در ادامه یادداشتهای انتشار اندروید استودیو ۳.۶ و پایینتر، و افزونه اندروید گریدل ۳.۶.۰ و پایینتر آمده است.
نسخههای قدیمیتر اندروید استودیو
۳.۶ (فوریه ۲۰۲۰)
اندروید استودیو ۳.۶ یک نسخه اصلی است که شامل مجموعهای از ویژگیها و بهبودهای جدید میشود.
همچنین مایلیم از همه مشارکتکنندگان جامعهمان که در انتشار این نسخه یاریمان کردهاند، تشکر کنیم.
۳.۶.۳ (آوریل ۲۰۲۰)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلفی است. برای مشاهدهی فهرست رفع اشکالات قابل توجه، پست مرتبط در وبلاگ بهروزرسانیهای انتشار را مطالعه کنید.
۳.۶.۲ (مارس ۲۰۲۰)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلفی است. برای مشاهدهی فهرست رفع اشکالات قابل توجه، پست مرتبط در وبلاگ بهروزرسانیهای انتشار را مطالعه کنید.
۳.۶.۱ (فوریه ۲۰۲۰)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلفی است. برای مشاهدهی فهرست رفع اشکالات قابل توجه، پست مرتبط در وبلاگ بهروزرسانیهای انتشار را مطالعه کنید.
ابزارهای طراحی
این نسخه از اندروید استودیو شامل بهروزرسانیهایی برای چندین ابزار طراحی، از جمله ویرایشگر طرحبندی (Layout Editor) و مدیریت منابع (Resource Manager) است.
نمای تقسیمشده و بزرگنمایی در ویرایشگرهای طراحی
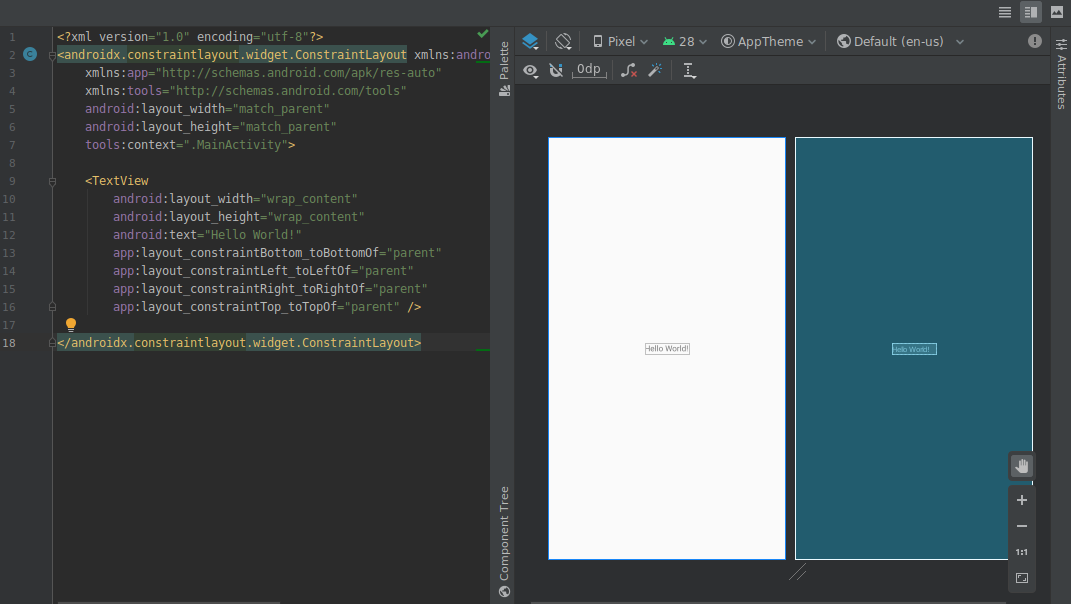
بهروزرسانیهای زیر برای ویرایشگرهای طراحی بصری در این نسخه گنجانده شده است:
ویرایشگرهای طراحی، مانند ویرایشگر طرحبندی و ویرایشگر ناوبری، اکنون یک نمای تقسیمشده ارائه میدهند که به شما امکان میدهد هر دو نمای طراحی و کد رابط کاربری خود را همزمان مشاهده کنید. در گوشه بالا سمت راست پنجره ویرایشگر، اکنون سه دکمه وجود دارد
 برای جابجایی بین گزینههای نمایش:
برای جابجایی بین گزینههای نمایش:- برای فعال کردن نمای تقسیمشده، روی نماد تقسیم کلیک کنید
 .
. - برای فعال کردن نمایش منبع XML، روی نماد منبع کلیک کنید
 .
. - برای فعال کردن نمای طراحی، روی نماد طراحی کلیک کنید
 .
.
- برای فعال کردن نمای تقسیمشده، روی نماد تقسیم کلیک کنید
کنترلهای مربوط به بزرگنمایی و جابجایی تصویر در ویرایشگرهای طراحی به یک پنل شناور در گوشه پایین سمت راست پنجره ویرایشگر منتقل شدهاند.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به بخش «ایجاد رابط کاربری با ویرایشگر طرحبندی» مراجعه کنید.
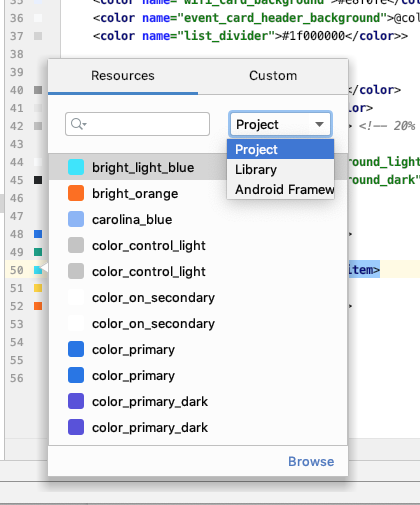
برگه منابع انتخابگر رنگ
برای کمک به شما در بهروزرسانی سریع مقادیر منابع رنگ در برنامهتان، هنگام استفاده از انتخابگر رنگ در XML یا ابزارهای طراحی، IDE اکنون مقادیر منابع رنگ را برای شما جمعآوری میکند.
مدیر منابع
مدیر منابع شامل بهروزرسانیهای زیر است:
- مدیر منابع اکنون از اکثر انواع منابع پشتیبانی میکند.
- هنگام جستجوی یک منبع، مدیر منابع اکنون نتایج تمام ماژولهای پروژه را نمایش میدهد. پیش از این، جستجوها فقط نتایج ماژول انتخاب شده را برمیگرداندند.
- دکمه فیلتر به شما امکان میدهد منابع را از ماژولهای وابسته محلی، کتابخانههای خارجی و چارچوب اندروید مشاهده کنید. همچنین میتوانید از فیلتر برای نمایش ویژگیهای قالب استفاده کنید.
- اکنون میتوانید با کلیک کردن در کادر متنی بالای منبع، نام آن را در طول فرآیند وارد کردن تغییر دهید.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به مدیریت منابع رابط کاربری برنامه خود با Resource Manager مراجعه کنید.
بهروزرسانیهای افزونهی اندروید Gradle
آخرین نسخه افزونه Android Gradle شامل بهروزرسانیهای زیادی از جمله بهینهسازی سرعت ساخت، پشتیبانی از افزونه انتشار Maven و پشتیبانی از View Binding است. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، یادداشتهای کامل انتشار را مطالعه کنید.
مشاهده اتصال
اتصال نما (View Binding) به شما این امکان را میدهد که با ایجاد یک کلاس اتصال برای هر فایل طرحبندی XML، کدی بنویسید که با نماها تعامل داشته باشد. این کلاسها شامل ارجاعات مستقیم به تمام نماهایی هستند که در طرحبندی مربوطه دارای شناسه (ID) هستند.
از آنجا که جایگزین findViewById() میشود، view binding خطر خطاهای اشارهگر تهی ناشی از شناسه نامعتبر view را از بین میبرد.
برای فعال کردن اتصال نما، باید از افزونه Android Gradle نسخه ۳.۶.۰ یا بالاتر استفاده کنید و موارد زیر را در فایل build.gradle هر ماژول قرار دهید:
گرووی
android { buildFeatures.viewBinding = true }
کاتلین
android { buildFeatures.viewBinding = true }
اعمال تغییرات
اکنون میتوانید یک کلاس اضافه کنید و سپس با کلیک روی « اعمال تغییرات کد» یا «اعمال تغییرات و راهاندازی مجدد فعالیت»، آن تغییر کد را در برنامه در حال اجرا اعمال کنید.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد تفاوت بین این دو اقدام، به اعمال تغییرات مراجعه کنید.
گزینه منوی Refactor برای فعال کردن پشتیبانی از Instant Apps
اکنون میتوانید ماژول پایه خود را در هر زمانی پس از ایجاد پروژه برنامه خود، به صورت زیر فعال کنید:
- با انتخاب View > Tool Windows > Project از نوار منو، پنل Project را باز کنید.
- روی ماژول پایه خود که معمولاً «app» نام دارد، کلیک راست کنید و گزینه Refactor > Enable Instant Apps Support را انتخاب کنید.
- در پنجرهای که ظاهر میشود، ماژول پایه خود را از منوی کشویی انتخاب کنید.
- روی تأیید کلیک کنید.
توجه: گزینه فعالسازی فوری ماژول برنامه پایه شما از ویزارد ایجاد پروژه جدید حذف شده است.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، «مروری بر Google Play Instant» را مطالعه کنید.
کد بایت کلاس و متد را در APK Analyzer از حالت مبهم خارج کنید
هنگام استفاده از APK Analyzer برای بررسی فایلهای DEX، میتوانید بایتکد کلاس و متد را به صورت زیر از حالت مبهم خارج کنید:
- از نوار منو، گزینه Build > Analyze APK را انتخاب کنید.
