添加依赖项时,您可能会遇到所需的依赖项问题 并且不同依赖项版本之间存在冲突。 下面介绍了如何分析依赖关系图并解决出现的常见问题。
有关修复涉及自定义 build 的依赖项解析错误的指南 逻辑,请参阅 自定义依赖项解析策略。
查看模块依赖项
一些直接依赖项可能具有自己的依赖项。此类依赖项称为“传递依赖项”。Gradle 将会自动为您收集并添加这些传递依赖项,无需您手动逐一加以声明。 Android Plugin for Gradle 提供了一项任务,用来列出 Gradle 为给定模块解析的依赖项。
对于每个模块,报告还会根据 build 变体、测试源代码集和类路径对依赖项进行分组。下面是一个应用模块的依赖项示例报告,其中按该模块的调试 build 变体的运行时类路径和该模块的插桩测试源代码集的编译类路径对依赖项进行了分组。
debugRuntimeClasspath - Dependencies for runtime/packaging
+--- :mylibrary (variant: debug)
+--- com.google.android.material:material:1.0.0@aar
+--- androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.0.2@aar
+--- androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3@aar
+--- androidx.fragment:fragment:1.0.0@aar
+--- androidx.vectordrawable:vectordrawable-animated:1.0.0@aar
+--- androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:1.0.0@aar
+--- androidx.legacy:legacy-support-core-ui:1.0.0@aar
...
debugAndroidTest
debugAndroidTestCompileClasspath - Dependencies for compilation
+--- androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.0@aar
+--- androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.1.1@aar
+--- androidx.test:runner:1.1.1@aar
+--- junit:junit:4.12@jar
...
如需运行该任务,请按以下步骤操作:
- 依次选择 View > Tool Windows > Gradle(或点击工具窗口栏中的 Gradle 图标
 )。
)。
- 依次展开 AppName > Tasks > android,然后双击 androidDependencies。Gradle 执行该任务后,系统应该会打开 Run 窗口以显示输出。
如需详细了解如何在 Gradle 中管理依赖项,请参阅 依赖项管理基础知识 。
排除传递依赖项
随着应用的范围不断扩大,它可能会包含许多依赖项,包括直接依赖项和传递依赖项(应用中导入的库所依赖的库)。
如需排除不再需要的传递依赖项,您可以使用 exclude 关键字,如下所示:
Kotlin
dependencies { implementation("some-library") { exclude(group = "com.example.imgtools", module = "native") } }
Groovy
dependencies { implementation('some-library') { exclude group: 'com.example.imgtools', module: 'native' } }
从测试配置中排除传递依赖项
如果您需要从测试中排除某些传递依赖项,上面所示的代码示例可能无法按预期发挥作用。这是因为,测试配置(例如 androidTestImplementation)扩展了模块的 implementation 配置。也就是说,当 Gradle 解析配置时,测试配置始终包含 implementation 依赖项。
因此,如需从测试中排除传递依赖项,则必须在执行代码时执行此操作,如下所示:
Kotlin
