レイアウトは、アプリケーション全体で視覚的な一貫性を維持するためのフレームワークを提供する構造テンプレートです。レイアウトでは、視覚的なグリッド、間隔、セクションを定義することで、情報と UI 要素を表示するためのまとまりのある整理された構造を構築します。

ハイライト
- ウェブやモバイルとは異なり、テレビの画面のアスペクト比は 16:9 に固定されています。
- 使いやすさと制御性を高めるために、水平軸と垂直軸に沿ってレイアウトを最適化します。
原則
TV レイアウトを設計する際の設計上の意思決定に役立つガイドライン。

大画面用に設計する
HDTV の普及に伴い、アスペクト比 16:9 の長方形のテレビが標準になりました。テレビは、従来、4:3 または 1.33:1 のアスペクト比の正方形で製造されていました。

Android プラットフォームでの設計
設計時には、他の Android デバイスと同様に、dp を使用して、密度が異なる画面に要素を均一に表示します。常に MDPI 解像度(960 ピクセル × 540 ピクセル)でデザインします。
MDPI では 1px = 1dp です。
アセットは 1080p を目標にする必要があります。これにより、Android システムは必要に応じてレイアウト エレメントを 720p にダウンスケールできます。
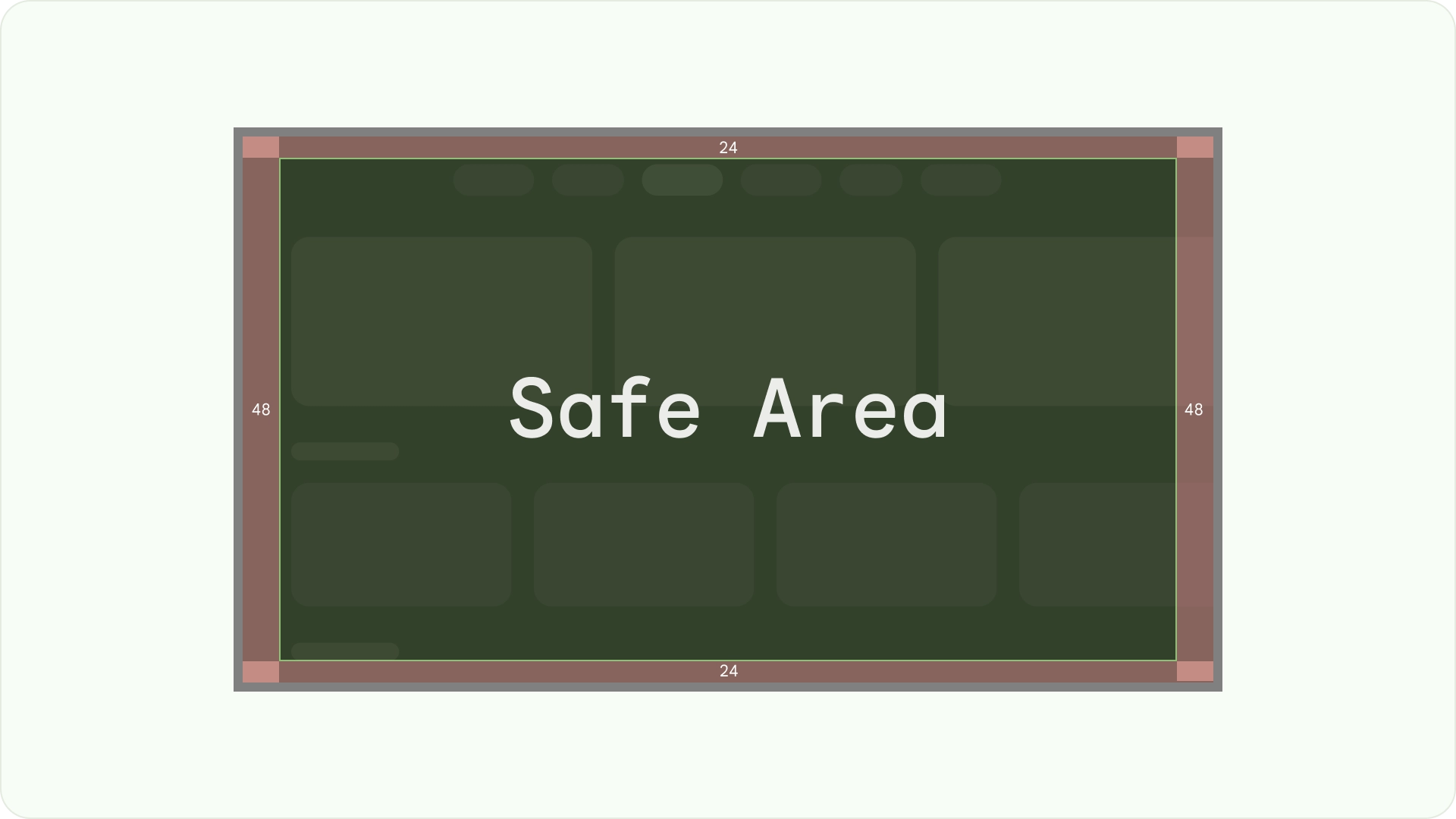
可視性とオーバースキャンの安全性を確保する
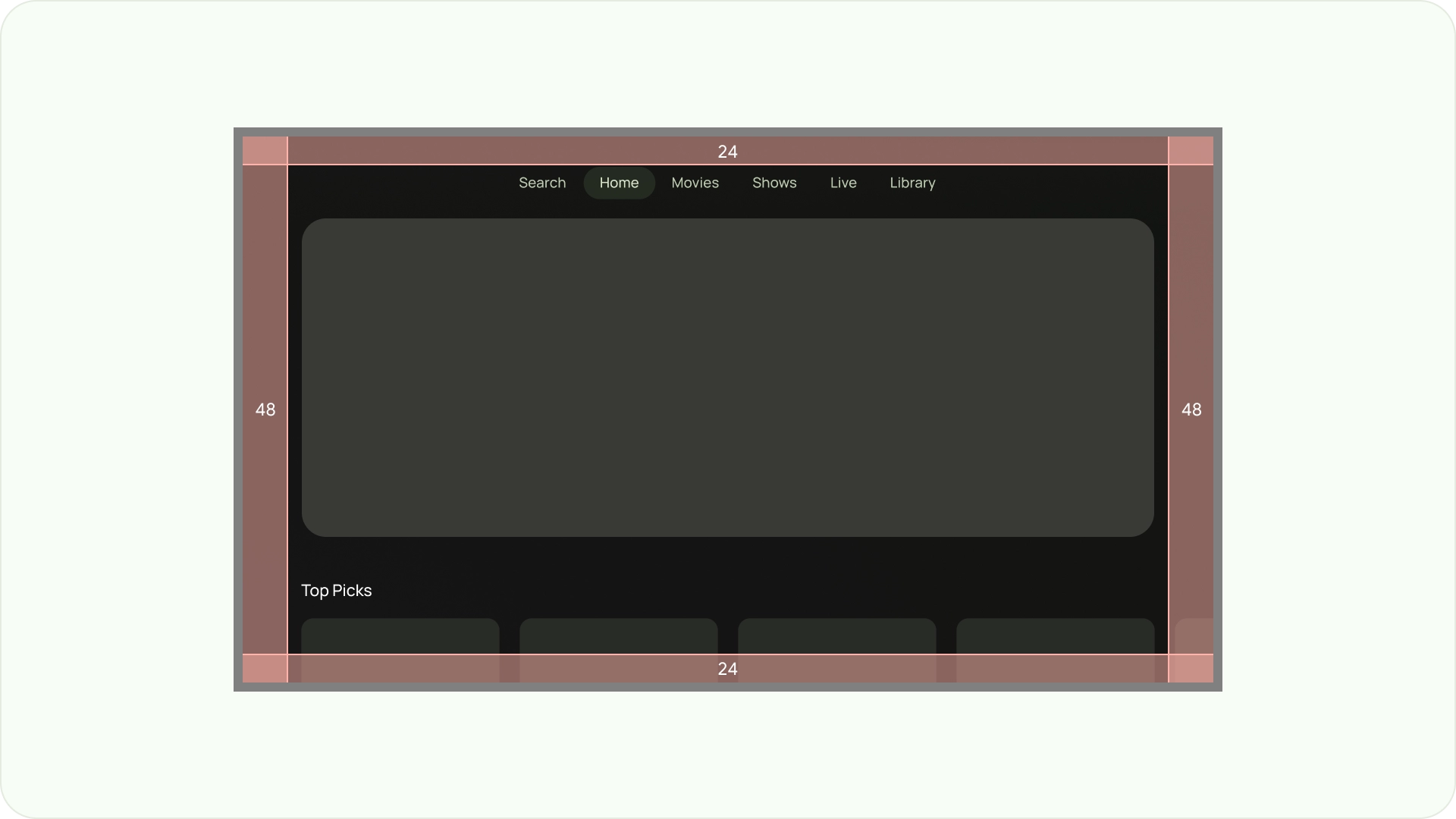
重要な要素が常にユーザーに表示されるようにします。そのためには、レイアウトの左右に 48 dp の 5%、上下に 27 dp の 5% のマージンを設定して要素を配置します。これにより、レイアウトの画面要素がオーバースキャン内に収まります。

