
रिस्पॉन्सिव और ऑप्टिमाइज़ किए गए ऐप्लिकेशन, रिस्पॉन्सिव लेआउट का इस्तेमाल करते हैं. ये लेआउट, अलग-अलग स्क्रीन साइज़ के हिसाब से अपने-आप बदल जाते हैं. इससे, उपयोगकर्ताओं को कुछ अतिरिक्त फ़ायदे मिलते हैं. साथ ही, उन्हें बेहतर और दिलचस्प अनुभव मिलता है.
रिस्पॉन्सिव डिज़ाइन की मदद से अहमियत जोड़ना
रिस्पॉन्सिव लेआउट, उपयोगकर्ता को बेहतर अनुभव देने के लिए बटन, टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड, और डायलॉग जैसे एलिमेंट को डाइनैमिक तौर पर फ़ॉर्मैट करते हैं और उनकी पोज़िशन तय करते हैं. रिस्पॉन्सिव डिज़ाइन के तरीकों का इस्तेमाल करके, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के उपयोगकर्ताओं को बड़ी स्क्रीन पर अपने-आप ज़्यादा फ़ायदे दें. रिस्पॉन्सिव डिज़ाइन के इस्तेमाल से, बड़ी स्क्रीन का इस्तेमाल करने वाले लोगों को बेहतर अनुभव मिलता है. जैसे, एक नज़र में ज़्यादा टेक्स्ट दिखना, स्क्रीन पर ज़्यादा कार्रवाइयां या बड़े और आसानी से ऐक्सेस किए जा सकने वाले टैप टारगेट.

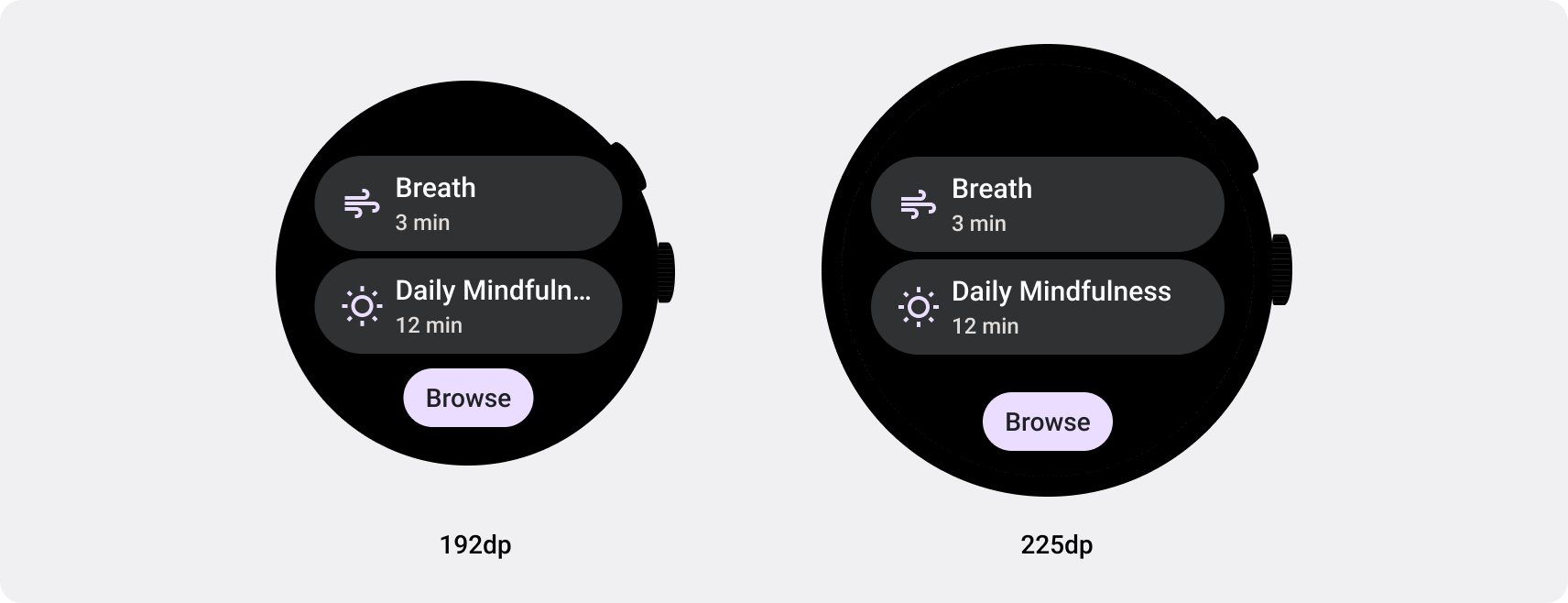
Wear OS के लिए रिस्पॉन्सिव ऐप्लिकेशन और टाइल बनाना
