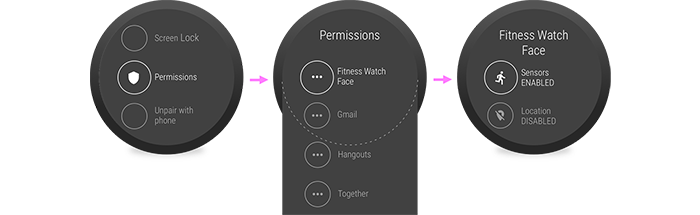
keywords: wear, permissions, collection_guideslandingwear image_path: images/training/wear/multiple_permissions.png
在 Wear OS 上要求權限和在行動應用程式中要求權限的方式類似,只是 Wear OS 能提供更多用途。本文假設您已經瞭解 Android 權限的運作方式。如果不太熟悉,請參閱「Android 中的權限運作方式」。
和行動應用程式一樣,使用者必須授予 Wear 應用程式權限,才能存取特定功能。請讓您的 Wear 應用程式在不要求任何權限的情況下,提供有意義的功能。
權限情境
在 Wear OS 上要求危險權限時,可能會遇到以下情境:
Wear 應用程式為正在穿戴式裝置上執行的應用程式要求權限。
Wear 應用程式為正在手機上執行的應用程式要求權限。
手機應用程式為正在穿戴式裝置上執行的應用程式要求權限。
手機應用程式要求取得只有在連接穿戴式裝置時才能使用的多項權限。
如要藉由實際執行的應用程式查看這些情境,請參閱 GitHub 上的 ExerciseSampleCompose 範例。