全画面表示
背景画面要素をオーバースキャン安全領域に合わせて調整またはクリッピングしないでください。代わりに、画面外の要素の一部を表示できるようにします。これにより、すべての画面で背景要素と画面外要素が正しく表示されます。
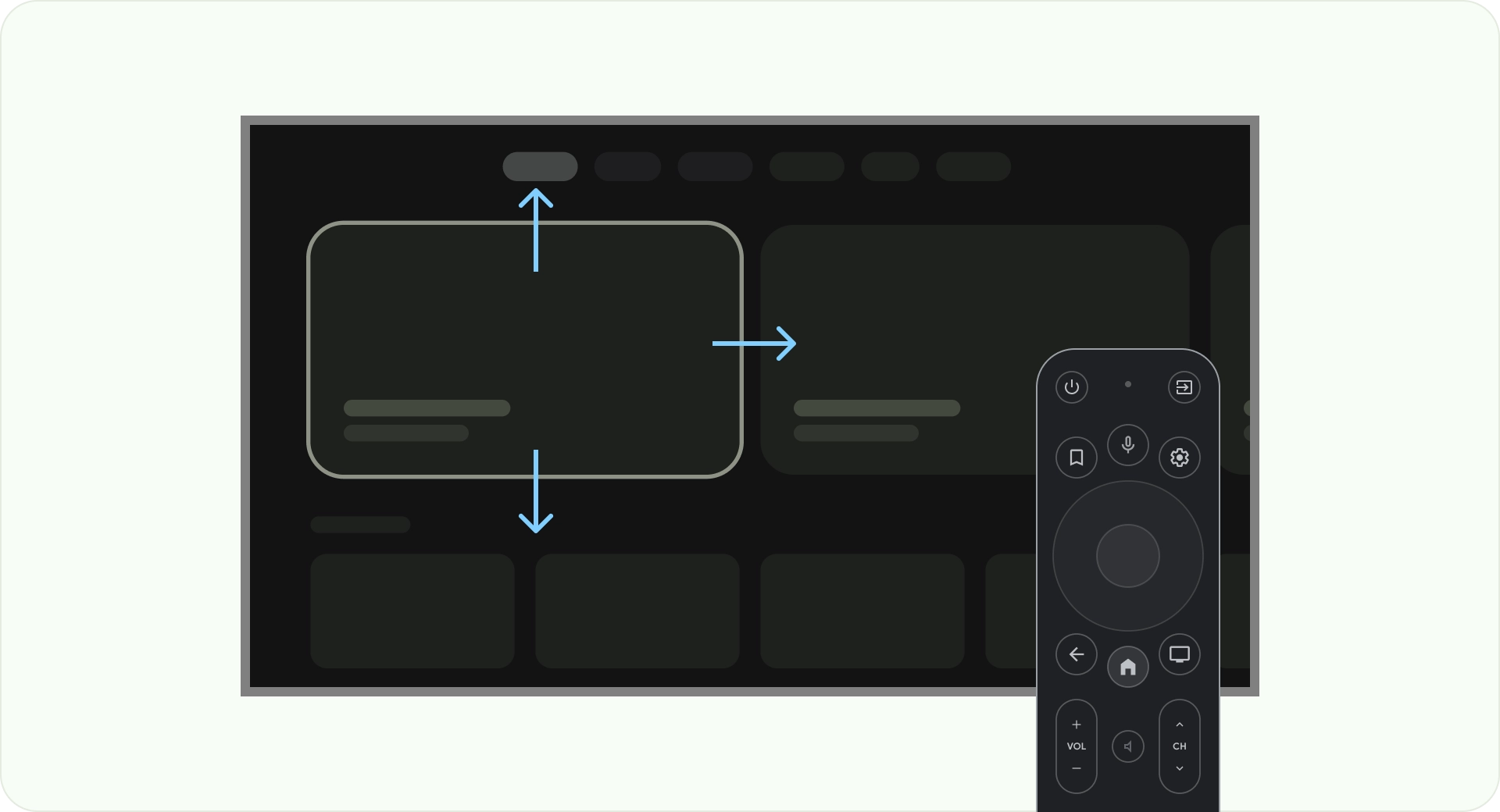
軸を使用して最適化する
ユーザーがテレビのリモコンをどのように使用しているかを検討します。テレビのインターフェースがリモコンで簡単に操作できることを確認します。各方向(上、下、左、右)に明確な目的とナビゲーション パターンを設定して、ユーザーがオプションの大きなグループを移動する方法を理解できるようにします。
レイアウト
テレビの画面サイズはデバイスによって異なります。最新のテレビのアスペクト比は 16:9 であるため、アプリの画面サイズは 960 ピクセル x 540 ピクセルにすることをおすすめします。これにより、すべての要素を HD 画面または 4K 画面に合わせて比例的にサイズ変更できます。

オーバースキャンの余白
オーバースキャン マージンは、コンテンツと画面の左右の端との間のスペースです。
960 * ~5% = 48dp
540 * ~5% = 27dp round off to 24dp
これらの境界マージンは、オーバースキャンの問題からプライマリ要素を保護します。コンテンツと情報を安全に保つには、5% のマージンのレイアウト(左右に 58 dp、上下に 28 dp)を使用します。
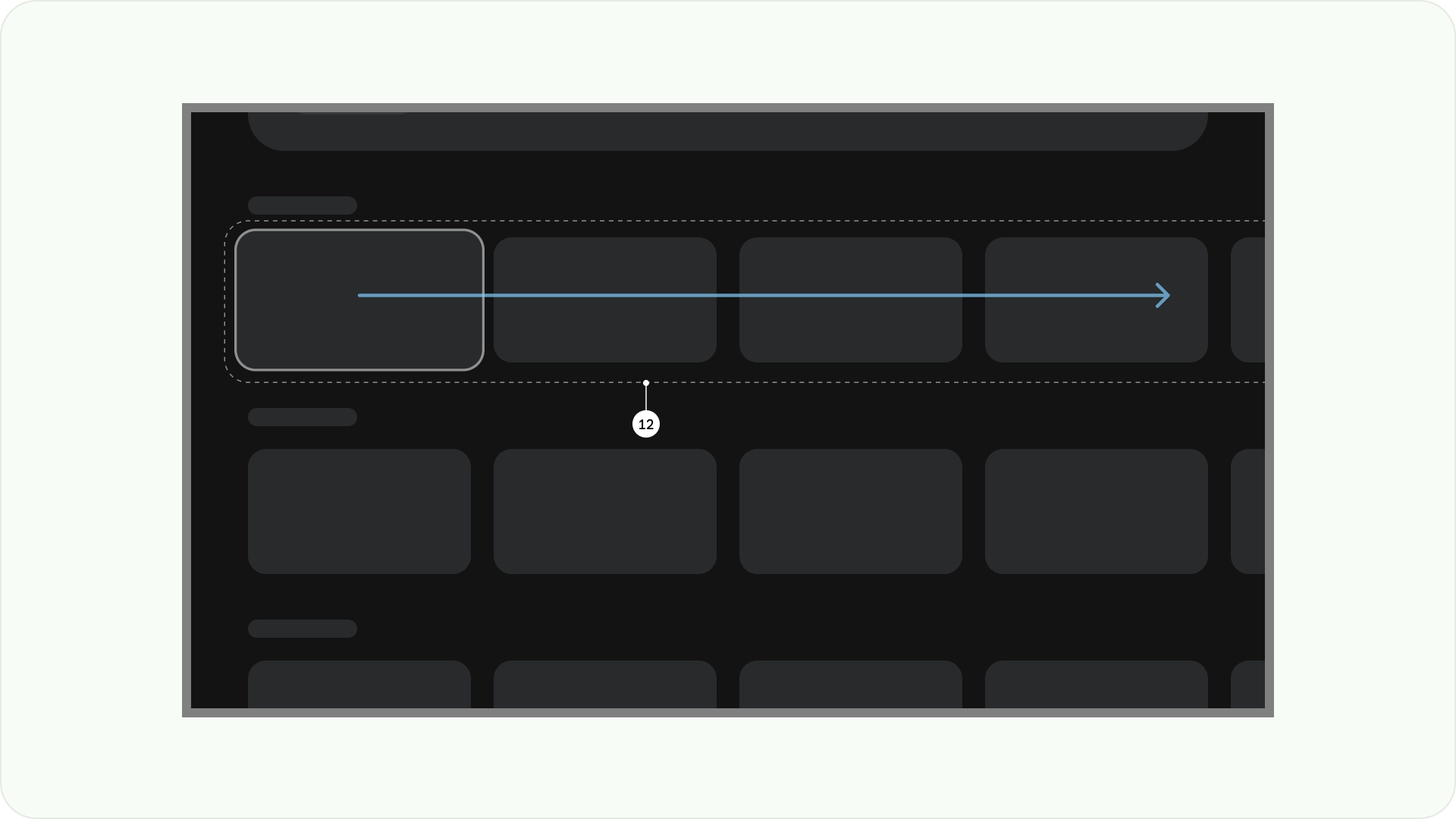
列とガター
コンテンツは、列とガターがある画面領域に配置されます。グリッドシステムには 12 列があります。ガターは、コンテンツを分割するために列の間に配置するスペースです。
幅 52 dp の列を 12 個使用し、列間に 20 dp のスペースを空けます。両側に 58 dp のスペースと、行間に 4 dp の垂直方向のスペースが必要です。