android.testVariants.all { compileConfiguration.exclude(group = "com.jakewharton.threetenabp", module = "threetenabp") runtimeConfiguration.exclude(group = "com.jakewharton.threetenabp", module = "threetenabp") }
Groovy
android.testVariants.all { variant -> variant.getCompileConfiguration().exclude group: 'com.jakewharton.threetenabp', module: 'threetenabp' variant.getRuntimeConfiguration().exclude group: 'com.jakewharton.threetenabp', module: 'threetenabp' }
注意:您仍可在依赖项代码块中使用 exclude 关键字(如排除依赖项部分的原始代码示例所示),以省略测试配置特有的(即其他配置不包含的)传递依赖项。
修复依赖项解析错误
当您向应用项目添加多个依赖项时,这些直接和传递依赖项可能会相互冲突。Android Gradle 插件会尝试妥善解决这些冲突,但有些冲突可能会导致编译时或运行时错误。
为帮助您调查是哪些依赖项导致了错误,请检查应用的依赖项树,从中查找出现了多次或存在版本冲突的依赖项。
如果无法轻松识别重复的依赖项,请尝试使用 Android Studio 的界面搜索包含重复类的依赖项,具体操作步骤如下:
- 从菜单栏中依次选择 Navigate > Class。
- 在弹出式搜索对话框中,确保已勾选 Include non-project items 旁边的框。
- 输入 build 错误中出现的类的名称。
- 检查结果以查找包含该类的依赖项。
下面几部分介绍您可能会遇到的不同类型的依赖项解析错误及其修复方法。
修复重复类错误
如果某个类多次出现在运行时类路径上,您会收到一条与以下内容类似的错误:
Program type already present com.example.MyClass
此错误通常是下列其中一种情况所致:
- 二进制文件依赖项包含一个库,该库也作为直接依赖项包含在您的应用中。例如,您的应用声明直接依赖于库 A 和库 B,但库 A 已在其二进制文件中包含库 B。
- 如需解决此问题,请取消将库 B 作为直接依赖项。
- 您的应用的本地二进制文件依赖项和远程二进制文件依赖项是同一个库。
- 如需解决此问题,请移除其中一个二进制文件依赖项。
解决类路径之间的冲突
当 Gradle 解析编译类路径时,会先解析运行时类路径,然后使用所得结果确定应添加到编译类路径的依赖项版本。换句话说,运行时类路径决定了下游类路径上完全相同的依赖项所需的版本号。
应用的运行时类路径还决定了 Gradle 需要对应用的测试 APK 的运行时类路径中的匹配依赖项使用的版本号。图 1 说明了类路径的层次结构。
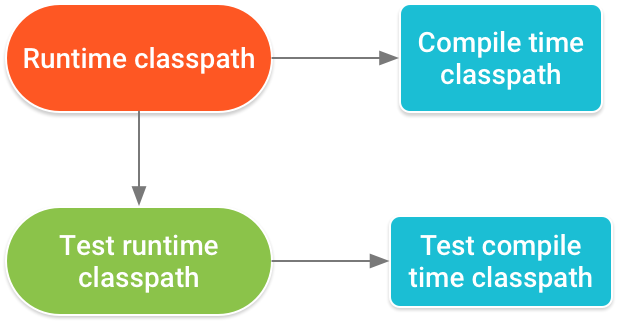
图 1. 出现在多个类路径中的依赖项的版本号必须根据此层次结构匹配。
例如,当应用使用 implementation 依赖项配置添加某个依赖项的一个版本,而库模块使用 runtimeOnly 配置添加该依赖项的另一个版本时,就可能发生多个类路径中出现同一依赖项的不同版本的冲突。
在解析对运行时和编译时类路径的依赖关系时,Android Gradle 插件 3.3.0 及更高版本会尝试自动解决某些下游版本冲突。例如,如果运行时类路径包含库 A 版本 2.0,而编译类路径包含库 A 版本 1.0,则插件会自动将对编译类路径的依赖关系更新为库 A 版本 2.0,以避免错误。
不过,如果运行时类路径包含库 A 版本 1.0,而编译类路径包含库 A 版本 2.0,插件不会将对编译类路径的依赖关系降级为库 A 版本 1.0,您仍会收到一条与以下内容类似的错误:
Conflict with dependency 'com.example.library:some-lib:2.0' in project 'my-library'. Resolved versions for runtime classpath (1.0) and compile classpath (2.0) differ.
如需解决此问题,请执行以下某项操作:
- 将所需版本的依赖项作为
api依赖项添加到库模块。也就是说,尽管只有库模块声明了相应依赖项,但应用模块同样能够访问其 API。 - 或者,您也可以同时在两个模块中声明相应依赖项,但应确保两个模块使用的依赖项版本相同。不妨考虑配置项目全局属性,以确保每个依赖项的版本在整个项目中保持一致。
