در حالی که بسیاری از برنامههای Android TV با مؤلفههای اصلی Android ساخته میشوند، مهم است که دسترسی به چارچوبها یا مؤلفههای شخص ثالث را نیز در نظر بگیرید، مخصوصاً هنگام استفاده از نماهای سفارشی .
اجزای نمای سفارشی که مستقیماً با OpenGL یا Canvas واسط میشوند ممکن است با سرویسهای دسترسپذیری مانند Talkback و Switch Access به خوبی کار نکنند.
برخی از مشکلات زیر را که ممکن است با روشن بودن Talkback رخ دهد، در نظر بگیرید:
- فوکوس دسترسی (مستطیل سبز) ممکن است در برنامه شما ناپدید شود.
- فوکوس دسترسپذیری ممکن است مرز کل صفحه را انتخاب کند.
- فوکوس دسترسپذیری ممکن است متحرک نباشد.
- چهار کلید جهت روی D-pad ممکن است هیچ تاثیری نداشته باشند، حتی اگر کد شما آنها را مدیریت کند.
اگر هر یک از این مشکلات را در برنامه خود مشاهده کردید، بررسی کنید که برنامه شما درخت AccessibilityNodeInfo خود را در معرض خدمات دسترسپذیری قرار دهد.
بقیه این راهنما راه حل ها و بهترین روش ها را برای رسیدگی به این مسائل ارائه می دهد.
رویدادهای D-pad توسط سرویسهای دسترسی مصرف میشوند
علت اصلی این موضوع این است که رویدادهای کلیدی توسط سرویسهای دسترسی مصرف میشوند.
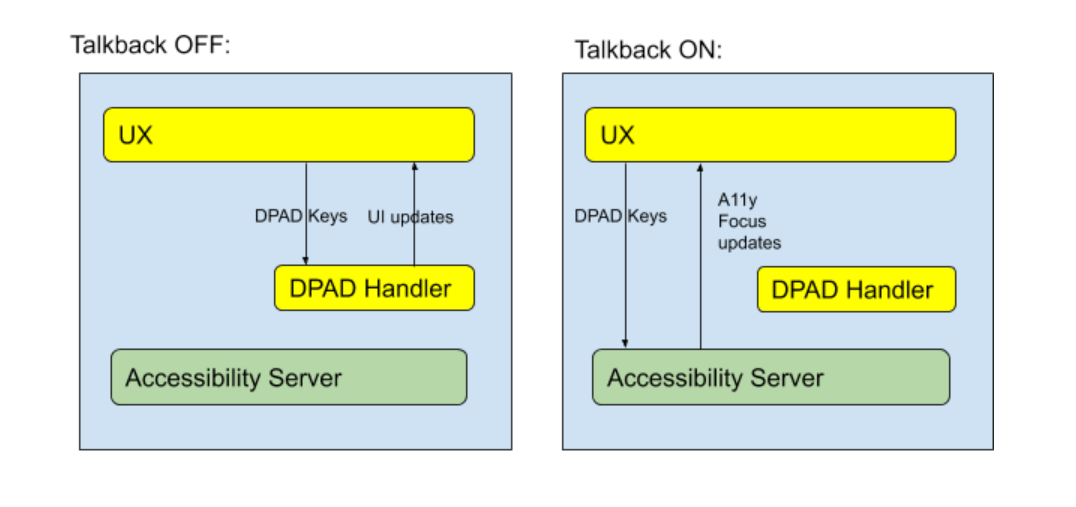 شکل 1. نمودارهایی که نحوه عملکرد سیستم را با روشن و خاموش کردن Talkback نشان می دهد.
شکل 1. نمودارهایی که نحوه عملکرد سیستم را با روشن و خاموش کردن Talkback نشان می دهد.
همانطور که در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است، وقتی Talkback روشن است، رویدادهای D-pad به کنترل کننده D-pad تعریف شده توسط توسعه دهنده منتقل نمی شوند. در عوض، خدمات دسترسپذیری رویدادهای کلیدی را دریافت میکنند تا بتوانند تمرکز دسترسی را تغییر دهند. از آنجایی که مؤلفههای سفارشی Android بهطور پیشفرض اطلاعاتی را درباره موقعیت خود روی صفحه در اختیار سرویسهای دسترسپذیری قرار نمیدهند، سرویسهای دسترسپذیری نمیتوانند تمرکز دسترسپذیری را برای برجسته کردن آنها تغییر دهند.
