Android Gradle 插件 3.6.0(2020 年 2 月)
此版本的 Android 插件需要使用以下工具:
| 最低版本 | 默认版本 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gradle | 5.6.4 | 5.6.4 | 如需了解详情,请参阅更新 Gradle。 |
| SDK Build Tools | 28.0.3 | 28.0.3 | 安装或配置 SDK Build Tools。 |
新功能
此版本的 Android Gradle 插件包含以下新功能。
视图绑定
在代码中引用视图时,视图绑定可确保编译时安全性。您现在可以将 findViewById() 替换为自动生成的绑定类引用。如需开始使用视图绑定,请在每个模块的 build.gradle 文件中添加以下代码:
android { viewBinding.enabled = true }
android { viewBinding.enabled = true }
如需了解详情,请参阅视图绑定文档。
支持 Maven Publish 插件
Android Gradle 插件支持 Maven Publish Gradle 插件,可让您将 build 工件发布到 Apache Maven 制品库。Android Gradle 插件会为应用或库模块中的每个 build 变体工件创建一个组件,您可以使用它来自定义要发布到 Maven 制品库的发布内容。
如需了解详情,请访问介绍如何使用 Maven Publish 插件的页面。
新的默认打包工具
在构建应用的调试版本时,该插件会使用一个新的打包工具 zipflinger 来构建 APK。这一新工具应该能够提高构建速度。如果新的打包工具无法正常运行,请报告 bug。您可以通过在 gradle.properties 文件中添加以下代码来恢复使用旧的打包工具:
android.useNewApkCreator=false
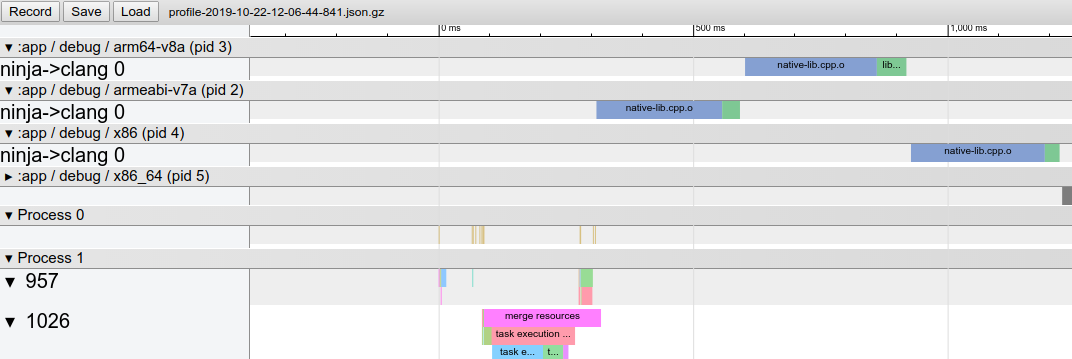
原生构建属性
您现在可以确定 Clang 构建和链接项目中的每个 C/C++ 文件所需的时间。Gradle 可以生成包含这些编译器事件时间戳的 Chrome 跟踪记录,以便您更清楚地了解构建项目所需的时间。如需生成此构建属性文件,请执行以下操作:
-
在运行 Gradle build 时添加标记
-Pandroid.enableProfileJson=true。例如:gradlew assembleDebug -Pandroid.enableProfileJson=true -
打开 Chrome 浏览器,然后在搜索栏中输入
chrome://tracing。 -
点击 Load 按钮并导航到
<var>project-root</var>/build/android-profile以查找文件。该文件的名称为profile-<var>timestamp</var>.json.gz。
您可以在查看器顶部附近查看原生构建属性数据:
行为变更
使用此版本的插件时,您可能会遇到以下行为方面的变更。
默认情况下,原生库以未压缩的形式打包
在构建应用时,插件现在默认会将 extractNativeLibs 设置为 "false"。也就是说,您的原生库将保持页面对齐状态并以未压缩的形式打包。虽然这样会增加上传大小,但您的用户会从以下优势中受益:
- 减小应用安装大小,因为平台可以直接从已安装的 APK 访问原生库,而无需创建库的副本。
- 减小下载文件大小,因为在 APK 或 Android App Bundle 中添加未压缩的原生库通常可提高 Play 商店的压缩率。
如果您希望 Android Gradle 插件改为打包压缩后的原生库,请在应用的清单中添加以下代码:
<application
android:extractNativeLibs="true"
... >
</application>
注意:extractNativeLibs 清单属性已被 useLegacyPackaging DSL 选项取代。如需了解详情,请参阅版本说明使用 DSL 打包压缩的原生库。
默认 NDK 版本
