Eclipse ADT プラグインはサポートが終了しています。Android Studio に移行し、ndk-build または CMake を使用してアプリのネイティブ ソースをコンパイル、ビルド、パッケージ化することをおすすめします。ndk-build との互換性により、ネイティブ プロジェクトを Eclipse から Android Studio に簡単に移行できます。Android の公式 IDE でのネイティブ開発について詳しくは、プロジェクトへの C / C++ コードへの追加に関するガイドをご覧ください。
インストール
NDK をインストールして設定する手順は次のとおりです。
- Android SDK コマンドライン ツールを入手してインストールします。
- NDK をダウンロードします。開発プラットフォームに合った適切なバージョンをダウンロードしてください。解凍したディレクトリは、ローカル ドライブのどこにでも配置できます。
PATH環境変数を、NDK が格納されているディレクトリの場所に更新します。
Eclipse の設定
アプリをビルドするときに NDK を使用するには、Eclipse が NDK の場所を認識している必要があります。次の手順に沿って、NDK の場所を設定します。
- Android SDK の一部としてインストールされている Eclipse を起動します。
- [Window] > [Preferences] を開きます。
- [Preferences] ウィンドウの左側のペインで、[Android] を選択します。 [Android] セクションが展開され、サブセクションが表示されます。
- [NDK] を選択します。[Preferences] ウィンドウの右側のペインで、NDK が含まれるディレクトリを参照します。
- [OK] をクリックして [Package Explorer] の表示に戻ります。
検証
Eclipse
NDK をインストールして正しくセットアップし、Eclipse を正しく設定したことを確認する手順は次のとおりです。
- 他の Android プロジェクトと同様に、hello-jni サンプルを
<ndk>/samples/から読み込みます。 - [Project Explorer] ペインで、プロジェクト名(HelloJni)を右クリックします。コンテキスト メニューが表示されます。
- コンテキスト メニューから [Android Tools] > [Add Native Support] を選択します。[Add Android Native Support] ウィンドウが表示されます。
- デフォルト ライブラリ名(「hello-jni」)に同意し、[Finish] をクリックします。
- アプリをビルドして実行します。
コマンドライン
コマンドラインからビルドする手順は次のとおりです。
- プロジェクトのルート ディレクトリに移動します。
- ndk-build を実行して、アプリのネイティブ コンポーネントをビルドします。そのためには、コマンド プロンプトで「
ndk-build」と入力します。 - Java で書かれた通常の Android アプリと同様に、プロジェクトをビルドしてインストールします。詳細については、ビルドを設定するガイドとコマンドラインから Gradle を実行するガイドをご覧ください。
NDK を正常にインストールして設定すると、ターゲット デバイスの画面は図 1 のように表示されます。
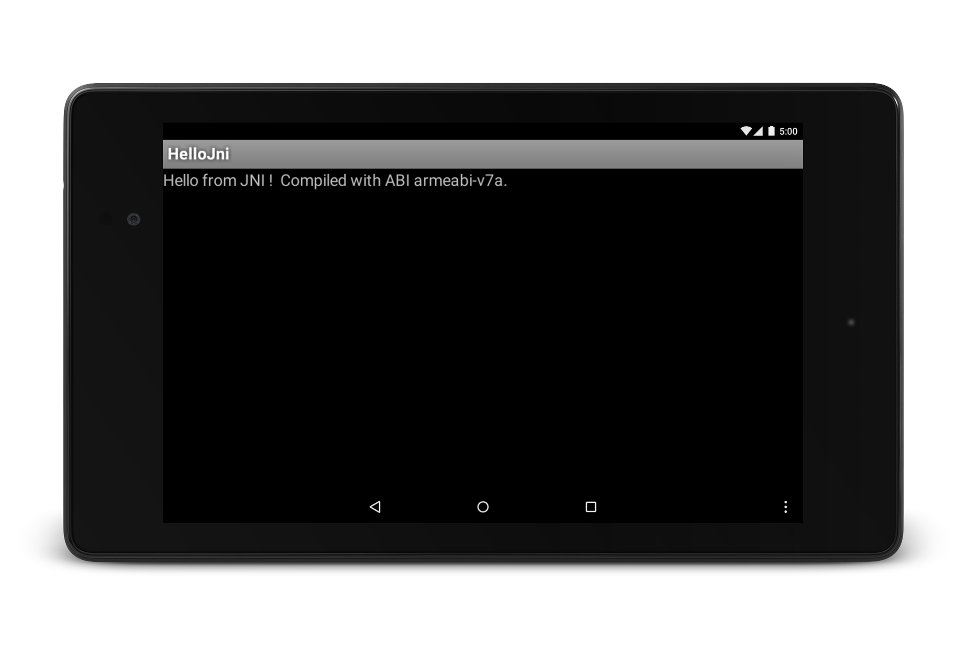
図 1. 正常に起動されたターゲット デバイスの画面