रिस्पॉन्सिव यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई), स्क्रीन के सभी उपलब्ध स्पेस का बेहतर तरीके से इस्तेमाल करने के लिए स्ट्रेच और बदलते हैं. इससे कोई फ़र्क़ नहीं पड़ता कि उन्हें किस साइज़ की स्क्रीन पर रेंडर किया जा रहा है. राउंड स्क्रीन पर रिस्पॉन्सिव लेआउट डिज़ाइन करते समय, स्क्रोलिंग और नॉन-स्क्रोलिंग व्यू, दोनों के लिए यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) एलिमेंट के स्केलिंग को बनाए रखने के साथ-साथ, लेआउट और कॉम्पोज़िशन को संतुलित बनाए रखने के लिए, अलग-अलग ज़रूरतें होती हैं. स्क्रोल किए जा सकने वाले व्यू के लिए, प्रतिशत का इस्तेमाल करके, ऊपर, नीचे, और किनारों के सभी मार्जिन तय करें. इससे, एलिमेंट को काटने से बचा जा सकता है और उन्हें सही अनुपात में स्केल किया जा सकता है. नॉन-स्क्रोलिंग व्यू के लिए, सभी मार्जिन के लिए प्रतिशत और वर्टिकल कंस्ट्रेंट का इस्तेमाल करें. इस तरह, बीच में मौजूद मुख्य कॉन्टेंट को उपलब्ध जगह के हिसाब से बड़ा किया जा सकता है.
रिस्पॉन्सिव लेआउट के लिए, कॉम्पोज़ और टाइल लागू करने के दिशा-निर्देश देखें.
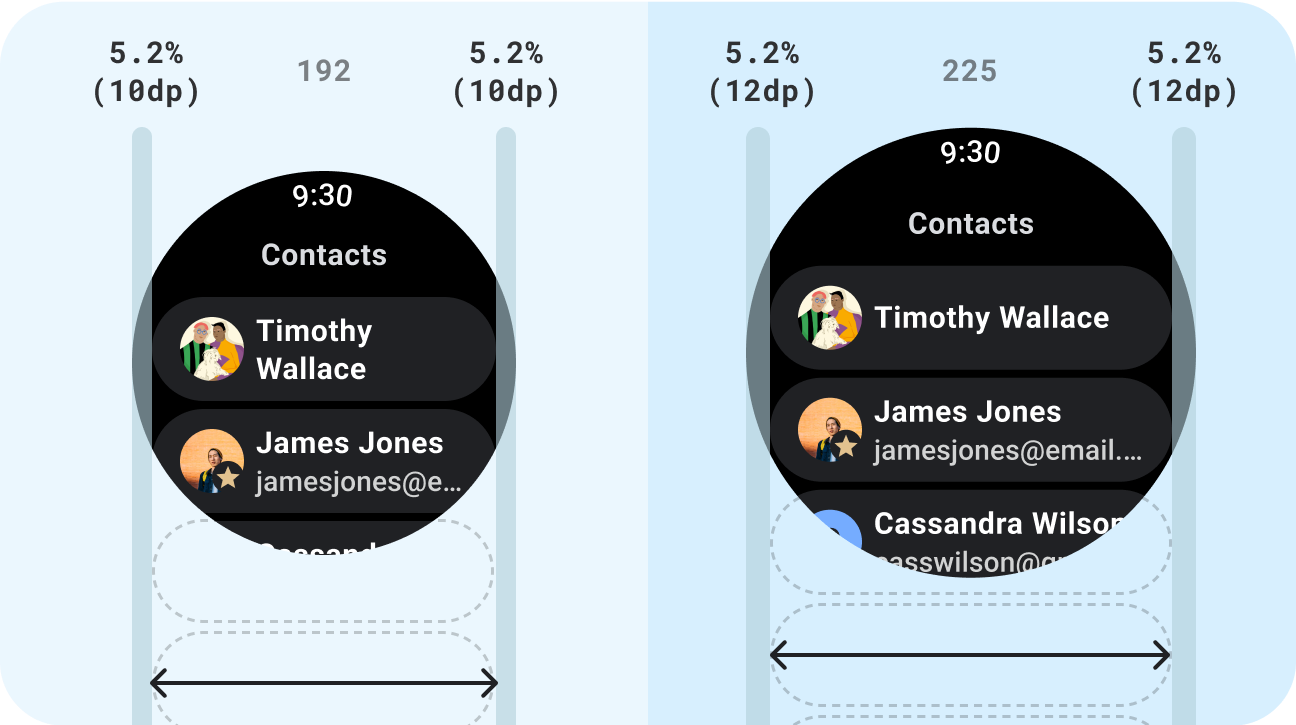
यह करें
- ऐसे स्टैंडर्ड कॉम्पोनेंट का इस्तेमाल करें जिन्हें ऐडैप्ट करने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया हो.
