Android 14 incluye excelentes funciones y APIs para desarrolladores. A continuación, se incluyen secciones que te ayudarán a obtener información sobre las funciones de tus apps y a comenzar a usar las APIs relacionadas.
Para obtener una lista detallada de las APIs agregadas, modificadas y quitadas, consulta el informe de diferencias de la API. Para obtener detalles sobre las APIs agregadas, consulta la referencia de la API de Android. En Android 14, busca las APIs que se agregaron en el nivel de API 34. Para obtener información sobre las áreas en las que los cambios de la plataforma podrían afectar tus apps, asegúrate de revisar los cambios en el comportamiento de Android 14 para apps orientadas a Android 14 y para todas las apps.
Internacionalización
Preferencias de idioma de las apps
Android 14 amplía las funciones del idioma de las apps que se introdujeron en Android 13 (nivel de API 33) con estas capacidades adicionales:
Genera automáticamente
localeConfigde una app: A partir de Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 y AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, puedes configurar tu app para que admita automáticamente las preferencias de idioma de las apps. En función de los recursos de tu proyecto, el complemento de Android para Gradle genera el archivoLocaleConfigy le agrega una referencia en el archivo de manifiesto final, por lo que ya no necesitas crear ni actualizar el archivo de forma manual. AGP usa los recursos en las carpetasresde los módulos de tu app y las dependencias de módulos de biblioteca para determinar las configuraciones regionales que se incluirán en el archivoLocaleConfig.Actualizaciones dinámicas para
localeConfigde una app: Usa los métodossetOverrideLocaleConfig()ygetOverrideLocaleConfig()deLocaleManagerpara actualizar, de forma dinámica, la lista de idiomas compatibles con tu app en la configuración del sistema del dispositivo. Usa esta flexibilidad para personalizar la lista de idiomas compatibles por región, ejecutar experimentos A/B o proporcionar una lista actualizada de configuraciones regionales si tu app usa envíos del servidor para la localización.Visibilidad del idioma de la app para editores de métodos de entrada (IME): Los IMEs pueden usar el método
getApplicationLocales()para verificar el idioma de la app actual y hacer coincidir el idioma IME con ese idioma.
API de Grammatical Inflection
Tres mil millones de personas hablan idiomas con género, es decir, idiomas en los que las categorías gramaticales, como sustantivos, verbos, adjetivos y preposiciones, inflexionan según el género de las personas y los objetos con las que te comunicas o sobre los que hablas. Tradicionalmente, muchos idiomas con género usan el género gramatical masculino como el género predeterminado o genérico.
Dirigirse a usuarios con un género gramatical incorrecto, por ejemplo, a mujeres con género gramatical masculino, puede tener un impacto negativo en su rendimiento y actitud. Por el contrario, una IU con un lenguaje que refleja, de forma correcta, el género gramatical del usuario puede mejorar su participación y proporcionar una experiencia más personalizada y más natural.
Para ayudarte a compilar una IU centrada en el usuario para idiomas con inflexión de género, Android 14 introduce la API de Grammatical Inflection, que te permite agregar compatibilidad con el género gramatical sin refactorizar la app.
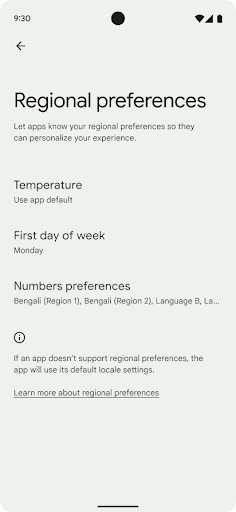
Preferencias regionales
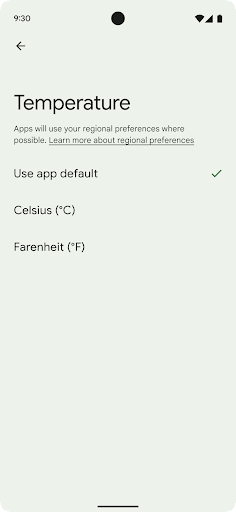
Las preferencias regionales permiten que los usuarios personalicen las unidades de temperatura, el primer día de la semana y los sistemas de numeración. Una persona europea que vive en los Estados Unidos podría preferir que las unidades de temperatura estén en Celsius en lugar de Fahrenheit y que las apps consideren el lunes como comienzo de la semana en lugar de los domingos, la opción predeterminada en EE.UU.