- در پنجرهای که ظاهر میشود، به APK مورد نظر برای بررسی بروید و آن را انتخاب کنید.
- روی باز کردن کلیک کنید.
- در APK Analyzer، فایل DEX مورد نظر برای بررسی را انتخاب کنید.
- در نمایشگر فایل DEX، فایل نگاشتهای ProGuard را برای APK که در حال تجزیه و تحلیل آن هستید، بارگذاری کنید .
- روی کلاس یا متدی که میخواهید بررسی کنید کلیک راست کرده و Show bytecode را انتخاب کنید.
ابزارهای بومی
بهروزرسانیهای زیر از توسعه بومی (C/C++) در اندروید استودیو پشتیبانی میکنند.
پشتیبانی کاتلین
ویژگیهای NDK زیر در اندروید استودیو که قبلاً در جاوا پشتیبانی میشدند، اکنون در کاتلین نیز پشتیبانی میشوند:
از یک اعلان JNI به تابع پیادهسازی مربوطه در C/C++ بروید. این نگاشت را با نگه داشتن نشانگر ماوس روی نشانگر آیتم C یا C++ نزدیک شماره خط در فایل کد منبع مدیریتشده مشاهده کنید.
به طور خودکار یک تابع پیادهسازی stub برای یک اعلان JNI ایجاد کنید. ابتدا اعلان JNI را تعریف کنید و سپس برای فعال کردن، «jni» یا نام متد را در فایل C/C++ تایپ کنید.
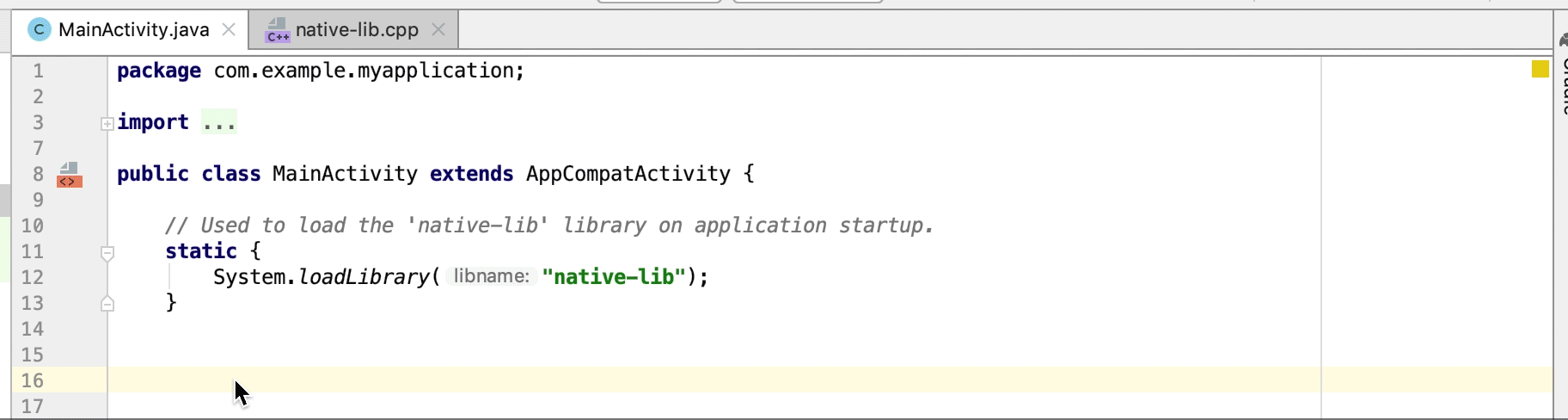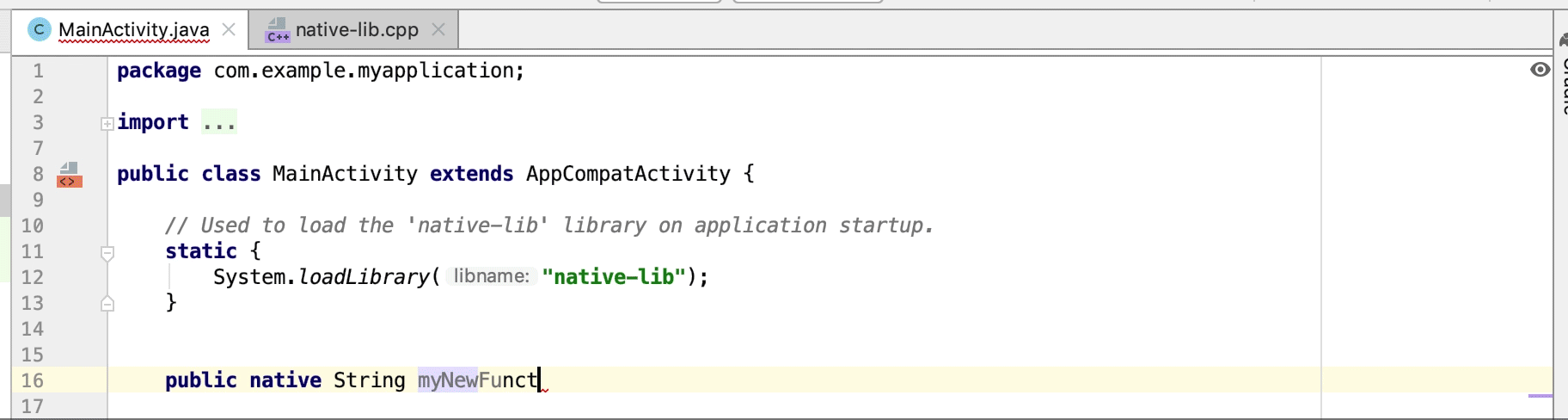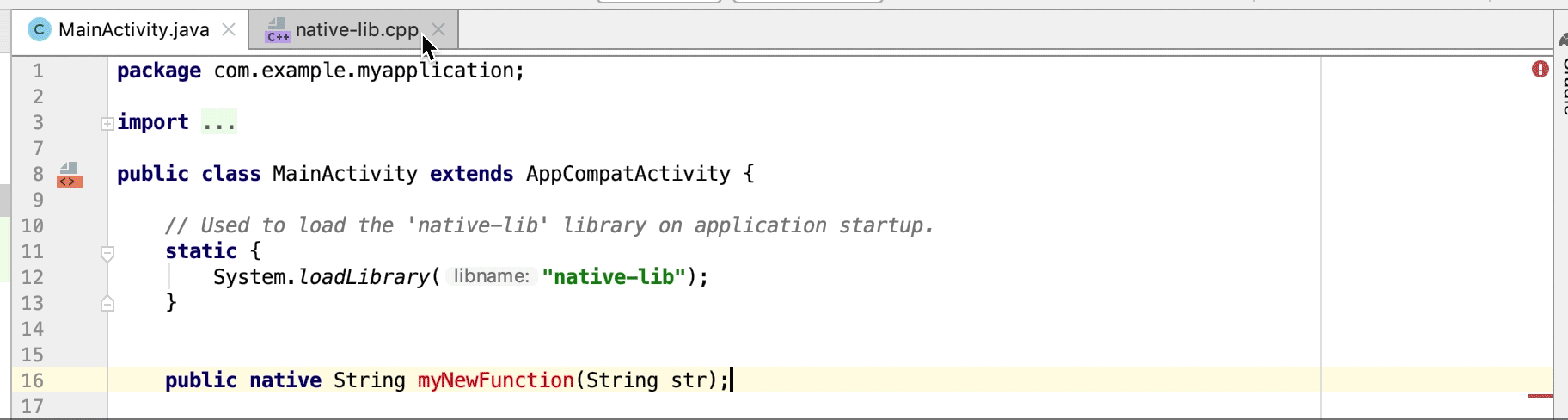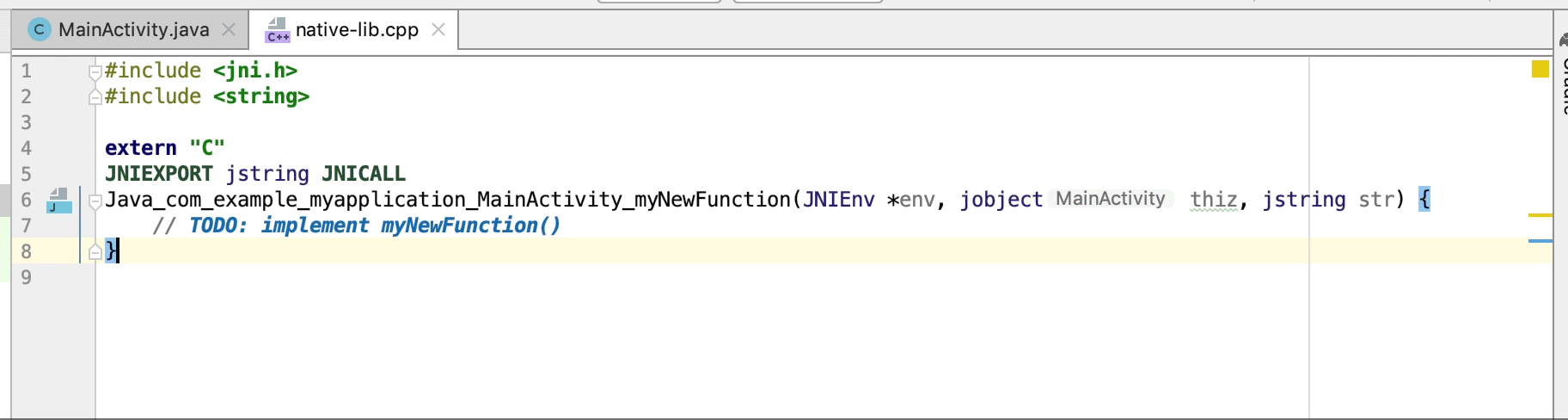
توابع پیادهسازی بومی استفاده نشده به عنوان هشدار در کد منبع برجسته میشوند. اعلانهای JNI با پیادهسازیهای از دست رفته نیز به عنوان خطا برجسته میشوند.
