แฟลชหน้าจอ หรือที่เรียกว่าแฟลชด้านหน้าหรือแฟลชเซลฟี จะใช้ความสว่างของหน้าจอโทรศัพท์ เพื่อส่องสว่างวัตถุเมื่อถ่ายภาพด้วยกล้องหน้า ในสภาพแสงน้อย ฟีเจอร์นี้พร้อมใช้งานในแอปกล้องดั้งเดิมและแอปโซเชียลมีเดียหลายแอป เนื่องจากคนส่วนใหญ่ถือโทรศัพท์ในระยะที่ใกล้พอเมื่อจัดเฟรมภาพบุคคลของตนเอง วิธีนี้จึงมีประสิทธิภาพ
อย่างไรก็ตาม นักพัฒนาแอปอาจประสบปัญหาในการติดตั้งใช้งานฟีเจอร์อย่างเหมาะสมและ รักษาคุณภาพการจับภาพที่ดีอย่างสม่ำเสมอในอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ คู่มือนี้แสดงวิธี ติดตั้งใช้งานฟีเจอร์นี้อย่างถูกต้องโดยใช้ Camera2 ซึ่งเป็น API เฟรมเวิร์กกล้อง Android ระดับต่ำ
เวิร์กโฟลว์ทั่วไป
หากต้องการใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้อย่างถูกต้อง ปัจจัยสำคัญ 2 ประการคือการใช้ ลำดับการวัดแสงก่อนการจับภาพ (การจับภาพก่อนการเปิดรับแสงอัตโนมัติ) และ เวลาในการดำเนินการ เวิร์กโฟลว์ทั่วไปแสดงในรูปที่ 1
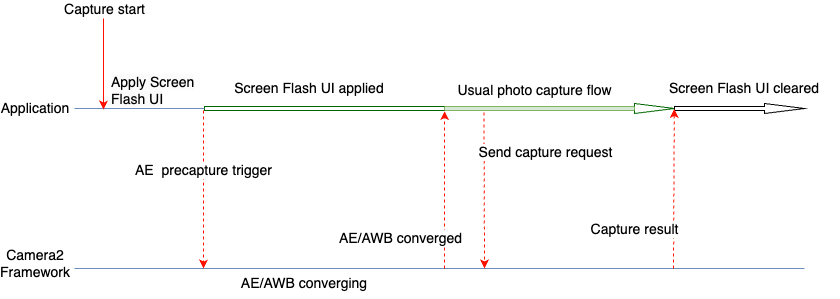
ขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้ใช้เมื่อต้องถ่ายภาพด้วยฟีเจอร์แฟลชหน้าจอ
- ใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลง UI ที่จำเป็นสำหรับแฟลชหน้าจอ ซึ่งจะให้แสงสว่างเพียงพอ
สำหรับการถ่ายรูปโดยใช้หน้าจอของอุปกรณ์ สําหรับกรณีการใช้งานทั่วไป Google
แนะนําให้เปลี่ยนแปลง UI ดังต่อไปนี้ตามที่ใช้ในการทดสอบ
- หน้าจอแอปถูกซ้อนทับด้วยสีขาว
- ความสว่างของหน้าจอจะเพิ่มขึ้นสูงสุด
- ตั้งค่าโหมดการเปิดรับแสงอัตโนมัติ (AE) เป็น
CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASHหากระบบรองรับ - ทริกเกอร์ลำดับการวัดแสงก่อนการจับภาพโดยใช้
CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER รอให้การเปิดรับแสงอัตโนมัติ (AE) และไวท์บาลานซ์อัตโนมัติ (AWB) ทำงาน
เมื่อรวมกันแล้ว ระบบจะใช้โฟลว์การจับภาพถ่ายปกติของแอป
ส่งคำขอจับภาพไปยังเฟรมเวิร์ก
รอรับผลการจับภาพ
รีเซ็ตโหมด AE หากตั้งค่า
CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASHไว้ล้างการเปลี่ยนแปลง UI สำหรับแฟลชหน้าจอ
โค้ดตัวอย่าง Camera2
ปิดหน้าจอแอปด้วยการวางซ้อนสีขาว
เพิ่ม View ในไฟล์ XML ของเลย์เอาต์ของแอปพลิเคชัน มุมมองมีความสูงเพียงพอที่จะอยู่เหนือองค์ประกอบ UI อื่นๆ ทั้งหมดในระหว่างการจับภาพหน้าจอ โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ระบบจะซ่อนไว้และจะแสดงเมื่อมีการใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลง UI ของหน้าจอ แฟลชเท่านั้น
ในโค้ดตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ สีขาว (#FFFFFF) จะใช้เป็นตัวอย่างสำหรับ
มุมมอง แอปพลิเคชันสามารถเลือกสีหรือเสนอสีหลายสีให้แก่ผู้ใช้
ตามข้อกำหนดของแอป
<View android:id="@+id/white_color_overlay" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#FFFFFF" android:visibility="invisible" android:elevation="8dp" />
เพิ่มความสว่างของหน้าจอให้สูงสุด
คุณเปลี่ยนความสว่างของหน้าจอในแอป Android ได้หลายวิธี วิธีหนึ่ง โดยตรงคือการเปลี่ยนพารามิเตอร์ screenBrightness ของ WindowManager ในการอ้างอิงหน้าต่างกิจกรรม
Kotlin
private var previousBrightness: Float = -1.0f private fun maximizeScreenBrightness() { activity?.window?.let { window -> window.attributes?.apply { previousBrightness = screenBrightness screenBrightness = 1f window.attributes = this } } } private fun restoreScreenBrightness() { activity?.window?.let { window -> window.attributes?.apply { screenBrightness = previousBrightness window.attributes = this } } }
