Android Gradle Plugin 3.4.0 (April 2019)
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
| Minimum version | Default version | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gradle | 5.1.1 | 5.1.1 | To learn more, see updating Gradle. When using Gradle 5.0 and higher, the default Gradle daemon memory heap size decreases from 1 GB to 512 MB. This might result in a build performance regression. To override this default setting, specify the Gradle daemon heap size in your project's gradle.properties file. |
| SDK Build Tools | 28.0.3 | 28.0.3 | Install or configure SDK Build Tools. |
This minor update supports compatibility with new default settings and features for package visibility in Android 11.
See the 4.0.1 release notes for details.
3.4.2 (July 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.4.2 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of noteable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog.
3.4.1 (May 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.4.1 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of noteable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog.
New features
-
New lint check dependency configurations: The behavior of
lintCheckshas changed and a new dependency configuration,lintPublish, has been introduced to give you more control over which lint checks are packaged in your Android libraries.-
lintChecks: This is an existing configuration that you should use for lint checks you want to only run when building your project locally. If you were previously using thelintChecksdependency configuration to include lint checks in the published AAR, you need to migrate those dependencies to instead use the newlintPublishconfiguration described below. -
lintPublish: Use this new configuration in library projects for lint checks you want to include in the published AAR, as shown below. This means that projects that consume your library also apply those lint checks.
The following code sample uses both dependency configurations in a local Android library project.
dependencies { // Executes lint checks from the ':lint' project at build time. lintChecks project(':lint') // Packages lint checks from the ':lintpublish' in the published AAR. lintPublish project(':lintpublish') }
dependencies { // Executes lint checks from the ':lint' project at build time. lintChecks(project(":lint")) // Packages lint checks from the ':lintpublish' in the published AAR. lintPublish(project(":lintpublish")) }
-
In general, packaging and signing tasks should see an overall build speed improvement. If you notice a performance regression related to these tasks, please report a bug.
-
Behavior changes
-
Android Instant Apps Feature plugin deprecation warning: If you’re still using the
com.android.featureplugin to build your instant app, Android Gradle plugin 3.4.0 will give throw you a deprecation warning. To make sure you can still build you instant app on future versions of the plugin, migrate your instant app to using the dynamic feature plugin, which also allows you to publish both your installed and instant app experiences from a single Android App Bundle. -
R8 enabled by default: R8 integrates desugaring, shrinking, obfuscating, optimizing, and dexing all in one step—resulting in noticeable build performance improvements. R8 was introduced in Android Gradle plugin 3.3.0 and is now enabled by default for both app and Android library projects using plugin 3.4.0 and higher.
The image below provides a high-level overview of the compile process before R8 was introduced.
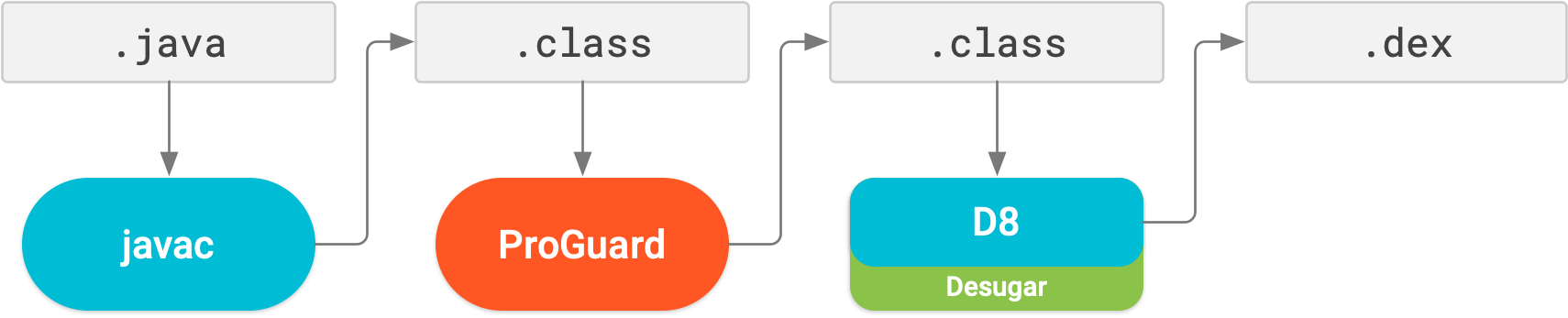
Now, with R8, desugaring, shrinking, obfuscating, optimizing, and dexing (D8) are all completed in one step, as illustrated below.