وقتی یک تابع پیادهسازی بومی را تغییر نام (بازسازی) میدهید، تمام اعلانهای JNI مربوطه بهروزرسانی میشوند. برای بهروزرسانی تابع پیادهسازی بومی، یک اعلان JNI را تغییر نام دهید.
بررسی امضا برای پیادهسازیهای JNI با محدودیت ضمنی.
سایر پیشرفتهای JNI
ویرایشگر کد در اندروید استودیو اکنون از گردش کار توسعه JNI یکپارچهتری پشتیبانی میکند، از جمله نکات نوع بهبود یافته، تکمیل خودکار، بازرسیها و اصلاح کد.
بارگذاری مجدد APK برای کتابخانههای بومی {:#3.6-reload-apk}
وقتی APK پروژه شما خارج از IDE بهروزرسانی میشود، دیگر نیازی به ایجاد پروژه جدید ندارید. اندروید استودیو تغییرات در APK را تشخیص میدهد و به شما امکان میدهد آن را دوباره وارد کنید.

منابع APK مخصوص کاتلین را ضمیمه کنید
اکنون میتوانید منابع APK خارجی مخصوص کاتلین را هنگام پروفایلبندی و اشکالزدایی APKهای از پیش ساخته شده، پیوست کنید. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به بخش «پیوست کردن منابع کاتلین/جاوا» مراجعه کنید.
تشخیص نشتی در Memory Profiler
هنگام تجزیه و تحلیل یک heap dump در Memory Profiler، اکنون میتوانید دادههای پروفایلبندی را که اندروید استودیو فکر میکند ممکن است نشاندهنده نشت حافظه برای نمونههای Activity و Fragment در برنامه شما باشد، فیلتر کنید.
انواع دادههایی که فیلتر نشان میدهد شامل موارد زیر است:
- نمونههای
Activityکه نابود شدهاند اما هنوز مورد ارجاع قرار میگیرند. - نمونههایی
FragmentکهFragmentManagerمعتبری ندارند اما همچنان مورد ارجاع قرار میگیرند.
منابع APK مخصوص کاتلین را ضمیمه کنید
اکنون میتوانید منابع APK خارجی مخصوص کاتلین را هنگام پروفایلبندی و اشکالزدایی APKهای از پیش ساخته شده، پیوست کنید. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به بخش «پیوست کردن منابع کاتلین/جاوا» مراجعه کنید.
تشخیص نشتی در Memory Profiler
هنگام تجزیه و تحلیل یک heap dump در Memory Profiler، اکنون میتوانید دادههای پروفایلبندی را که اندروید استودیو فکر میکند ممکن است نشاندهنده نشت حافظه برای نمونههای Activity و Fragment در برنامه شما باشد، فیلتر کنید.
انواع دادههایی که فیلتر نشان میدهد شامل موارد زیر است:
- نمونههای
Activityکه نابود شدهاند اما هنوز مورد ارجاع قرار میگیرند. - نمونههایی
FragmentکهFragmentManagerمعتبری ندارند اما همچنان مورد ارجاع قرار میگیرند.
در شرایط خاص، مانند موارد زیر، فیلتر ممکن است نتایج مثبت کاذب ارائه دهد:
- یک
Fragmentایجاد شده است اما هنوز استفاده نشده است. - یک
Fragmentدر حال ذخیره شدن است اما نه به عنوان بخشی از یکFragmentTransaction.
برای استفاده از این ویژگی، ابتدا یک heap dump را ضبط کنید یا یک فایل heap dump را به اندروید استودیو وارد کنید . برای نمایش fragmentها و activityهایی که ممکن است باعث نشت حافظه شوند، کادر انتخاب Activity/Fragment Leaks را در قسمت heap dump از Memory Profiler انتخاب کنید.
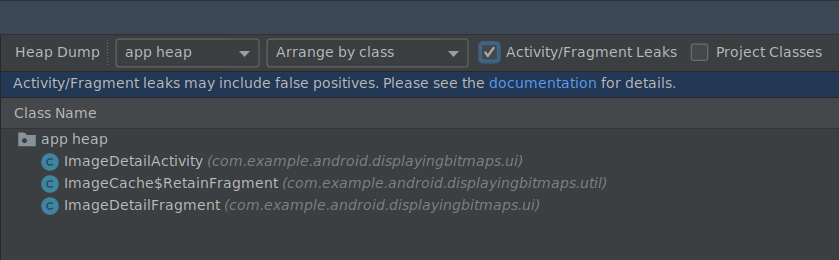
فیلتر کردن یک فایل heap dump برای یافتن نشت حافظه.
شبیهسازها
اندروید استودیو ۳.۶ به شما کمک میکند تا از چندین بهروزرسانی موجود در شبیهساز اندروید ۲۹.۲.۷ و بالاتر، همانطور که در زیر توضیح داده شده است، بهرهمند شوید.
پشتیبانی موقعیت مکانی بهبود یافته
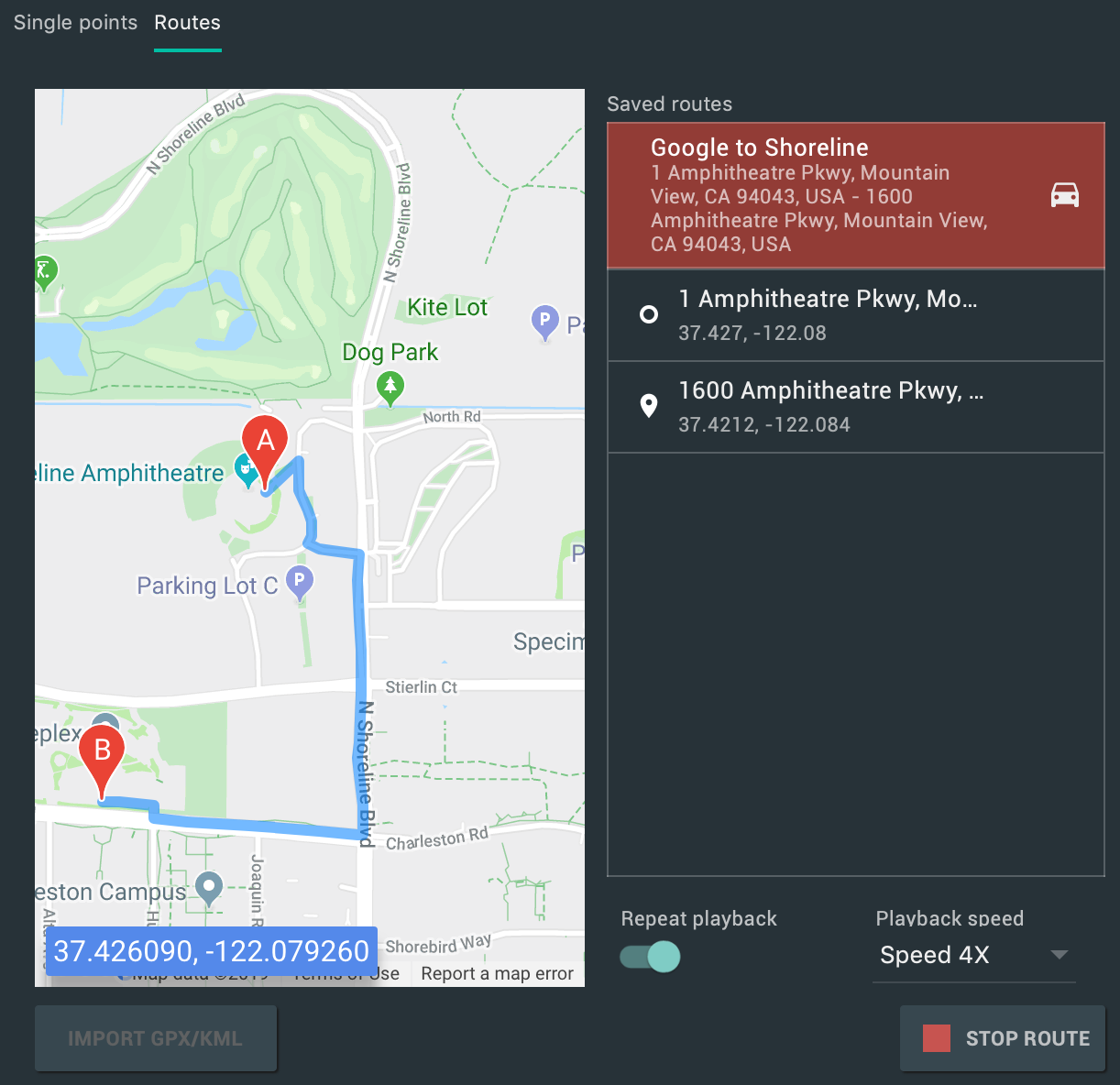
شبیهساز اندروید نسخه ۲۹.۲.۷ و بالاتر، پشتیبانی بیشتری برای شبیهسازی مختصات GPS و اطلاعات مسیر ارائه میدهد. وقتی کنترلهای توسعهیافتهی شبیهسازها را باز میکنید، گزینههای موجود در تب موقعیت مکانی اکنون در دو تب سازماندهی شدهاند: نقاط تکی و مسیرها .
