
Wear OS 向けのマテリアル デザインにより、魅力的なアプリ エクスペリエンスを実現できます。
ユースケースを把握する
スマートウォッチでは、健康やフィットネスの目標に対する進捗状況の確認など、情報を一目で確認することができます。また、インスタント メッセージへの応答などをすばやく行えます。スマートウォッチ向けアプリをデザインする際は、こうしたユースケースに着目してください。
スマートウォッチのインターフェースには、モバイル デバイスにはない、以下のような固有の使用機会があります。
- 体に密着していることで(センサー、モーション検知により)可能になる入力
- ウォッチフェイスの追加機能、通知、タイルなど、ひと目でわかる情報とアクションに対するすばやいアクセス
スマートウォッチには制約もあります。
- 画面スペースが狭い
- 情報密度が低い
- バッテリー駆動時間が短い
スマートウォッチ向けアプリを設計する際は、プラットフォームの機能と制約の両方を考慮してください。

すべきこと
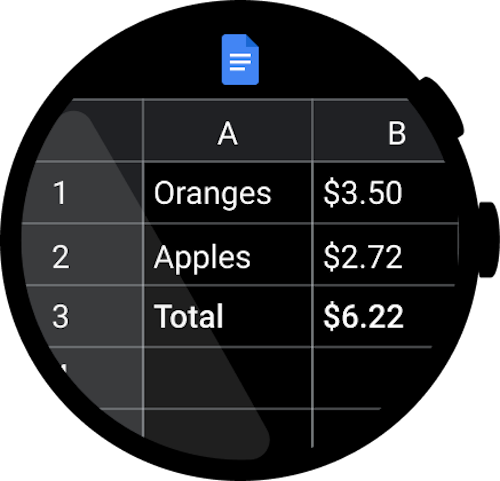
すべきでないこと
デザインをテストする
Wear OS デバイスの大半は丸い画面を備えており、正方形のディスプレイより UI のスペースが 22% 少なくなっています。また、円形の画面で文字を読みやすくするには余白を大きくとる必要があります。
Wear OS 向けのマテリアル デザインにより、魅力的なアプリ エクスペリエンスを実現できます。このガイドで説明している原則に沿った Wear OS アプリの例を、スクリーンショットで以下に示します。
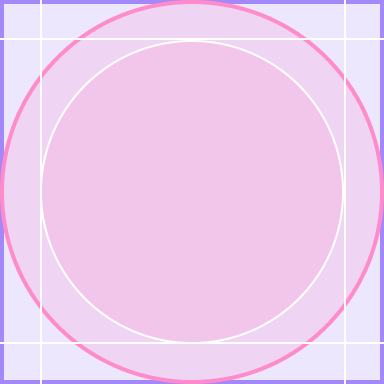
すべきこと

すべきでないこと
アプリの例
Wear OS 向けのマテリアル デザインにより、魅力的なアプリ エクスペリエンスを実現できます。このガイドで説明している原則に沿った Wear OS アプリの例を、スクリーンショットで以下に示します。
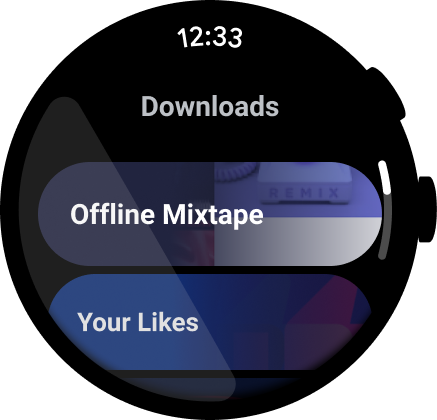
図 1. メディアアプリの例。
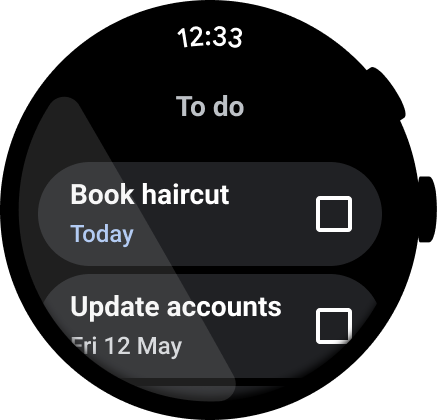
図 2. タスク管理アプリの例。
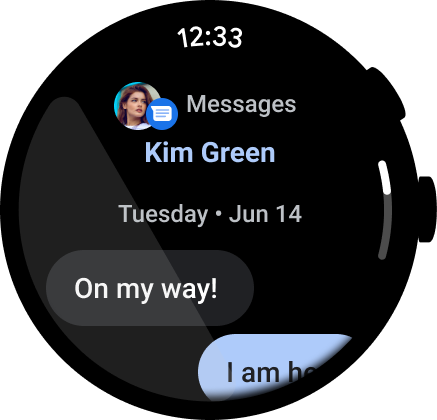
図 3. インスタント メッセージ アプリの例。

図 4. ストップウォッチ アプリの例。
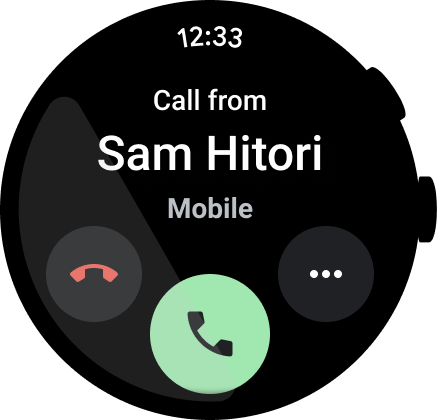
図 5. 電話アプリの例。

図 6. 電卓アプリの例。