レイアウト パターン
目的とディスプレイ デバイスに応じて、水平スタック レイアウト、垂直スタック レイアウト、グリッド レイアウトの 3 つのレイアウト パターンを使用できます。
横方向のスタック レイアウト
水平方向のスタック レイアウトでは、コンポーネントが横方向に配置されます。サイズ、比率、形式は異なります。このレイアウトは、コンテンツとコンポーネントをグループ化するためによく使用されます。
縦型スタック レイアウト
垂直スタック レイアウトでは、コンポーネントを垂直方向に配置し、サイズ、比率、形式を柔軟に設定できます。さまざまなタイプのテキスト、インタラクティブ コンポーネント、レイアウト パターンをグループ化するためによく使用されます。

グリッド レイアウト
グリッドは、交差する列と行の集合であり、グリッド レイアウトは、このグリッドにコンテンツを表示します。コンテンツを論理的に配置し、ユーザーが簡単に移動して閲覧できるようにします。
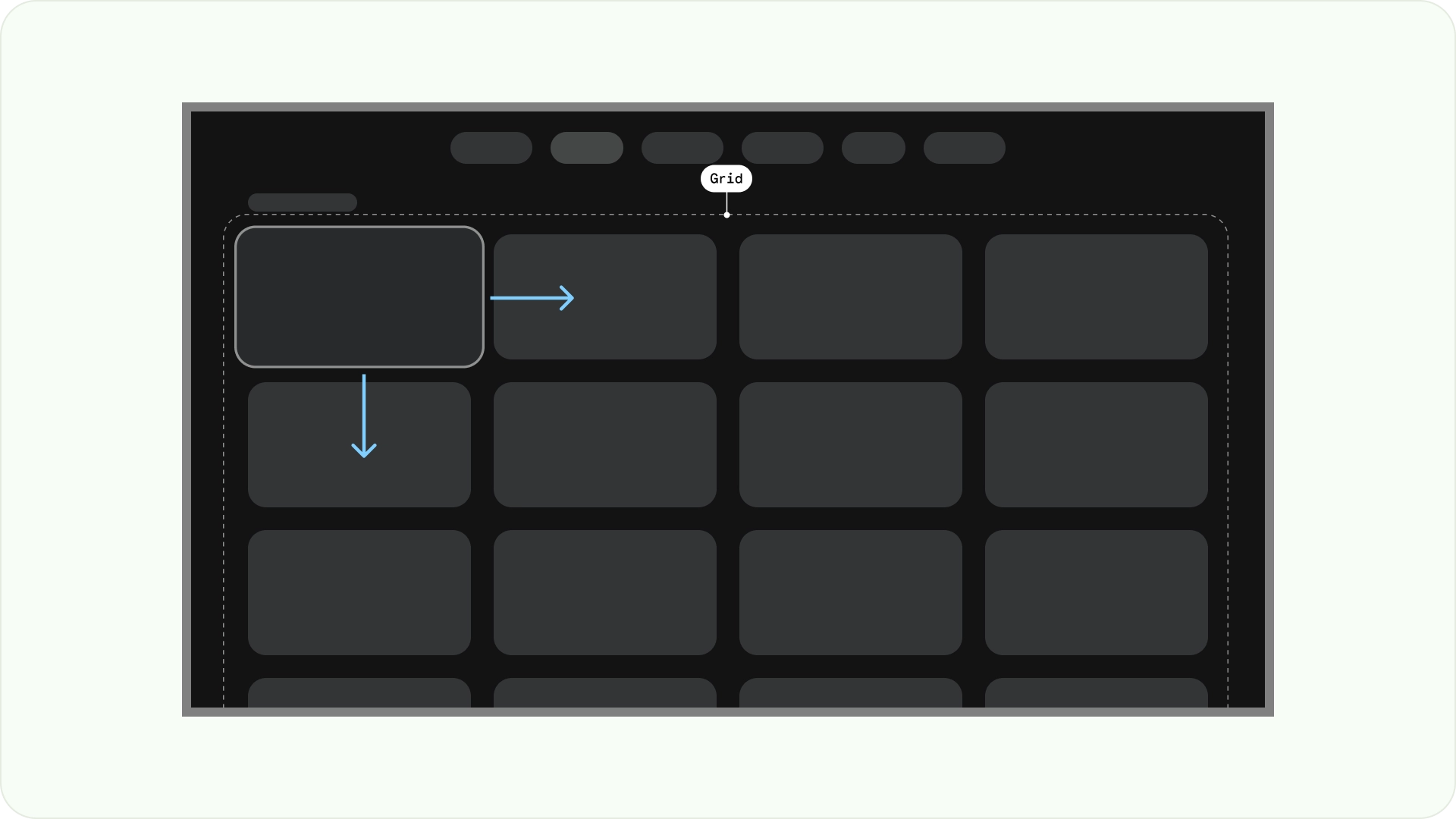
重複しないようにするには、アイテム間のパディングと、フォーカス状態のサイズ増加を考慮することが重要です。たとえば、フォーカスされているコンポーネント(カードなど)がハイライト表示される場合があります。推奨されるグリッド レイアウト(52 dp の 12 列、20 dp のガター)を使用する場合は、カードで推奨されるコンポーネント レイアウトとプレビューをご覧ください。