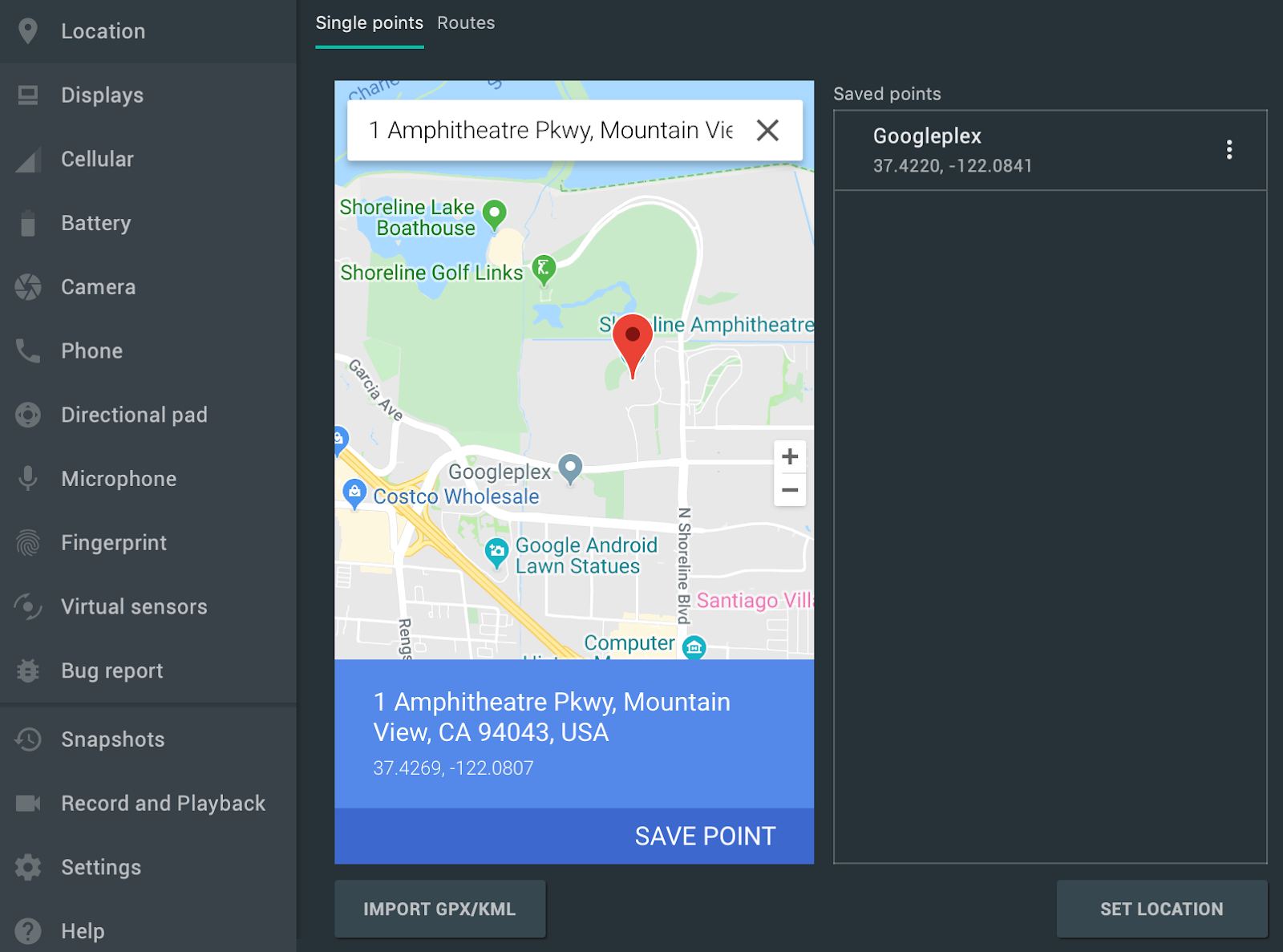
امتیازهای تکی
در تب «نقاط تکی» ، میتوانید از نمای وب گوگل مپ برای جستجوی نقاط مورد علاقه استفاده کنید، درست همانطور که هنگام استفاده از گوگل مپ در تلفن یا مرورگر انجام میدهید. وقتی مکانی را در نقشه جستجو میکنید یا روی آن کلیک میکنید، میتوانید با انتخاب «ذخیره نقطه» در نزدیکی پایین نقشه، مکان را ذخیره کنید. تمام مکانهای ذخیره شده شما در سمت راست پنجره کنترلهای توسعهیافته فهرست شدهاند.
برای تنظیم مکان شبیهسازها روی مکانی که روی نقشه انتخاب کردهاید، روی دکمهی «تنظیم مکان» در نزدیکی پایین سمت راست پنجرهی کنترلهای توسعهیافته کلیک کنید.
 .
.
مسیرها
مشابه تب نقاط تکی ، تب مسیرها یک نمای وب گوگل مپ ارائه میدهد که میتوانید از آن برای ایجاد مسیری بین دو یا چند مکان استفاده کنید. برای ایجاد و ذخیره یک مسیر، موارد زیر را انجام دهید:
- در نمای نقشه، از فیلد متن برای جستجوی اولین مقصد در مسیر خود استفاده کنید.
- مکان مورد نظر را از نتایج جستجو انتخاب کنید.
- دکمه پیمایش را انتخاب کنید.
- نقطه شروع مسیر خود را از روی نقشه انتخاب کنید.
- (اختیاری) برای افزودن ایستگاههای بیشتر به مسیر خود، روی «افزودن مقصد» کلیک کنید.
- با کلیک روی ذخیره مسیر در نمای نقشه، مسیر خود را ذخیره کنید.
- یک نام برای مسیر انتخاب کنید و روی ذخیره کلیک کنید.
برای شبیهسازی شبیهساز با دنبال کردن مسیری که ذخیره کردهاید، مسیر را از لیست مسیرهای ذخیرهشده انتخاب کنید و روی «اجرای مسیر» در نزدیکی پایین سمت راست پنجرهی Extended controls کلیک کنید. برای توقف شبیهسازی، روی «توقف مسیر» کلیک کنید.
 .
.
برای شبیهسازی مداوم شبیهساز در مسیر مشخصشده، کلید کنار «تکرار پخش» را فعال کنید. برای تغییر سرعت دنبال کردن مسیر مشخصشده توسط شبیهساز، از منوی کشویی «سرعت پخش» گزینهای را انتخاب کنید.
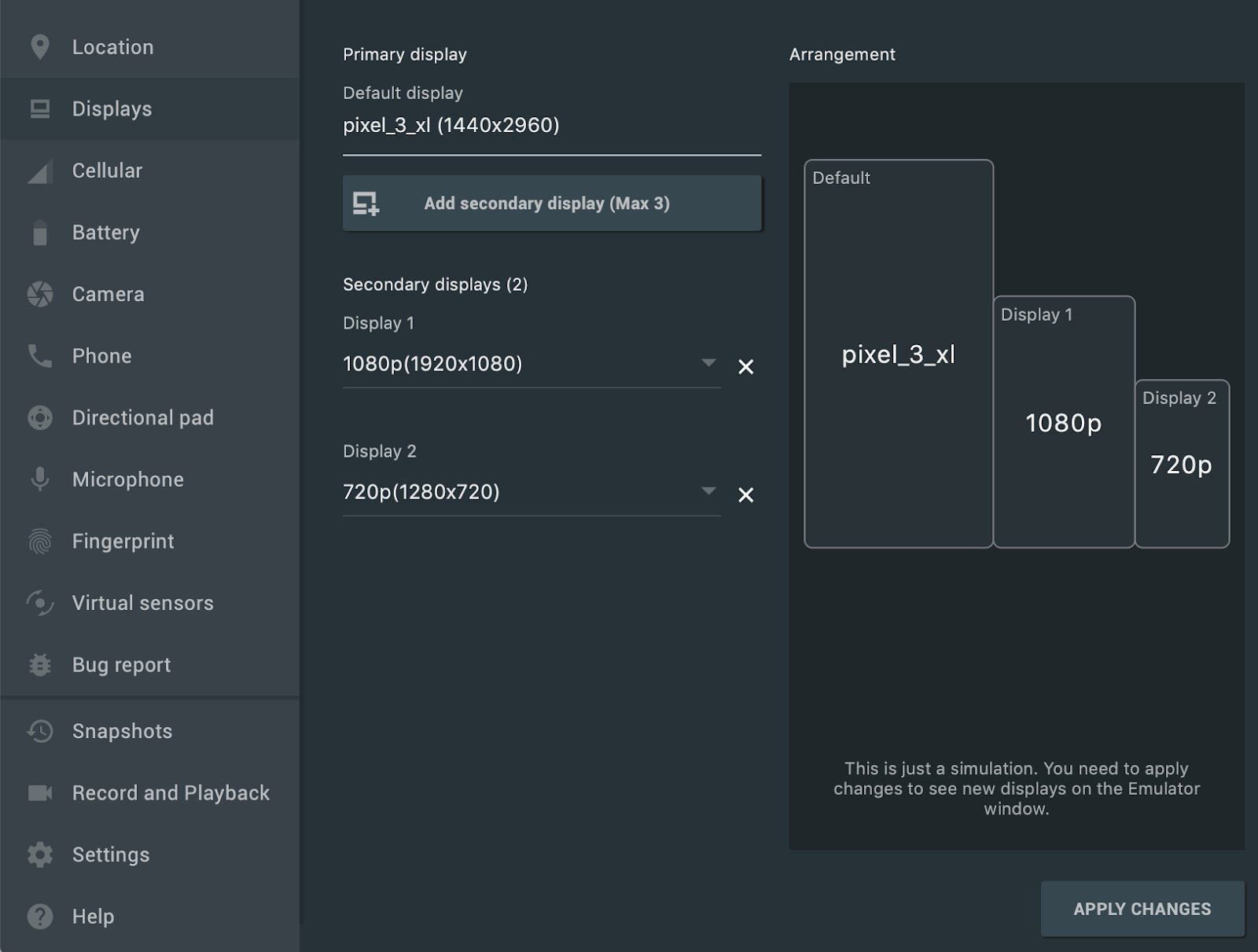
پشتیبانی از چند نمایشگر
شبیهساز اندروید اکنون به شما امکان میدهد برنامه خود را در چندین نمایشگر مستقر کنید، که از ابعاد قابل تنظیم پشتیبانی میکنند و میتوانند به شما در آزمایش برنامههایی که از چند پنجره و چند نمایشگر پشتیبانی میکنند، کمک کنند. در حالی که یک دستگاه مجازی در حال اجرا است، میتوانید حداکثر دو نمایشگر اضافی را به شرح زیر اضافه کنید:
کنترلهای توسعهیافته را باز کنید و به برگه نمایشها بروید.