Java
private float mPreviousBrightness = -1.0f; private void maximizeScreenBrightness() { if (getActivity() == null || getActivity().getWindow() == null) { return; } Window window = getActivity().getWindow(); WindowManager.LayoutParams attributes = window.getAttributes(); mPreviousBrightness = attributes.screenBrightness; attributes.screenBrightness = 1f; window.setAttributes(attributes); } private void restoreScreenBrightness() { if (getActivity() == null || getActivity().getWindow() == null) { return; } Window window = getActivity().getWindow(); WindowManager.LayoutParams attributes = window.getAttributes(); attributes.screenBrightness = mPreviousBrightness; window.setAttributes(attributes); }
ตั้งค่าโหมด AE เป็น CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH
CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH พร้อมใช้งานกับ API ระดับ 28 ขึ้นไป
อย่างไรก็ตาม โหมด AE นี้ไม่พร้อมใช้งานในอุปกรณ์บางรุ่น ดังนั้นโปรดตรวจสอบว่าโหมด AE พร้อมใช้งานหรือไม่
และตั้งค่าตามนั้น หากต้องการตรวจสอบความพร้อมใช้งาน ให้ใช้ CameraCharacteristics#CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_MODES
Kotlin
private val characteristics: CameraCharacteristics by lazy { cameraManager.getCameraCharacteristics(cameraId) } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.P) private fun isExternalFlashAeModeAvailable() = characteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_MODES) ?.contains(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH) ?: false
Java
try { mCharacteristics = mCameraManager.getCameraCharacteristics(mCameraId); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.P) private boolean isExternalFlashAeModeAvailable() { int[] availableAeModes = mCharacteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_MODES); for (int aeMode : availableAeModes) { if (aeMode == CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH) { return true; } } return false; }
หากแอปพลิเคชันมีการตั้งค่าคำขอจับภาพซ้ำ (จำเป็นสำหรับ ตัวอย่าง) โหมด AE จะต้องตั้งค่าเป็นคำขอซ้ำ ไม่เช่นนั้น ระบบอาจ ลบล้างด้วยโหมด AE เริ่มต้นหรือโหมด AE อื่นที่ผู้ใช้ตั้งค่าไว้ในการจับภาพ ที่ทำซ้ำครั้งถัดไป หากเกิดกรณีนี้ขึ้น กล้องอาจมีเวลาไม่เพียงพอที่จะดำเนินการทั้งหมด ตามปกติสำหรับโหมด AE ของแฟลชภายนอก
โปรดตรวจสอบผลการจับภาพในการเรียกกลับการจับภาพซ้ำและรอให้โหมด AE อัปเดตในผลลัพธ์ เพื่อช่วยให้มั่นใจว่ากล้องจะประมวลผลคำขออัปเดตโหมด AE เสร็จสมบูรณ์
Capture callback that can wait for AE mode to be updated
ข้อมูลโค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีดำเนินการ
Kotlin
