瞭解如何處理不同的手錶形狀後,請決定要使用何種錶面。
常見的應用程式版面配置如下:
- 單一畫面 (最簡單):不必捲動畫面即可看到所有 UI 元素。
- 垂直容器 (最常用):超出螢幕可見部分的內容,需捲動畫面查看。
- 其他版面配置類型:清單、分頁或 2D 平移。
後續章節將說明這些版面配置類型。如果您需要多個螢幕畫面,可以結合使用各種版面配置類型。
注意:如果是活動,請從 ComponentActivity 繼承,如果您使用片段,則從 FragmentActivity 繼承。其他活動類型使用的是行動裝置專用的 UI 元素,Wear OS 不需要這類元素。
單一畫面
使用者不用捲動畫面,就能在單一畫面中看到所有元素。這表示您只能加入少量元素。

圖 1. 單一畫面版面配置示例。
單一畫面很適合搭配使用 BoxInsetLayout 結合 ConstraintLayout 來排列元素。
垂直容器
垂直容器是最常見的應用程式版面配置類型。部分內容不會顯示在畫面上,但只要捲動畫面即可查看。
圖 2 顯示幾種完整的應用程式版面配置,其中只有部分內容可以在智慧手錶的圓形螢幕上顯示。在這些示例中,主要內容位於容器頂端部分,其他關鍵使用者歷程 (CUJ) 和設定則位於容器底部。這是配置內容的最佳做法。
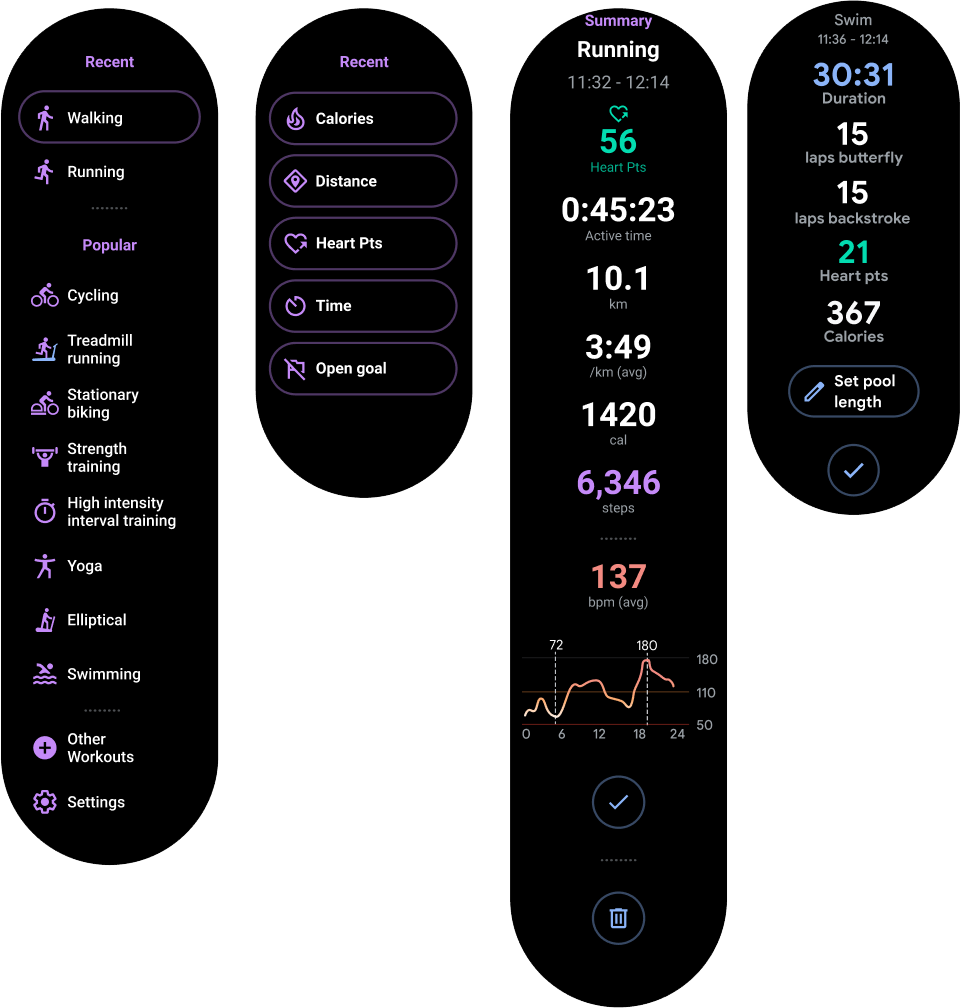
圖 2:垂直容器版面配置示例。
與單一畫面的應用程式版面配置不同,請不要使用 BoxInsetLayout,改為在 NestedScrollView 中使用 ConstraintLayout。請在 ConstraintLayout 中放置任何最適合您應用程式的小工具。這麼做可讓您充分利用圓形螢幕側邊的額外空間。
圖 3:NestedScrollView 內的 ConstraintLayout 中的內容。
請確保垂直容器中位於頂端及底部的內容夠小,以符合圓形螢幕的頂端及底部畫面,如圖 3 示例所示。
注意:請盡可能在 XML 中設定 android:scrollbars="vertical",將捲動指標新增到 NestedScrollView。這麼做可讓使用者知道往下還有更多內容,並協助他們瞭解目前已讀取的內容,屬於所有內容中的哪個部分。
應用程式版面配置的其他選項
-
清單:透過針對穿戴式裝置介面最佳化的
WearableRecyclerView小工具顯示大量資料。詳情請參閱「在 Wear OS 上建立清單」。 - 水平分頁:如果應用程式的用途會顯示多個同層畫面,請使用水平滑動功能。如果您使用水平分頁,則必須支援從左側邊緣滑動關閉的功能。
- 2D 平移:適用於地圖這類用途。使用者可以將畫面往不同方向拖曳平移。如果您的活動會佔據整個螢幕畫面,請啟用滑動關閉功能。

