View 기반 레이아웃을 사용하는 경우 전환을 구현하는 데는 세 가지 기본 옵션이 있습니다. Material 구성요소 라이브러리의 SwitchMaterial 구성요소를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<com.google.android.material.switchmaterial.SwitchMaterial
android:id="@+id/material_switch"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/material_switch"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
기존 앱은 다음 예와 같이 이전 SwitchCompat AppCompat 구성요소를 계속 사용할 수 있습니다.
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.SwitchCompat
android:id="@+id/switchcompat"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/switchcompat"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
다음 예는 UI가 눈에 띄게 다른 또 다른 기존 구성요소인 AppCompatToggleButton를 보여줍니다.
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/toggle_button_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/toggle"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/toggle"
android:text="@string/toggle_button" />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatToggleButton
android:id="@+id/toggle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/toggle_button_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
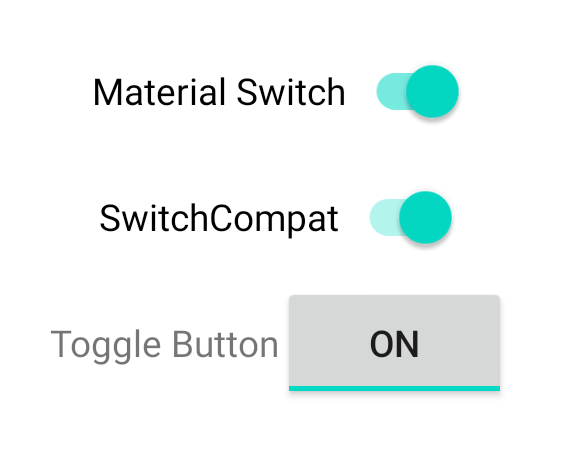
이 세 가지 구성요소는 동일한 동작을 제공하지만 모양이 다릅니다. SwitchMaterial와 SwitchCompat의 차이는 미묘하지만 AppCompatToggleButton는 눈에 띄게 다릅니다.
상태 변경 처리
SwitchMaterial, SwitchCompat, AppCompatToggleButton는 모두 CompoundButton의 서브클래스이므로 확인된 상태 변경을 처리하기 위한 공통 메커니즘을 제공합니다. 다음 예와 같이 CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener의 인스턴스를 구현하고 버튼에 추가합니다.
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) val binding: SwitchLayoutBinding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener { _, isChecked -> if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } } } }
자바
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); SwitchLayoutBinding binding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener((buttonView, isChecked) -> { if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } }); } }
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener는 단일 추상 메서드 인터페이스(또는 SAM 인터페이스)이므로 람다로 구현할 수 있습니다. 람다는 선택된 상태가 변경될 때마다 호출되며 람다에 전달되는 isChecked 불리언 값은 새 선택된 상태를 나타냅니다.

