En este documento, se muestran los pasos de configuración básicos y el flujo de trabajo de la herramienta Batterystats y la secuencia de comandos de Battery Historian. Si quieres obtener información sobre cómo usar Battery Historian para inspeccionar los patrones de consumo de batería, consulta Cómo analizar el consumo con Battery Historian.
Batterystats es una herramienta del framework de Android que recopila datos sobre la batería en tu dispositivo. Puedes usar adb para volcar los datos sobre la batería recopilados en tu máquina de desarrollo y crear un informe que puedas analizar con Battery Historian. Esta herramienta convierte el informe de Batterystats en una visualización HTML que puedes ver en tu navegador.
Batterystats y Battery Historian son útiles para lo siguiente:
- Mostrarte cómo y en qué lugar usan corriente de la batería los procesos
- Identificar las tareas de tu app que puedas aplazar o quitar para mejorar la duración de batería.
Cómo instalar Battery Historian
Puedes instalar Battery Historian con Docker. Si deseas conocer métodos de instalación alternativos, incluido el desarrollo a partir del código fuente, consulta el archivo README en la página de GitHub del proyecto. Para completar la instalación con Docker, sigue estos pasos:
Para instalar Docker, sigue las instrucciones que se indican en el sitio web de Docker. Funciona con cualquier tipo de suscripción, incluida una suscripción Personal gratuita.
Para confirmar que Docker esté instalado correctamente, abre la línea de comandos y escribe el siguiente comando:
docker run hello-worldSi Docker está instalado correctamente, muestra un resultado similar al siguiente:
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 78445dd45222: Pull complete Digest: sha256:c5515758d4c5e1e838e9cd307f6c6a0d620b5e07e6f927b07d05f6d12a1ac8d7 Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminalInicia la app de Docker Desktop, que es un frontend de la GUI para Docker, antes de ejecutar la imagen de Battery Historian. Cuando lo ejecutas, se inicializan las herramientas de Docker. Battery Historian no se ejecutará hasta que lo hagas al menos una vez.
Ejecuta Battery Historian desde la línea de comandos cuando lo ejecutes por primera vez. La app de Docker Desktop no te permite especificar el puerto en el que se ejecutará el servidor web. Puedes hacer esto desde la línea de comandos: Sin embargo, después de ejecutar con éxito el contenedor desde la línea de comandos, se crea una entrada en Docker Desktop, y luego puedes iniciarla con el mismo puerto de objeto de escucha desde Docker Desktop.
Usa el siguiente comando para ejecutar la imagen de Battery Historian:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Battery Historian usa el puerto que elijas, como se especifica en
port_number.Navega a Battery Historian en tu navegador para confirmar que se esté ejecutando. La dirección varía según tu sistema operativo:
- Para Linux y Mac
- Battery Historian está disponible en
http://localhost:port_number. - Para Windows
- Una vez que abres Docker, te indica la dirección IP de la máquina que lo está usando. Por ejemplo, si la dirección IP es 123.456.78.90, Battery Historian está disponible en
http://123.456.78.90:port_number.
Luego, se mostrará la página de inicio de Battery Historian, en la que podrás subir y ver estadísticas de la batería.
Figura 1: Página de inicio de Battery Historian
Cómo recopilar datos con Batterystats
Si deseas recopilar datos de tu dispositivo con Batterystats y abrirlos en Battery Historian, haz lo siguiente:
Conecta el dispositivo móvil a la computadora.
Desde una ventana de terminal, cierra el servidor
adben ejecución con el siguiente comando:adb kill-serverEjecuta el siguiente comando para reiniciar
adby verificar si hay dispositivos conectados.adb devicesMuestra tu dispositivo, de manera similar al siguiente resultado de ejemplo.

Figura 2: Resultado de adb devices, que muestra un dispositivo conectadoSi no aparece ningún dispositivo, asegúrate de que el teléfono esté conectado y de que la depuración por USB esté habilitada. Luego, detén y reinicia
adb.Ejecuta el siguiente comando para restablecer la recopilación de datos sobre la batería:
adb shell dumpsys batterystats --resetEl dispositivo siempre recopila Batterystats y demás información de depuración en segundo plano. El restablecimiento borra los datos anteriores recopilados sobre la batería. Si no lo restableces, el resultado puede ser muy grande.
Desconecta el dispositivo de la computadora de manera que solo use corriente de la batería del dispositivo.
Usa tu app y realiza acciones para las que quieras recopilar datos. Por ejemplo, desconéctate de la red Wi-Fi y envía datos a la nube.
Vuelve a conectar el teléfono.
Asegúrate de que se reconozca tu teléfono y ejecuta el siguiente comando:
adb devicesEjecuta el siguiente comando para volcar todos los datos de la batería. Es posible que esta acción tarde unos minutos:
adb shell dumpsys batterystats > [path/]batterystats.txt
Se creará el archivo
batterystats.txten el directorio que especifiques con el argumento de ruta de acceso opcional. Si no especificas una ruta de acceso, se creará el archivo en el directorio principal.Crea un informe a partir de datos sin procesar.