Los nuevos menús de configuración de Android para estas preferencias les proporcionan a los usuarios una ubicación detectable y centralizada para cambiar las preferencias de las apps. Estas preferencias también se mantienen en copias de seguridad y restablecimientos. Varias APIs y algunos intents, como getTemperatureUnit y getFirstDayOfWeek, le otorgan a tu app acceso de lectura a las preferencias de los usuarios, por lo que tu app puede ajustar la forma en que muestra la información. También puedes registrar un BroadcastReceiver en ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED para controlar los cambios de configuración regional cuando cambien las preferencias regionales.
Para encontrar esta configuración, abre la app de Configuración y dirígete a Sistema > Idiomas y entrada > Preferencias regionales.
Accesibilidad
Escalamiento de fuente no lineal al 200%
A partir de Android 14, el sistema admite el escalamiento de la fuente hasta el 200%, lo que les brinda a los usuarios opciones de accesibilidad adicionales.
Para evitar que los elementos de texto grandes en la pantalla escalen demasiado, el sistema aplica una curva de escalamiento no lineal. Esta estrategia de escalamiento implica que el texto grande no escala a la misma velocidad que uno más pequeño. El escalamiento de fuente no lineal ayuda a preservar la jerarquía proporcional entre elementos de diferentes tamaños y, al mismo tiempo, mitiga los problemas con el escalamiento lineal de texto en grados altos (como el texto cortado o el texto que se vuelve más difícil de leer por su gran tamaño de visualización).
Prueba tu app con el escalamiento de fuente no lineal
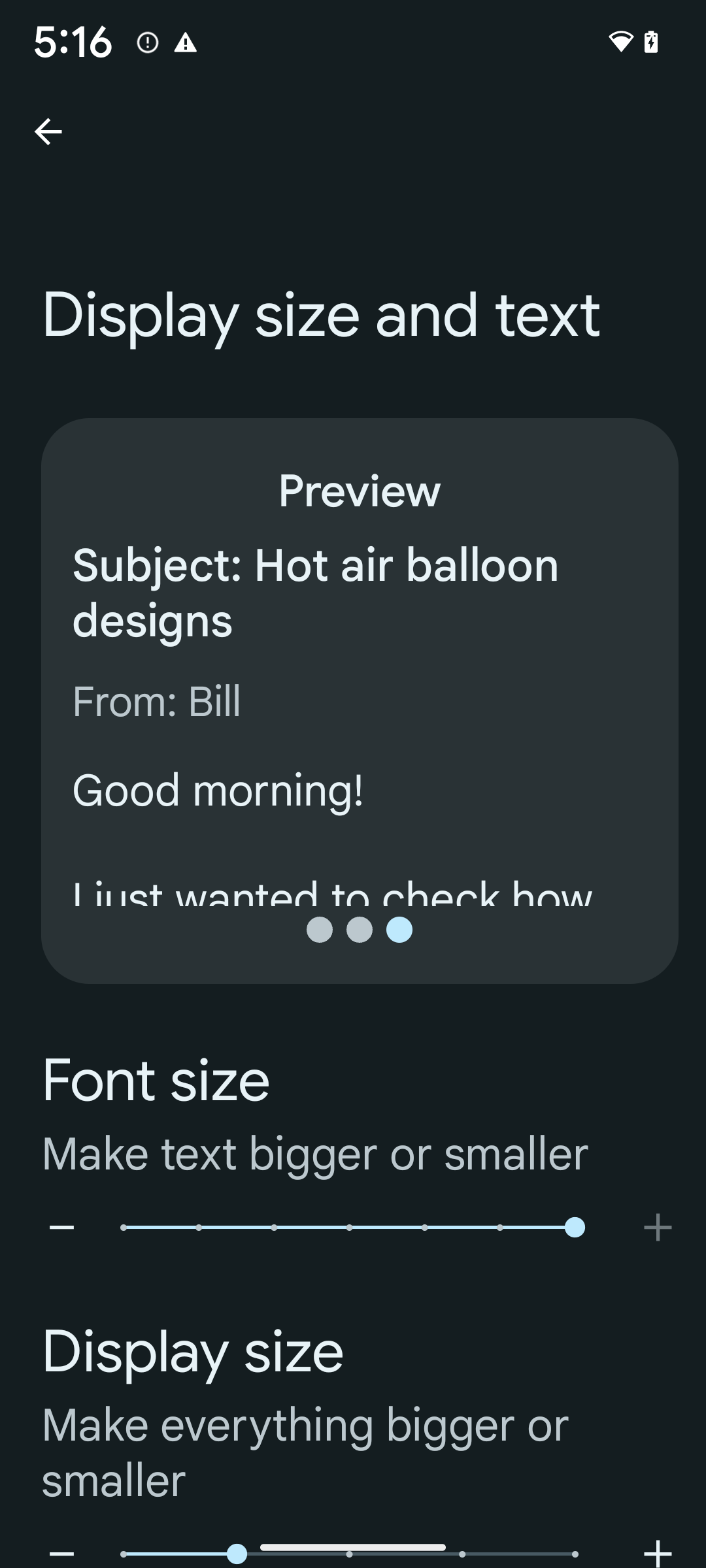
Si ya usas unidades de píxeles escalables (sp) para definir el tamaño del texto, estas opciones adicionales y las mejoras en el escalamiento se aplicarán automáticamente al texto de tu app. Sin embargo, debes realizar pruebas de la IU con el tamaño de fuente máximo habilitado (200%) para asegurarte de que tu app aplique los tamaños de fuente correctamente y pueda admitir tamaños de fuente más grandes sin afectar la usabilidad.