- अडैप्टिव लेआउट का इस्तेमाल करें, जो सभी स्क्रीन साइज़ के हिसाब से आसानी से अडजस्ट हो जाते हैं.
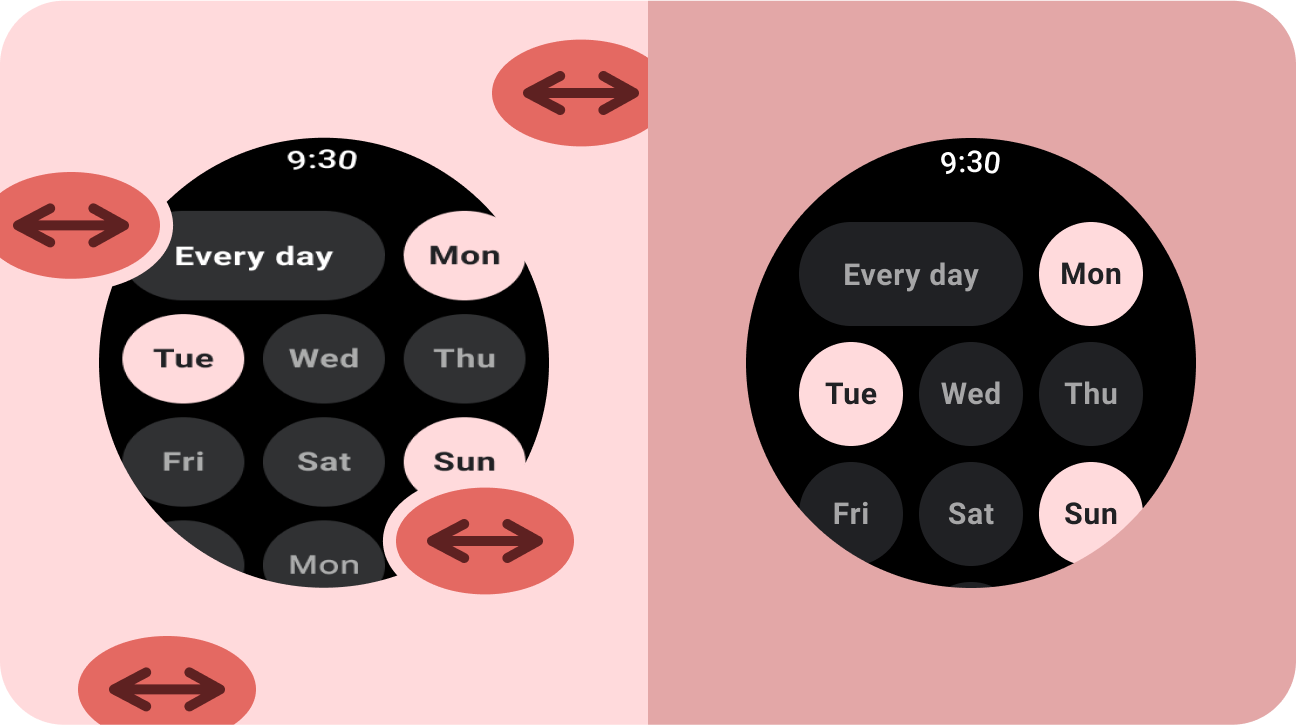
यह न करें
- अतिरिक्त जगह भरने के लिए, यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) एलिमेंट (टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड, बटन, डायलॉग) को बड़ा करें.
- फ़ॉन्ट के साइज़ बढ़ाएं (अगर वे मुख्य रूप से ग्राफ़िक के मकसद से इस्तेमाल नहीं किए जा रहे हैं).
अगला चरण: उपयोगकर्ताओं के हिसाब से बदलने वाला और अलग-अलग तरह का कॉन्टेंट
अडैप्टिव और अलग ऐप्लिकेशन, उपयोगकर्ता को ऐसा अनुभव देते हैं जो छोटी स्क्रीन वाले डिवाइसों पर नहीं मिल सकता.
