، وننصح باستخدام نقطة تفتيش بمقدار 225dp لعرض معلومات إضافية ووظائف محسّنة على شاشات الساعة الأكبر حجمًا.
تأكَّد من أنّ المكوّنات تملأ العرض المتاح.
تم تصميم جميع المكوّنات لتتوافق مع جميع الأجهزة، ما يعني أنّها تملأ العرض المتاح والارتفاع. تأكَّد من أنّ لديك الهوامش اللازمة لضمان عدم اقتطاع المحتوى بواسطة الشاشة المستديرة.
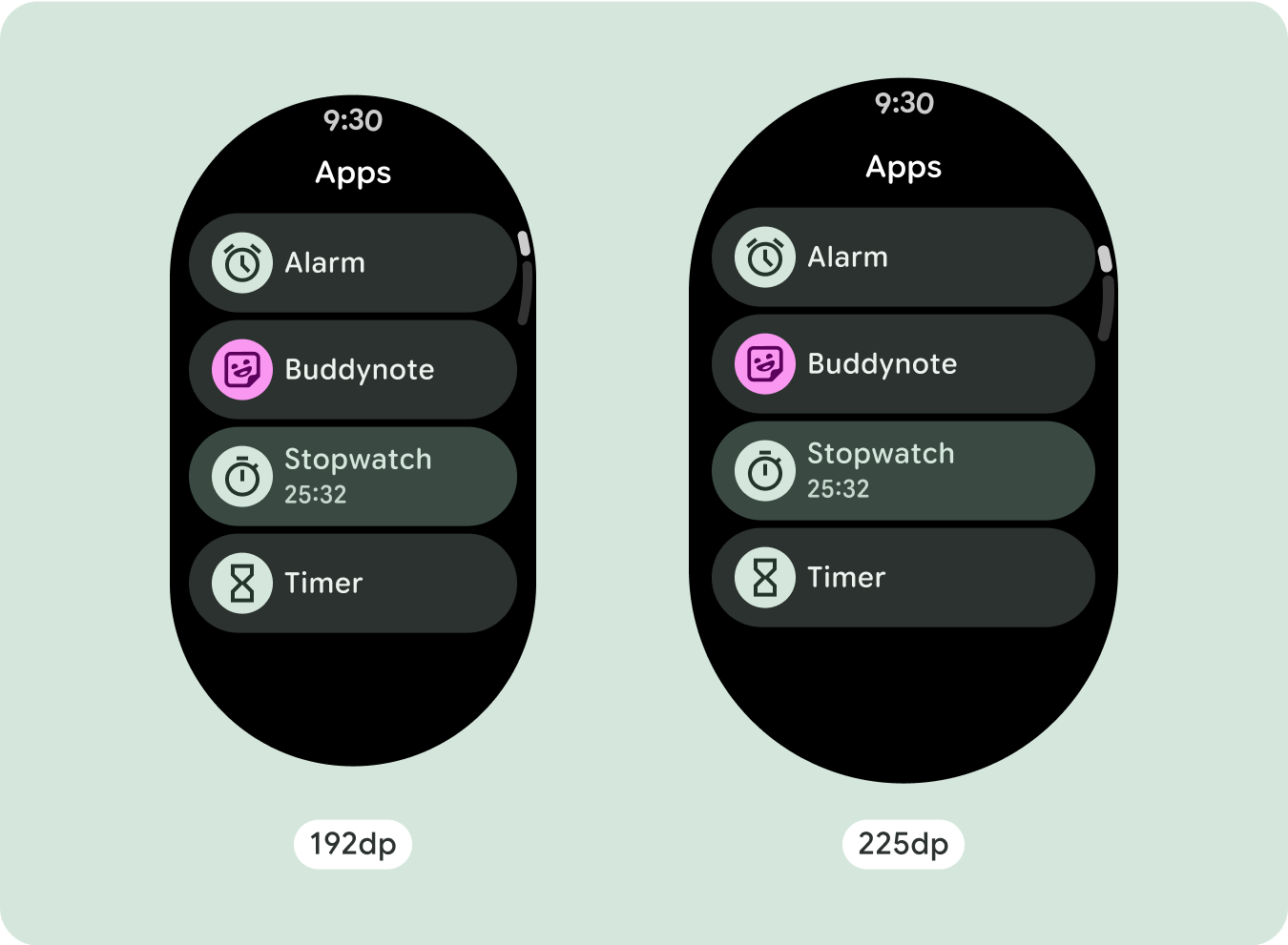
عرض أحرف نصية إضافية