با کلیک روی «افزودن نمایشگر ثانویه»، نمایشگر دیگری اضافه کنید.
از منوی کشویی زیر بخش Secondary displays ، یکی از موارد زیر را انجام دهید:
یکی از نسبتهای ابعاد از پیش تعیینشده را انتخاب کنید
گزینه سفارشی (custom) را انتخاب کنید و ارتفاع ، عرض و dpi را برای نمایشگر سفارشی خود تنظیم کنید.
(اختیاری) برای افزودن نمایشگر سوم، روی افزودن نمایشگر ثانویه کلیک کنید.
برای افزودن نمایشگر(های) مشخص شده به دستگاه مجازی در حال اجرا، روی اعمال تغییرات کلیک کنید.
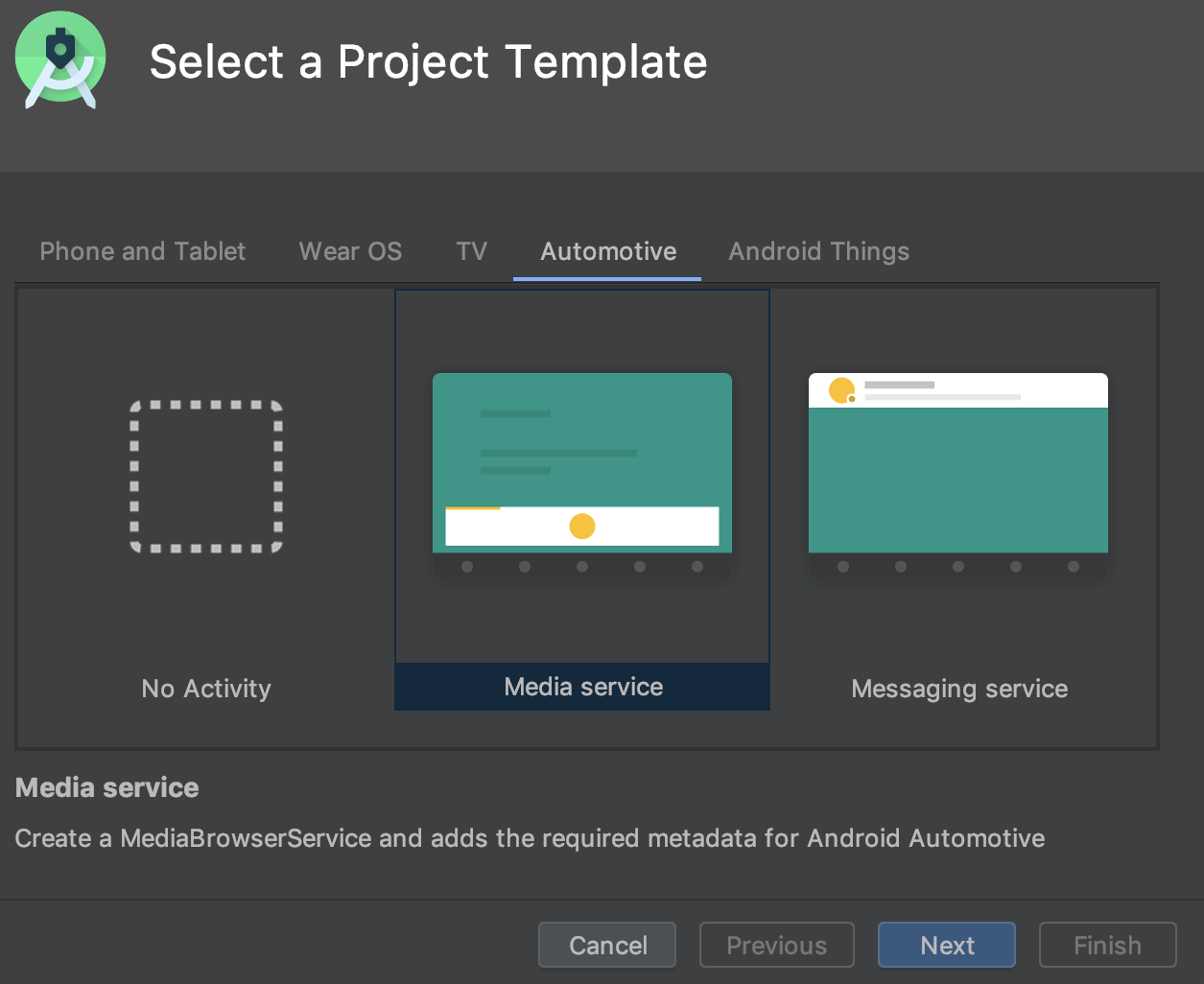
دستگاههای مجازی جدید و قالبهای پروژه برای سیستم عامل اندروید اتوموبیل
وقتی با استفاده از اندروید استودیو یک پروژه جدید ایجاد میکنید، اکنون میتوانید از سه قالب موجود در برگه Automotive در ویزارد Create New Project یکی را انتخاب کنید: No Activity ، Media service و Messaging service . برای پروژههای موجود، میتوانید با انتخاب File > New > New Module از نوار منو و انتخاب Automotive Module ، پشتیبانی از دستگاههای Android Automotive را اضافه کنید. سپس ویزارد Create New Module شما را در ایجاد یک ماژول جدید با استفاده از یکی از قالبهای پروژه Android Automotive راهنمایی میکند.
 .
.
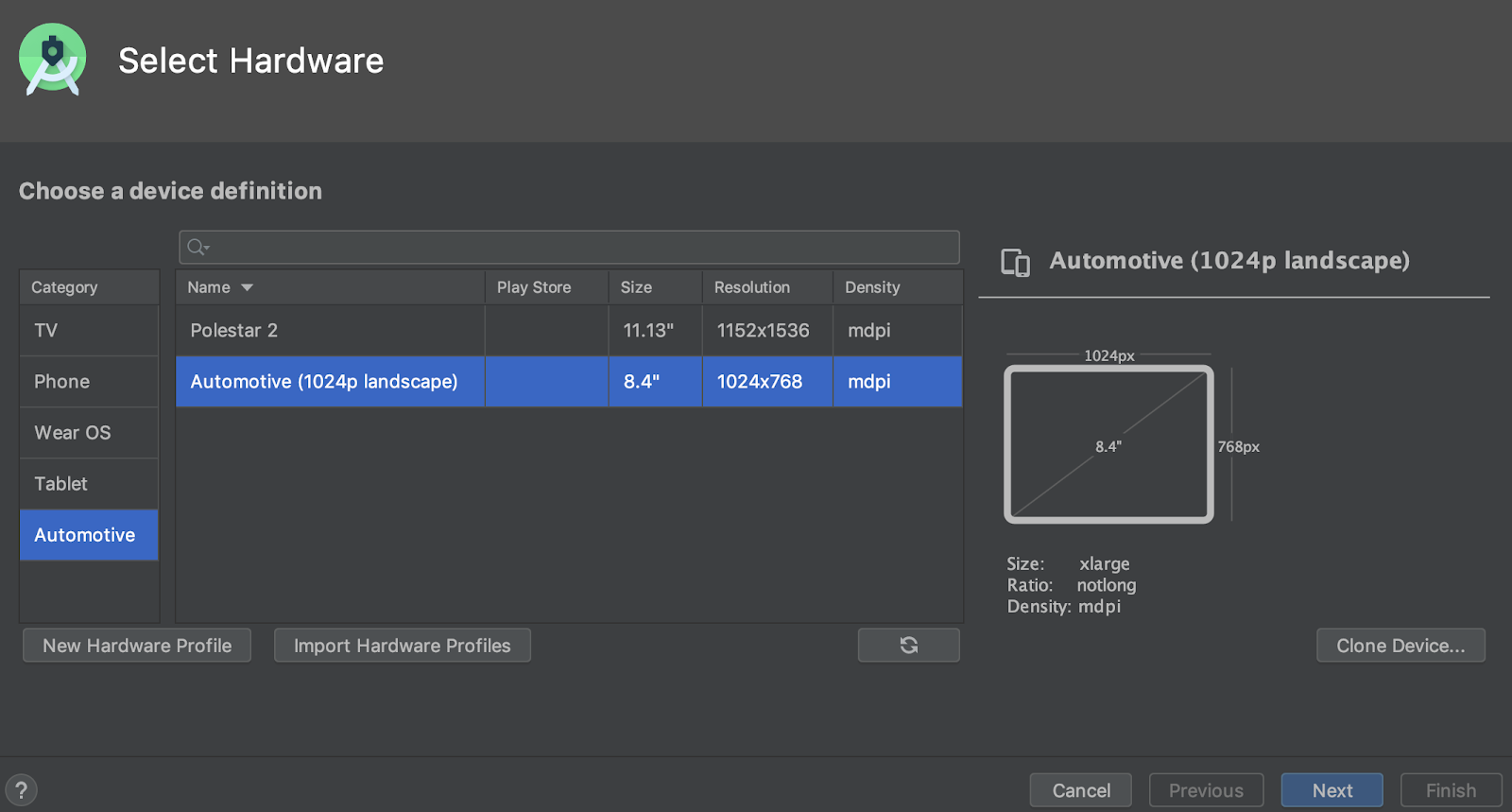
علاوه بر این، اکنون میتوانید با انتخاب یکی از گزینههای زیر در برگه Automotive در ویزارد پیکربندی دستگاه مجازی ، یک دستگاه مجازی اندروید (AVD) برای دستگاههای دارای سیستم عامل Android Automotive ایجاد کنید .