以下各節將說明這些情境。如需要求權限的詳細資訊,請參閱「權限要求模式」一節。
Wear 應用程式要求穿戴式裝置權限
當 Wear 應用程式為正在穿戴式裝置上執行的應用程式要求權限時,系統會顯示對話方塊,提示使用者授予權限。在您的應用程式中,請僅在使用者清楚瞭解為何需要該權限執行特定作業時,才要求權限。
請詳閱「權限原則」,確保您能為使用者提供最佳體驗,並且別忘了查看 shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(),並視需要提供其他資訊。
如果應用程式或錶面一次要求多項權限,系統會逐一顯示權限要求。
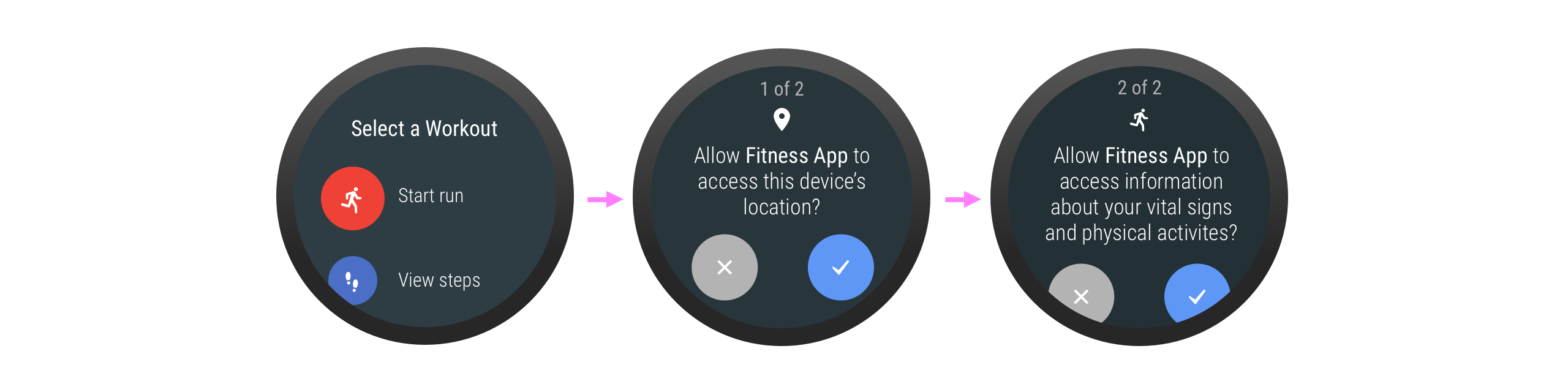
Wear 應用程式要求手機權限
當 Wear 應用程式要求手機權限 (例如穿戴式應用程式要求存取行動版應用程式的相片或其他機密資料) 時,Wear 應用程式必須引導使用者在手機上授予權限。接著,手機應用程式就可以使用一個活動向使用者提供其他資訊。活動中包含兩個按鈕:一個用於授予權限,另一個則用於拒絕授予權限。

手機應用程式要求穿戴式裝置權限