レイアウト構造
テレビのレイアウトを設計する際に適切な判断を行うために、ここではいくつかのレイアウト構造を紹介します。テレビ画面を横方向に分割することで、さまざまなタイプのコンポーネントを分離し、情報の階層とナビゲーション ロジックを伝達できます。ペインには複数の単位列を含めることができます。各パネルには、スタック レイアウトやグリッド レイアウトなど、さまざまなレイアウト パターンをホストできます。
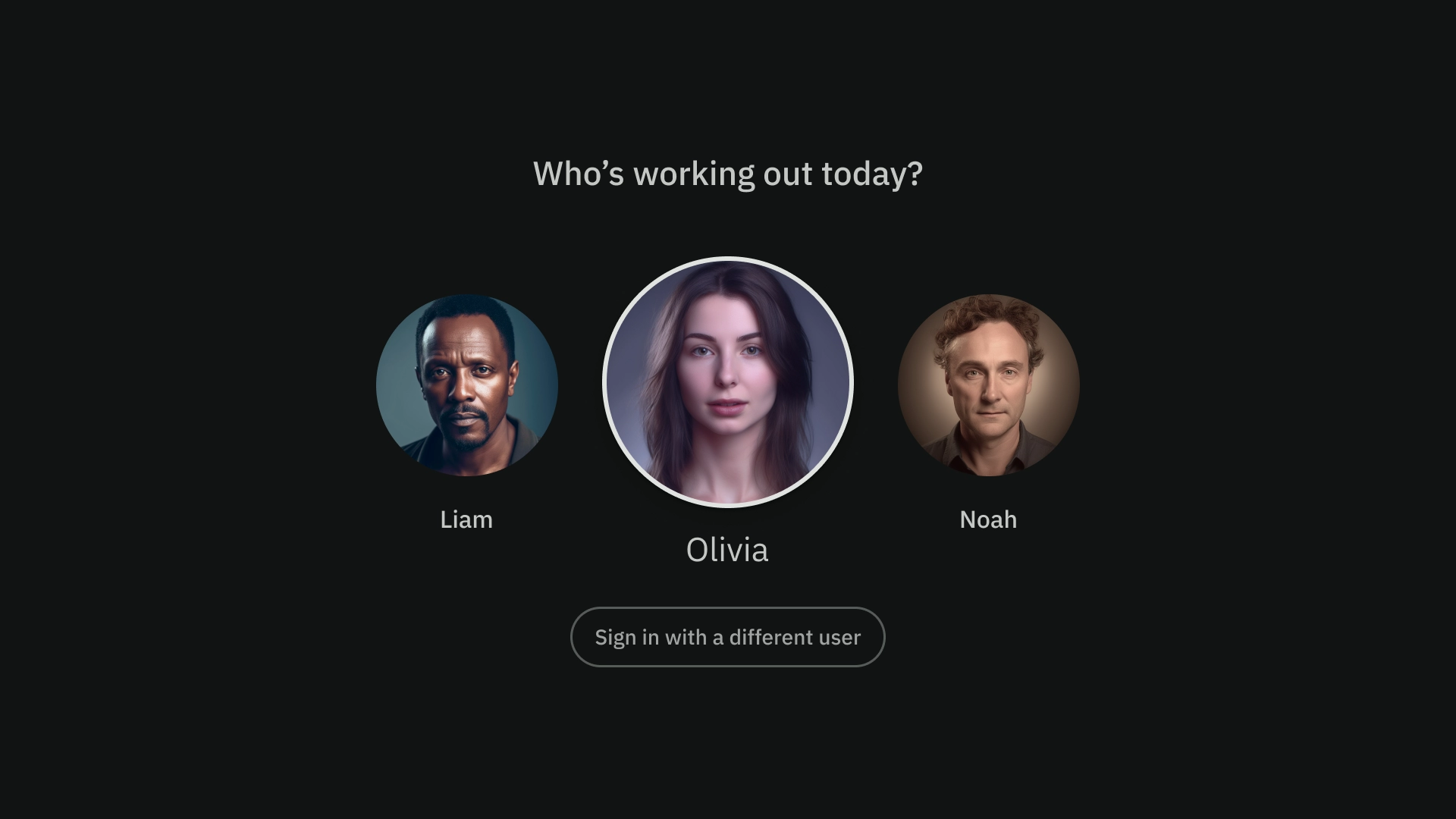
シングルペイン レイアウト
シングルペイン レイアウトは、メインのコンテンツに注目を集めるのに役立ちます。コンテンツ重視のエクスペリエンスと重要な情報ページで使用します。
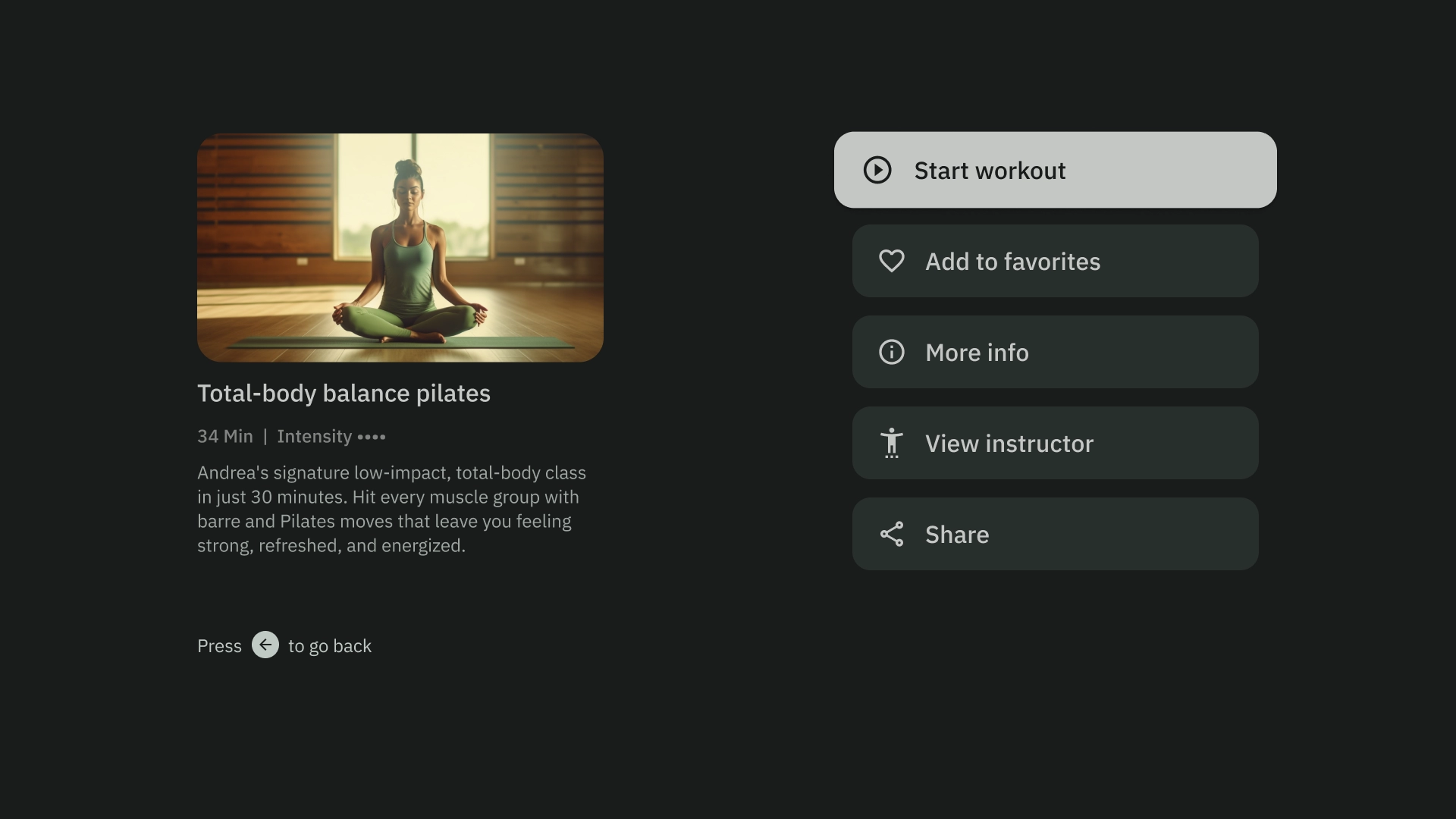
2 ペイン レイアウト
2 ペイン レイアウトは、ページに階層型コンテンツを表示する場合に効果的です。タスク フォワード エクスペリエンスで広く使用されています。
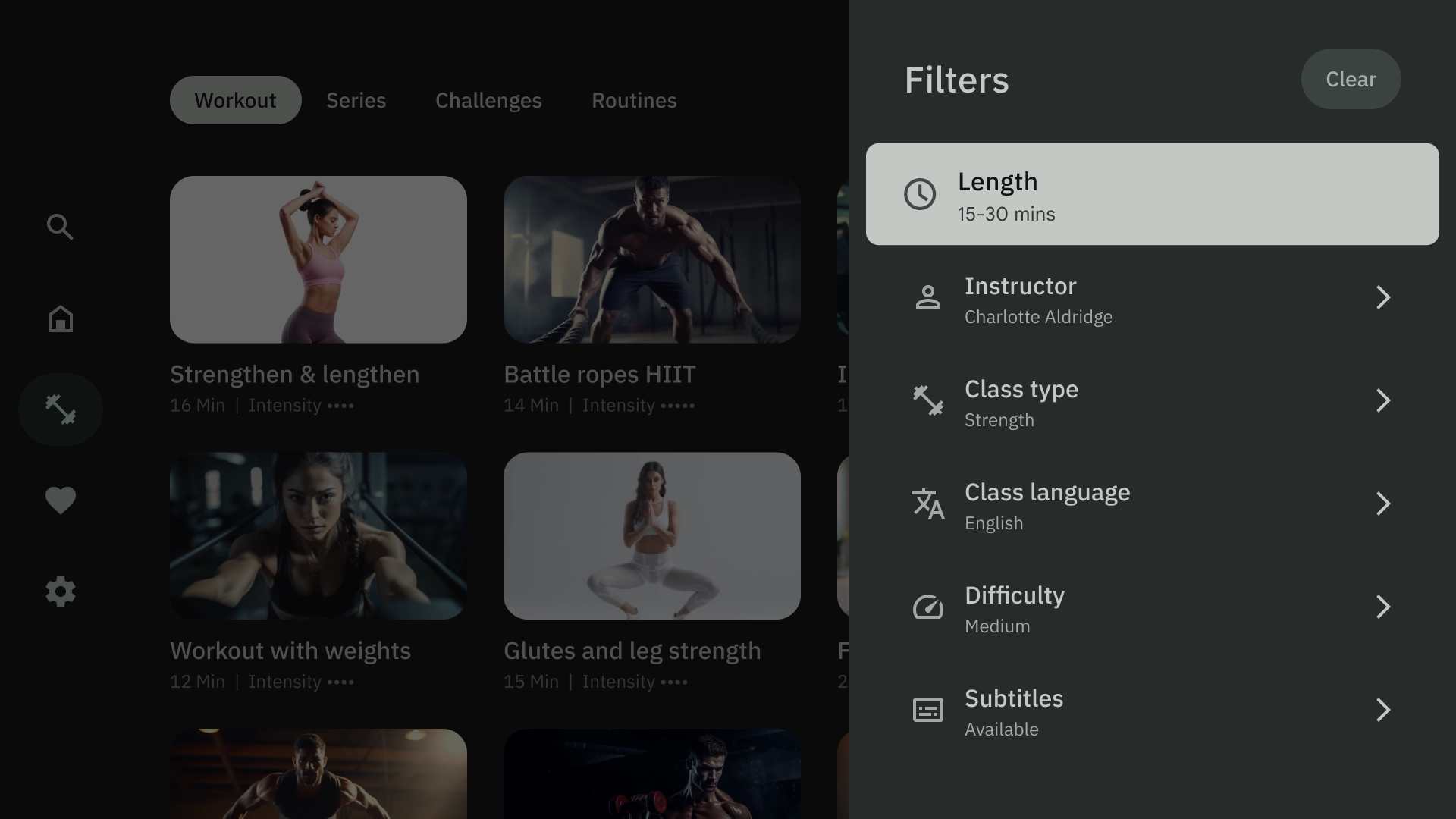
認知的過負荷
複雑で不明確なコンテンツは、混乱や不満を招き、エンゲージメントの低下につながる可能性があります。デザインをスキャンしやすいようにし、不要な情報を省き、重要な情報のみを表示します。
コンテンツをグループ化するためにパネルを使いすぎないようにします。これにより、ユーザーに不要な認知負荷と階層がもたらされます。