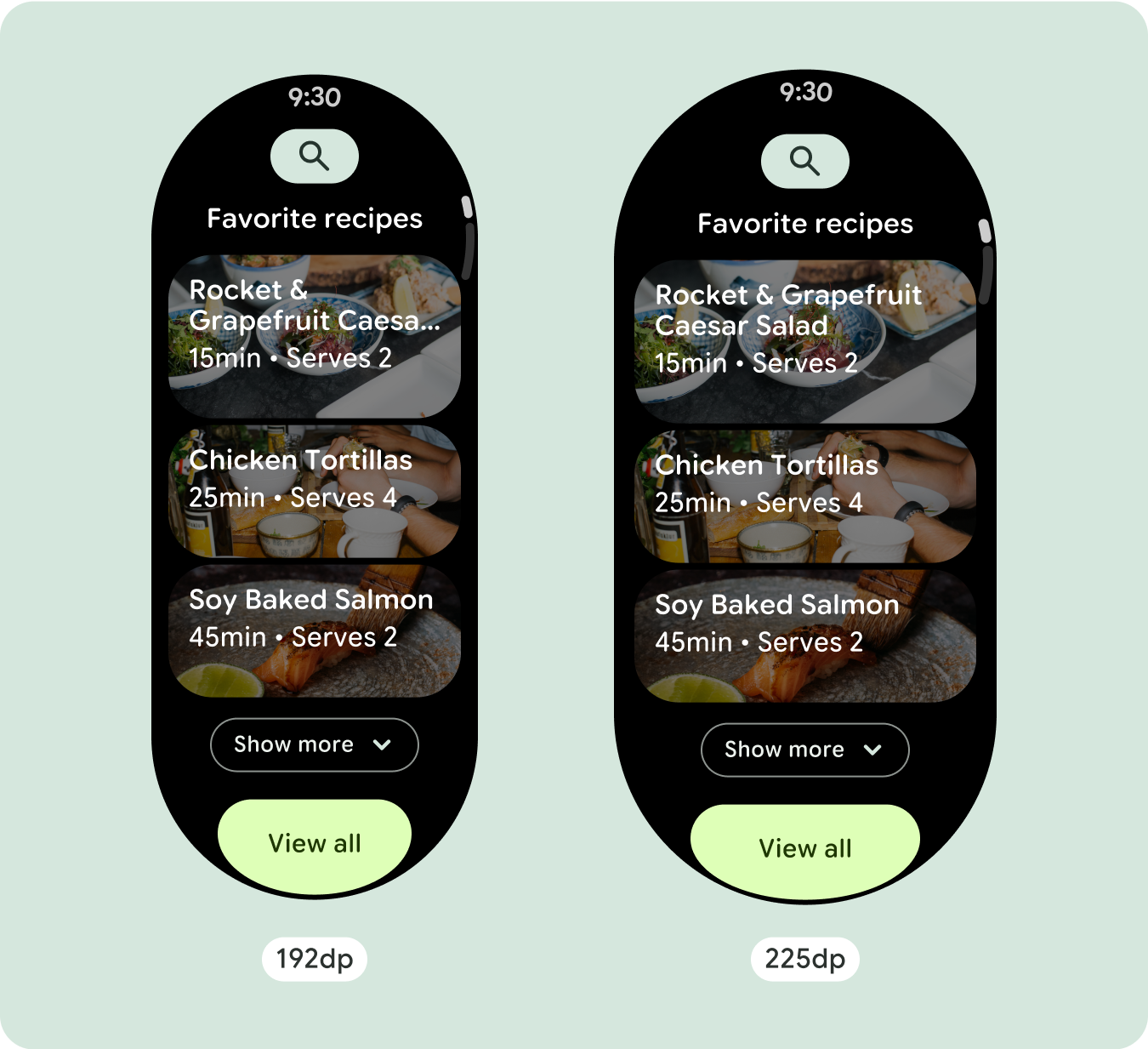
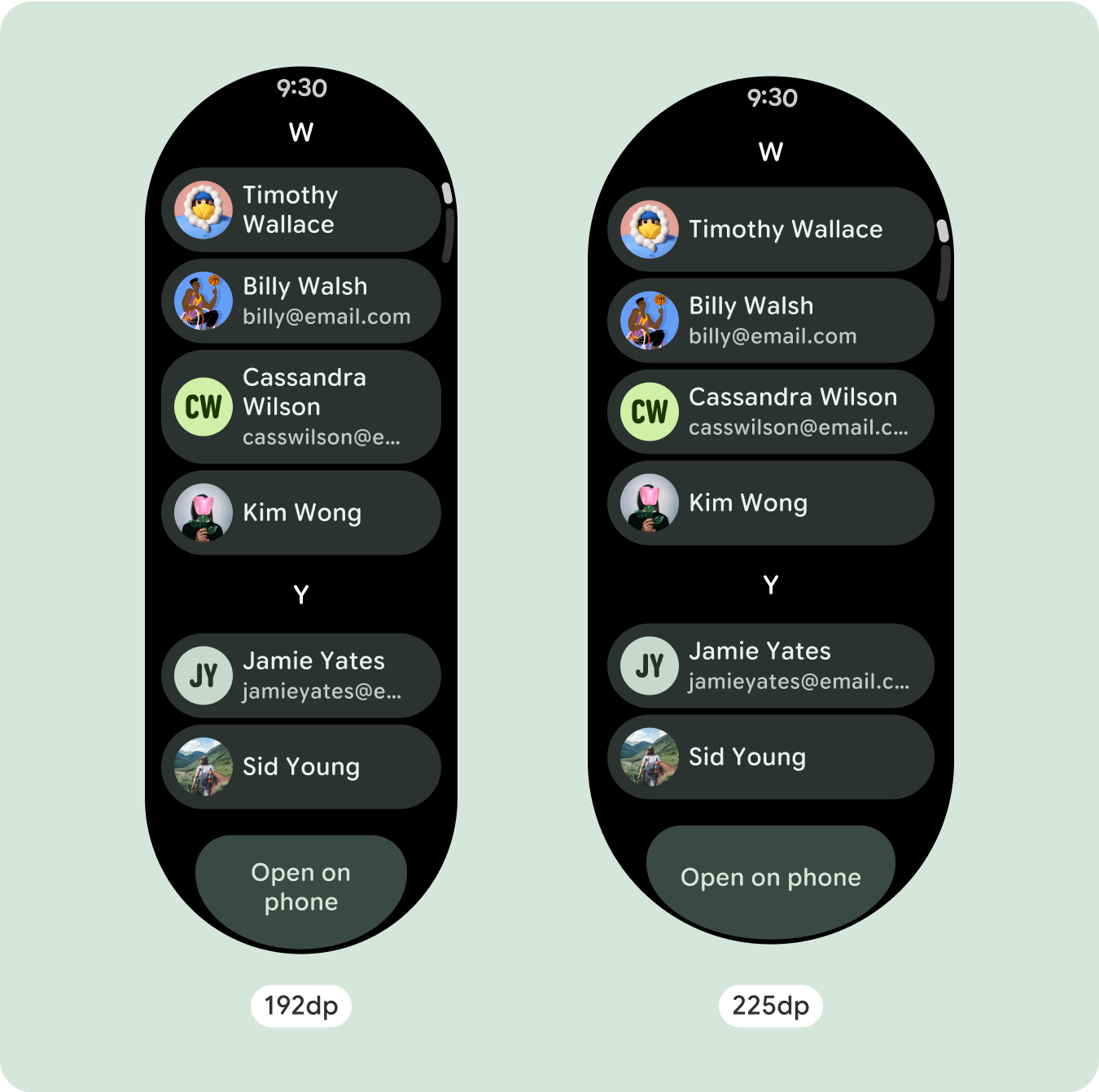
تحتوي معظم المكوّنات على مربّعات نص تملأ العرض المتاح. وهذا يعني أنّه يزداد عدد الأحرف تلقائيًا مع زيادة عرض الشاشة.