private val repeatingCaptureCallback = object : CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback() { private var targetAeMode: Int? = null private var aeModeUpdateDeferred: CompletableDeferred? = null suspend fun awaitAeModeUpdate(targetAeMode: Int) { this.targetAeMode = targetAeMode aeModeUpdateDeferred = CompletableDeferred() // Makes the current coroutine wait until aeModeUpdateDeferred is completed. It is // completed once targetAeMode is found in the following capture callbacks aeModeUpdateDeferred?.await() } private fun process(result: CaptureResult) { // Checks if AE mode is updated and completes any awaiting Deferred aeModeUpdateDeferred?.let { val aeMode = result[CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_MODE] if (aeMode == targetAeMode) { it.complete(Unit) } } } override fun onCaptureCompleted( session: CameraCaptureSession, request: CaptureRequest, result: TotalCaptureResult ) { super.onCaptureCompleted(session, request, result) process(result) } }
Java
static class AwaitingCaptureCallback extends CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback { private int mTargetAeMode; private CountDownLatch mAeModeUpdateLatch = null; public void awaitAeModeUpdate(int targetAeMode) { mTargetAeMode = targetAeMode; mAeModeUpdateLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); // Makes the current thread wait until mAeModeUpdateLatch is released, it will be // released once targetAeMode is found in the capture callbacks below try { mAeModeUpdateLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void process(CaptureResult result) { // Checks if AE mode is updated and decrements the count of any awaiting latch if (mAeModeUpdateLatch != null) { int aeMode = result.get(CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_MODE); if (aeMode == mTargetAeMode) { mAeModeUpdateLatch.countDown(); } } } @Override public void onCaptureCompleted(@NonNull CameraCaptureSession session, @NonNull CaptureRequest request, @NonNull TotalCaptureResult result) { super.onCaptureCompleted(session, request, result); process(result); } } private final AwaitingCaptureCallback mRepeatingCaptureCallback = new AwaitingCaptureCallback();
ตั้งค่าคำขอที่ทำซ้ำเพื่อเปิดหรือปิดโหมด AE
เมื่อมี Capture Callback แล้ว ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้จะแสดงวิธีตั้งค่า คำขอที่ทำซ้ำ
Kotlin
/** [HandlerThread] where all camera operations run */ private val cameraThread = HandlerThread("CameraThread").apply { start() } /** [Handler] corresponding to [cameraThread] */ private val cameraHandler = Handler(cameraThread.looper) private suspend fun enableExternalFlashAeMode() { if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 28 && isExternalFlashAeModeAvailable()) { session.setRepeatingRequest( camera.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW).apply { addTarget(previewSurface) set( CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE, CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH ) }.build(), repeatingCaptureCallback, cameraHandler ) // Wait for the request to be processed by camera repeatingCaptureCallback.awaitAeModeUpdate(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH) } } private fun disableExternalFlashAeMode() { if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 28 && isExternalFlashAeModeAvailable()) { session.setRepeatingRequest( camera.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW).apply { addTarget(previewSurface) }.build(), repeatingCaptureCallback, cameraHandler ) } }