すべきこと
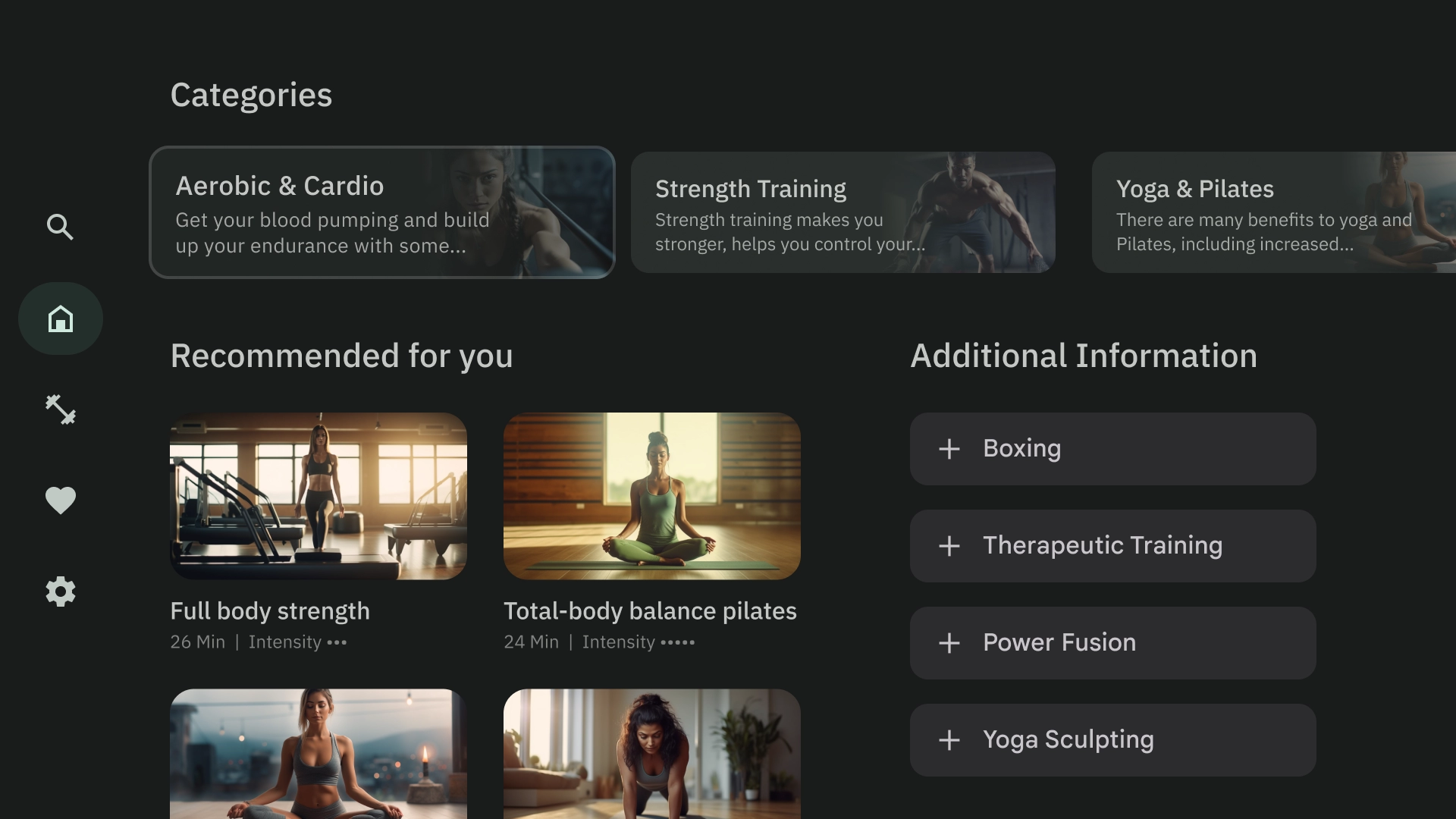
すべきでないこと
階層とナビゲーションを表現する
パネルは、コンテンツを視覚的に分離して整理します。ユーザーのガイダンスに役立ち、より直感的なインターフェースを作成してエクスペリエンスを向上させることができます。

すべきこと
すべきでないこと
レイアウト テンプレート
レイアウト テンプレートを使用すると、秩序、一貫性、親しみやすさを促進できます。このデザインにより、ユーザーが現在地と移動先を明確に把握できる快適な UI エクスペリエンスが実現します。
参照
ブラウザ テンプレートでは、メディア コンテンツの「クラスタ」または行が垂直方向に積み重ねて表示されます。ユーザーは上下に移動して行をブラウジングし、左右に移動して特定の行のコンテンツをブラウジングします。

