نظرًا لأن شاشات التلفزيون يتم عرضها عادةً من مسافة بعيدة، فإن الواجهات التي تستخدم أسلوب الخط الأكبر تكون أكثر وضوحًا وراحة للمستخدمين. يتضمن مقياس النوع الافتراضي لـ TV Design أنماط كتابة متباينة ومرنة لدعم مجموعة واسعة من حالات الاستخدام.
أهمّ الميزات
- أعط الأولوية لاستخدام أسلوب الخط الأكبر للحصول على تجربة مشاهدة أكثر راحة على شاشات التلفزيون.
- الخط التلقائي لـ Android TV هو Roboto.
- اختر خطوطًا مميّزة وسهلة القراءة لتعكس نمط علامتك التجارية على أفضل وجه.
- تأكد من أن الخطوط سهلة القراءة بنظرة سريعة، مع العرض المناسب والتحجيم البصري.
- قم بإقران الخطوط المجانية؛ على سبيل المثال، استخدم sans-serif للنص الأساسي والتسميات.
- زيادة الوضوح من خلال تجنُّب الخطوط الزخرفية
خطوط
الخطوط الطباعية التلقائية
يتميّز Android TV بالخط الطباعي الخاص به، وهو Roboto، الذي تم تحسينه من أجل الوضوح والوضوح. يمكنك استخدام Roboto للحصول على عنصر واجهة مستخدم عملي لا يحمل علامة تجارية، ويتم عرضه على أفضل وجه من خلال تجربة النظام الأساسي الأصلية.

الخطوط الطباعية المختلفة
عند الاقتضاء، استخدم خطًا مميزًا يعكس نمط علامتك التجارية. فيما يلي الأشياء الرئيسية التي يجب التفكير فيها عند اختيار خط:
- الوضوح - لتحسين مقروئية النص عن بُعد، استخدِم الخطوط الطباعية ذات العدّادات الكبيرة والتحجيم البصري البسيط. التأكد من تمييز الحروف عن بعضها البعض.
- سهولة القراءة بنظرة سريعة: يجب أن يكون عرض الخط على أي نص على التلفزيون واضحًا، إذ لا يمكن التعرّف على الخطوط الأكثر سمكًا على الفور.
- إقران خطوط تكميلية - إذا أردت استخدام خطوط متعددة، استخدِم الخط الطباعي San-serif للنص الأساسي والتصنيفات.
- إذا أمكن، تجنَّب الخطوط الزخرفية. في حين أن أحجام الخطوط على التلفزيون أكبر من أحجام الشاشات الأخرى، فإن سهولة قراءة نص واجهة المستخدم هي الأولوية. تجنَّب الخطوط التي لا يمكن أن تعمل كنص أساسي.