Para habilitar el tamaño de la fuente al 200%, sigue estos pasos:
- Abre la app de Configuración y dirígete a Accesibilidad > Tamaño y texto de la pantalla.
- En la opción Tamaño de fuente, presiona el ícono de signo más (+) hasta que se habilite la configuración de tamaño máximo de fuente, como se muestra en la imagen que acompaña esta sección.
Usa unidades de píxeles ajustados (sp) para los tamaños de texto
Recuerda que siempre debes especificar los tamaños de texto en unidades de sp. Cuando tu app usa unidades de sp, Android puede aplicar el tamaño de texto que prefiere el usuario y escalarlo de forma correcta.
No uses unidades de sp para el padding ni definas alturas de vista suponiendo un padding implícito: Con el escalamiento de fuente no lineal, las dimensiones de sp podrían no ser proporcionales, por lo que 4 sp + 20 sp podría no ser igual a 24 sp.
Convierte unidades de píxeles ajustados (sp)
Usa TypedValue.applyDimension() para convertir unidades de sp en píxeles y TypedValue.deriveDimension() para convertir píxeles en sp. Estos métodos aplican automáticamente la curva de escalamiento no lineal adecuada.
Evita codificar la ecuación con Configuration.fontScale o DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Como el escalamiento de fuente no es lineal, el campo scaledDensity ya no es preciso. El campo fontScale solo debe usarse con fines informativos, ya que las fuentes ya no se ajustan con un solo valor escalar.
Usa unidades sp para lineHeight
Siempre define android:lineHeight con unidades sp en lugar de dp, de modo que la altura de la línea se ajuste junto con el texto. De lo contrario, si tu texto está en sp, pero tu lineHeight está en dp o px, no se ajustará y se verá apretado.
TextView corrige automáticamente el lineHeight para que se conserven las proporciones deseadas, pero solo si textSize y lineHeight se definen en unidades sp.
Cámara y contenido multimedia
Ultra HDR para imágenes

Android 14 agrega compatibilidad con imágenes de alto rango dinámico (HDR) que retienen más información del sensor cuando se toma una foto, lo que permite colores vivos y un mayor contraste. Android usa el formato Ultra HDR, que es totalmente retrocompatible con las imágenes JPEG, lo que permite que las apps interactúen sin problemas con las imágenes HDR y las muestren en rango dinámico estándar (SDR) según sea necesario.
El framework renderiza estas imágenes en la IU en HDR de forma automática cuando tu app habilita el uso de la IU HDR para su ventana de actividad, ya sea a través de una entrada de manifiesto o en el tiempo de ejecución mediante una llamada a Window.setColorMode(). También puedes capturar imágenes estáticas Ultra HDR comprimidas en dispositivos compatibles. Con más colores recuperados del sensor, la edición posterior puede ser más flexible. El Gainmap asociado con las imágenes Ultra HDR se puede usar para renderizarlas con OpenGL o Vulkan.