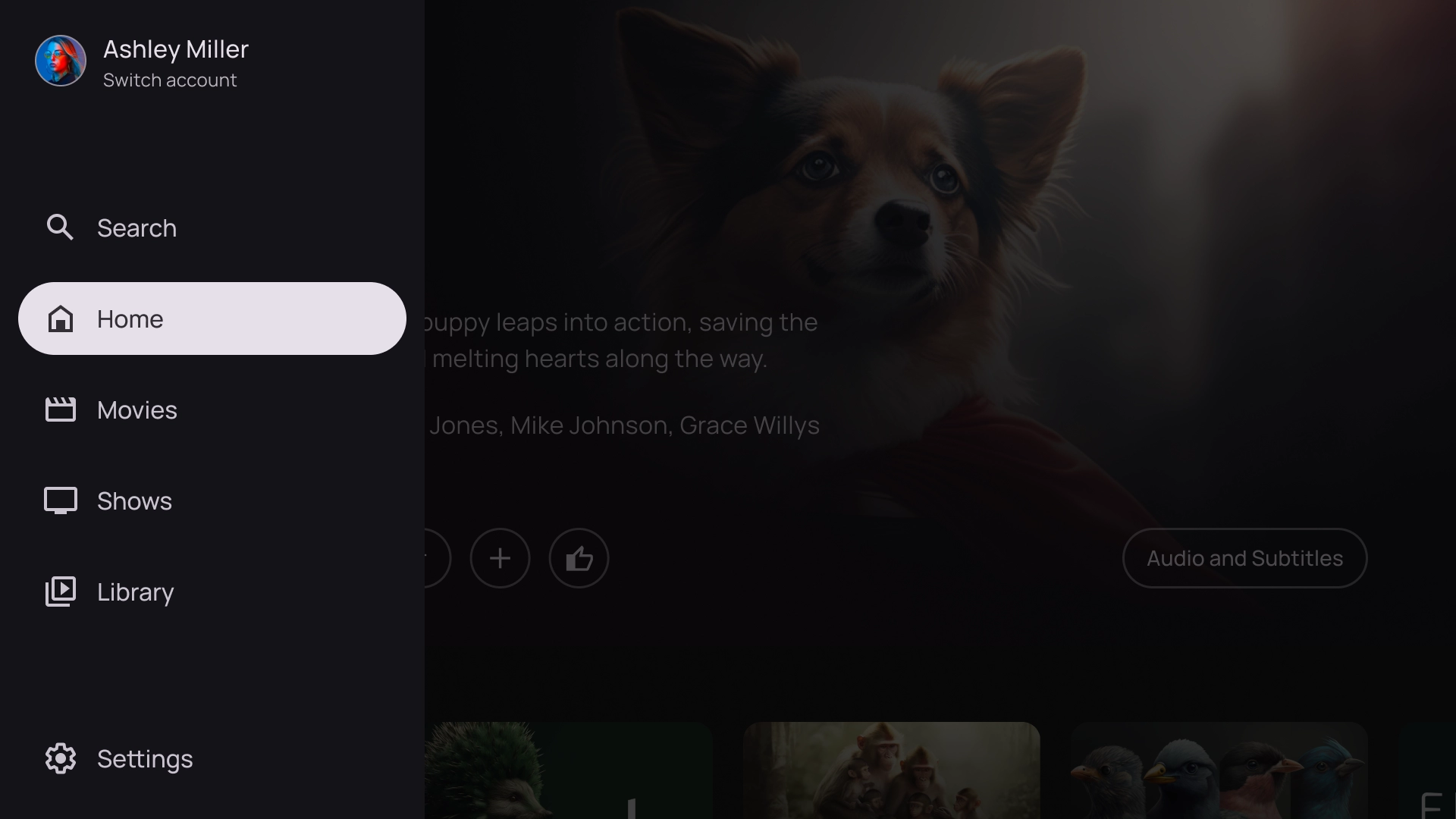
左オーバーレイ
左側のナビゲーション テンプレートでは、画面の左側にオーバーレイ パネルが表示されます。通常は、バックグラウンドのコンテンツに関連して操作できるナビゲーションやアイテムが表示されます。
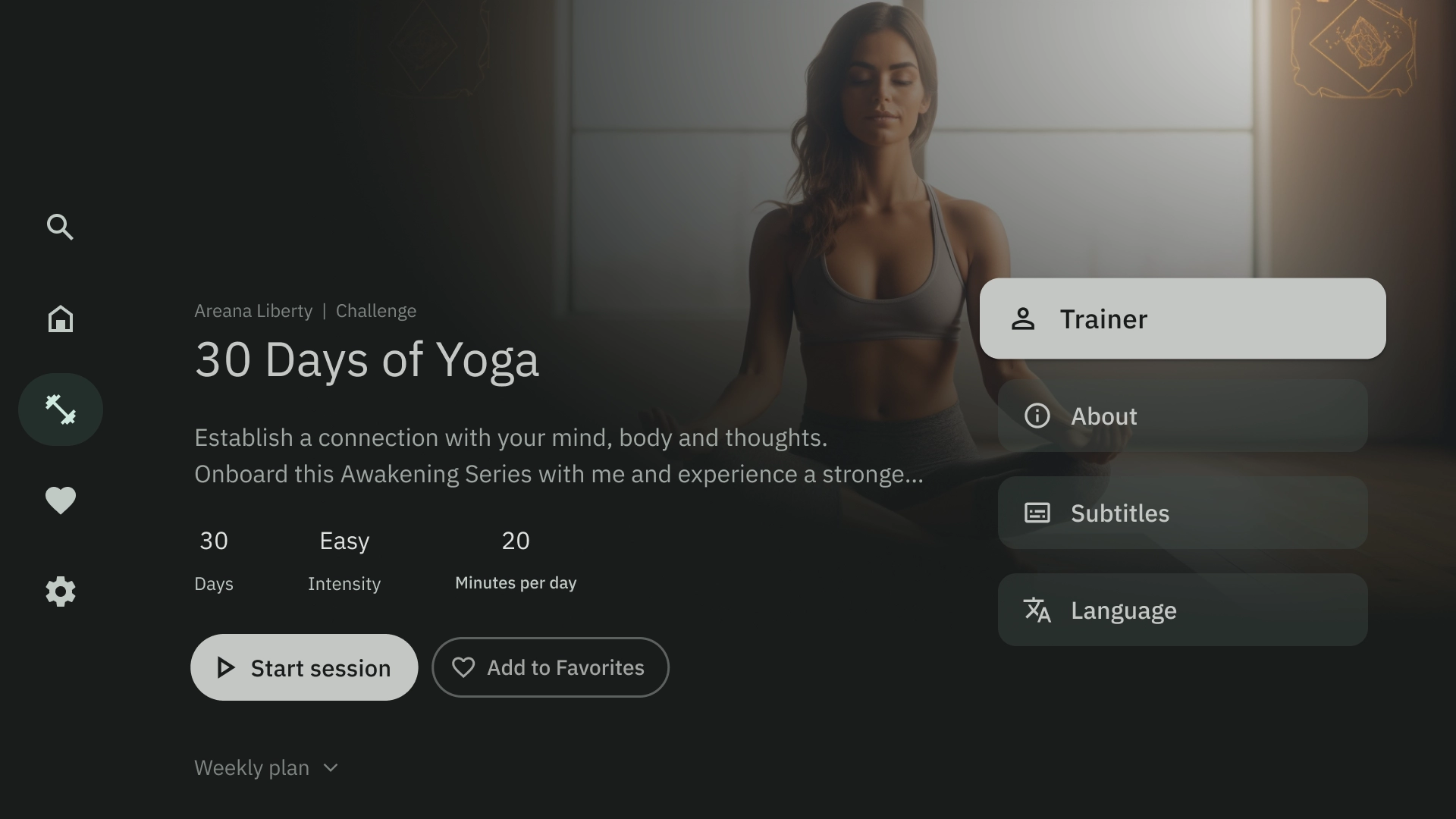
右オーバーレイ
右側のオーバーレイ テンプレートでは、画面の右側にオーバーレイ パネルが表示されます。通常、バックグラウンドのコンテンツとは独立して操作できるアイテムが表示されます。
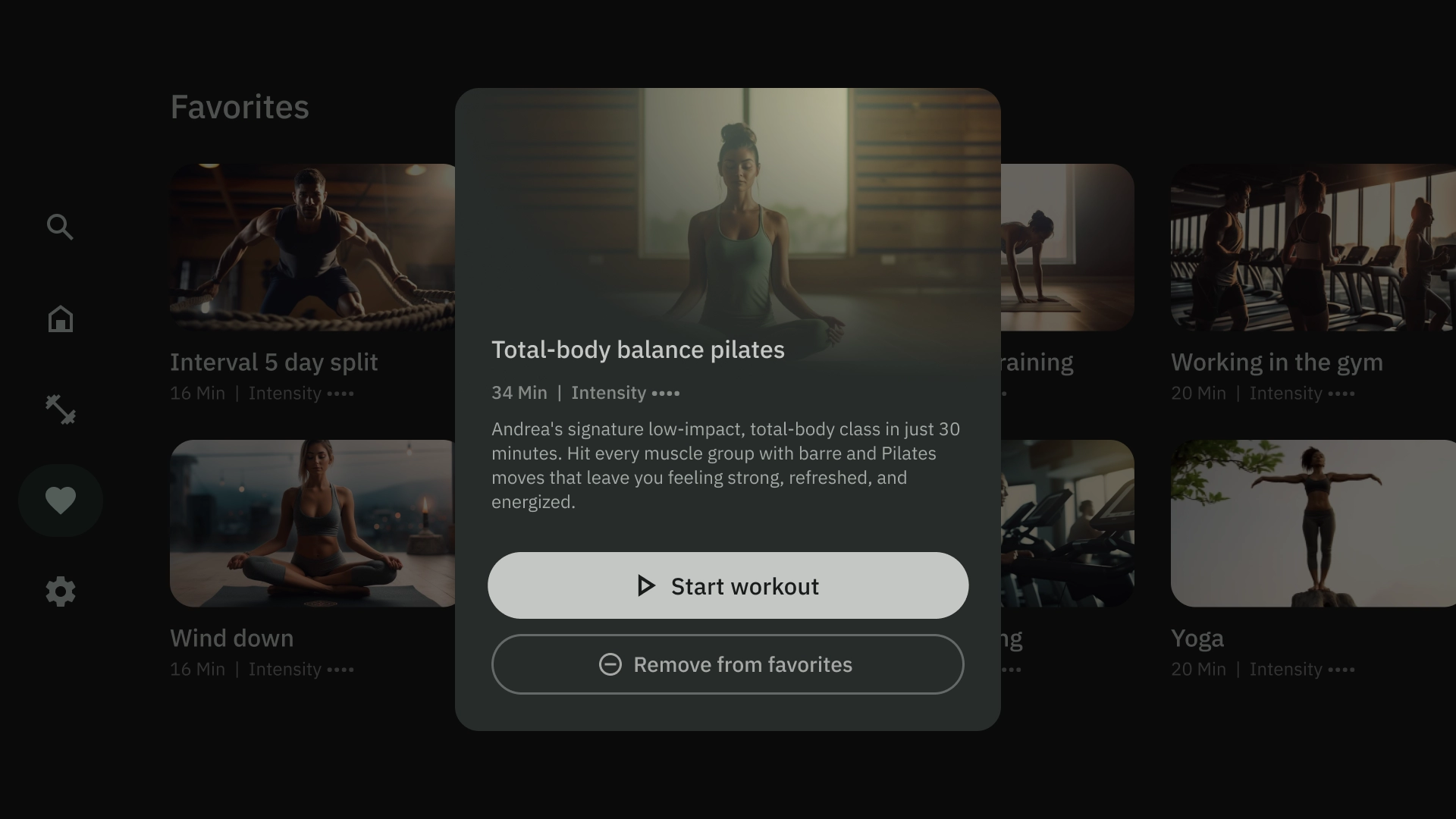
中央オーバーレイ
中央オーバーレイ テンプレートでは、既存のビューの上にオーバーレイされるモーダル要素が表示されます。緊急情報を伝達したり、意思決定を促したりするために使用されます。
下部オーバーレイ