Java
private void setupCameraThread() { // HandlerThread where all camera operations run HandlerThread cameraThread = new HandlerThread("CameraThread"); cameraThread.start(); // Handler corresponding to cameraThread mCameraHandler = new Handler(cameraThread.getLooper()); } private void enableExternalFlashAeMode() { if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 28 && isExternalFlashAeModeAvailable()) { try { CaptureRequest.Builder requestBuilder = mCamera.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW); requestBuilder.addTarget(mPreviewSurface); requestBuilder.set(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE, CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH); mSession.setRepeatingRequest(requestBuilder.build(), mRepeatingCaptureCallback, mCameraHandler); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // Wait for the request to be processed by camera mRepeatingCaptureCallback.awaitAeModeUpdate(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH); } } private void disableExternalFlashAeMode() { if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 28 && isExternalFlashAeModeAvailable()) { try { CaptureRequest.Builder requestBuilder = mCamera.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW); requestBuilder.addTarget(mPreviewSurface); mSession.setRepeatingRequest(requestBuilder.build(), mRepeatingCaptureCallback, mCameraHandler); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
ทริกเกอร์ลำดับการจับภาพล่วงหน้า
หากต้องการทริกเกอร์ลำดับการวัดการใช้งานก่อนการจับภาพ คุณสามารถส่ง
CaptureRequest ที่ตั้งค่า CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER_START เป็นคำขอได้ คุณต้องรอให้ระบบประมวลผลคำขอก่อน แล้วรอให้ AE และ AWB บรรจบกัน
แม้ว่าทริกเกอร์ก่อนการจับภาพจะใช้คำขอจับภาพเดียว แต่การรอให้ AE และ AWB ทำงานร่วมกันนั้นต้องใช้ความซับซ้อนมากขึ้น คุณติดตามสถานะ AE และสถานะ AWB ได้โดยใช้การเรียกกลับการจับภาพที่ตั้งค่าเป็นคำขอที่ทำซ้ำ
การอัปเดตการเรียกกลับที่เกิดซ้ำเดียวกันจะช่วยให้โค้ดมีความเรียบง่าย แอปพลิเคชันมักต้องใช้พรีวิวซึ่งจะตั้งค่าคำขอที่ทำซ้ำ ขณะตั้งค่ากล้อง ดังนั้น คุณจึงตั้งค่าการเรียกกลับการจับภาพซ้ำเป็นการเรียกใช้คำขอซ้ำครั้งแรกนั้นได้เพียงครั้งเดียว จากนั้นนำไปใช้ซ้ำเพื่อตรวจสอบผลลัพธ์และรอ
บันทึกการอัปเดตรหัสเรียกกลับเพื่อรอการบรรจบกัน
หากต้องการอัปเดตการเรียกกลับของการจับภาพซ้ำ ให้ใช้ข้อมูลโค้ดต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