- Polestar 2 : یک AVD ایجاد کنید که واحد هد Polestar 2 را شبیهسازی کند.
- خودرو (1024p افقی) : یک AVD برای پخش کنندههای صوتی خودرو اندروید با وضوح عمومی 1024 در 768 پیکسل ایجاد کنید.
 .
.
دانلودهای SDK قابل از سرگیری
هنگام دانلود اجزا و ابزارهای SDK با استفاده از SDK Manager، اندروید استودیو اکنون به شما امکان میدهد دانلودهایی را که قطع شدهاند (مثلاً به دلیل مشکل شبکه) از سر بگیرید، به جای اینکه دانلود را از ابتدا مجدداً شروع کنید. این بهبود به ویژه برای دانلودهای بزرگ، مانند شبیهساز اندروید یا تصاویر سیستم، زمانی که اتصال اینترنت ناپایدار است، مفید است.
علاوه بر این، اگر یک کار دانلود SDK در پسزمینه در حال اجرا دارید، اکنون میتوانید با استفاده از کنترلهای موجود در نوار وضعیت، دانلود را متوقف یا از سر بگیرید.

یک وظیفه دانلود در پسزمینه در نوار وضعیت با کنترلهای جدید که به شما امکان مکث یا از سرگیری دانلود را میدهد.
Win32 منسوخ شده است
نسخه ۳۲ بیتی ویندوز اندروید استودیو پس از دسامبر ۲۰۱۹ دیگر بهروزرسانی دریافت نخواهد کرد و پس از دسامبر ۲۰۲۰ نیز دیگر پشتیبانی نخواهد شد. میتوانید به استفاده از اندروید استودیو ادامه دهید. با این حال، برای دریافت بهروزرسانیهای بیشتر، سیستم عامل خود را به نسخه ۶۴ بیتی ویندوز ارتقا دهید.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، وبلاگ استهلاک ویندوز ۳۲ بیتی را مطالعه کنید.
گزینه جدید برای بهینهسازی زمان همگامسازی Gradle
در نسخههای قبلی، اندروید استودیو لیست تمام وظایف Gradle را در طول Gradle Sync بازیابی میکرد. برای پروژههای بزرگ، بازیابی لیست وظایف میتواند باعث کندی زمان همگامسازی شود.
برای بهبود عملکرد Gradle Sync، به File > Settings > Experimental بروید و گزینهی «در طول همگامسازی Gradle، لیست وظایف Gradle را نسازید» را انتخاب کنید.
وقتی این گزینه را فعال میکنید، اندروید استودیو در حین همگامسازی، از ساخت لیست وظایف صرفنظر میکند، که به Gradle Sync اجازه میدهد سریعتر تکمیل شود و پاسخگویی رابط کاربری را بهبود بخشد. به خاطر داشته باشید، وقتی IDE از ساخت لیست وظایف صرفنظر میکند، لیست وظایف در پنل Gradle خالی هستند و تکمیل خودکار نام وظیفه در فایلهای ساخت کار نمیکند.
مکان جدید برای فعال/غیرفعال کردن حالت آفلاین Gradle
برای فعال یا غیرفعال کردن حالت آفلاین Gradle، ابتدا از نوار منو، View > Tool Windows > Gradle را انتخاب کنید. سپس، در نزدیکی بالای پنجره Gradle ، روی Toggle Offline Mode کلیک کنید.  .
.
اینتلیجی آیدیا ۲۰۱۹.۲
محیط توسعه یکپارچه (IDE) اندروید استودیو (Android Studio) با بهبودهایی از IntelliJ IDEA تا نسخه ۲۰۱۹.۲ بهروزرسانی شده است.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد بهبودهای سایر نسخههای IntelliJ که به صورت تجمعی با نسخه ۲۰۱۹.۲ گنجانده شدهاند، به صفحات زیر مراجعه کنید:
مشارکتکنندگان جامعه
از همه مشارکتکنندگان جامعه ما که به ما در کشف اشکالات و راههای دیگر برای بهبود اندروید استودیو ۳.۶ کمک کردهاند، سپاسگزاریم. به طور خاص، مایلیم از افراد زیر که اشکالات را گزارش کردند، تشکر کنیم:
۳.۵ (آگوست ۲۰۱۹)
اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ یک نسخهٔ بزرگ و نتیجهٔ پروژهٔ ماربل است. از زمان انتشار اندروید استودیو ۳.۳ ، پروژهٔ ماربل شامل چندین نسخه بوده است که بر بهبود سه حوزهٔ اصلی این IDE تمرکز دارند: سلامت سیستم ، بهبود ویژگیها و رفع اشکالات.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد این بهروزرسانیها و سایر بهروزرسانیهای پروژه Marble، پست وبلاگ توسعهدهندگان اندروید یا بخشهای زیر را مطالعه کنید.
همچنین میخواهیم از همه مشارکتکنندگان جامعهمان که در انتشار این نسخه کمک کردهاند، تشکر کنیم.
۳.۵.۳ (دسامبر ۲۰۱۹)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلف و بهبود عملکرد است.
۳.۵.۲ (نوامبر ۲۰۱۹)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلف و بهبود عملکرد است. برای مشاهدهی فهرست رفع اشکالات قابل توجه، پست مرتبط را در وبلاگ بهروزرسانیهای انتشار مطالعه کنید.
۳.۵.۱ (اکتبر ۲۰۱۹)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلف و بهبود عملکرد است. برای مشاهدهی فهرست رفع اشکالات قابل توجه، پست مرتبط را در وبلاگ بهروزرسانیهای انتشار مطالعه کنید.
پروژه مرمر: سلامت سیستم
این بخش تغییرات اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ را که بر بهبود سلامت سیستم متمرکز هستند، شرح میدهد.
تنظیمات حافظه توصیه شده
اندروید استودیو اکنون اگر تشخیص دهد که میتوانید با افزایش حداکثر مقدار رمی که سیستم عامل شما باید برای فرآیندهای اندروید استودیو، مانند IDE اصلی، سرویس Gradle و سرویس Kotlin اختصاص دهد، عملکرد را بهبود بخشید، به شما اطلاع میدهد. میتوانید با کلیک روی پیوند اقدام در اعلان، تنظیمات پیشنهادی را بپذیرید، یا میتوانید با انتخاب File > Settings (یا Android Studio > Preferences در macOS) و سپس یافتن بخش تنظیمات حافظه در قسمت Appearance & Behavior > System Settings ، این تنظیمات را به صورت دستی تنظیم کنید. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به Maximum heap size مراجعه کنید.

اعلانی درباره تنظیمات حافظه پیشنهادی.
گزارش استفاده از حافظه
گاهی اوقات، بازتولید و گزارش مشکلات حافظه در اندروید استودیو دشوار است. برای کمک به حل این مشکل، اندروید استودیو به شما امکان میدهد با کلیک روی Help > Analyze Memory Usage از نوار منو، یک گزارش استفاده از حافظه ایجاد کنید. وقتی این کار را انجام میدهید، IDE قبل از اینکه از شما بپرسد آیا میخواهید دادهها را برای شناسایی منبع مشکلات حافظه به تیم اندروید استودیو ارسال کنید یا خیر، آنها را به صورت محلی برای اطلاعات شخصی بررسی میکند. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به بخش «اجرای گزارش استفاده از حافظه» مراجعه کنید.
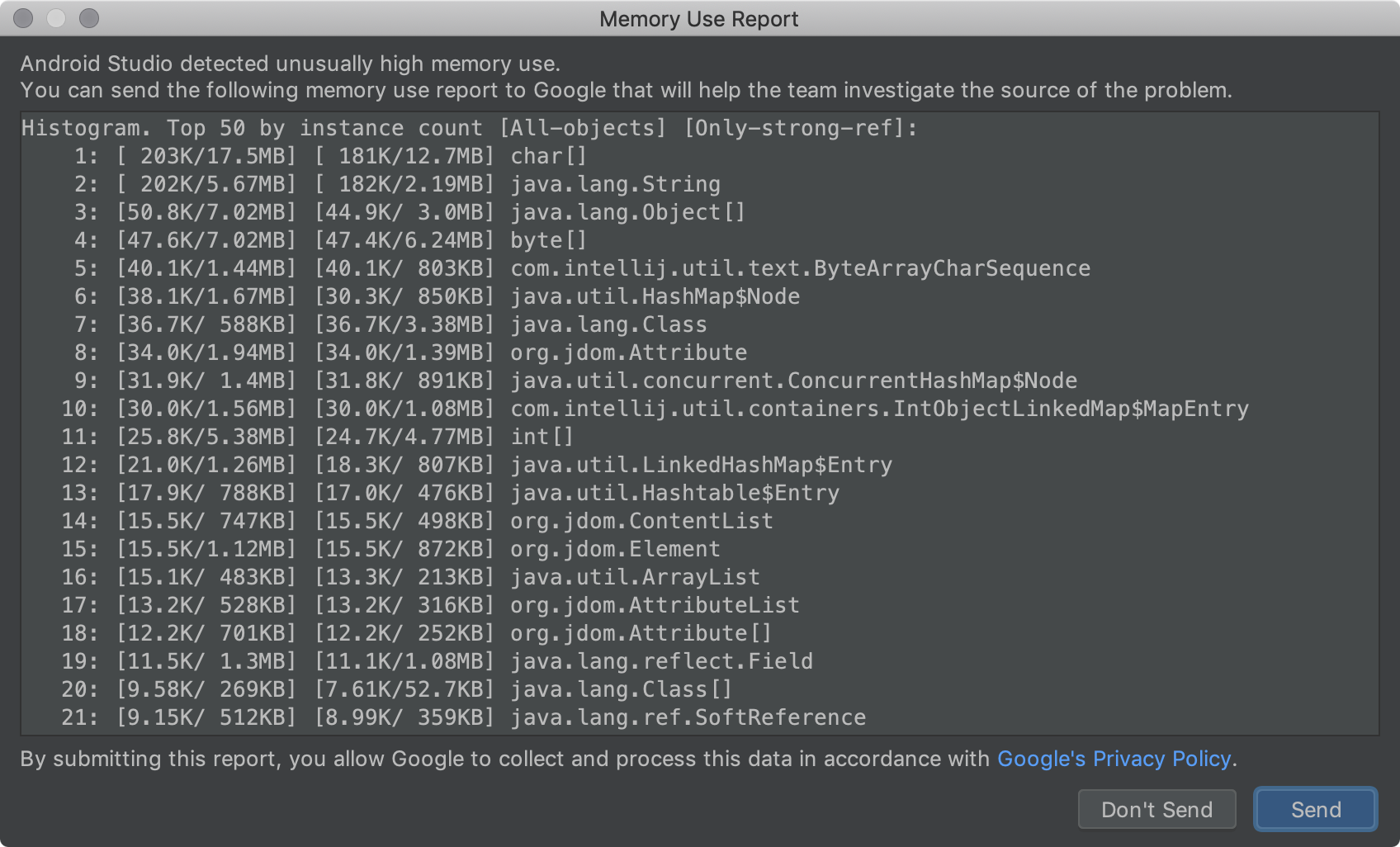
گزارش استفاده از حافظه
ویندوز: بهینهسازی ورودی/خروجی فایل آنتیویروس
اندروید استودیو اکنون به طور خودکار بررسی میکند که آیا دایرکتوریهای خاصی از پروژه از اسکن آنتیویروس در لحظه مستثنی شدهاند یا خیر. هنگامی که بتوان تنظیماتی را برای بهبود عملکرد ساخت انجام داد، اندروید استودیو به شما اطلاع میدهد و دستورالعملهایی در مورد نحوه بهینهسازی پیکربندی آنتیویروس شما ارائه میدهد. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به بخش «به حداقل رساندن تأثیر نرمافزار آنتیویروس بر سرعت ساخت» مراجعه کنید.
