Dzięki GnssLogger w wersji 3.1 użytkownicy mogą wyświetlać i analizować surowe dane GNSS na ekranie Pomiarów.
Oto ekran Dane oraz kilka wskazówek, które pomogą Ci w pełni wykorzystać te dane:
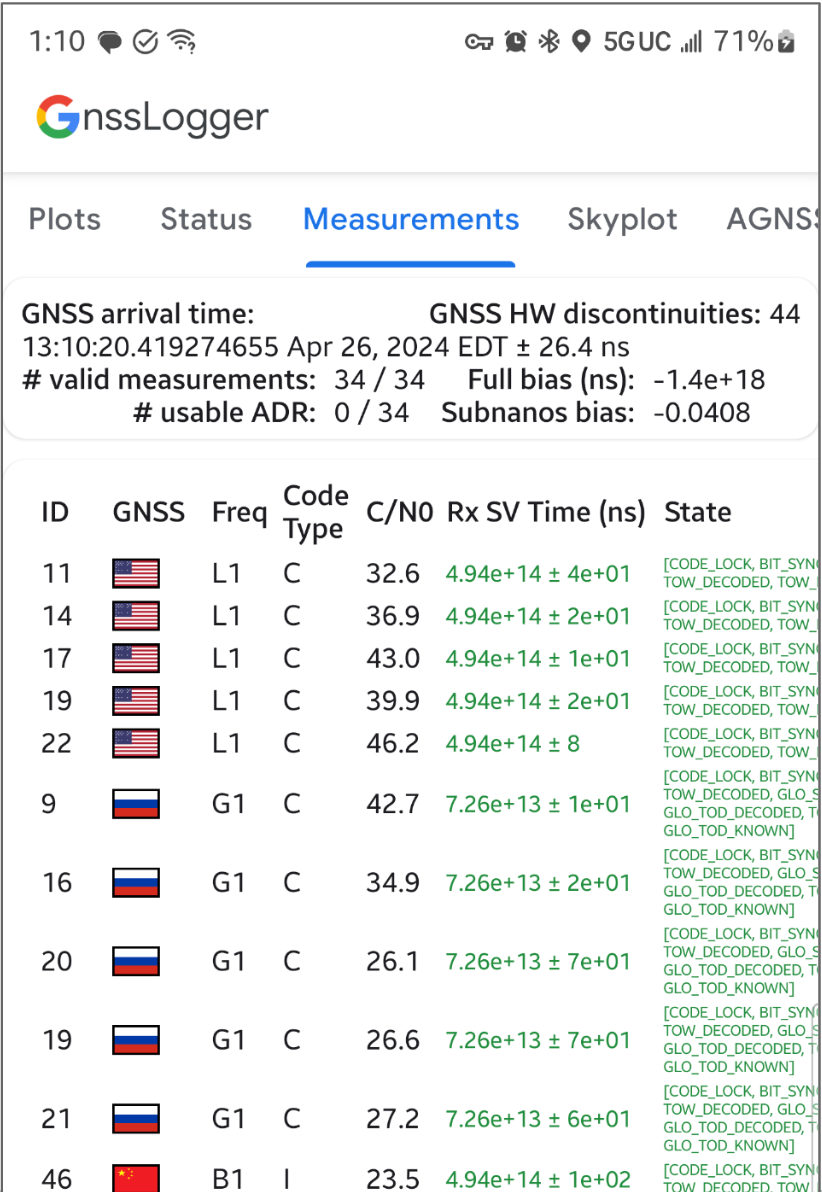
Na karcie u góry:
- W lewym górnym rogu znajdują się dane zegara GNSS (odpowiadające wartości
GnssClock). - W prawym górnym rogu widać liczbę przerw w przetwarzaniu sygnałów GNSS przez sprzęt (z
GnssClock.getHardwareClockDiscontinuityCount), co pomaga określić, czy cykl pracy jest włączony czy wyłączony. Gdy ten licznik wzrasta, oznacza to, że nastąpiło przerwanie ciągłego monitorowania sygnałów GNSS (np. cykl pracy jest włączony). Dalej na karcie znajdziesz informacje zbiorcze dotyczące wszystkich pomiarów:- # prawidłowe pomiary – aby pomiar został uznany za prawidłowy, w
GnssMeasurement.getStatemuszą być ustawione flagiSTATE_CODE_LOCKiSTATE_TOW_KNOWNlubSTATE_TOW_DECODED. - # użyteczny skumulowany zakres delty (ADR) – aby ADR lub faza przenoszenia mogła być uznana za użyteczną do pozycjonowania, musi być ustawiona flaga
ADR_STATE_VALIDi nie mogą być ustawione flagiADR_STATE_RESETaniADR_STATE_CYCLE_SLIPwGnssMeasurement.getAccumulatedDeltaRangeState.