كتابة المقياس
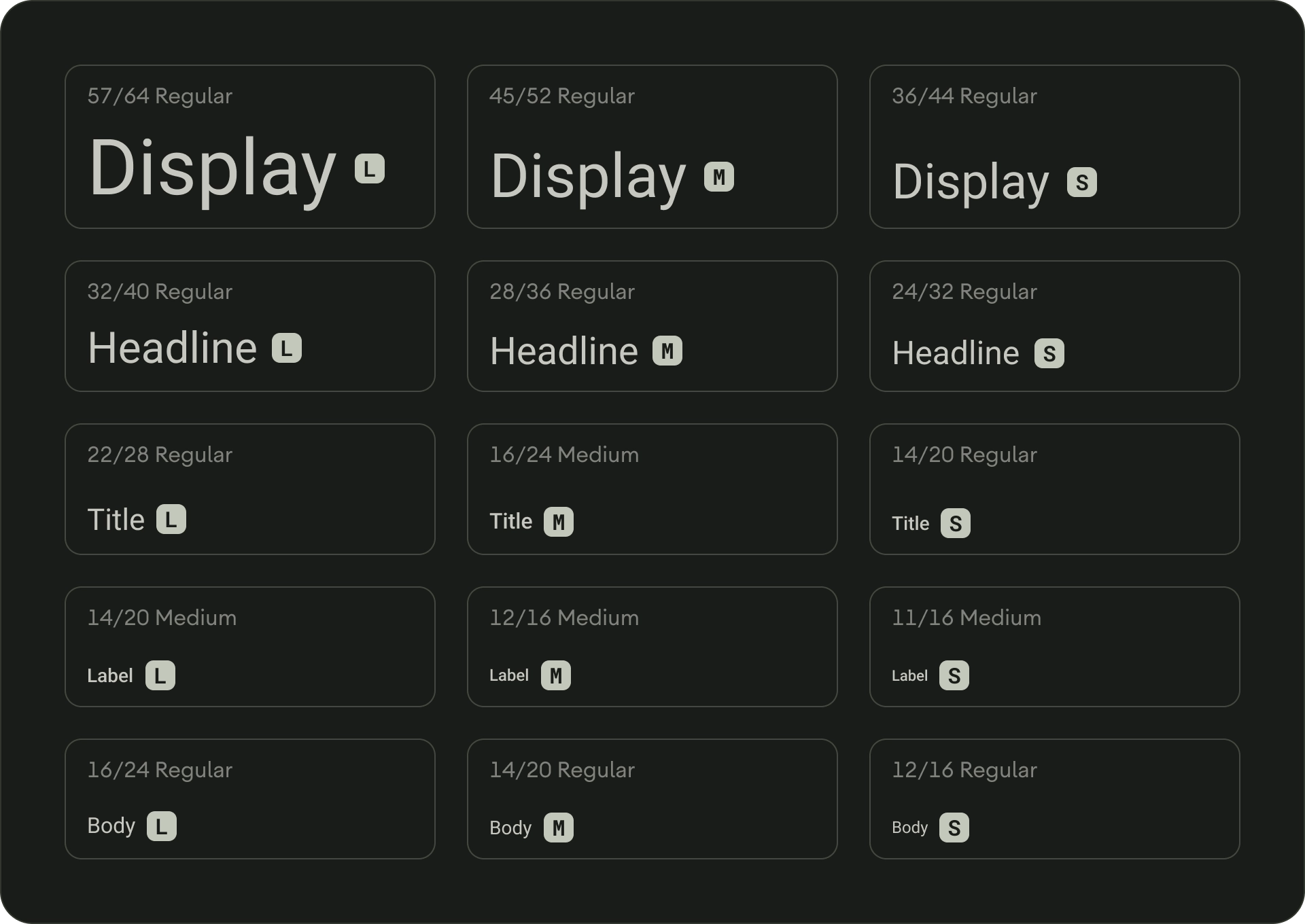
مقياس الكتابة هو مجموعة من أنماط الخطوط التي يمكن استخدامها في أي تطبيق. يضمن ذلك نمطًا مرنًا ومتسقًا في الوقت نفسه يلبّي مجموعة من الأغراض. مقياس نوع تصميم التلفزيون عبارة عن مزيج من 15 نمطًا، لكل منها تطبيق ومعنى مقصود. يتم تعيينها بناءً على الاستخدام، مثل "الشبكة الإعلانية" أو "العنوان"، ويتم تجميعها في فئات على أساس الحجم (كبير أو صغير). يستخدم مقياس الكتابة الافتراضي في TV Design Roboto لجميع العناوين والتسميات والنص الأساسي لإنشاء تجربة طباعة موحدة.
للتعرف على الرموز المميزة لأسلوب الخط وتخصيص الخطوط، انتقل إلى Material Design 3.
أدوار النوع
الشاشة
تتوفر ثلاثة أنماط للعرض في مقياس النوع الافتراضي: كبير ومتوسط وصغير. بصفتها أكبر نص على الشاشة، يتم حجز أنماط العرض الكبيرة للمقاطع النصية القصيرة والمهمة أو الأرقام. يمكن استخدامها للعنوان الرئيسي للشاشة. لا تستخدم أنماط عرض كبيرة لعناوين الأقسام أو المجموعات.

Headline
العناوين هي الأنسب للنصوص القصيرة عالية التوكيد. يمكن أن تكون هذه الأنماط جيدة لتمييز الفقرات الأساسية من النص أو مناطق المحتوى المهمة. تُستخدم للعناوين في العروض الدوارة المميزة والمجموعات الشاملة. يمكن للعناوين الرئيسية أيضًا الاستفادة من الخطوط الطباعية المعبّرة، وتوفير ارتفاع السطر المناسب وتباعد الأحرف في الحفاظ على سهولة القراءة.
العنوان
أنماط العناوين أصغر من أنماط العناوين. استخدم العناوين لنص موجز متوسط التوكيد. على سبيل المثال، ضع في اعتبارك استخدام العناوين لتقسيم فقرات ثانوية من النص أو مناطق ثانوية من المحتوى.
استخدِم العناوين لعناصر واجهة المستخدم مثل البطاقات أو القوائم. تكون أحجام العناوين مضغوطة مع توفير مستوى مفيد من البروز والوضوح.
الهيكل
تُستخدم أنماط النص الأساسي للمقاطع النصية الأطول في تطبيقك. استخدم الخطوط الطباعية التي يمكن قراءتها بأحجام أصغر والتي يمكن قراءتها بوضوح في الفقرات الطويلة. تجنب الخطوط الزخرفية للنص الأساسي نظرًا لأنه قد يكون من الصعب قراءتها من مسافة بعيدة.

التصنيف
أنماط التصنيفات أصغر حجمًا وعملية، حيث تُستخدم لأشياء مثل النص داخل المكونات أو للنص الصغير جدًا في نص المحتوى، مثل التسميات التوضيحية. الأزرار، على سبيل المثال، تستخدم تصنيف "نمط كبير".