Zoom, enfoque, Postview y más en las extensiones de cámara
Android 14 actualiza y mejora las extensiones de la cámara, lo que permite que las apps manejen tiempos de procesamiento más largos, lo que permite mejorar las imágenes con algoritmos intensivos en procesamiento, como la fotografía con poca luz en dispositivos compatibles. Estas funciones les brindan a los usuarios una experiencia aún más sólida cuando usan las funciones de extensión de la cámara. Entre los ejemplos de estas mejoras, se incluyen los siguientes:
- La estimación de latencia de procesamiento de capturas estáticas dinámicas proporciona estimaciones de latencia de capturas estáticas mucho más precisas en función de las condiciones actuales de la escena y el entorno. Llama a
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()para obtener un objetoStillCaptureLatencyque tenga dos métodos de estimación de latencia. El métodogetCaptureLatency()muestra la latencia estimada entreonCaptureStartedyonCaptureProcessStarted(), y el métodogetProcessingLatency()muestra la latencia estimada entreonCaptureProcessStarted()y el fotograma procesado final que está disponible. - Compatibilidad con devoluciones de llamada de progreso de captura para que las apps puedan mostrar el progreso actual de las operaciones de procesamiento de capturas estáticas de larga duración. Puedes verificar si esta función está disponible con
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailabley, si es así, implementar la devolución de llamadaonCaptureProcessProgressed(), que tiene el progreso (de 0 a 100) pasado como parámetro. Metadatos específicos de la extensión, como
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHpara marcar la cantidad de un efecto de extensión, como la cantidad de desenfoque de fondo conEXTENSION_BOKEHFunción de vista posterior para la captura de imágenes fijas en extensiones de cámara, que proporciona una imagen menos procesada más rápido que la imagen final. Si una extensión tiene una latencia de procesamiento mayor, se puede proporcionar una imagen posterior a la vista como marcador de posición para mejorar la UX y cambiarla más adelante por la imagen final. Puedes verificar si esta función está disponible con
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Luego, puedes pasar unOutputConfigurationaExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Compatibilidad con
SurfaceView, que permite una ruta de renderización de vista previa más optimizada y eficiente en términos de energía.Se agregó compatibilidad con el enfoque y el zoom con un toque durante el uso de la extensión.
Zoom en el sensor
Cuando REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE en CameraCharacteristics contiene SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, tu app puede usar capacidades avanzadas del sensor para darle a una transmisión RAW recortada los mismos píxeles que el campo de visión completo con un CaptureRequest con un objetivo RAW que tiene el caso de uso de transmisión configurado en CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
Cuando se implementan los controles de anulación de solicitudes, la cámara actualizada les brinda a los usuarios control de zoom incluso antes de que estén listos otros controles de la cámara.
Audio USB sin pérdida
Android 14 admite formatos de audio sin pérdida para experiencias de nivel de audiófilo con auriculares con cable USB. Puedes consultar un dispositivo USB para obtener sus atributos de mezclador preferidos, registrar un objeto de escucha para detectar cambios en los atributos de mezclador preferidos y configurar los atributos de mezclador con la clase AudioMixerAttributes. Esta clase representa el formato, como la máscara de canales, la tasa de muestreo y el comportamiento del mezclador de audio. La clase permite que el audio se envíe directamente, sin mezclar, ajustar el volumen ni procesar efectos.
Productividad y herramientas para desarrolladores
Credential Manager
Android 14 agrega Credential Manager como una API de la plataforma, con compatibilidad adicional con dispositivos Android 4.4 (nivel de API 19) a través de una biblioteca de Jetpack que usa los Servicios de Google Play. El objetivo de Credential Manager es facilitar el acceso de los usuarios con APIs que recuperan y almacenan credenciales con proveedores de credenciales configurados por el usuario. El Administrador de credenciales admite varios métodos de acceso, como nombres de usuario y contraseñas, llaves de acceso y soluciones de acceso federado (como Acceder con Google) en una sola API.
Las llaves de acceso ofrecen muchas ventajas. Por ejemplo, las llaves de acceso se basan en estándares de la industria, pueden funcionar en diferentes sistemas operativos y ecosistemas de navegadores, y se pueden usar con sitios web y apps.
Para obtener más información, consulta la documentación de Credential Manager y las llaves de acceso y la entrada de blog sobre Credential Manager y las llaves de acceso.
Health Connect
Health Connect es un repositorio integrado en el dispositivo para los datos de salud y fitness del usuario. Permite a los usuarios compartir datos entre sus apps favoritas, con un solo lugar para controlar qué datos quieren compartir con estas apps.