ボトム オーバーレイ テンプレートは、ボトムシートでよく使用されます。ボトムシートは、画面の下部に固定された補足的なコンテンツを含むサーフェスです。現在のページのコンテキストを失うことなく、ミニフローを作成できます。
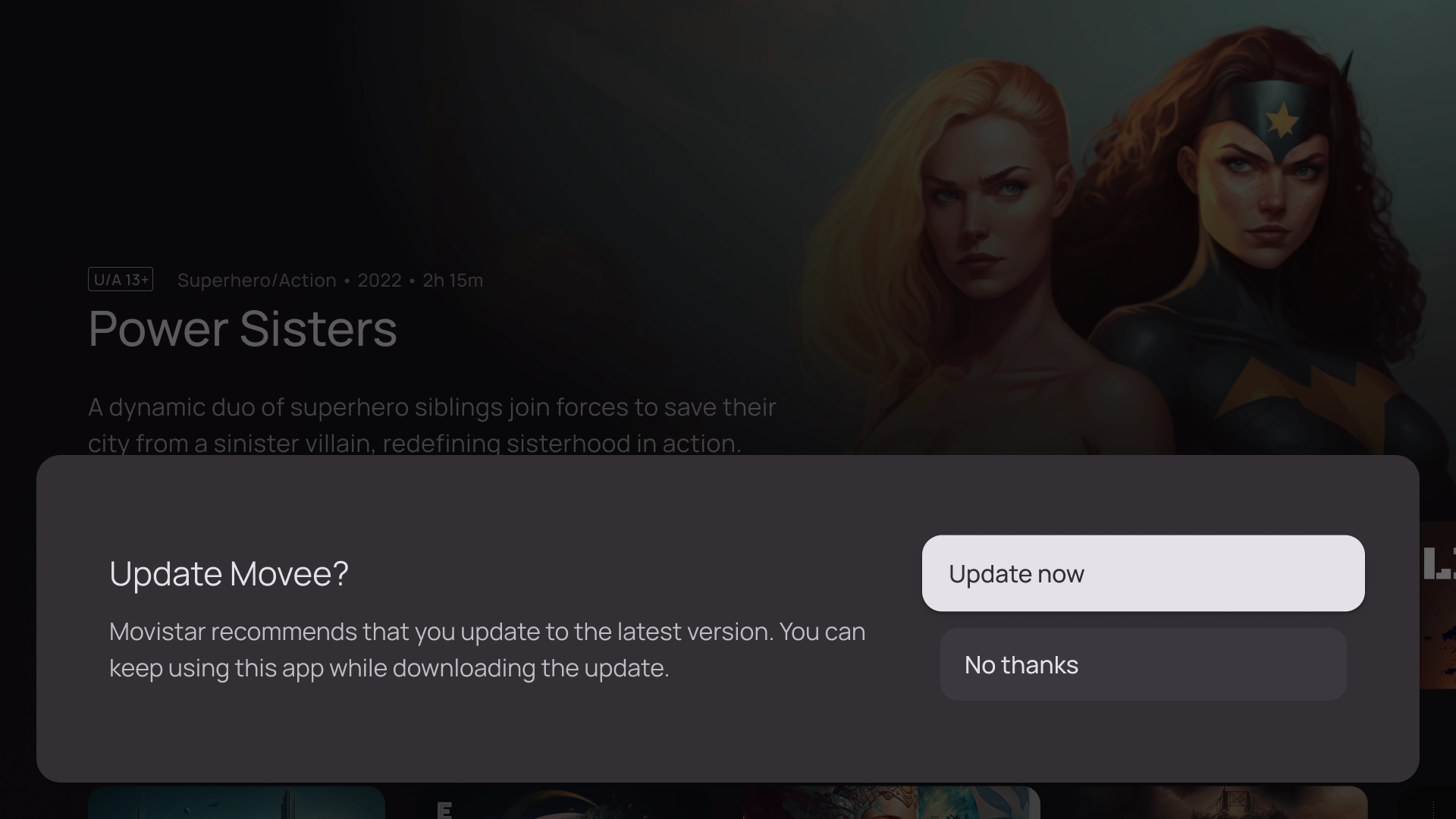
操作
アクション テンプレートでは、左側にタイトルとサブタイトル、右側にオプションまたはアクションが表示されます。通常、このテンプレートでは、ユーザーに選択肢の作成やアクションの実行を求めます。
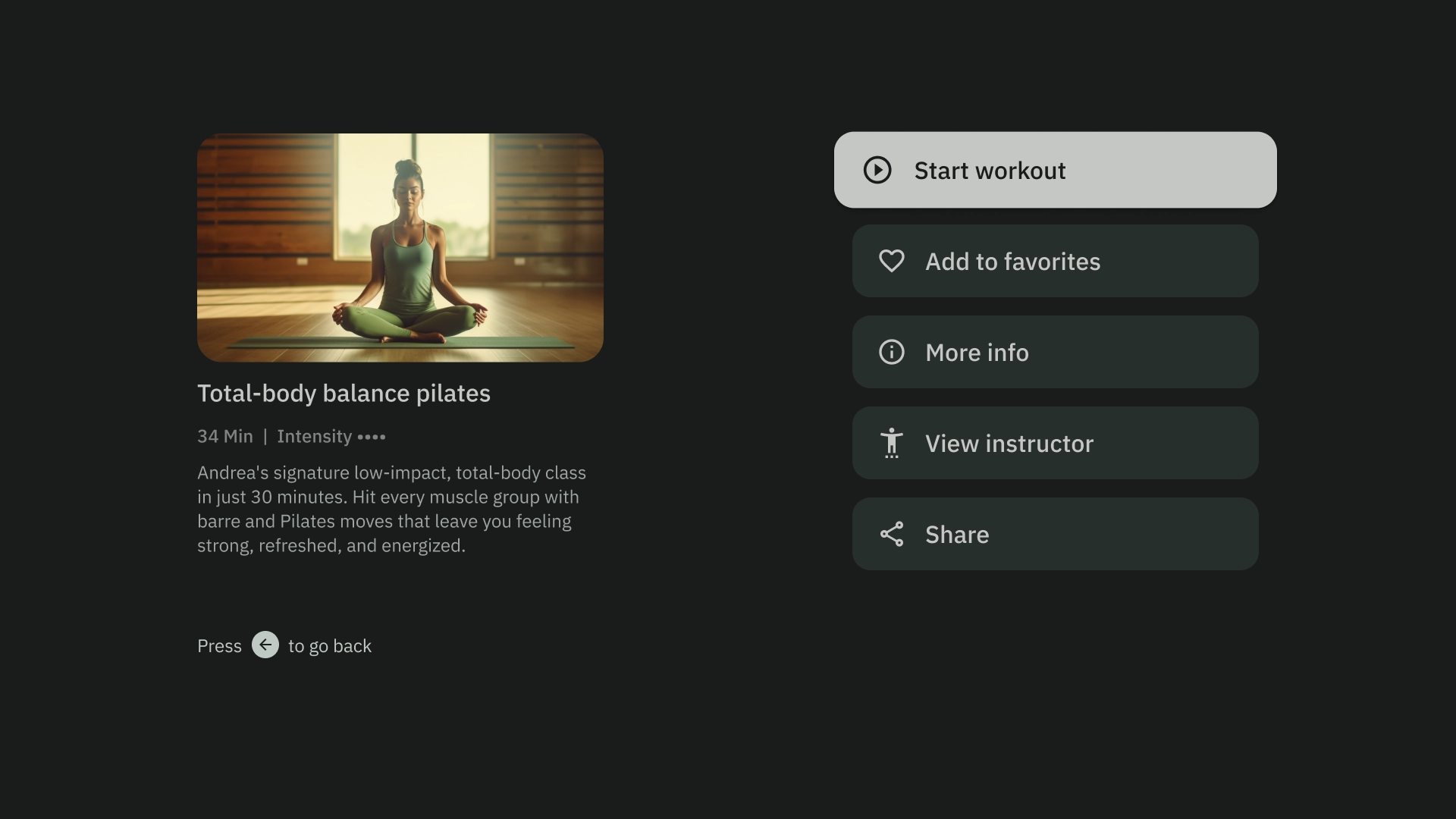
コンテンツの詳細
コンテンツの詳細テンプレートでは、コンテンツが横方向の積み重ねレイアウトで表示されます。コンテンツには通常、タイトル、メタデータ、簡単な説明、クイック アクション、関連情報クラスタが含まれます。
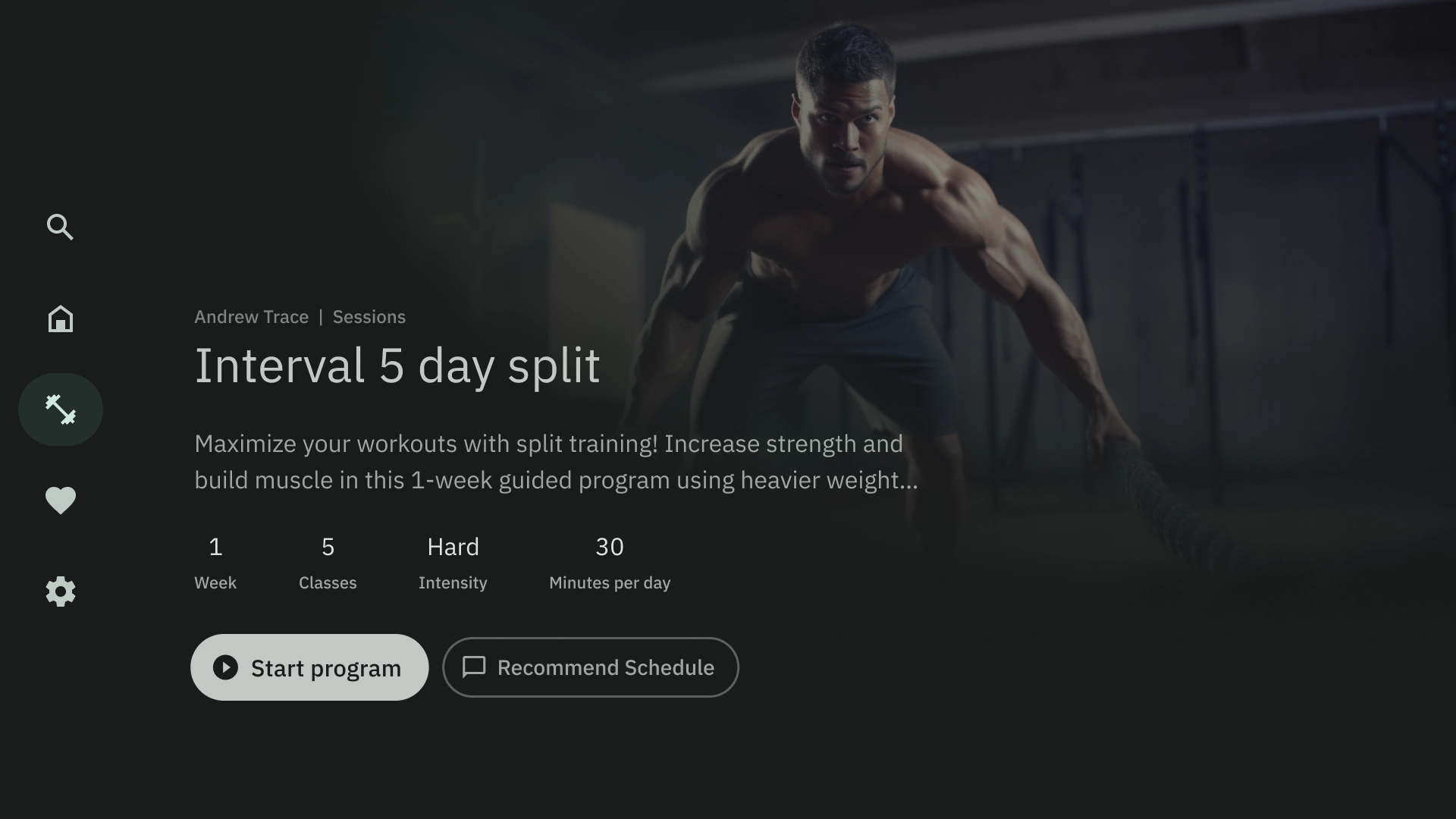
コンパイル
コンパイル テンプレートでは、画面の左側にアイテムの詳細(ポッドキャストなど)が表示され、右側のパネルにその要素(エピソードなど)が表示されます。