现在,如果您下载了多个版本的 NDK,Android Gradle 插件会选择一个默认版本来编译源代码文件。以前,该插件选择的是最新下载的 NDK 版本。使用模块的 build.gradle 文件中的 android.ndkVersion 属性可替换插件选择的默认版本。
简化了 R 类的生成过程
Android Gradle 插件通过仅为项目中的每个库模块生成一个 R 类并与其他模块依赖项共享这些 R 类,简化了编译类路径。这项优化应该会加快构建速度,但您需要注意以下事项:
- 由于编译器与上游模块依赖项共享 R 类,因此项目中的每个模块都必须使用独一无二的软件包名称。
- 库的 R 类对其他项目依赖项的可见性取决于用于将库添加为依赖项的配置。例如,如果库 A 将库 B 添加为“api”依赖项,则库 A 和其他依赖于库 A 的库都可以访问库 B 的 R 类。不过,如果库 A 使用
implementation依赖项配置,其他库可能就无权访问库 B 的 R 类。如需了解详情,请参阅依赖项配置。
移除默认配置中缺少的资源
对于库模块,如果您添加了未包含在默认资源集内的语言资源(例如,将 hello_world 作为字符串资源添加到 /values-es/strings.xml 中,但未在 /values/strings.xml 中定义该资源),Android Gradle 插件在编译项目时将不会再添加该资源。这种行为变更应该会减少 Resource Not Found 运行时异常,并提高构建速度。
D8 现在遵循注解的类保留政策
现在,在编译应用时,D8 会遵循注解应用的类保留政策,并且这些注解在运行时不再可用。将应用的目标 SDK 设置为 API 级别 23 时,也存在此行为;此前,在使用旧版本的 Android Gradle 插件和 D8 编译应用时,会允许在运行时访问这些注解。
其他行为变更
-
aaptOptions.noCompress在所有平台(针对 APK 和软件包)上都不再区分大小写,并且遵循使用大写字符的路径。 -
现在,数据绑定默认为增量式。如需了解详情,请参阅问题 #110061530。
-
现在,包括 Roboelectric 单元测试在内的所有单元测试都可以完全缓存。如需了解详情,请参阅问题 #115873047。
bug 修复
此版本的 Android Gradle 插件包含以下 bug 修复:
- 现在,使用数据绑定的库模块支持 Robolectric 单元测试。如需了解详情,请参阅问题 #126775542。
- 现在,您可在启用 Gradle 的并行执行模式的情况下跨多个模块运行
connectedAndroidTest任务。
已知问题
本部分介绍 Android Gradle 插件 3.6.0 中存在的已知问题。
Android lint 任务的执行速度过慢
Android lint 由于解析基础架构性能降低,导致在某些代码构造中对 lambda 的推断类型的计算速度变慢,因此可能需要更长时间才能完成某些项目。
此问题会报告为 IDEA bug,并将在 Android Gradle 插件 4.0 中修复。
缺少清单类 {:#agp-missing-manifest}
如果您的应用在其清单中定义自定义权限,Android Gradle 插件通常会生成 Manifest.java 类,用于以字符串常量的形式添加您的自定义权限。该插件会将此类与您的应用打包在一起,以便于您在运行时更轻松地引用这些权限。
在 Android Gradle 插件 3.6.0 中无法生成清单类。如果您使用此版本的插件构建应用,并且该应用引用了清单类,您可能会看到 ClassNotFoundException 异常。如需解决此问题,请执行以下某项操作:
-
通过完全限定名称引用自定义权限。例如
"com.example.myapp.permission.DEADLY_ACTIVITY"。 -
定义您自己的常量,如下所示:
public final class CustomPermissions { public static final class permission { public static final String DEADLY_ACTIVITY="com.example.myapp.permission.DEADLY_ACTIVITY"; } }