En dispositivos con versiones de Android anteriores a Android 14, Health Connect está disponible para descargarse como app en Google Play Store. A partir de Android 14, Health Connect forma parte de la plataforma y recibe actualizaciones a través de las actualizaciones del sistema de Google Play sin necesidad de una descarga independiente. Con esto, Health Connect se puede actualizar con frecuencia, y tus apps pueden depender de que Health Connect esté disponible en dispositivos que ejecutan Android 14 o versiones posteriores. Los usuarios pueden acceder a Health Connect desde la configuración de su dispositivo, con controles de privacidad integrados en la configuración del sistema.
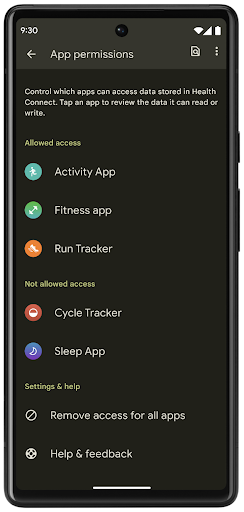
Health Connect incluye varias funciones nuevas en Android 14, como las rutas de ejercicio, que permiten a los usuarios compartir una ruta de su entrenamiento que se puede visualizar en un mapa. Una ruta se define como una lista de ubicaciones guardadas dentro de un período, y tu app puede insertar rutas en sesiones de ejercicio y vincularlas. Para garantizar que los usuarios tengan un control total sobre estos datos sensibles, deben permitir compartir rutas individuales con otras apps.
Para obtener más información, consulta la documentación de Health Connection y la entrada de blog sobre Novedades de Android Health.
Actualizaciones de OpenJDK 17
Android 14 continúa la tarea de actualizar las bibliotecas principales de Android para alinearlas con las funciones de las versiones más recientes de LTS de OpenJDK, lo que incluye las actualizaciones de bibliotecas y la compatibilidad con el lenguaje Java 17 para desarrolladores de apps y plataformas.
Se incluyen las siguientes funciones y mejoras:
- Se actualizaron aproximadamente 300 clases
java.basepara admitir Java 17. - Bloques de texto, que introducen literales de cadena de varias líneas en el lenguaje de programación Java.
- Coincidencia de patrones para instanceof, que permite que un objeto se trate como si tuviera un tipo específico en un
instanceofsin variables adicionales. - Clases selladas, que te permiten restringir qué clases e interfaces pueden extenderlas o implementarlas.
Gracias a las actualizaciones del sistema de Google Play (Project Mainline), más de 600 millones de dispositivos están habilitados para recibir las actualizaciones más recientes de Android Runtime (ART) que incluyen estos cambios. Esto forma parte de nuestro compromiso de brindar a las apps un entorno más seguro y coherente en todos los dispositivos, y de ofrecer funciones y capacidades nuevas a los usuarios, independientemente de los lanzamientos de la plataforma.
Java y OpenJDK son marcas o marcas registradas de Oracle o sus afiliados.
Mejoras para tiendas de aplicaciones
Android 14 introduce varias APIs de PackageInstaller que permiten que las tiendas de aplicaciones mejoren la experiencia del usuario.
Solicita aprobación para la instalación antes de realizar la descarga
La instalación o actualización de una app puede requerir aprobación del usuario.
Por ejemplo, cuando un instalador que usa el permiso REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES intenta instalar una app nueva. En versiones anteriores de Android, las tiendas de aplicaciones solo pueden solicitar la aprobación del usuario después de que se escriben los APK en la sesión de instalación y esta está confirmada.
A partir de Android 14, el método requestUserPreapproval() les permite a los instaladores solicitar la aprobación del usuario antes de confirmar la sesión de instalación. Esta mejora permite que una tienda de aplicaciones aplace la descarga de cualquier APK hasta que el usuario haya aprobado la instalación. Además, una vez que un usuario aprobó la instalación, la tienda de aplicaciones puede descargarla e instalarla en segundo plano sin interrumpir al usuario.
Reclama la responsabilidad de las actualizaciones futuras
El método setRequestUpdateOwnership() permite que un instalador le indique al sistema que tiene la responsabilidad de las actualizaciones futuras de una app que instala. Esta función permite actualizar la aplicación forzosa de la propiedad, es decir, que solo el propietario de la actualización puede instalar actualizaciones automáticas en la app. La aplicación forzosa de la actualización de la propiedad ayuda a garantizar que los usuarios reciban actualizaciones solo desde la tienda de aplicaciones prevista.