- # prawidłowe pomiary – aby pomiar został uznany za prawidłowy, w
Jeśli urządzenie zawsze raportuje 0 użytecznych ADR, nawet gdy znajduje się na otwartej przestrzeni z wyłączonym cyklem pracy, oznacza to, że urządzenie nie obsługuje pomiarów fazy nośnej, które można wykorzystać do zapewnienia wysokiej dokładności GNSS.
Na dolnej karcie każdy wiersz odpowiada pojedynczej GnssMeasurement.
- Kolumna Typ kodu zawiera dokładny typ sygnału GNSS z użyciem typów kodów zdefiniowanych w RINEX 4.01. Na przykład sygnały GPS L1 z typem kodu „C” oznaczają L1 C/A, co wskazuje ostatnia litera w trzyliterowym kodzie w tabelach RINEX. W przypadku GPS L5 Q typ kodu to „Q”. Informacje o innych konstelacjach GNSS znajdziesz w tabelach na końcu tego dokumentu.
- W kolumnie Czas SV odbiornika (ns) tekst jest zielony, jeśli pomiar jest prawidłowy.
- W kolumnie Stan stan jest też zielony, jeśli pomiar jest prawidłowy. Stan zawiera czytelną dla człowieka wersję flag bitowych ustawionych w polu GnssMeasurement.getState().
