ऑडियो ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, क्लाइंट/सर्वर डिज़ाइन को सबसे अच्छा आर्किटेक्चर माना जाता है. क्लाइंट, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में मौजूद एक गतिविधि है. इसमें MediaBrowser, मीडिया कंट्रोलर, और यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) शामिल होता है. सर्वर एक MediaBrowserService है, जिसमें प्लेयर और मीडिया सेशन होता है.
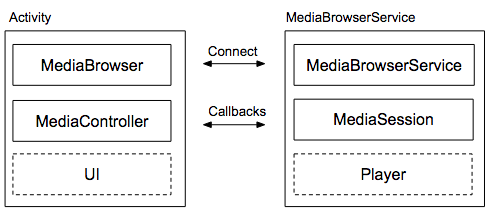
MediaBrowserService में दो मुख्य सुविधाएं मिलती हैं:
MediaBrowserServiceका इस्तेमाल करने पर,MediaBrowserवाले अन्य कॉम्पोनेंट और ऐप्लिकेशन आपकी सेवा का पता लगा सकते हैं. साथ ही, वे अपना मीडिया कंट्रोलर बना सकते हैं, आपके मीडिया सेशन से कनेक्ट हो सकते हैं, और प्लेयर को कंट्रोल कर सकते हैं. Wear OS और Android Auto ऐप्लिकेशन, इसी तरीके से आपके मीडिया ऐप्लिकेशन का ऐक्सेस पाते हैं.- यह एक वैकल्पिक ब्राउज़िंग एपीआई भी उपलब्ध कराता है. ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, इस सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करना ज़रूरी नहीं है. ब्राउज़िंग एपीआई की मदद से क्लाइंट, सेवा से क्वेरी कर सकते हैं. साथ ही, कॉन्टेंट के क्रम को दिखा सकते हैं. यह क्रम, प्लेलिस्ट, मीडिया लाइब्रेरी या किसी अन्य तरह के कलेक्शन को दिखा सकता है.
- मीडिया ब्राउज़र सेवा बनाना
- मीडिया ब्राउज़र सेवा बनाने का तरीका, जिसमें मीडिया सेशन शामिल हो. साथ ही, क्लाइंट कनेक्शन मैनेज करने और ऑडियो चलाने के दौरान फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा बनने का तरीका.
- मीडिया ब्राउज़र क्लाइंट बनाना
- यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) और मीडिया कंट्रोलर वाली मीडिया ब्राउज़र क्लाइंट गतिविधि बनाने का तरीका. साथ ही, मीडिया ब्राउज़र सेवा से कनेक्ट करने और उससे कम्यूनिकेट करने का तरीका.
- मीडिया सेशन कॉलबैक
- इसमें बताया गया है कि मीडिया सेशन कॉलबैक के तरीके, मीडिया सेशन, मीडिया ब्राउज़र सेवा, और सूचनाओं और ब्रॉडकास्ट रिसीवर जैसे ऐप्लिकेशन के अन्य कॉम्पोनेंट को कैसे मैनेज करते हैं.
- यूनिवर्सल Android Music Player का सैंपल
- GitHub के इस सैंपल में, ऐसा मीडिया ऐप्लिकेशन लागू करने का तरीका बताया गया है जो बैकग्राउंड में ऑडियो चलाने की सुविधा देता है. साथ ही, इसमें एक मीडिया लाइब्रेरी भी होती है जिसे अन्य ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ शेयर किया जा सकता है.