private val repeatingCaptureCallback = object : CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback() { private var targetAeMode: Int? = null private var aeModeUpdateDeferred: CompletableDeferred? = null private var convergenceDeferred: CompletableDeferred? = null suspend fun awaitAeModeUpdate(targetAeMode: Int) { this.targetAeMode = targetAeMode aeModeUpdateDeferred = CompletableDeferred() // Makes the current coroutine wait until aeModeUpdateDeferred is completed. It is // completed once targetAeMode is found in the following capture callbacks aeModeUpdateDeferred?.await() } suspend fun awaitAeAwbConvergence() { convergenceDeferred = CompletableDeferred() // Makes the current coroutine wait until convergenceDeferred is completed, it will be // completed once both AE & AWB are reported as converged in the capture callbacks below convergenceDeferred?.await() } private fun process(result: CaptureResult) { // Checks if AE mode is updated and completes any awaiting Deferred aeModeUpdateDeferred?.let { val aeMode = result[CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_MODE] if (aeMode == targetAeMode) { it.complete(Unit) } } // Checks for convergence and completes any awaiting Deferred convergenceDeferred?.let { val aeState = result[CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_STATE] val awbState = result[CaptureResult.CONTROL_AWB_STATE] val isAeReady = ( aeState == null // May be null in some devices (e.g. legacy camera HW level) || aeState == CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_STATE_CONVERGED || aeState == CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_STATE_FLASH_REQUIRED ) val isAwbReady = ( awbState == null // May be null in some devices (e.g. legacy camera HW level) || awbState == CaptureResult.CONTROL_AWB_STATE_CONVERGED ) if (isAeReady && isAwbReady) { // if any non-null convergenceDeferred is set, complete it it.complete(Unit) } } } override fun onCaptureCompleted( session: CameraCaptureSession, request: CaptureRequest, result: TotalCaptureResult ) { super.onCaptureCompleted(session, request, result) process(result) } }
Java
static class AwaitingCaptureCallback extends CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback { private int mTargetAeMode; private CountDownLatch mAeModeUpdateLatch = null; private CountDownLatch mConvergenceLatch = null; public void awaitAeModeUpdate(int targetAeMode) { mTargetAeMode = targetAeMode; mAeModeUpdateLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); // Makes the current thread wait until mAeModeUpdateLatch is released, it will be // released once targetAeMode is found in the capture callbacks below try { mAeModeUpdateLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void awaitAeAwbConvergence() { mConvergenceLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); // Makes the current coroutine wait until mConvergenceLatch is released, it will be // released once both AE & AWB are reported as converged in the capture callbacks below try { mConvergenceLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void process(CaptureResult result) { // Checks if AE mode is updated and decrements the count of any awaiting latch if (mAeModeUpdateLatch != null) { int aeMode = result.get(CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_MODE); if (aeMode == mTargetAeMode) { mAeModeUpdateLatch.countDown(); } } // Checks for convergence and decrements the count of any awaiting latch if (mConvergenceLatch != null) { Integer aeState = result.get(CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_STATE); Integer awbState = result.get(CaptureResult.CONTROL_AWB_STATE); boolean isAeReady = ( aeState == null // May be null in some devices (e.g. legacy camera HW level) || aeState == CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_STATE_CONVERGED || aeState == CaptureResult.CONTROL_AE_STATE_FLASH_REQUIRED ); boolean isAwbReady = ( awbState == null // May be null in some devices (e.g. legacy camera HW level) || awbState == CaptureResult.CONTROL_AWB_STATE_CONVERGED ); if (isAeReady && isAwbReady) { mConvergenceLatch.countDown(); mConvergenceLatch = null; } } } @Override public void onCaptureCompleted(@NonNull CameraCaptureSession session, @NonNull CaptureRequest request, @NonNull TotalCaptureResult result) { super.onCaptureCompleted(session, request, result); process(result); } }
ตั้งค่าการเรียกกลับเป็นคำขอที่ทำซ้ำระหว่างการตั้งค่ากล้อง
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้ช่วยให้คุณตั้งค่าการเรียกกลับเป็นคำขอที่ทำซ้ำ ระหว่างการเริ่มต้นได้
Kotlin
// Open the selected camera camera = openCamera(cameraManager, cameraId, cameraHandler) // Creates list of Surfaces where the camera will output frames val targets = listOf(previewSurface, imageReaderSurface) // Start a capture session using our open camera and list of Surfaces where frames will go session = createCameraCaptureSession(camera, targets, cameraHandler) val captureRequest = camera.createCaptureRequest( CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW).apply { addTarget(previewSurface) } // This will keep sending the capture request as frequently as possible until the // session is torn down or session.stopRepeating() is called session.setRepeatingRequest(captureRequest.build(), repeatingCaptureCallback, cameraHandler)
Java
// Open the selected camera mCamera = openCamera(mCameraManager, mCameraId, mCameraHandler); // Creates list of Surfaces where the camera will output frames Listtargets = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(mPreviewSurface, mImageReaderSurface)); // Start a capture session using our open camera and list of Surfaces where frames will go mSession = createCaptureSession(mCamera, targets, mCameraHandler); try { CaptureRequest.Builder requestBuilder = mCamera.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW); requestBuilder.addTarget(mPreviewSurface); // This will keep sending the capture request as frequently as possible until the // session is torn down or session.stopRepeating() is called mSession.setRepeatingRequest(requestBuilder.build(), mRepeatingCaptureCallback, mCameraHandler); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