إنشاء تصميمات مكيّفة ومميّزة
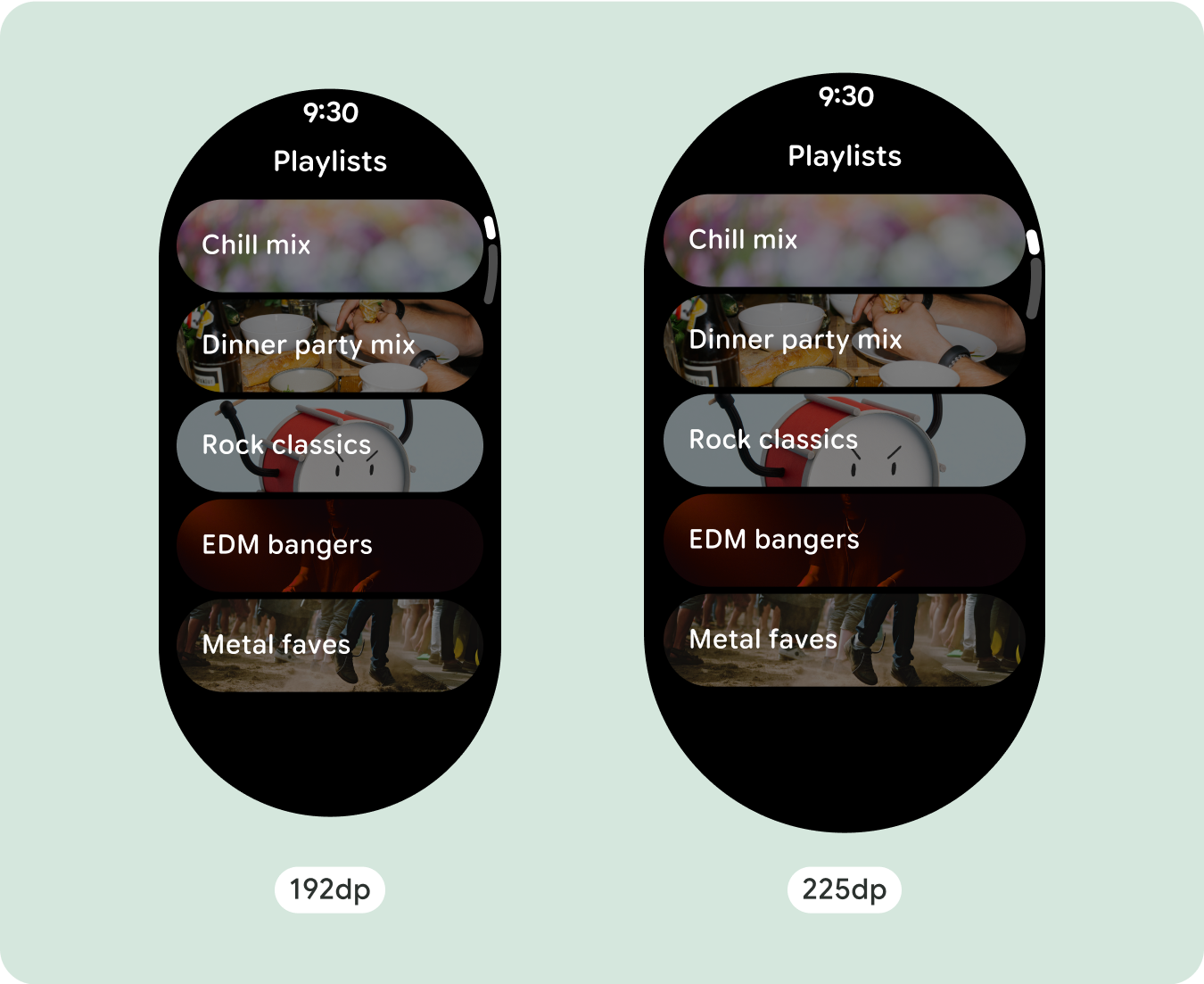
بما أنّ تنسيقات التمرير ستُظهر تلقائيًا المزيد مما كان مخفيًا سابقًا أسفل الشاشة المُثبَّتة، ليس عليك اتّخاذ الكثير من الإجراءات لإضافة قيمة. يملؤ كل مكوّن العرض المتاح، وفي بعض الحالات، قد يحصل المكوّن على صفوف إضافية من النص (مثل البطاقات)، أو يتم تمديد المكوّنات لملء العرض المتاح (مثل أزرار الرموز).
للاستفادة إلى أقصى حد من المساحة الإضافية على أحجام الشاشات الأكبر، أضِف نقطة فاصل حجم عند 225dp. تتيح نقطة التوقف هذه عرض محتوى إضافي، أو تضمين المزيد من الأزرار