Adaptive design is the practice of designing layouts that adapt to specific breakpoints and devices.
To implement adaptive layouts effectively:
- First, consider the device's window class width to determine layout changes, then adjust for height.
- Android leverages responsive design concepts, similar to web development, employing flexible grids and images to create layouts that respond effectively to their context.
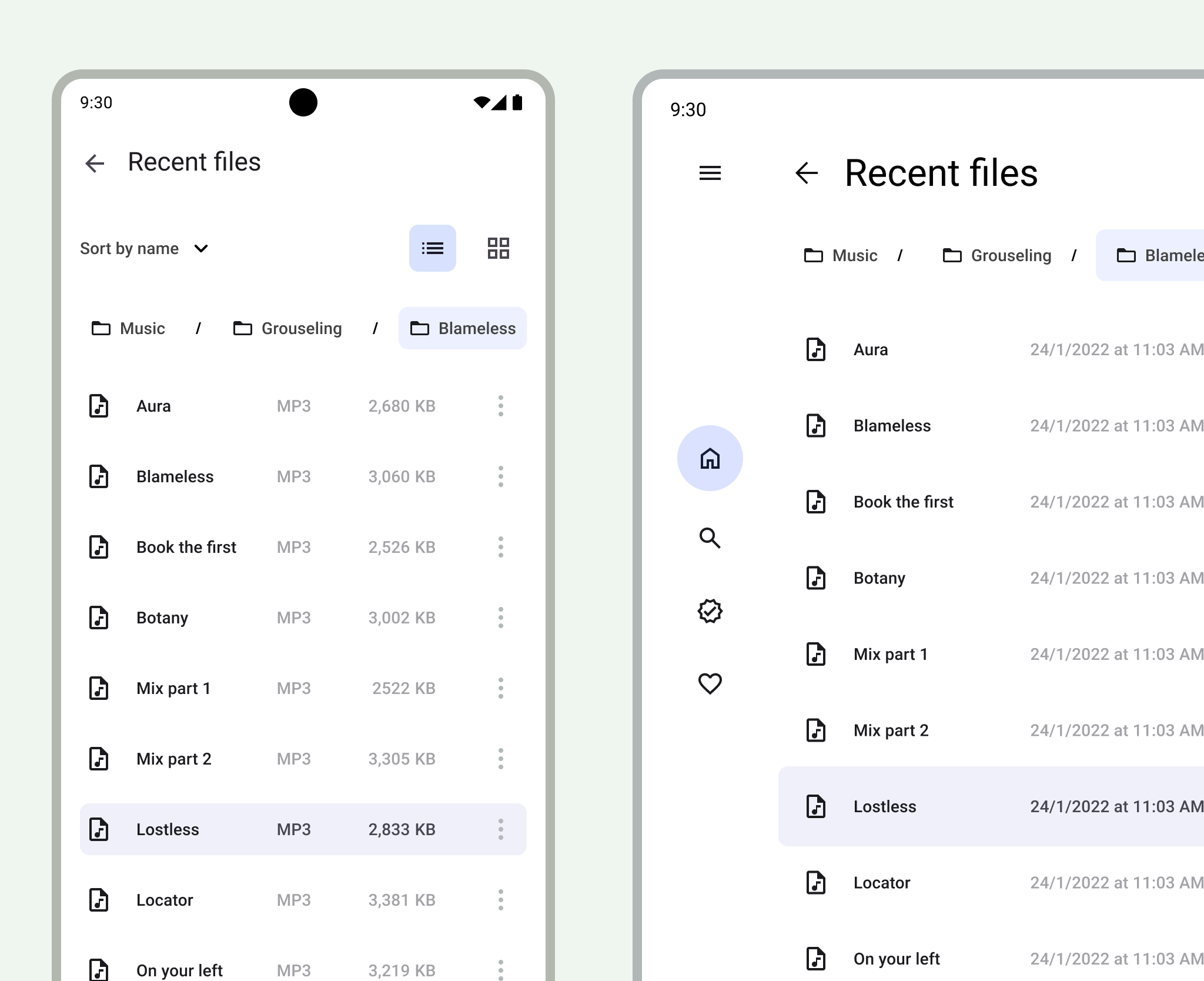
For design guidelines about adapting layouts to expanded screen sizes, read the Support different screen sizes developers guide in Compose and the M3 Applying Layout page. You can also check out the Android large screen canonical gallery for inspiration and implementation of large screen layouts.
Think adaptive
Adaptive should be be the default when designing your app. The Android mobile market is constantly evolving, so you can't only think of mobile as handset phones. Instead it should include everything from handset phones, foldables, tablets, and everything in between.
While certain features and use cases may not make sense on every screen size or form factor. Adaptive design allows your users more freedom regarding ergonomics, usability, and app quality.
Methods and quality
You can start by designing key screens (communicate the essential concepts or your app) with class sizes as breakpoints to act as guidelines for the rest of your app. These hero experiences can highlight differentiated adaptive and form factor qualities. Or design content to be responsive at a foundational level by notating how content should be constrained, expand, or reflow.
Do
Don't
Do
Use intrinsic and visual containers to group elements together. Panes can move in, hide, expand, be constrained, or pop up. Thinking with panes makes designing across all mobile devices easier.
Allow elements to shift and rearrange by focusing on how elements adapt to the grid. Consider vertical change for elements and combine with constraints and presentation changes.
A high quality app should meet the differentiated tier in core app and large screen quality guidelines.
For more on layouts, check out the Material Design 3 (M3) Understanding layout page.