การทริกเกอร์และการรอการทำงานของลำดับก่อนการจับภาพ
เมื่อตั้งค่าการเรียกกลับแล้ว คุณจะใช้ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้เพื่อทริกเกอร์และรอซีเควนซ์ก่อนการจับภาพได้
Kotlin
private suspend fun runPrecaptureSequence() { // Creates a new capture request with CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER_START val captureRequest = session.device.createCaptureRequest( CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW ).apply { addTarget(previewSurface) set( CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER, CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER_START ) } val precaptureDeferred = CompletableDeferred() session.capture(captureRequest.build(), object: CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback() { override fun onCaptureCompleted( session: CameraCaptureSession, request: CaptureRequest, result: TotalCaptureResult ) { // Waiting for this callback ensures the precapture request has been processed precaptureDeferred.complete(Unit) } }, cameraHandler) precaptureDeferred.await() // Precapture trigger request has been processed, we can wait for AE & AWB convergence now repeatingCaptureCallback.awaitAeAwbConvergence() }
Java
private void runPrecaptureSequence() { // Creates a new capture request with CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER_START try { CaptureRequest.Builder requestBuilder = mSession.getDevice().createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW); requestBuilder.addTarget(mPreviewSurface); requestBuilder.set(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER, CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER_START); CountDownLatch precaptureLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); mSession.capture(requestBuilder.build(), new CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback() { @Override public void onCaptureCompleted(@NonNull CameraCaptureSession session, @NonNull CaptureRequest request, @NonNull TotalCaptureResult result) { Log.d(TAG, "CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER_START processed"); // Waiting for this callback ensures the precapture request has been processed precaptureLatch.countDown(); } }, mCameraHandler); precaptureLatch.await(); // Precapture trigger request has been processed, we can wait for AE & AWB convergence now mRepeatingCaptureCallback.awaitAeAwbConvergence(); } catch (CameraAccessException | InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
รวมทุกอย่างเข้าด้วยกัน
เมื่อคอมโพเนนต์หลักทั้งหมดพร้อมใช้งาน เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ต้องถ่ายภาพ เช่น เมื่อผู้ใช้คลิกปุ่มจับภาพเพื่อถ่ายรูป ขั้นตอนทั้งหมดจะดำเนินการตามลำดับที่ระบุไว้ในการอภิปรายและตัวอย่างโค้ดก่อนหน้านี้ได้
Kotlin