如果使用者正在使用手機應用程式,而應用程式要求穿戴式裝置權限 (例如預先載入音樂以免手機連線中斷),手機應用程式會引導使用者在穿戴式裝置上授予權限。穿戴式裝置版本的應用程式會使用 requestPermissions() 方法觸發系統權限對話方塊。
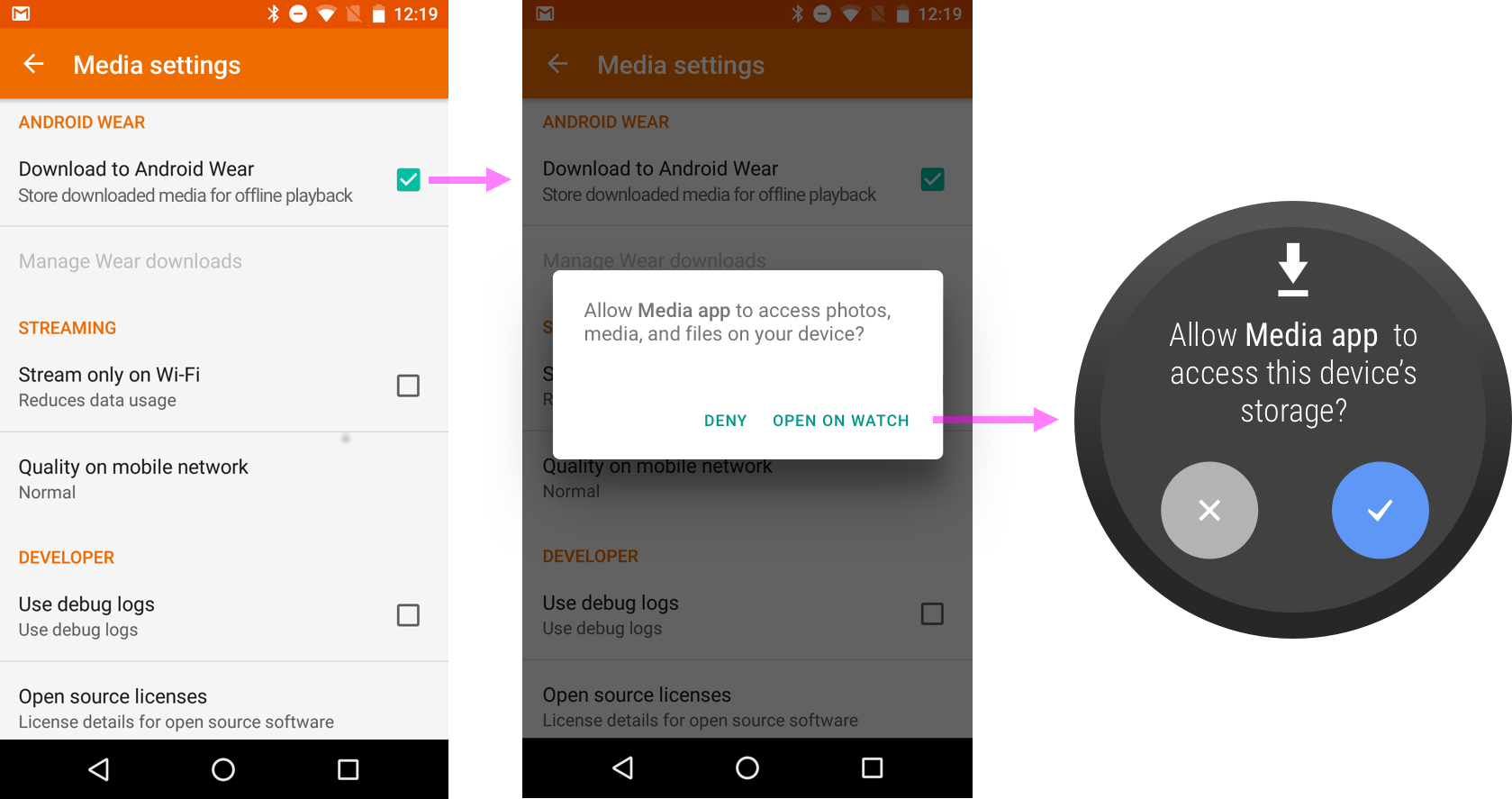
手機應用程式同時要求多項權限
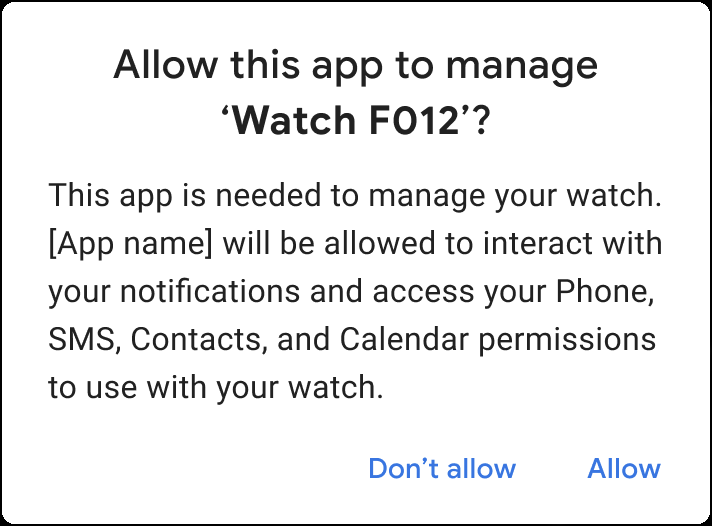
Android 12 (API 級別 31) 以上版本的隨附應用程式可在與手錶連線後,使用隨附裝置的設定檔。透過使用設定檔,應用程式能夠整合多種裝置類型專用權限的授予程序,只要一個步驟就能處理完畢,可簡化註冊流程。
連線到裝置時,系統便會授予這些隨附應用程式整合的權限,並只在裝置連線期間有效。刪除應用程式或移除連線後,系統會一併移除權限。詳情請參閱 AssociationRequest.Builder.setDeviceProfile()。
權限要求模式
向使用者要求權限的模式有很多種。以下按照優先順序排列:
在使用情境中要求:當有特定功能明確需要某項權限,但執行整個應用程式並不需要該權限時。
在使用情境中說明:當要求權限的理由並不明確,且執行整個應用程式並不需要該權限時。