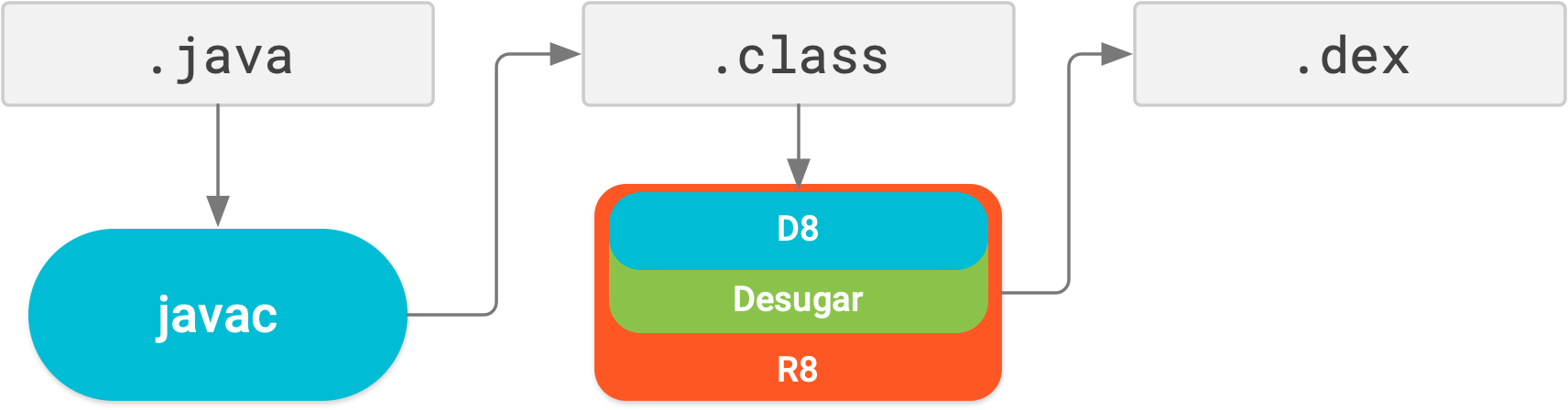
Keep in mind, R8 is designed to work with your existing ProGuard rules, so you’ll likely not need to take any actions to benefit from R8. However, because it’s a different technology to ProGuard that’s designed specifically for Android projects, shrinking and optimization may result in removing code that ProGuard may have not. So, in this unlikely situation, you might need to add additional rules to keep that code in your build output.
If you experience issues using R8, read the
R8 compatibility FAQ
to check if there’s a solution to your issue. If a solution isn’t documented,
please report a bug.
You can disable R8 by adding one of the following lines to your project’s
gradle.properties file:
# Disables R8 for Android Library modules only.
android.enableR8.libraries = false
# Disables R8 for all modules.
android.enableR8 = false
Note: For a given build type, if you set
useProguard to false in your app
module's build.gradle file, the Android Gradle plugin uses R8
to shrink your app's code for that build type, regardless of whether you
disable R8 in your project's gradle.properties file.
-
ndkCompileis deprecated: You now get a build error if you try to usendkBuildto compile your native libraries. You should instead use either CMake or ndk-build to Add C and C++ code to your project.
Known issues
-
The correct usage of unique package names are currently not enforced but will become more strict on later versions of the plugin. On Android Gradle plugin version 3.4.0, you can opt-in to check whether your project declares acceptable package names by adding the line below to your
gradle.propertiesfile.android.uniquePackageNames = trueTo learn more about setting a package name through the Android Gradle plugin, see Set the application ID.