// User clicks captureButton to take picture captureButton.setOnClickListener { v -> // Apply the screen flash related UI changes whiteColorOverlayView.visibility = View.VISIBLE maximizeScreenBrightness() // Perform I/O heavy operations in a different scope lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) { // Enable external flash AE mode and wait for it to be processed enableExternalFlashAeMode() // Run precapture sequence and wait for it to complete runPrecaptureSequence() // Start taking picture and wait for it to complete takePhoto() disableExternalFlashAeMode() v.post { // Clear the screen flash related UI changes restoreScreenBrightness() whiteColorOverlayView.visibility = View.INVISIBLE } } }
Java
// User clicks captureButton to take picture mCaptureButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // Apply the screen flash related UI changes mWhiteColorOverlayView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); maximizeScreenBrightness(); // Perform heavy operations in a different thread Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(() -> { // Enable external flash AE mode and wait for it to be processed enableExternalFlashAeMode(); // Run precapture sequence and wait for it to complete runPrecaptureSequence(); // Start taking picture and wait for it to complete takePhoto(); disableExternalFlashAeMode(); v.post(() -> { // Clear the screen flash related UI changes restoreScreenBrightness(); mWhiteColorOverlayView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); }); }); } });
รูปภาพตัวอย่าง
คุณดูตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้เพื่อดูว่าเกิดอะไรขึ้นเมื่อใช้การกะพริบของหน้าจออย่างไม่ถูกต้องและเมื่อใช้อย่างถูกต้อง
เมื่อทำไม่ถูกต้อง
หากไม่ได้ใช้การกะพริบของหน้าจออย่างถูกต้อง คุณจะได้รับผลลัพธ์ที่ไม่สอดคล้องกันใน การจับภาพ อุปกรณ์ และสภาพแสงต่างๆ บ่อยครั้งที่รูปภาพที่ถ่ายมีปัญหา การเปิดรับแสงหรือสีที่ไม่ดี สำหรับอุปกรณ์บางเครื่อง ข้อบกพร่องประเภทนี้จะเห็นได้ชัดเจนยิ่งขึ้นในสภาพแสงที่เฉพาะเจาะจง เช่น สภาพแวดล้อมที่มีแสงน้อยแทนที่จะเป็นสภาพแวดล้อมที่มืดสนิท
ตารางต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างปัญหาดังกล่าว รูปภาพเหล่านี้ถ่ายใน โครงสร้างพื้นฐานของห้องทดลอง CameraX โดยแหล่งกำเนิดแสงยังคงเป็นสีขาวนวล แหล่งกำเนิดแสงสีขาวนวลนี้ช่วยให้คุณเห็นว่าสีน้ำเงินที่เจือปนเป็นปัญหาจริง ไม่ใช่ผลข้างเคียงจากแหล่งกำเนิดแสง
| สภาพแวดล้อม | แสงน้อยเกินไป | การเปิดรับแสงมากเกินไป | การปรับสมดุลสีเขียว-แดง |
|---|---|---|---|
| สภาพแวดล้อมมืด (ไม่มีแหล่งกำเนิดแสงนอกจากโทรศัพท์) |

|

|
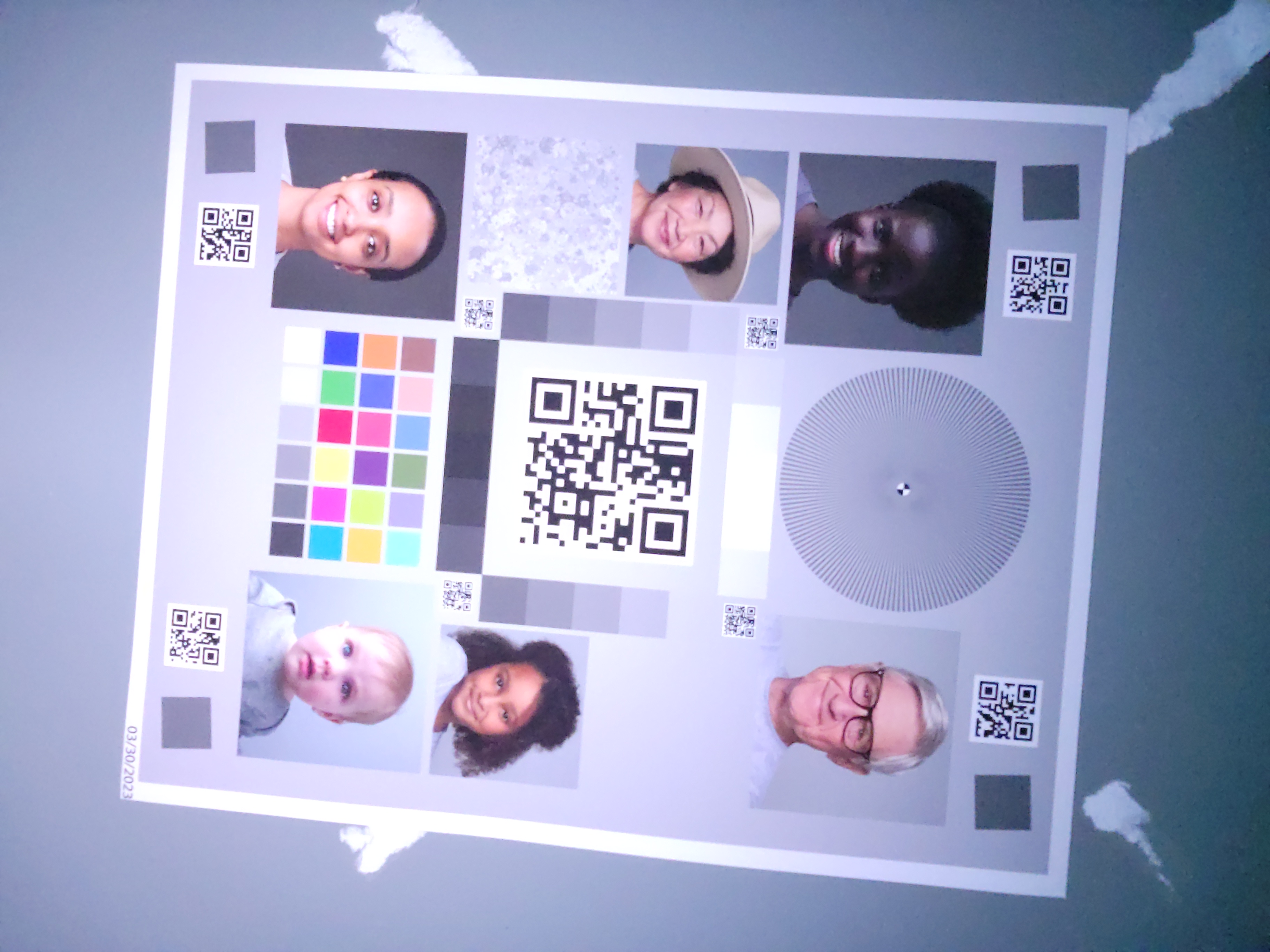

|
| แสงน้อย (แหล่งกำเนิดแสงเพิ่มเติมประมาณ 3 ลักซ์) |

|

|

|
เมื่อทำอย่างถูกต้อง
เมื่อใช้การติดตั้งใช้งานมาตรฐานสำหรับอุปกรณ์และเงื่อนไขเดียวกัน คุณจะเห็นผลลัพธ์ในตารางต่อไปนี้
| สภาพแวดล้อม | ภาพสว่างไม่พอ (แก้ไขแล้ว) | การเปิดรับแสงมากเกินไป (แก้ไขแล้ว) | การปรับสมดุลสีเขียว-แดง (คงที่) |
|---|---|---|---|
| สภาพแวดล้อมมืด (ไม่มีแหล่งกำเนิดแสงนอกจากโทรศัพท์) |

|

|
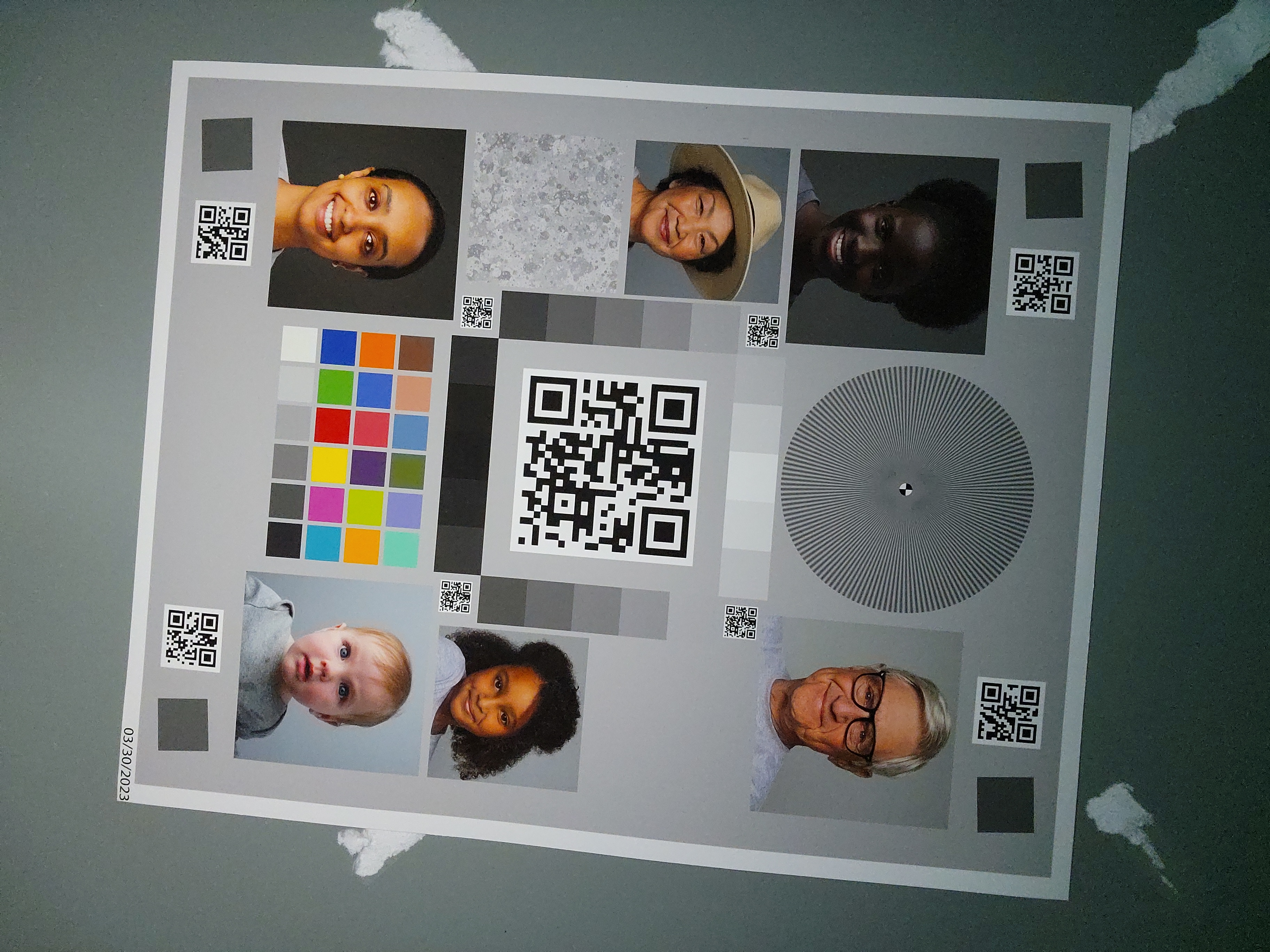

|
| แสงน้อย (แหล่งกำเนิดแสงเพิ่มเติมประมาณ 3 ลักซ์) |

|

|

|
ดังที่สังเกตได้ คุณภาพของรูปภาพจะดีขึ้นอย่างมากเมื่อใช้การติดตั้งใช้งานมาตรฐาน