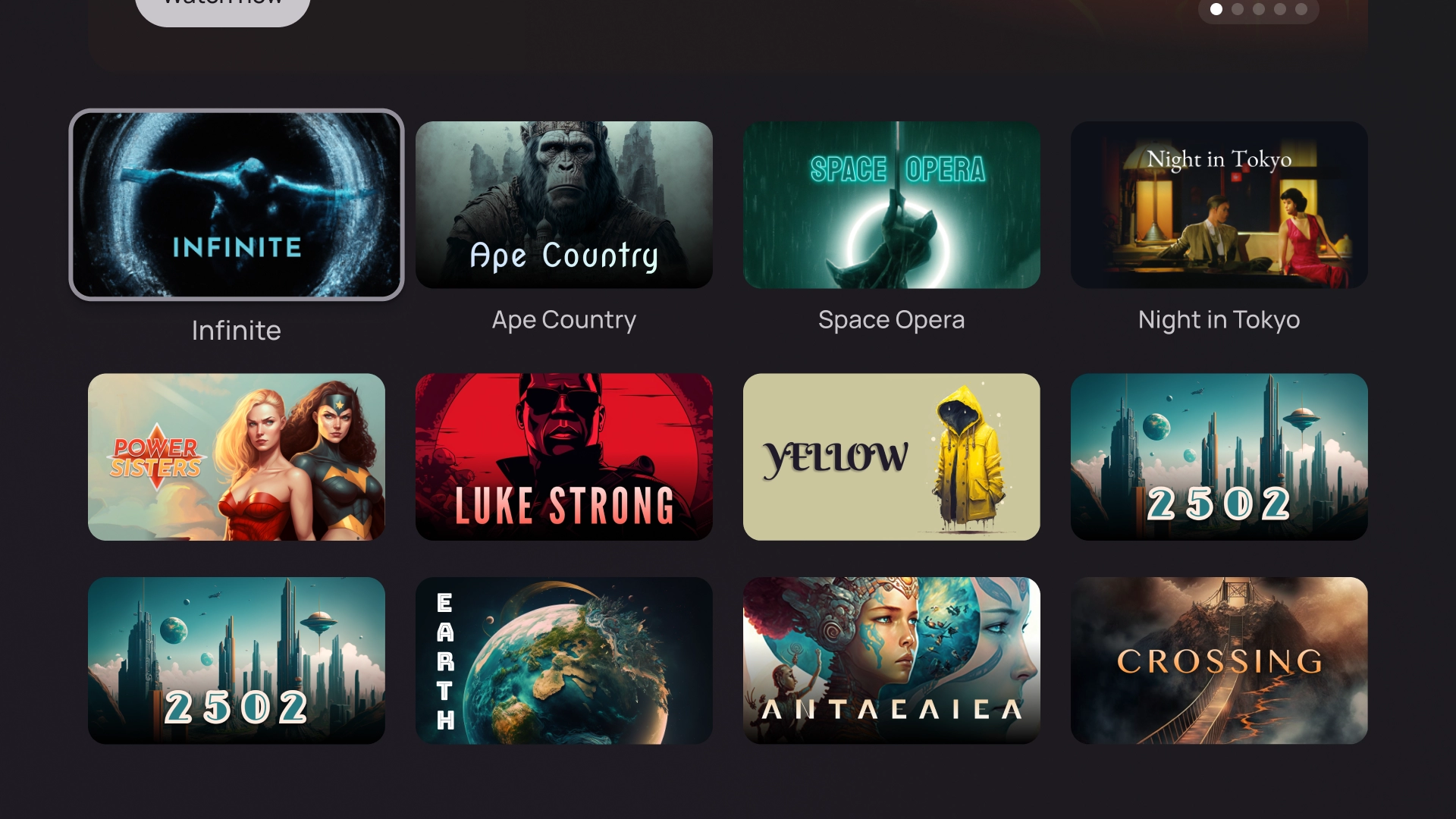
グリッド
グリッド テンプレートでは、コンテンツのコレクションを整理されたグリッドに表示します。明確なリモート ナビゲーション ロジックと最適なブラウジング エクスペリエンスが備わったコンテンツを紹介します。
警告
アラート テンプレートでは、メッセージが全画面表示されます。通常、アラートのブロックを解除して前の画面に戻るには、操作が必要です。
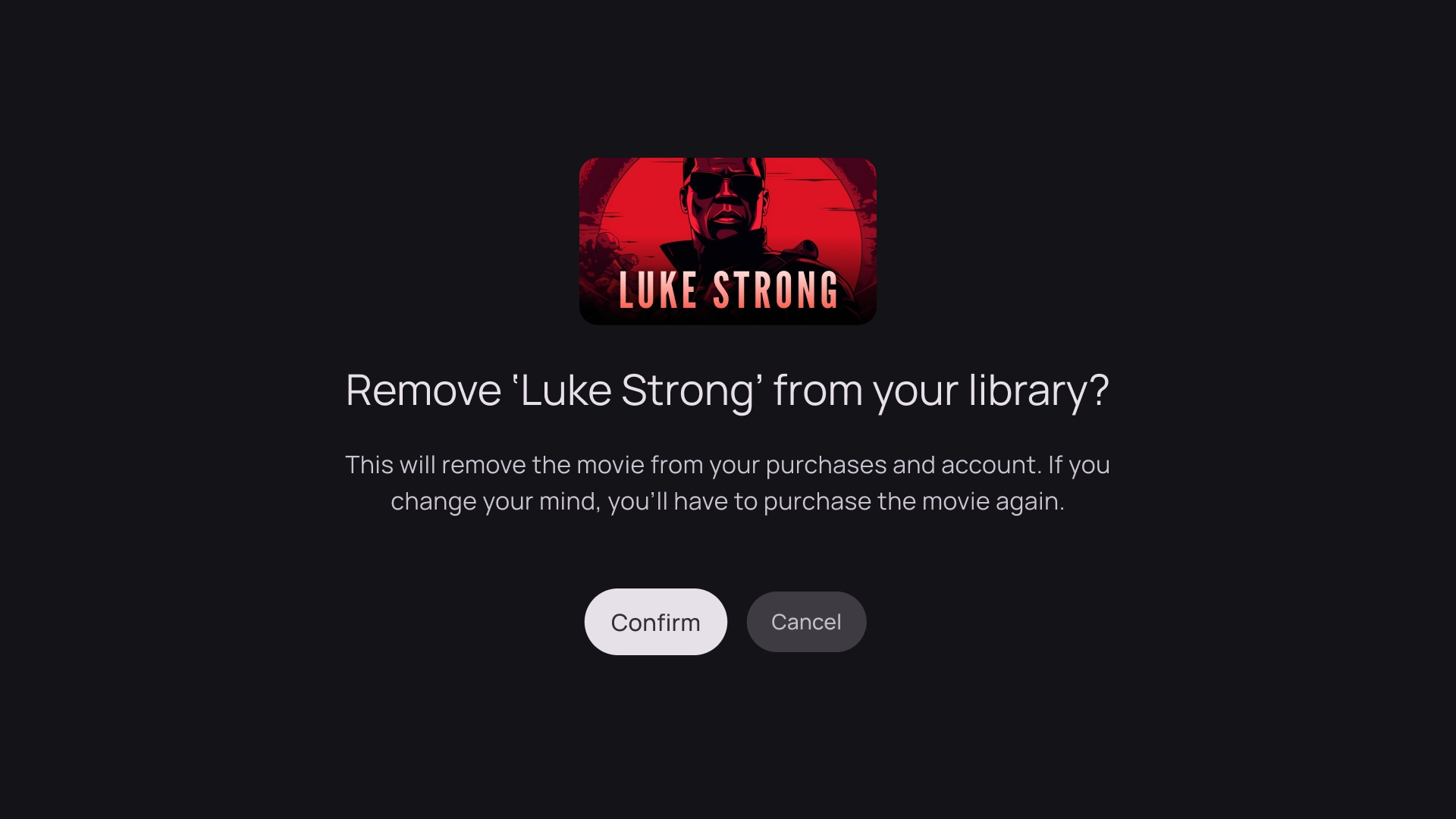
カード列
1 つのカード レイアウト
カードの幅 - 844 dp

2 つのカードのレイアウト
カードの幅 - 412 dp

3 つのカードのレイアウト
カードの幅 - 268 dp

4 枚のカード レイアウト
カードの幅 - 196 dp

5 枚のカード レイアウト
カードの幅 - 124 dp