以下各節將說明這些模式。
在使用情境中要求
在使用者清楚瞭解為何需要該權限執行特定作業時,才要求權限。如果使用者瞭解權限和欲使用功能之間的關聯,授予權限的意願會比較高。
例如,應用程式可能需要使用者的位置資訊來顯示附近的景點。當使用者輕觸搜尋附近地點時,應用程式可以立即要求位置存取權,因為搜尋附近地點和位置存取權之間的關係十分明確。由於關係明確,因此應用程式不需要顯示額外的說明畫面。
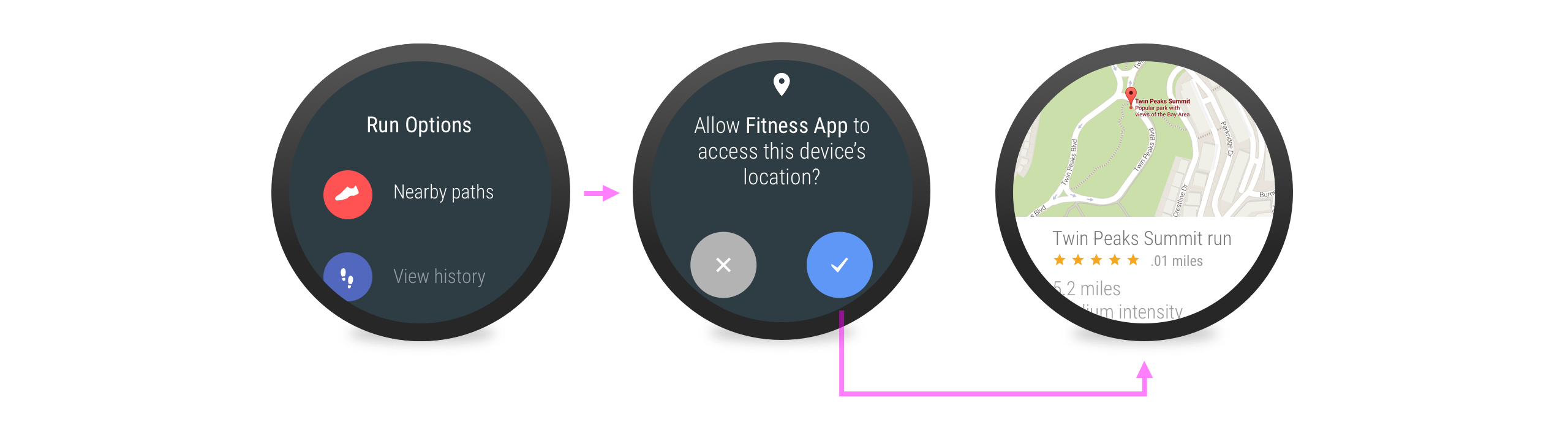
在使用情境中說明
圖 6. 顯示在使用情境中說明的範例。應用程式不需要權限就能啟動計時器,但是內嵌說明提示顯示有部分活動 (偵測位置權限) 遭到鎖定。使用者輕觸提示後便會開啟權限要求畫面,允許使用者解鎖位置偵測功能。
請使用 shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale() 協助應用程式決定是否該提供詳細資訊。詳情請參閱「要求應用程式權限」。另外,您也可以查看 GitHub 上的揚聲器應用程式範例,瞭解如何處理顯示資訊。
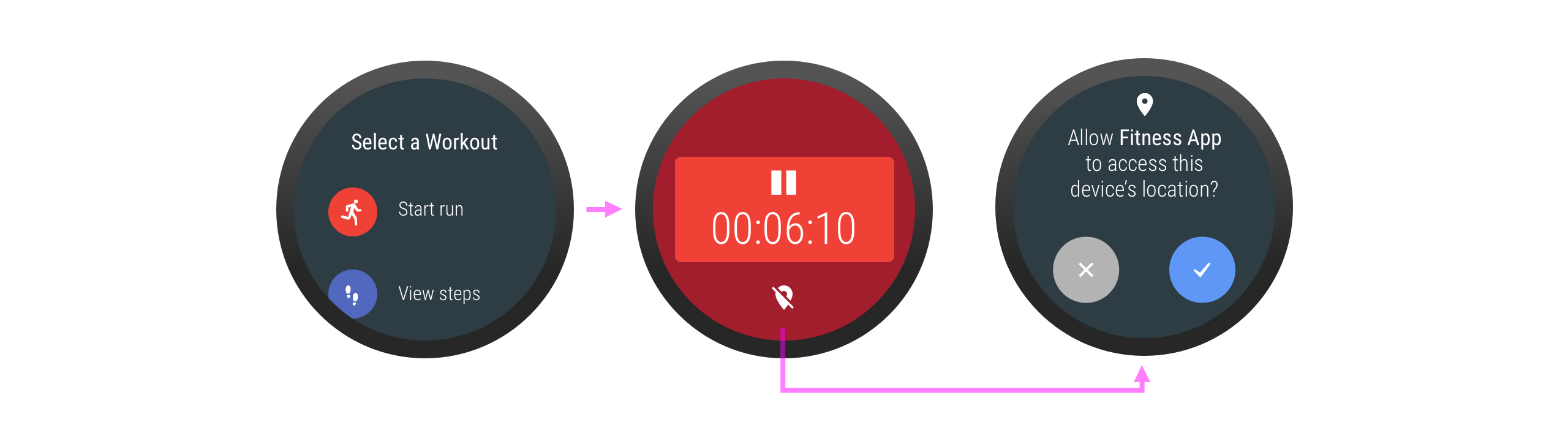
處理權限要求遭拒的情況