پروژه مرمر: پرداخت ویژه
این بخش تغییرات اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ را که بر بهبود ویژگیهای موجود متمرکز هستند، شرح میدهد.
اعمال تغییرات
«اعمال تغییرات» به شما امکان میدهد تغییرات کد و منابع را بدون راهاندازی مجدد برنامه - و در برخی موارد، بدون راهاندازی مجدد فعالیت فعلی - به برنامه در حال اجرا اعمال کنید. «اعمال تغییرات» رویکردی کاملاً جدید برای حفظ وضعیت برنامه شما پیادهسازی میکند. برخلاف «اجرای فوری» که بایتکد APK شما را بازنویسی میکرد، «اعمال تغییرات» با استفاده از ابزار زمان اجرا پشتیبانیشده در اندروید ۸.۰ (سطح API ۲۶) یا بالاتر، کلاسها را در لحظه تعریف مجدد میکند.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به اعمال تغییرات مراجعه کنید.
دکمههای نوار ابزار برای اعمال تغییرات.
جریان استقرار برنامه
این IDE یک منوی کشویی جدید دارد که به شما امکان میدهد به سرعت دستگاهی را که میخواهید برنامه خود را روی آن مستقر کنید، انتخاب کنید. این منو همچنین شامل گزینه جدیدی است که به شما امکان میدهد برنامه خود را به طور همزمان روی چندین دستگاه اجرا کنید.
منوی کشویی دستگاه هدف.
بهبود همگامسازی Gradle و تشخیص حافظه پنهان
اکنون IDE بهتر تشخیص میدهد که Gradle هنگام کاهش مصرف هارد دیسک، چه زمانی به صورت دورهای حافظه پنهان ساخت شما را پاک میکند. در نسخههای قبلی، این وضعیت باعث میشد IDE وابستگیهای از دست رفته را گزارش دهد و همگامسازی Gradle با شکست مواجه شود. اکنون، IDE به سادگی وابستگیها را در صورت نیاز دانلود میکند تا اطمینان حاصل شود که همگامسازی Gradle با موفقیت انجام میشود.
بهبود خروجی خطای ساخت
ساخت  پنجره اکنون گزارش خطای بهتری، مانند پیوند به فایل و خط خطای گزارش شده، برای فرآیندهای ساخت زیر ارائه میدهد:
پنجره اکنون گزارش خطای بهتری، مانند پیوند به فایل و خط خطای گزارش شده، برای فرآیندهای ساخت زیر ارائه میدهد:
- کامپایل و لینک کردن AAPT
- R8 و پروگارد
- دکسینگ
- ادغام منابع
- تجزیه فایل XML
- کامپایل جاوا، کاتلینک و سیمیک
ارتقاء پروژه
تجربه بهروزرسانی بهبود یافته تا اطلاعات و اقدامات بیشتری را برای کمک به شما در بهروزرسانی IDE و افزونه Android Gradle ارائه دهد. به عنوان مثال، خطاهای همگامسازی و ساخت بیشتر شامل اقداماتی برای کمک به شما در کاهش خطاها هنگام بهروزرسانی است.
مهم است که به خاطر داشته باشید، میتوانید IDE را مستقل از سایر اجزا، مانند افزونه Android Gradle، بهروزرسانی کنید. بنابراین، میتوانید با خیال راحت IDE را به محض انتشار نسخه جدیدتر بهروزرسانی کنید و سایر اجزا را بعداً بهروزرسانی کنید.
ویرایشگر طرحبندی
اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ شامل چندین بهبود در تجسم طرحبندی، مدیریت و تعامل است.
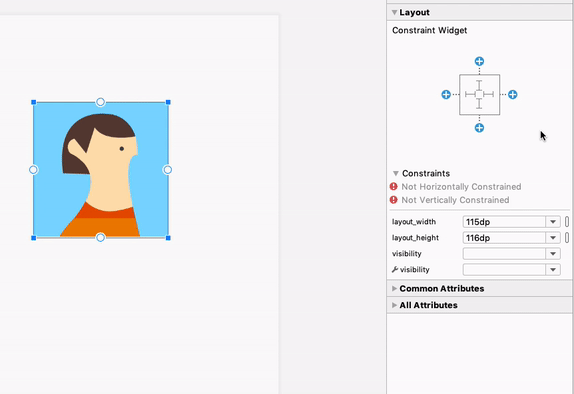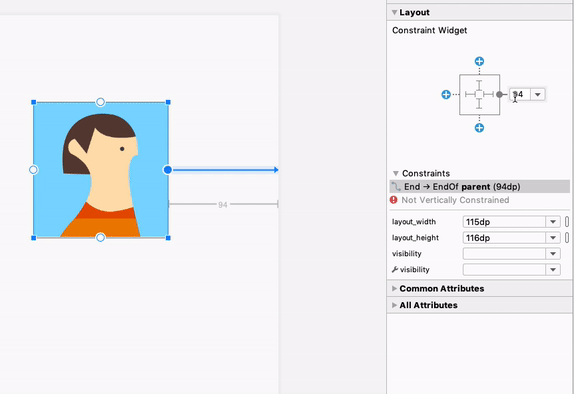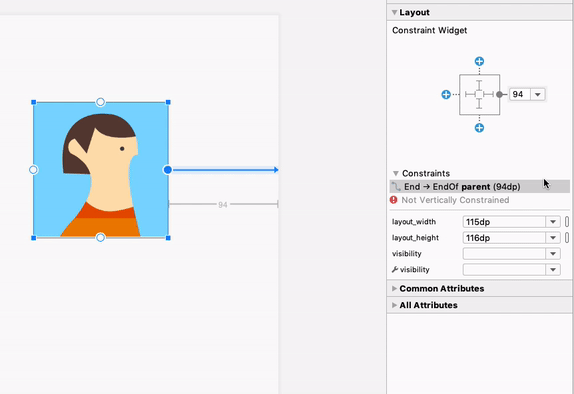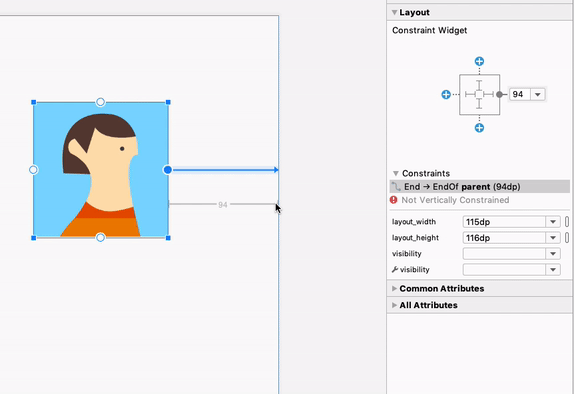
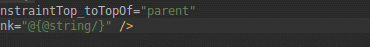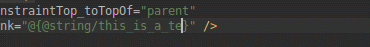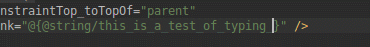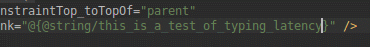
هنگام کار با ConstraintLayout ، بخش جدید Constraints در پنل Attributes ، روابط محدودیتهای کامپوننت رابط کاربری انتخاب شده را فهرست میکند. میتوانید یک محدودیت را یا از سطح طراحی یا از لیست محدودیتها انتخاب کنید تا محدودیت در هر دو ناحیه برجسته شود.