أو البيانات، أو تغيير التنسيق ليناسب الشاشة الأكبر حجمًا بشكل أفضل. يتطلّب ذلك تصميمًا مختلفًا لكل نقطة توقّف. يمكن أن يتضمّن تصميم الشاشة الكبيرة (225 بكسل أو أكثر) العناصر الإضافية التالية:
زيادة حجم المكونات الحالية أو تغيير حالتها
ويمكن إجراء ذلك لعرض المزيد من التفاصيل أو لتسهيل الاطّلاع على المحتوى.

تنسيقات محسّنة ومتباينة
يمكن أن يتغيّر التنسيق قليلاً بعد نقطة التوقف التي تبلغ 225dp، وذلك لتحسين المحتوى أعلى الصفحة في العرض التلقائي، ولكن يجب أن يظلّ كل المحتوى نفسه أسفل الصفحة متاحًا بغض النظر عن حجم الشاشة.
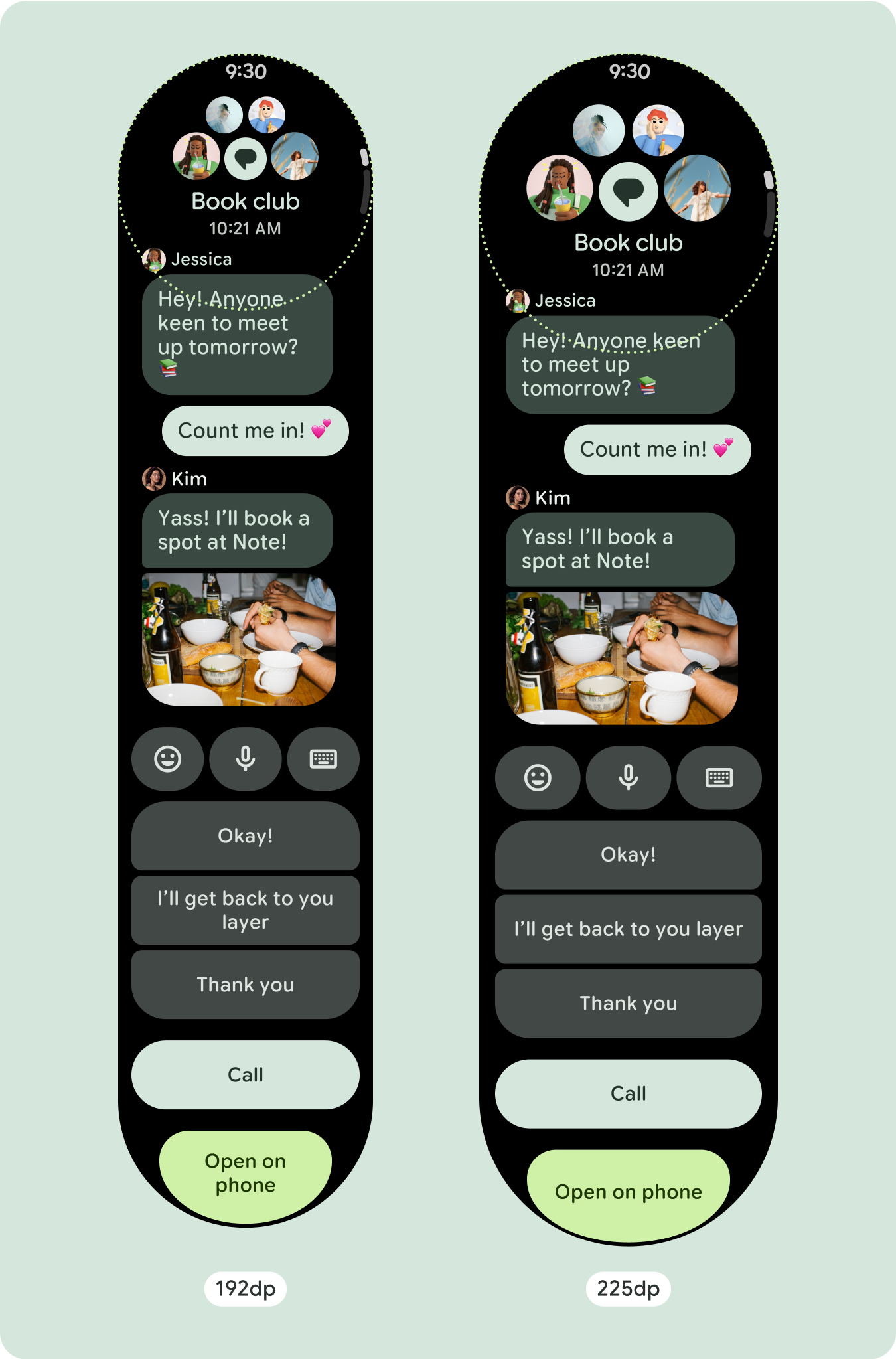
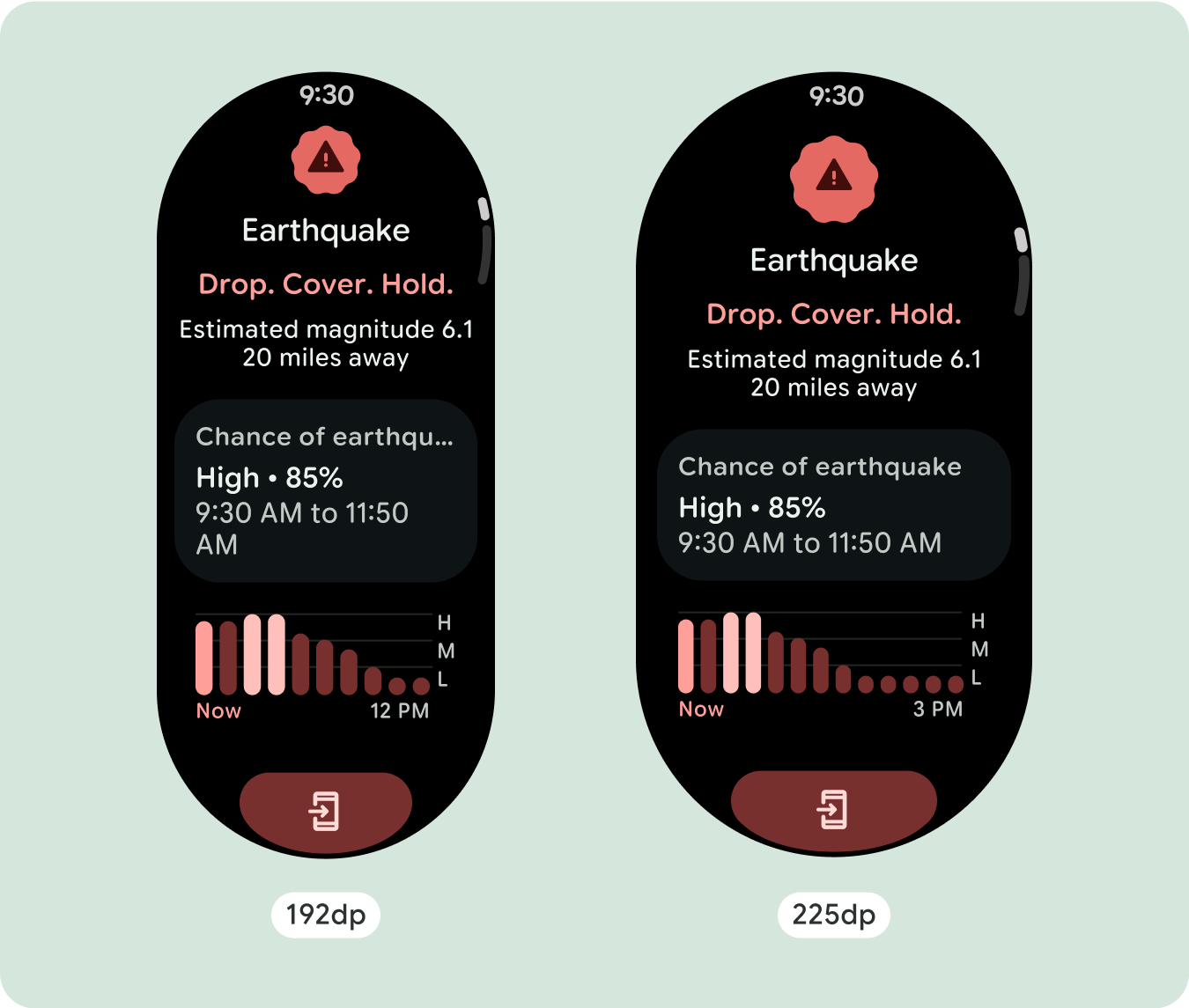
السلوك المتجاوب والمكيّف
ستتكيف جميع المكوّنات في مكتبة "الإنشاء" تلقائيًا مع حجم الشاشة الموسّع، وستزيد من العرض والارتفاع. إنّ مشاهدات التمرير التي تستخدم ممارسات التصميم السريع الاستجابة عادةً ما تتكيّف مع مجموعة من أحجام الشاشات. ومع ذلك، في بعض الحالات الخاصة، يمكنك استخدام نقطة توقّف لتجاهل السمات وتحسين التنسيقات التي تؤدي إلى توسيع الوظائف أو تحسين إمكانية الاطّلاع السريع أو ملاءمة المحتوى بشكلٍ أفضل على الشاشة.
يجب تحديد جميع الهوامش العلوية والسفلية والجانبية كنسب مئوية لتجنُّب
الاقتصاص وتوفير مقياس نسبي للعناصر. يُرجى العِلم أنّه عندما ينتقل المستخدم للأسفل أو للأعلى، يظهر الرمز
PositionIndicator ويلتصق تلقائيًا بإطار
الشاشة بغض النظر عن حجمه.
قائمة التحقق
- طبِّق الهوامش المقترَحة للأعلى والأسفل والجانبَين.
- حدِّد الهوامش الخارجية بقيم مئوية لمنع الاقتصاص في بداية الحاوية القابلة للتقديم أو الإيقاف ونهايتها.
- طبِّق الهوامش في قيم DP الثابتة بين عناصر واجهة المستخدم.
- ننصحك بتطبيق نقطة توقّف عند 225dp لعرض محتوى إضافي أو لتسهيل الاطّلاع على المحتوى الحالي على شاشات أكبر حجمًا.