- Para dispositivos con Android 7.0 y versiones posteriores:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.zip
- Para dispositivos con Android 6.0 y versiones inferiores:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.txt
El informe de errores puede tardar varios minutos en completarse. No desconectes el dispositivo ni canceles el proceso hasta que se complete.
Al igual que con
batterystats.txt, se crearán estos archivos en el directorio que especifiques con el argumentopathopcional. Si no especificas una ruta de acceso, se crearán en el directorio principal.Si todavía no se está ejecutando Battery Historian, usa el siguiente comando:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Si quieres ver tus datos en Battery Historian, ábrelo en tu navegador. En Mac y Linux, Battery Historian se ejecuta en
http://localhost:port_number. En Windows, lo hace enhttp://your_IP_address:port_number.Haz clic en Browse y luego selecciona el archivo de informe de errores que creaste anteriormente.
Haz clic en Enviar. Battery Historian abrirá un gráfico creado a partir de los datos de Batterystats.
Cómo ver datos con los gráficos de Battery Historian
En el gráfico de Battery Historian se muestran eventos relacionados con la batería a lo largo del tiempo.
En cada fila, se muestra un segmento de barra de color cuando un componente del sistema está activo y, por lo tanto, usa corriente de la batería. En el gráfico, no se muestra cuánta batería usa el componente (solo se muestra si la app está activa). Los gráficos están organizados por categoría, y se muestra una barra por cada categoría a lo largo del tiempo, como se puede apreciar en el eje X del gráfico.
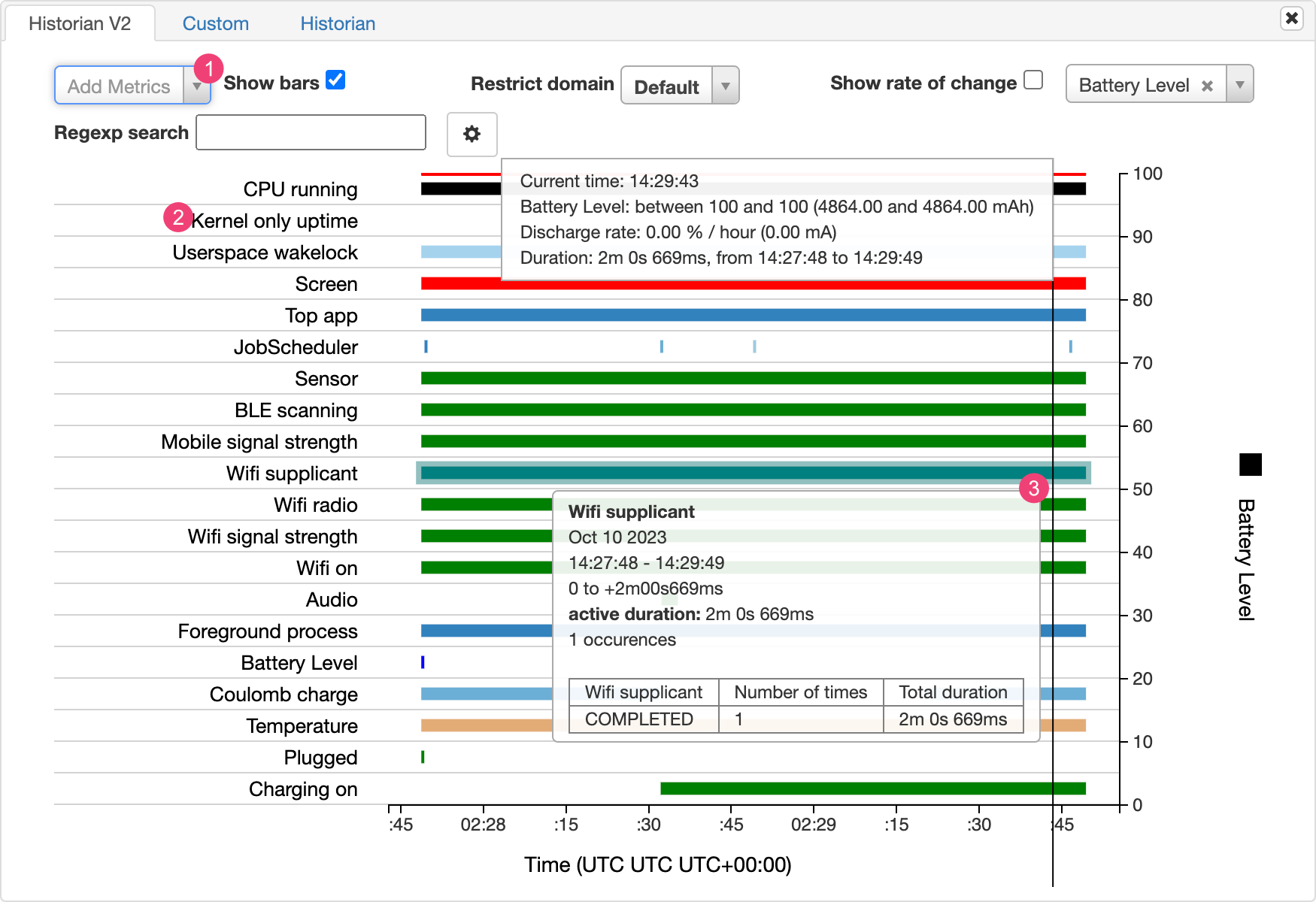
- Agrega métricas adicionales de la lista desplegable.