Przesyłać opinie na temat nowych funkcji za pomocą publicznego narzędzia do zgłaszania problemów.
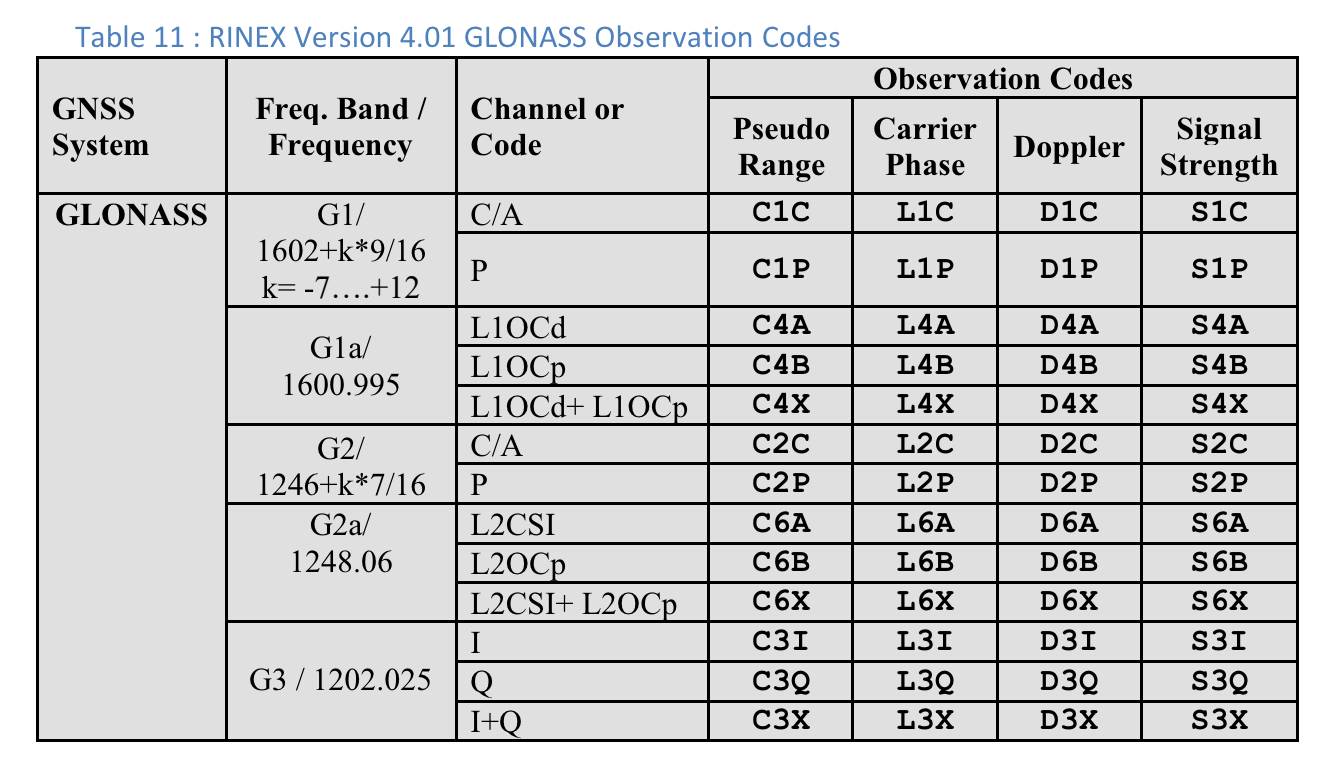
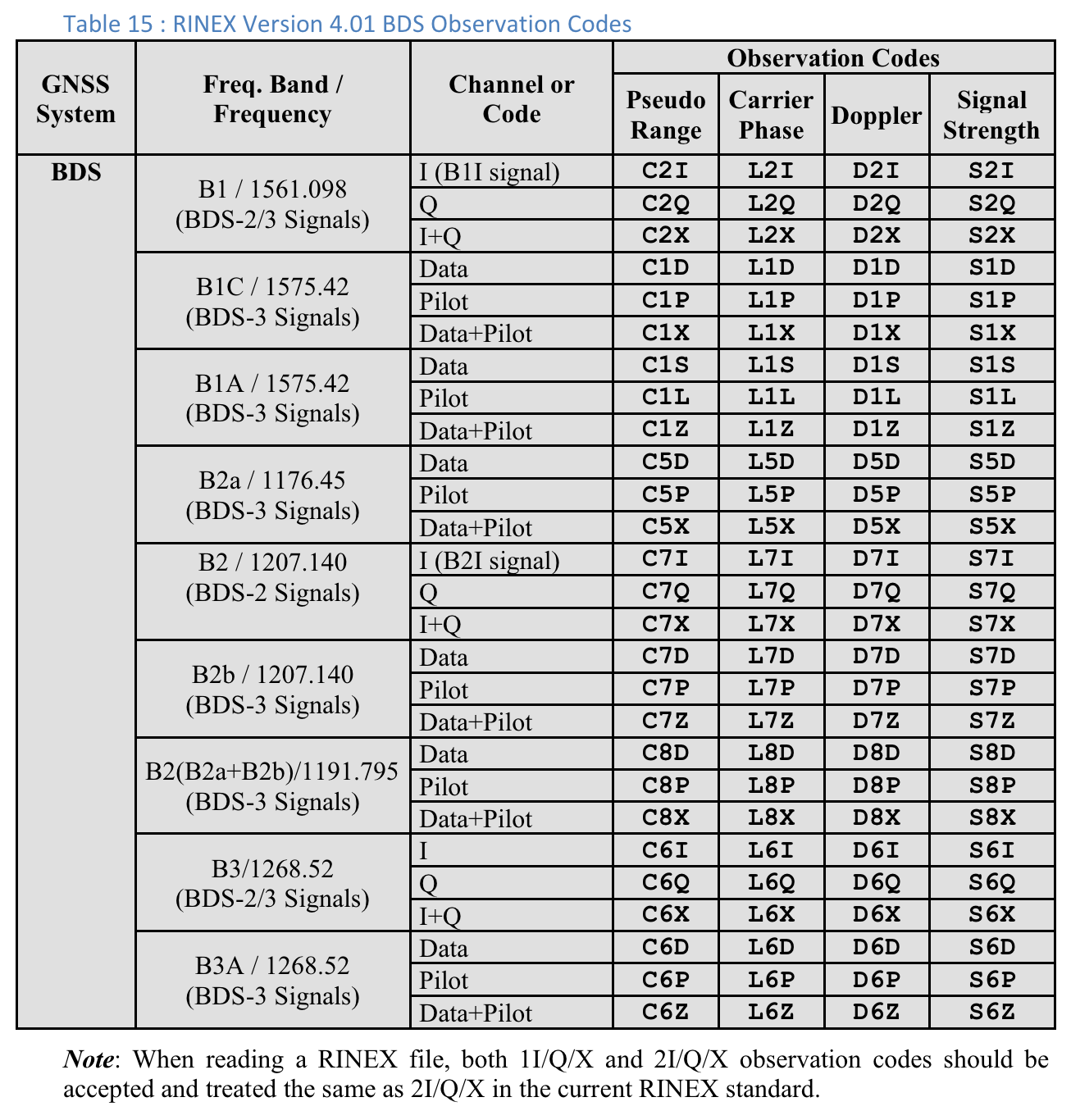
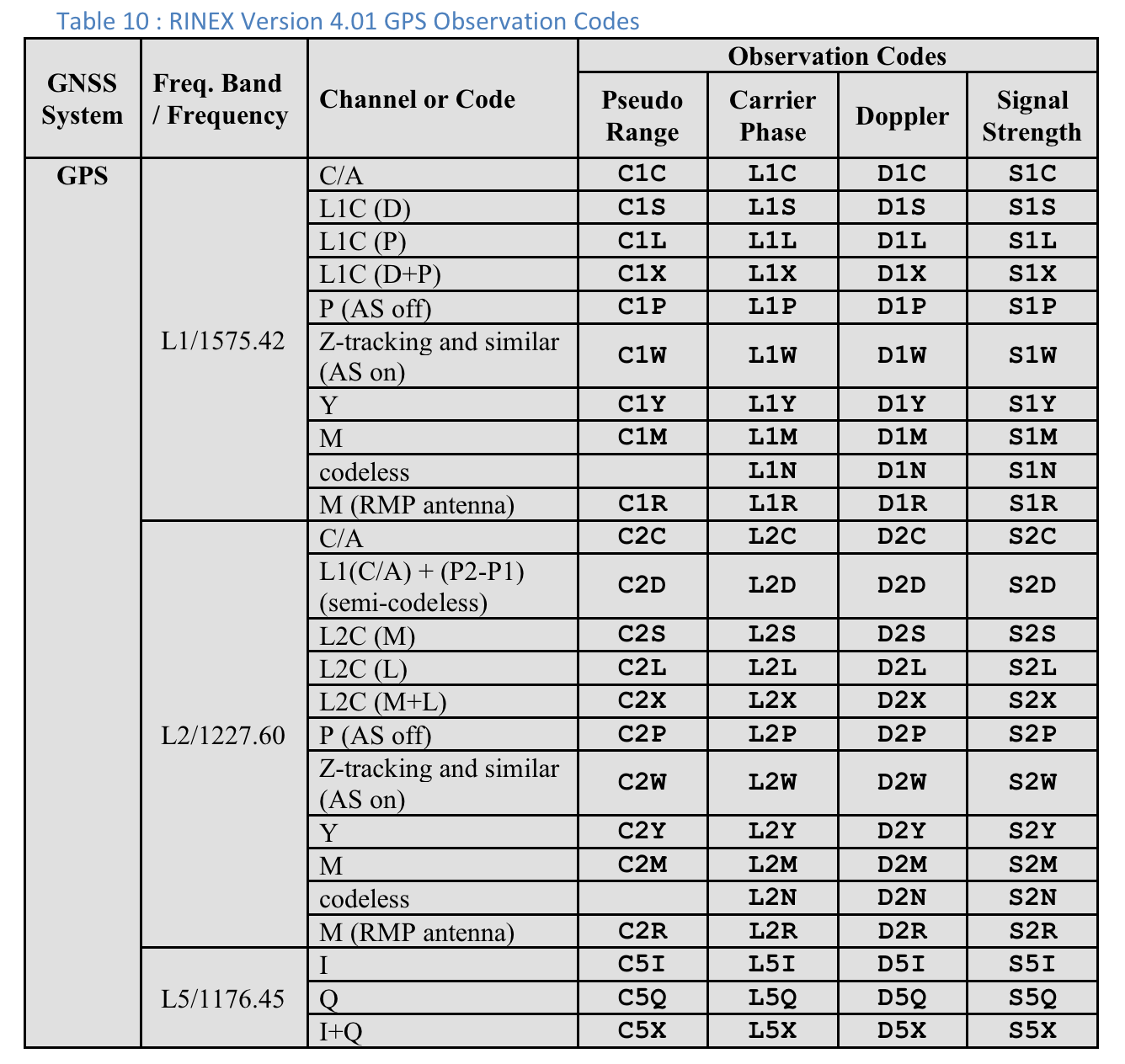
Tabela 10. Kody obserwacji GPS RINEX w wersji 4.01
W przypadku każdego pomiaru „Typ kodu” to ostatnia litera wartości „Zakres pseudo” zdefiniowanej w specyfikacji RINEX 4.01 dla odpowiedniego systemu GNSS i częstotliwości nośnej. Na przykład „C” jest używane w przypadku GPS L1 [C/A], a „Q” w przypadku GPS L5 Q.