سایر خدمات دسترسپذیری نیز به طور مشابه تحت تأثیر قرار میگیرند: رویدادهای D-pad نیز ممکن است هنگام استفاده از «دسترسی سوئیچ» مصرف شوند.
از آنجایی که رویدادهای D-pad به سرویسهای دسترسپذیری ارسال میشوند و آن سرویس نمیداند اجزای رابط کاربری در یک نمای سفارشی کجا هستند، باید AccessibilityNodeInfo را برای برنامهتان پیادهسازی کنید تا رویدادهای کلیدی را به درستی ارسال کند.
اطلاعات را در معرض خدمات دسترسی قرار دهید
برای ارائه خدمات دسترسپذیری با اطلاعات کافی درباره مکان و شرح نماهای سفارشی، AccessibilityNodeInfo را پیادهسازی کنید تا جزئیات هر مؤلفه را در معرض دید قرار دهید. برای تعریف رابطه منطقی نماها به طوری که سرویسهای دسترسپذیری بتوانند تمرکز را مدیریت کنند، ExploreByTouchHelper پیادهسازی کنید و آن را با استفاده از ViewCompat.setAccessibilityDelegate(View, AccessibilityDelegateCompat) برای نماهای سفارشی تنظیم کنید.
هنگام پیاده سازی ExploreByTouchHelper ، چهار روش انتزاعی آن را نادیده بگیرید:
کاتلین
// Return the virtual view ID whose view is covered by the input point (x, y). protected fun getVirtualViewAt(x: Float, y: Float): Int // Fill the virtual view ID list into the input parameter virtualViewIds. protected fun getVisibleVirtualViews(virtualViewIds: List<Int>) // For the view whose virtualViewId is the input virtualViewId, populate the // accessibility node information into the AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat parameter. protected fun onPopulateNodeForVirtualView(virtualViewId: Int, @NonNull node: AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat) // Set the accessibility handling when perform action. protected fun onPerformActionForVirtualView(virtualViewId: Int, action: Int, @Nullable arguments: Bundle): Boolean
جاوا
// Return the virtual view ID whose view is covered by the input point (x, y). protected int getVirtualViewAt(float x, float y) // Fill the virtual view ID list into the input parameter virtualViewIds. protected void getVisibleVirtualViews(List<Integer> virtualViewIds) // For the view whose virtualViewId is the input virtualViewId, populate the // accessibility node information into the AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat parameter. protected void onPopulateNodeForVirtualView(int virtualViewId, @NonNull AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat node) // Set the accessibility handling when perform action. protected boolean onPerformActionForVirtualView(int virtualViewId, int action, @Nullable Bundle arguments)
برای جزئیات بیشتر، Google I/O 2013 - فعال کردن دسترسی نابینا و کم بینا را در Android تماشا کنید یا درباره پر کردن رویدادهای دسترسی بیشتر بخوانید.
بهترین شیوه ها
مورد نیاز:
AccessibilityNodeInfo.getBoundsInScreen()باید موقعیت کامپوننت را مشخص کند.مورد نیاز:
AccessibilityNodeInfo.setVisibleToUser()باید نمایان بودن مؤلفه را منعکس کند.مورد نیاز:
AccessibilityNodeInfo.getContentDescription()باید توضیحات محتوا را برای اعلام Talkback مشخص کند.AccessibilityNodeInfo.setClassName()را مشخص کنید تا سرویس ها بتوانند نوع مؤلفه را تشخیص دهند.هنگام پیاده سازی
performAction()، عمل را با استفاده ازAccessibilityEventمربوطه منعکس کنید.برای اجرای انواع عملکردهای بیشتر، مانند
ACTION_CLICK،AccessibilityNodeInfo.addAction(ACTION_CLICK)را با استفاده از منطق مربوطه درperformAction()فراخوانی کنید.در صورت امکان، وضعیت جزء را برای
setFocusable(),setClickable(),setScrollable()و روش های مشابه منعکس کنید.اسناد
AccessibilityNodeInfoرا مرور کنید تا روشهای دیگری را که خدمات دسترسپذیری میتوانند با اجزای شما تعامل بهتری داشته باشند، شناسایی کنید.
نمونه
برای مشاهده بهترین روشها برای افزودن پشتیبانی دسترسپذیری به برنامهها با استفاده از نماهای سفارشی، با نمونه دسترسی سفارشی برای Android TV مشورت کنید.