- Mantén el puntero sobre el nombre de la métrica para ver más información sobre cada métrica, incluida una clave de los colores que se usan en el gráfico.
- Mantén el puntero sobre una barra para ver información más detallada sobre esa métrica y las estadísticas de la batería en un punto específico del cronograma.
Resultados adicionales de Batterystats
Puedes ver información adicional del archivo batterystats.txt en la sección de estadísticas ubicada debajo del gráfico de Battery Historian.
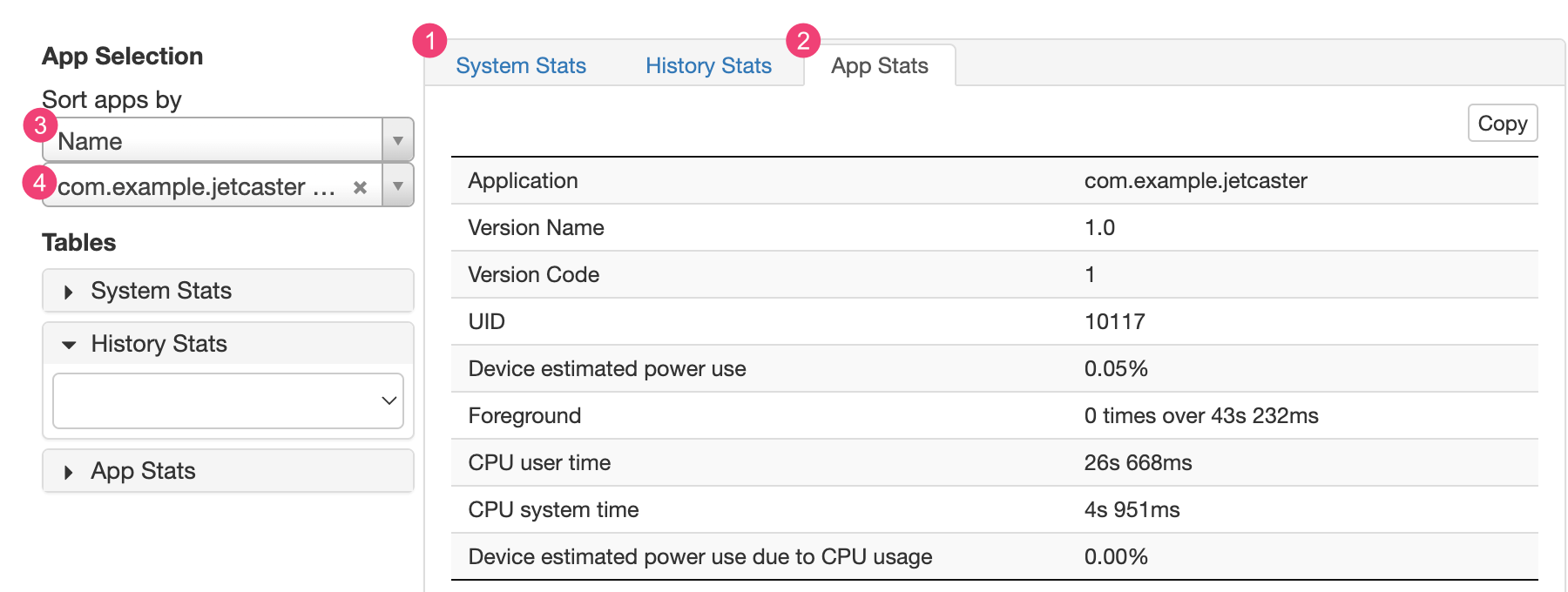
En la pestaña 1 System Stats, se incluyen estadísticas de todo el sistema, como los niveles de señal de telefonía celular y el brillo de la pantalla. Esta información ofrece un panorama general de lo que sucede con el dispositivo. Esta sección es particularmente útil para asegurarte de que ningún evento externo afecte tu prueba.
En la pestaña 2 App Stats, se incluye información sobre apps específicas. Ordena la lista de apps con la lista desplegable 3 Sort apps by del panel App Selection. Puedes seleccionar una app específica para ver las estadísticas mediante la lista desplegable de apps 4.