Użytkownicy mogą przewijać w prawo, aby zobaczyć dodatkowe kolumny dla każdego pomiaru:
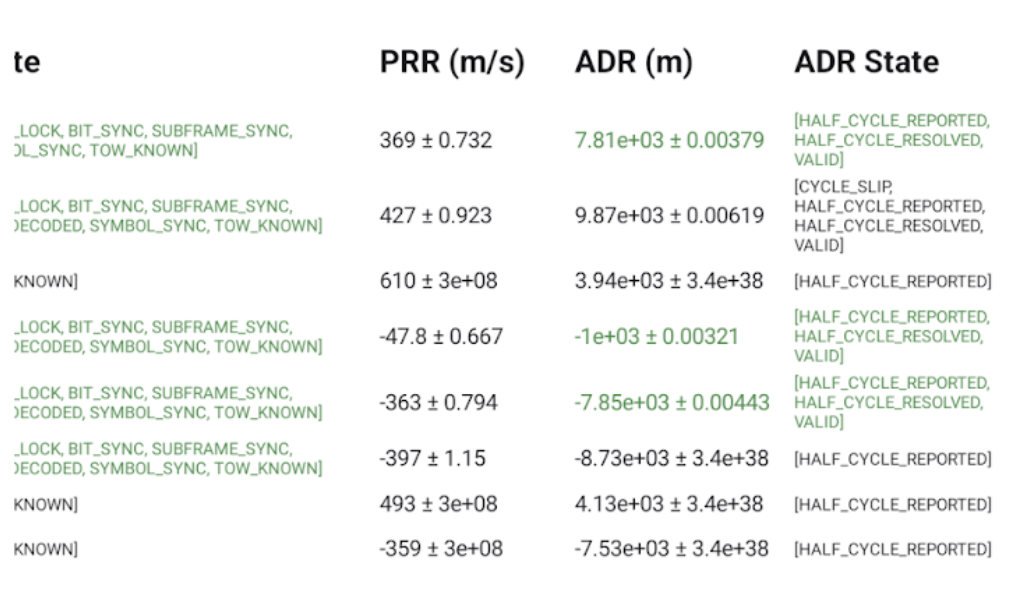
- PRR to pseudoszybkość w metrach na sekundę z GnssMeasurement.getPseudorangeRateMetersPerSecond().
- Kolumna Stan ADR zawiera wersję zrozumiałą dla człowieka flag bitowych określonych w kolumnie GnssMeasurement.getAccumulatedDeltaRangeState(). Jeśli ADR jest odpowiedni do pozycjonowania, tekst w polach ADR (m) i Stan ADR jest zielony.