Cualquier otro instalador, incluidos los que usan el permiso INSTALL_PACKAGES, deben recibir la aprobación explícita del usuario para instalar una actualización. Si un usuario decide continuar con la actualización desde otra fuente, la propiedad de esta se perderá.
Actualiza las apps en momentos menos disruptivos
Por lo general, las tiendas de aplicaciones quieren evitar actualizar una app que está en uso de forma activa, ya que esto produce que se finalicen los procesos en ejecución de la app, lo que podría interrumpir lo que el usuario estaba haciendo.
A partir de Android 14, la API de InstallConstraints les brinda a los instaladores una forma de garantizar que las actualizaciones de apps se realicen en un momento oportuno. Por ejemplo, una tienda de aplicaciones puede llamar al método commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() para asegurarse de que una actualización solo se confirme cuando el usuario ya no interactúa con la app en cuestión.
Instala divisiones opcionales sin inconvenientes
Con los APK divididos, las funciones de una app se pueden entregar en archivos APK separados, en lugar de un APK monolítico. Los APK divididos permiten que las tiendas de aplicaciones optimicen la entrega de diferentes componentes de las apps. Por ejemplo, las tiendas de aplicaciones pueden realizar optimizaciones en función de las propiedades del dispositivo de destino. La API de PackageInstaller es compatible con las divisiones desde su introducción en el nivel de API 22.
En Android 14, el método setDontKillApp() permite que un instalador indique que los procesos en ejecución de la app no deberían finalizar cuando se instalan nuevas divisiones. Las tiendas de aplicaciones pueden usar esta función para instalar funciones nuevas de una app sin inconvenientes mientras el usuario la usa.
Paquetes de metadatos de la app
A partir de Android 14, el instalador de paquetes de Android te permite especificar metadatos de la app, como las prácticas de seguridad de los datos, para incluir en las páginas de la tienda de aplicaciones, como Google Play.
Detecta cuando los usuarios toman capturas de pantalla del dispositivo
Para crear una experiencia más estandarizada para detectar capturas de pantalla, Android 14 introduce una API de detección de capturas de pantalla que preserva la privacidad. Esta API permite que las apps registren devoluciones de llamada por actividad. Estas devoluciones de llamada se invocan y se notifica al usuario cuando toma una captura de pantalla mientras esa actividad está visible.
Experiencia del usuario
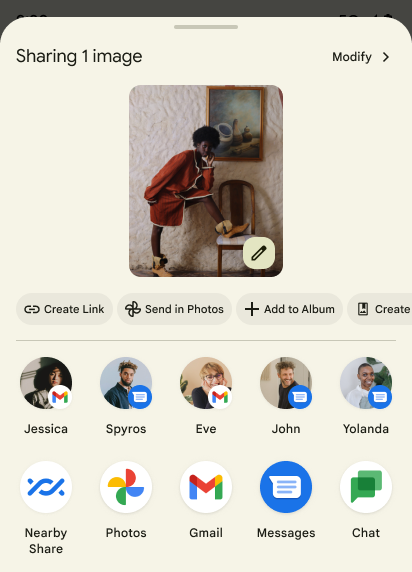
Acciones personalizadas y clasificación mejorada de Sharesheet
Android 14 actualiza la hoja compartida del sistema para admitir acciones personalizadas de la app y resultados informativos de la versión preliminar para los usuarios.
Agrega acciones personalizadas
Con Android 14, tu app puede agregar acciones personalizadas a la hoja compartida del sistema que invoca.