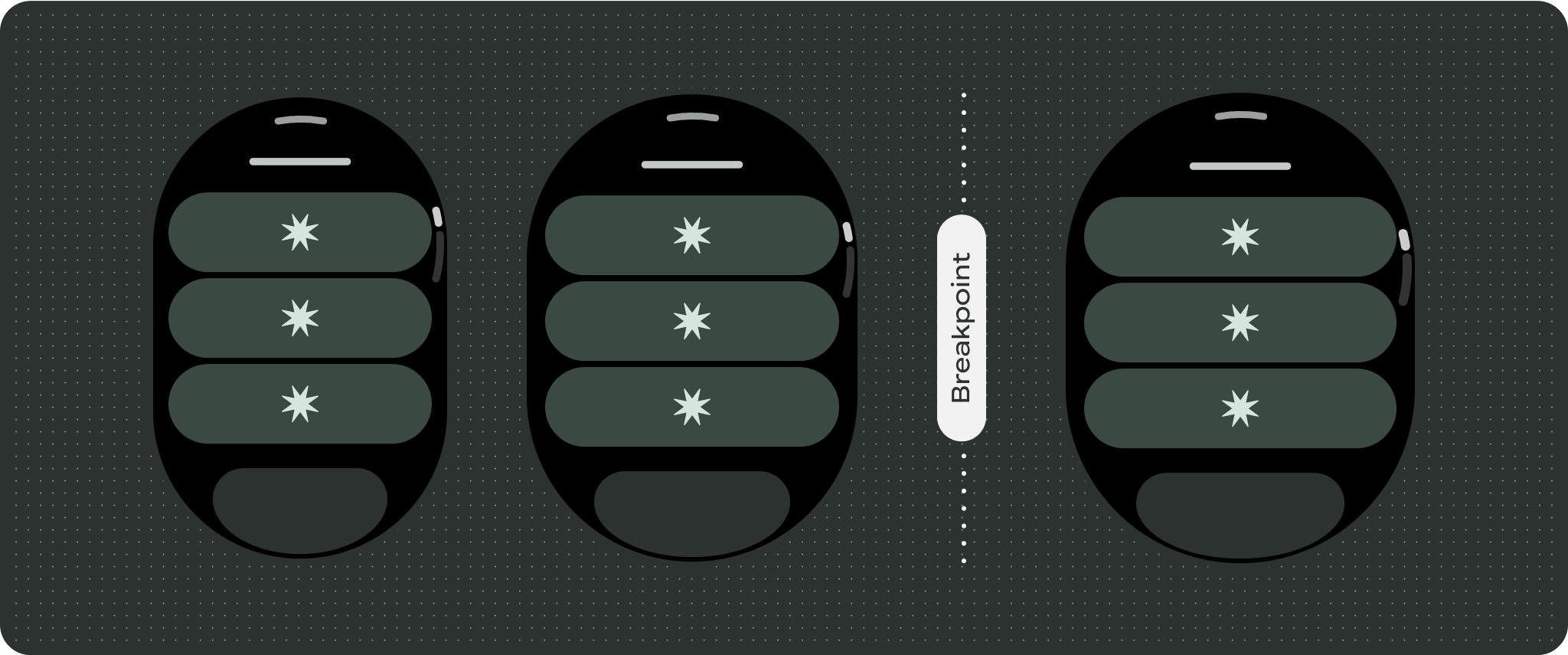
إنشاء تجارب مختلفة
يمكن تخصيص طرق العرض التي تتيح الانتقال للأعلى أو للأسفل بشكل كبير، مع إمكانية إضافة أي مجموعة من المكوّنات بأي ترتيب. يمكن أن تتغيّر الهوامش العلوية والسفلية استنادًا إلى المكونات التي تظهر في الأعلى والأسفل. ويهدف ذلك إلى منع اقتطاع المحتوى بسبب منحنى الشاشة المتزايد.