如果使用者拒絕授予的權限對目標活動影響不大,請勿禁止使用者繼續進行該活動。如果活動的某些部分因權限要求遭拒而停用,請向使用者提供實用的圖像說明。
圖 7. 顯示鎖頭圖示,表示由於使用者未授予使用權限,因此該功能遭到鎖定。
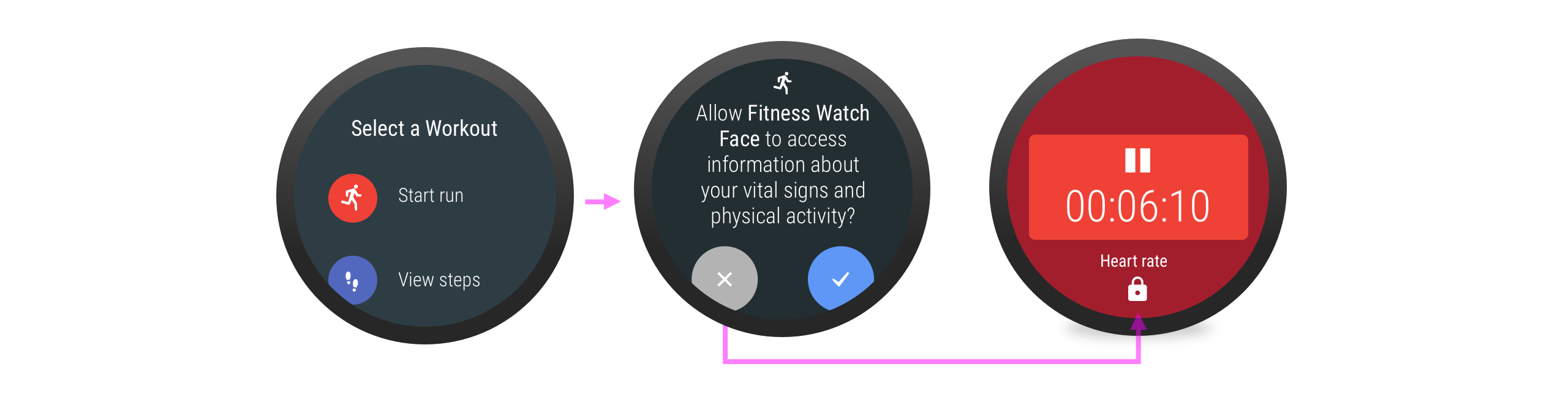
如果之前遭拒的穿戴式裝置權限對話方塊再度出現,其中會顯示「拒絕,不再顯示」的選項。當使用者選取此選項後,之後只能前往穿戴式裝置的「設定」應用程式,才能允許授予這項權限。
進一步瞭解如何「處理權限要求遭拒的情況」。
服務權限
只有活動才能呼叫 requestPermissions() 方法,因此若使用者透過服務 (例如透過錶面) 和應用程式互動,則該服務必須先開啟活動才能要求權限。請在這個活動中,詳細說明為何需要該權限。
一般情況下,請不要為錶面要求權限。您可以改為實作小工具,讓使用者透過小工具選擇要顯示的資料。
設定
使用者隨時可以在「設定」中變更 Wear 應用程式的權限。當使用者嘗試執行需要權限的作業時,請先呼叫 checkSelfPermission() 方法,查看應用程式是否具備執行作業的權限。
即使使用者先前已授予權限,還是請執行這項檢查,因為使用者可能之後又撤銷該權限。