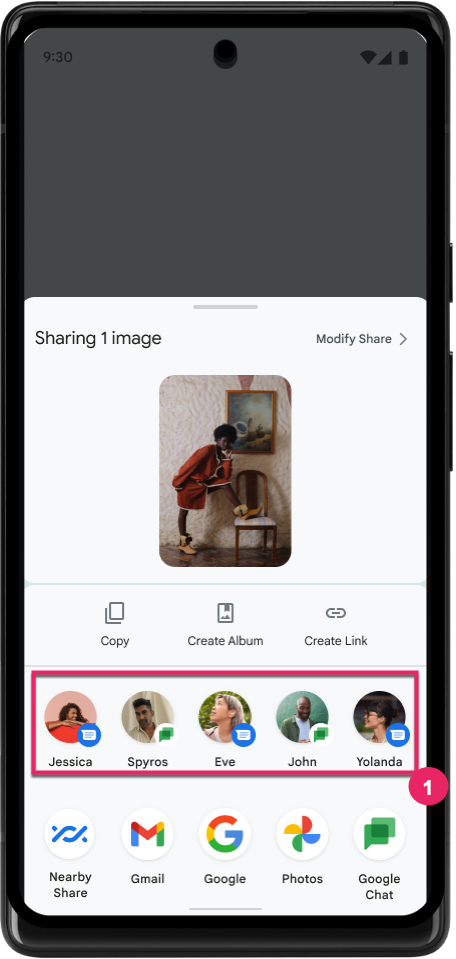
Mejora la clasificación de los objetivos de Direct Share
Android 14 usa más indicadores de las apps para determinar la clasificación de los objetivos de Direct Share para proporcionarles resultados más útiles al usuario. Para proporcionar el indicador más útil para la clasificación, sigue las instrucciones para mejorar las clasificaciones de tus objetivos de Direct Share. Las apps de comunicación también pueden informar el uso de combinaciones de teclas para los mensajes entrantes y salientes.
Compatibilidad con animaciones integradas y personalizadas para el gesto atrás predictivo
En Android 13, se introdujo la animación de atrás predictivo a la página principal detrás de una opción para desarrolladores. Cuando se usa en una app compatible que tiene habilitada la opción para desarrolladores, al deslizar hacia atrás, se muestra una animación que indica que el gesto de retroceso permite cerrar la app y regresar a la pantalla principal.
Android 14 incluye varias mejoras y orientación nueva para el gesto atrás predictivo:
- Puedes configurar
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=truepara habilitar las animaciones del sistema de atrás predictivo por actividad en lugar de para toda la app. - Agregamos nuevas animaciones del sistema para acompañar la animación de regreso a la pantalla principal de Android 13. Las nuevas animaciones del sistema son las de cambio de actividad y cambio de tarea, que obtienes automáticamente después de la migración al gesto atrás predictivo.
- Agregamos nuevas animaciones de componentes de material para las hojas inferiores, las hojas laterales y la búsqueda.
- Creamos una guía de diseño para crear transiciones y animaciones personalizadas en la app.
- Agregamos nuevas APIs para admitir animaciones de transición en la app:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressedyhandleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressedyonBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Usa
overrideActivityTransitionen lugar deoverridePendingTransitionpara las transiciones que responden cuando el usuario desliza el dedo hacia atrás
Con esta versión preliminar de Android 14, todas las funciones de atrás predictivo permanecen detrás de una opción para desarrolladores. Consulta la guía para desarrolladores para migrar tu app al gesto atrás predictivo, así como la guía para desarrolladores para crear transiciones personalizadas en la app.
Anulaciones por app del fabricante de dispositivos con pantalla grande
Las anulaciones por app permiten que los fabricantes de dispositivos cambien el comportamiento de las apps en dispositivos con pantallas grandes. Por ejemplo, la anulación FORCE_RESIZE_APP le indica al sistema que cambie el tamaño de la app para que se ajuste a las dimensiones de la pantalla (evitando el modo de compatibilidad de tamaño) incluso si se configuró resizeableActivity="false" en el manifiesto de la app.
Las anulaciones están diseñadas para mejorar la experiencia del usuario en pantallas grandes.
Las nuevas propiedades del manifiesto te permiten inhabilitar algunas anulaciones del fabricante de dispositivos para tu app.
Anulaciones por app para usuarios de pantallas grandes
Las anulaciones por app cambian el comportamiento de las apps en dispositivos con pantallas grandes. Por ejemplo, la anulación del fabricante del dispositivo OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE establece la relación de aspecto de la app en 16:9, independientemente de su configuración.
QPR1 de Android 14 permite que los usuarios apliquen anulaciones por app a través de un nuevo menú de configuración en dispositivos con pantalla grande.
Compartir pantalla de una app
La función de compartir pantalla de una app permite a los usuarios compartir una ventana de la app en lugar de toda la pantalla del dispositivo durante la grabación de contenido de pantalla.
Con el uso compartido de pantalla de la app, la barra de estado, la barra de navegación, las notificaciones y otros elementos de la IU del sistema se excluyen de la pantalla compartida. Solo se comparte el contenido de la app seleccionada.
