Các thiết bị chạy Android có thẻ SIM và eSIM sử dụng các mã nhận dạng sau trong API điện thoại, bao gồm cả TelephonyManager và SubscriptionManager:
- Mã gói thuê bao: mã nhận dạng duy nhất của một gói thuê bao trên thiết bị di động.
- Mã hoặc chỉ mục vị trí logic: chỉ mục duy nhất tham chiếu đến vị trí SIM logic. Mã vùng logic bắt đầu từ 0 và tăng lên tuỳ thuộc vào số lượng khe đang hoạt động được hỗ trợ trên thiết bị. Ví dụ: thiết bị hai SIM thường có khe 0 và khe 1. Nếu có nhiều khe thực tế nhưng chỉ hỗ trợ một khe đang hoạt động, thì thiết bị sẽ chỉ có mã vùng logic bằng 0.
- Chỉ mục vị trí thực tế hoặc mã nhận dạng: chỉ mục duy nhất đề cập đến vị trí lắp đặt SIM thực. Mã vị trí thực bắt đầu từ 0 và tăng lên tuỳ thuộc vào số lượng khe thực tế trên thiết bị. Giá trị này khác với số lượng khe logic mà một thiết bị có, tương ứng với số lượng khe đang hoạt động mà một thiết bị có thể sử dụng. Ví dụ: một thiết bị chuyển đổi giữa chế độ 2 SIM và một SIM có thể luôn có 2 khe cắm vật lý, nhưng ở chế độ một SIM thì thiết bị sẽ chỉ có một khe logic.
- Mã thẻ: mã nhận dạng duy nhất dùng để nhận dạng một thẻ UiccCard.
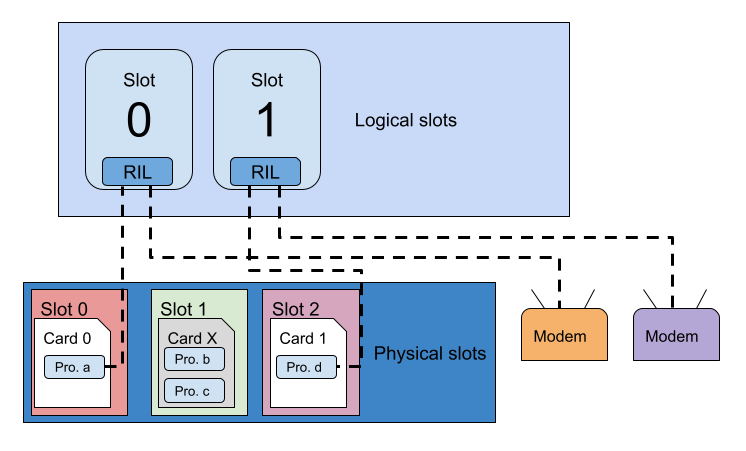
Trong biểu đồ trước:
- Thiết bị có 2 khe logic.
- Trong vị trí thực 0, có một thẻ UICC thực có hồ sơ đang hoạt động.
- Trong vùng thực 2 là một eUICC có hồ sơ đang hoạt động.
- Vị trí thực tế 1 hiện không được sử dụng.
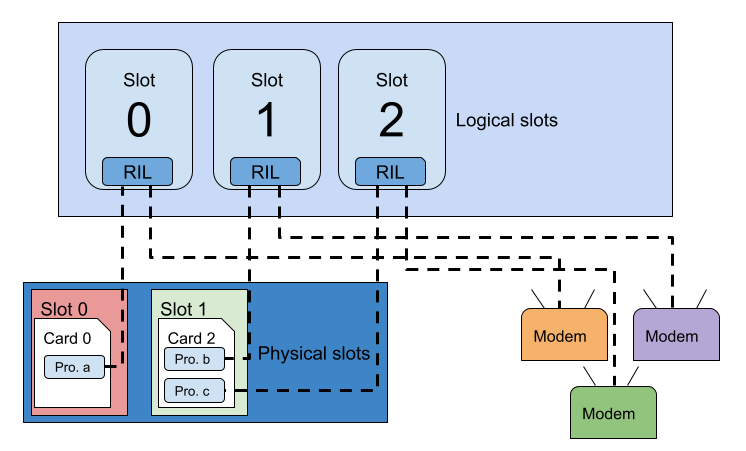
Trong biểu đồ trước:
- Thiết bị có 3 khe logic.
- Trong vị trí thực 0, có một thẻ UICC thực có hồ sơ đang hoạt động.
- Trong vùng thực 1 là một eUICC có hai cấu hình đã tải xuống, cả hai đều hoạt động bằng MEP (Nhiều cấu hình được bật).
Mở tính năng hỗ trợ trình đọc Open Mobile API (OMAPI)
Trên Android 11 trở lên, Open Mobile API (OMAPI) hỗ trợ việc kiểm tra phần cứng hỗ trợ eSE, SD và UICC trên các thiết bị có các cờ sau:
Sử dụng các giá trị này với getSystemAvailableFeatures() hoặc hasSystemFeature() để kiểm tra khả năng hỗ trợ thiết bị.