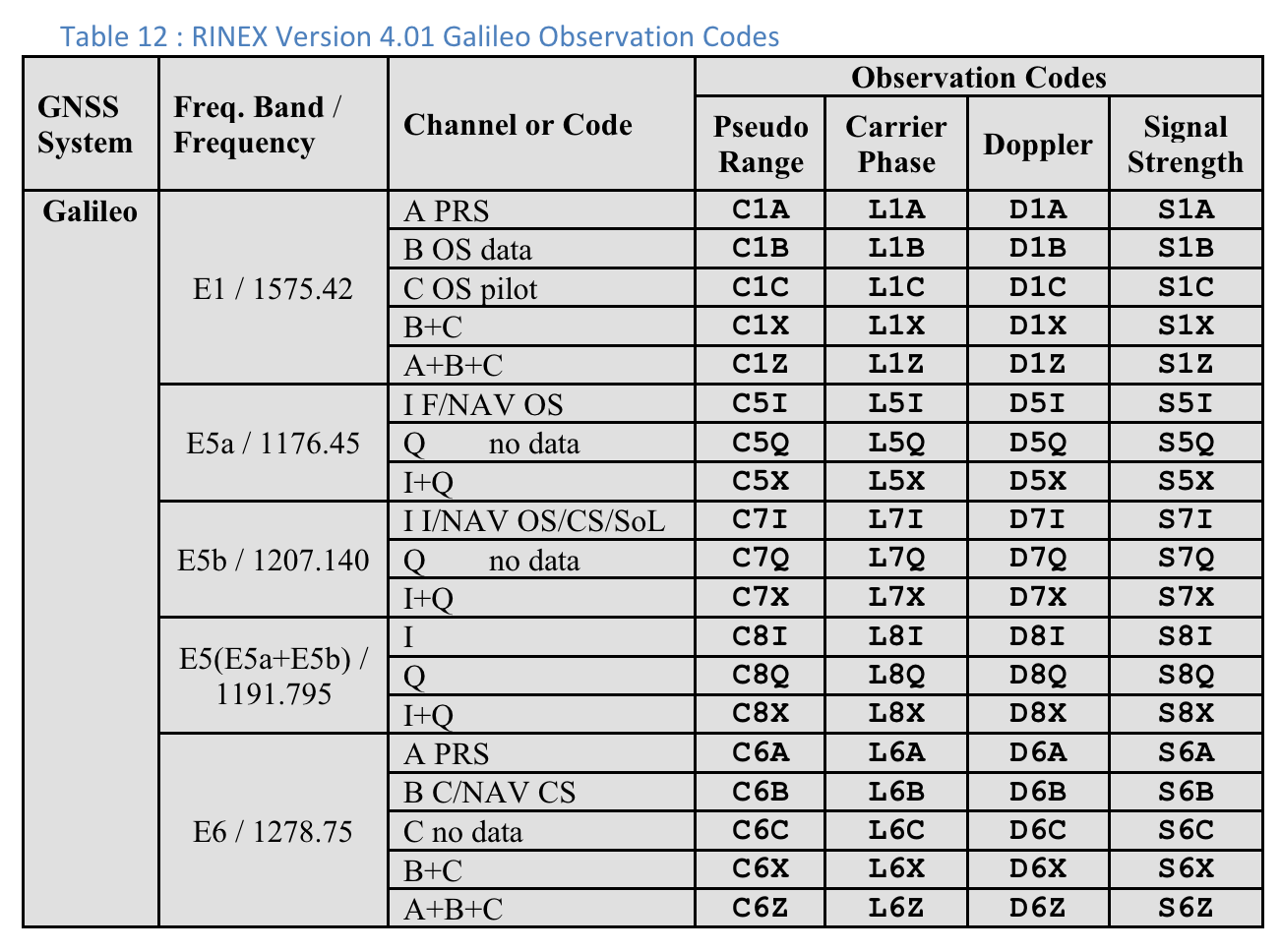
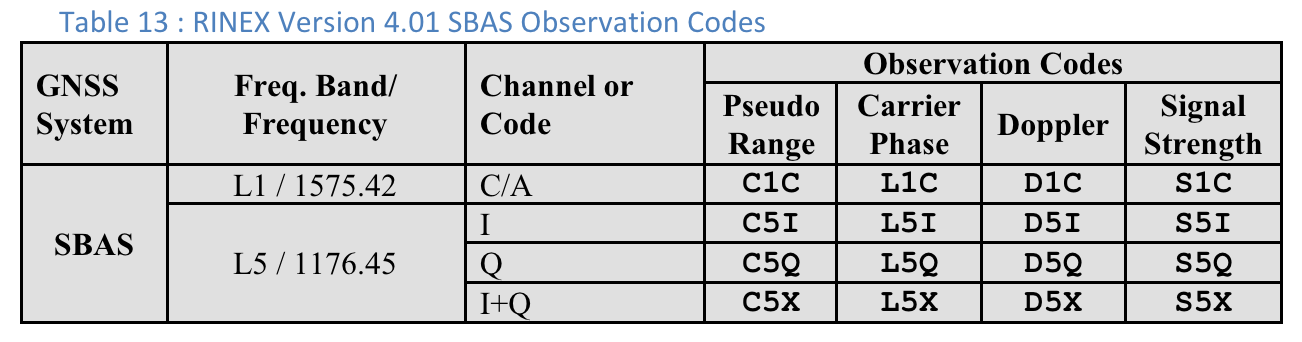
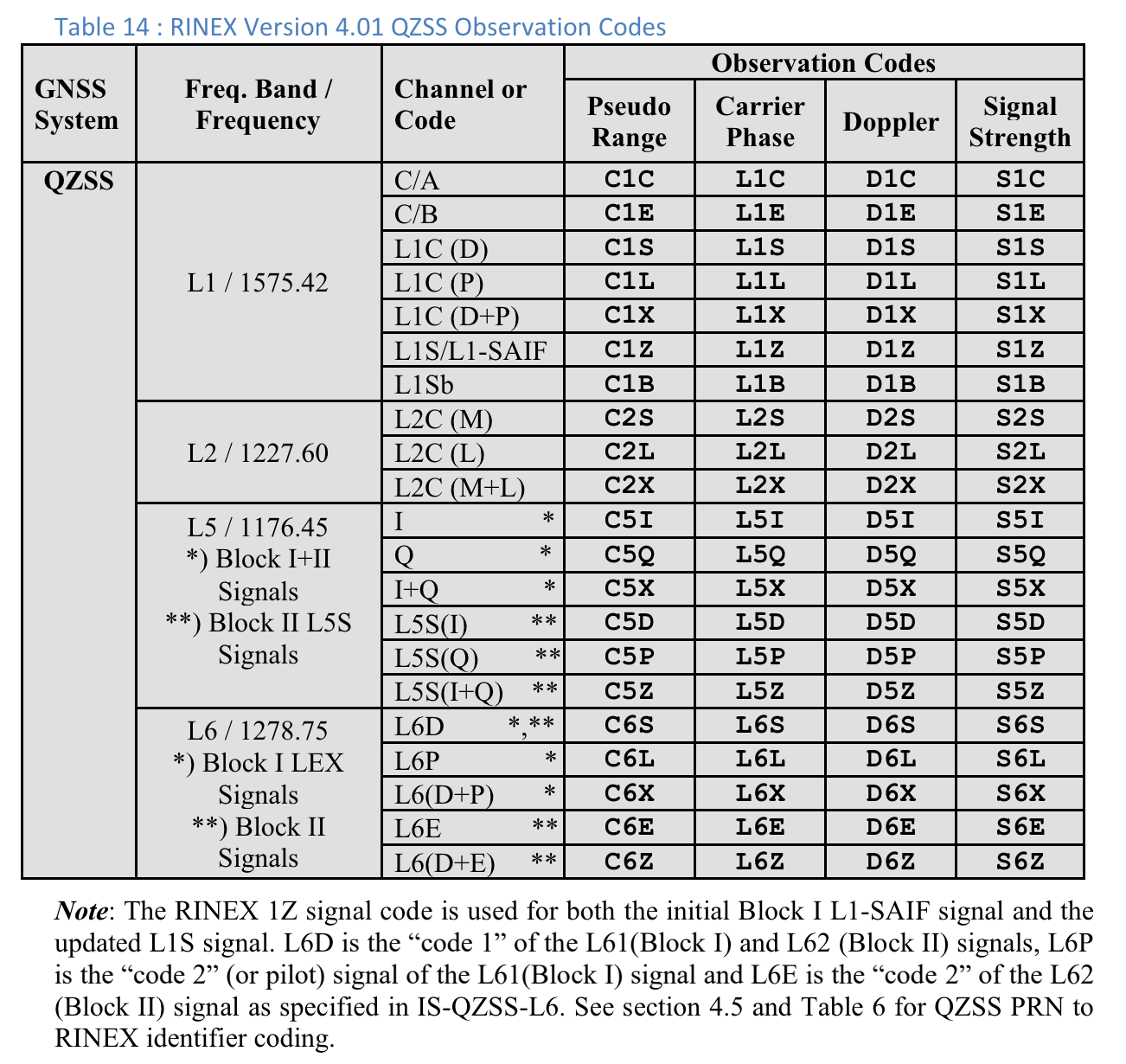
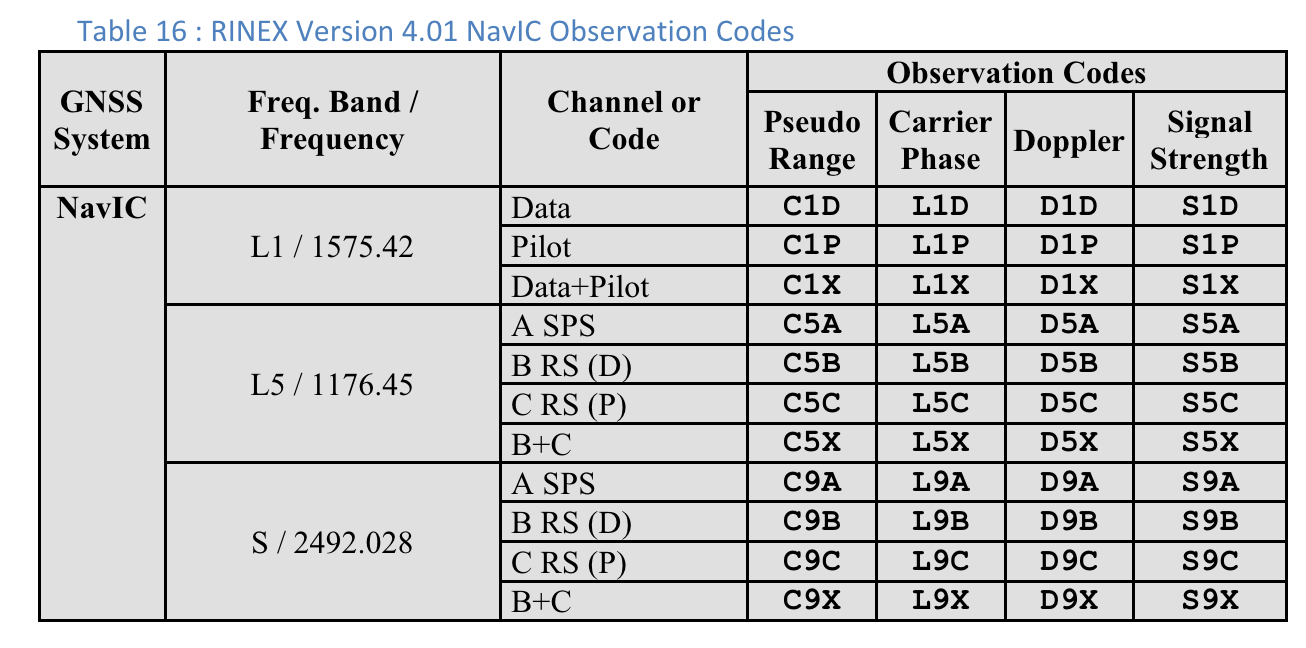
Kody obserwacji RINEX 4.01
Ostatnia z 3 liter w kolumnie Pseudo Range w kodach obserwacji RINEX to wartość Typ kodu widoczna na ekranie Pomiarów w GnssLogger.
Poniżej, dla wygody użytkowników, zamieszczamy tabele ze specyfikacji RINEX 4.01. Szczegółowe informacje znajdziesz w pełnej specyfikacji.