El uso compartido de pantalla de la app mejora la productividad y la privacidad, ya que permite que los usuarios ejecuten varias apps, pero limitan el uso compartido de contenido a una sola app.
Respuesta inteligente potenciada por LLM en Gboard en el Pixel 8 Pro
En los dispositivos Pixel 8 Pro con la actualización de funciones de diciembre, los desarrolladores pueden probar respuestas inteligentes de mayor calidad en Gboard con la tecnología de modelos de lenguaje grandes (LLM) integrados en el dispositivo que se ejecutan en Google Tensor.
Esta función está disponible como versión preliminar limitada para inglés de EE.UU. en WhatsApp, Line y KakaoTalk. Requiere el uso de un dispositivo Pixel 8 Pro con Gboard como teclado.
Para probarlo, primero habilita la función en Configuración > Opciones para desarrolladores > Configuración de AICore > Habilitar Aicore persistente.
A continuación, abre una conversación en una app compatible para ver la respuesta inteligente potenciada por LLM en la barra de sugerencias de Gboard en respuesta a los mensajes entrantes.
Gráficos
Las rutas de acceso son consultables e interpolables
La API de Path de Android es un mecanismo potente y flexible para crear y renderizar gráficos vectoriales, con la capacidad de dibujar o rellenar una ruta, construir una ruta a partir de segmentos de línea o curvas cuadráticas o cúbicas, realizar operaciones booleanas para obtener formas aún más complejas o todas estas acciones de forma simultánea. Una limitación es la capacidad de descubrir lo que hay realmente en un objeto Path; los componentes internos del objeto son opacos para los llamadores después de su creación.
Para crear un Path, debes llamar a métodos como moveTo(), lineTo() y cubicTo() para agregar segmentos de ruta. Sin embargo, no hay forma de preguntarle a esa ruta cuáles son los segmentos, por lo que debes conservar esa información en el momento de la creación.
A partir de Android 14, puedes consultar rutas de acceso para descubrir su contenido.
Primero, debes obtener un objeto PathIterator con la API de Path.getPathIterator:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
A continuación, puedes llamar a PathIterator para iterar a través de los segmentos uno por uno y recuperar todos los datos necesarios de cada segmento. En este ejemplo, se usan objetos PathIterator.Segment, que agrupan los datos por ti:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator también tiene una versión de next() no asignable en la que puedes pasar un búfer para contener los datos de puntos.
Uno de los casos de uso importantes para consultar datos de Path es la interpolación. Por ejemplo, podrías animar (o transformar) entre dos rutas diferentes. Para simplificar aún más ese caso de uso, Android 14 también incluye el método interpolate() en Path. Si suponemos que las dos rutas de acceso tienen la misma estructura interna, el método interpolate() crea un Path nuevo con ese resultado interpolado. En este ejemplo, se muestra una ruta cuya forma está incompleta (una interpolación lineal de 0.5) entre path y otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
La biblioteca graphics-path de Jetpack también habilita APIs similares para versiones anteriores de Android.
Mallas personalizadas con sombreadores de vértices y fragmentos
Android admite desde hace mucho tiempo el dibujo de mallas de triángulos con sombreado personalizado, pero el formato de malla de entrada se limitó a algunas combinaciones de atributos predefinidos. Android 14 agrega compatibilidad con mallas personalizadas, que se pueden definir como triángulos o tiras de triángulos, y, de manera opcional, se pueden indexar. Estas mallas se especifican con atributos personalizados, pasos de vértices, variaciones y sombreadores de vértices y fragmentos escritos en AGSL.
El sombreador de vértices define las variaciones, como la posición y el color, mientras que el sombreador de fragmentos puede definir de manera opcional el color del píxel, por lo general, con las variaciones creadas por el sombreador de vértices. Si el sombreador de fragmentos proporciona el color, se combina con el color Paint actual con el modo de combinación seleccionado cuando se dibuja la malla. Los uniformes se pueden pasar a los sombreadores de fragmentos y vértices para obtener mayor flexibilidad.
Procesador de búfer de hardware para Canvas
Para ayudar a usar la API de Canvas de Android y dibujar con aceleración de hardware en un HardwareBuffer, Android 14 presenta HardwareBufferRenderer. Esta API es
particularmente útil cuando tu caso de uso involucra la comunicación con el sistema
a través de SurfaceControl para una latencia baja
dibujo.