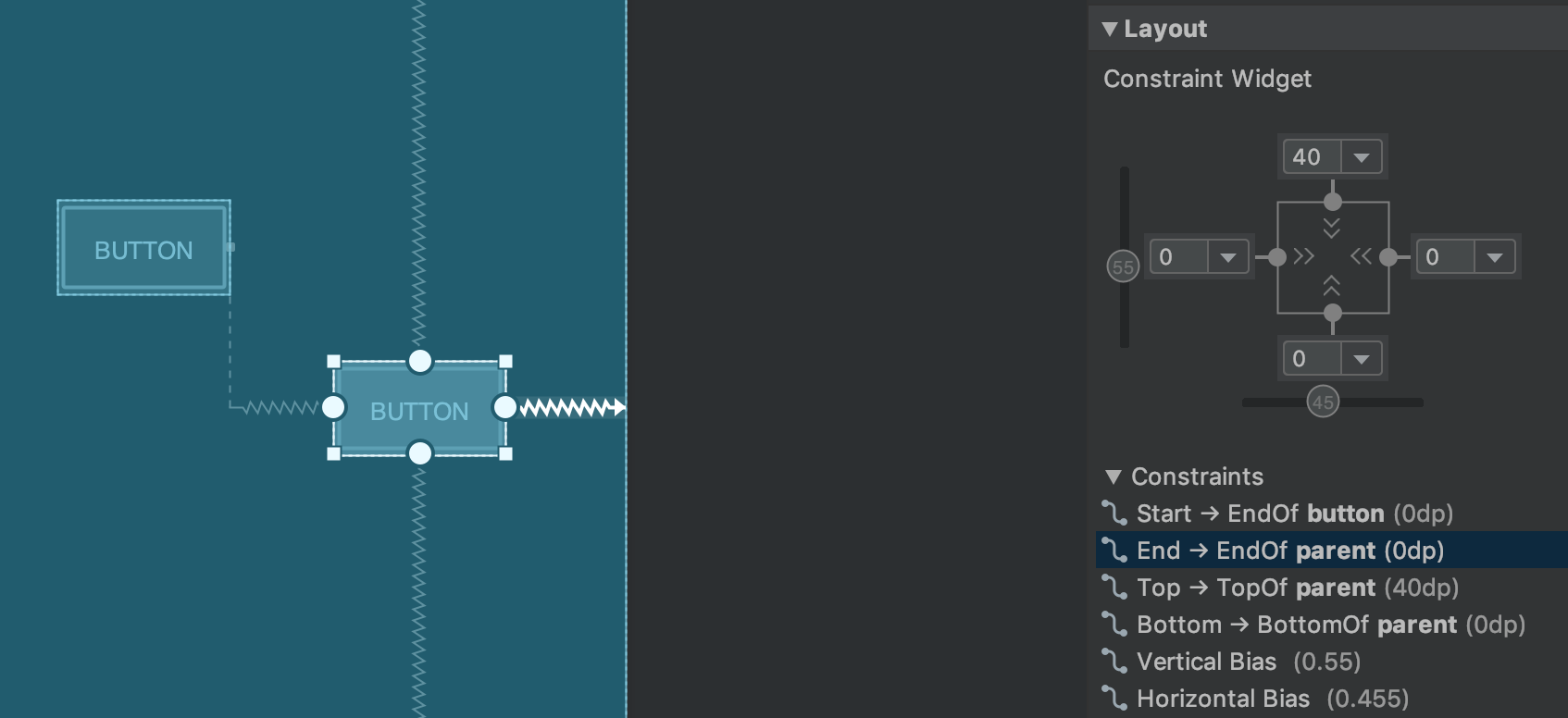
روابط محدودیت برای یک عنصر رابط کاربری انتخاب شده.
به طور مشابه، اکنون میتوانید با انتخاب یک قید و فشردن کلید Delete ، آن را حذف کنید. همچنین میتوانید با نگه داشتن کلید Control (در macOS، Command ) و کلیک روی لنگر قید، یک قید را حذف کنید. توجه داشته باشید که وقتی کلید Control یا Command را نگه دارید و ماوس را روی یک لنگر نگه دارید، هر قید مرتبط قرمز میشود تا نشان دهد که میتوانید برای حذف آنها کلیک کنید.
وقتی یک نما انتخاب میشود، میتوانید با کلیک روی هر یک از آیکونهای + در بخش ابزارک محدودیتها در پنل ویژگیها ، همانطور که در تصویر زیر نشان داده شده است، یک محدودیت ایجاد کنید. وقتی یک محدودیت جدید ایجاد میکنید، ویرایشگر طرحبندی اکنون محدودیت را انتخاب و برجسته میکند و بازخورد بصری فوری را برای آنچه که تازه اضافه کردهاید ارائه میدهد.
استفاده از ویجت محدودیت برای ایجاد محدودیتها.
هنگام ایجاد یک قید، ویرایشگر طرحبندی اکنون فقط نقاط لنگر واجد شرایط را که میتوانید به آنها محدود کنید، نشان میدهد. پیش از این، ویرایشگر طرحبندی تمام نقاط لنگر را در تمام نماها، صرف نظر از اینکه آیا میتوانستید به آنها محدود شوید یا خیر، برجسته میکرد. علاوه بر این، اکنون یک پوشش آبی رنگ، هدف قید را برجسته میکند. این برجستهسازی به ویژه هنگام تلاش برای محدود کردن به مؤلفهای که با مؤلفه دیگر همپوشانی دارد، مفید است.
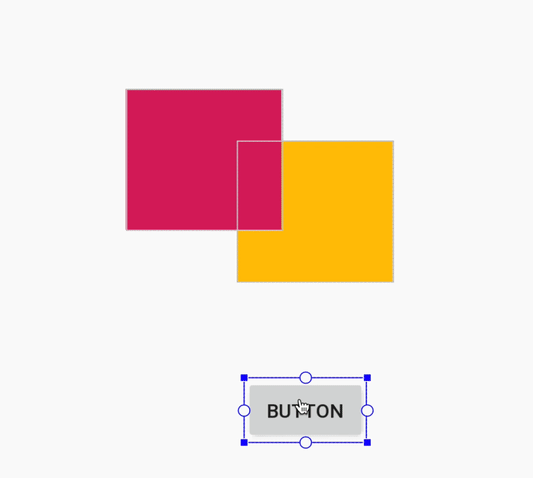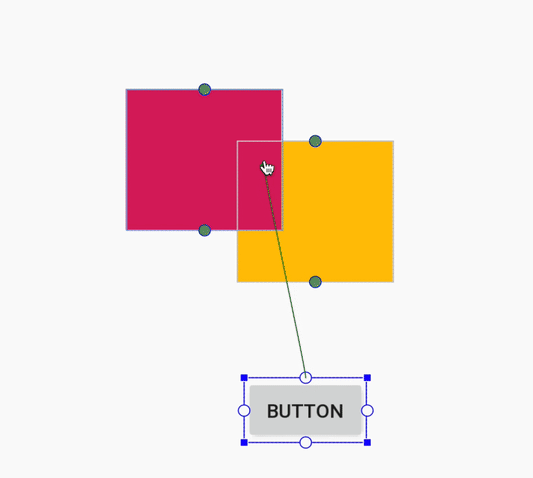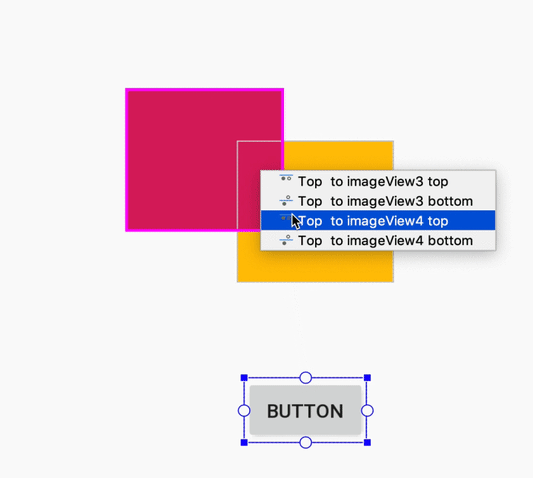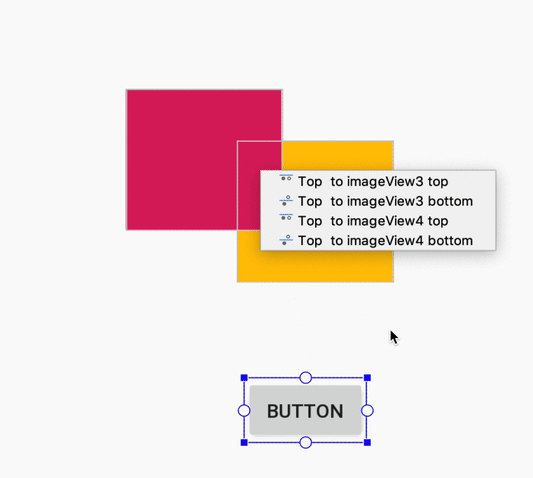
ایجاد محدودیت برای یک کامپوننت همپوشانی در اندروید استودیو ۳.۴
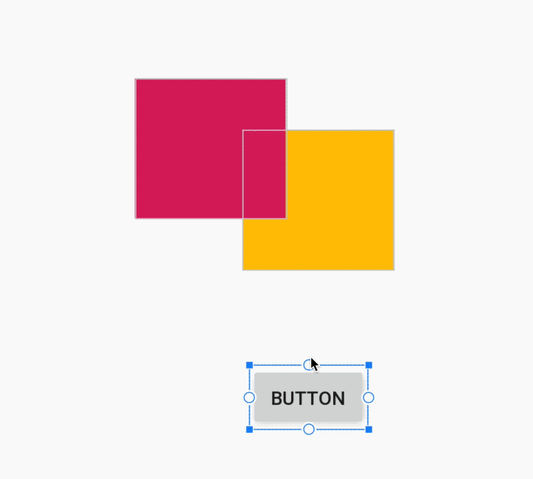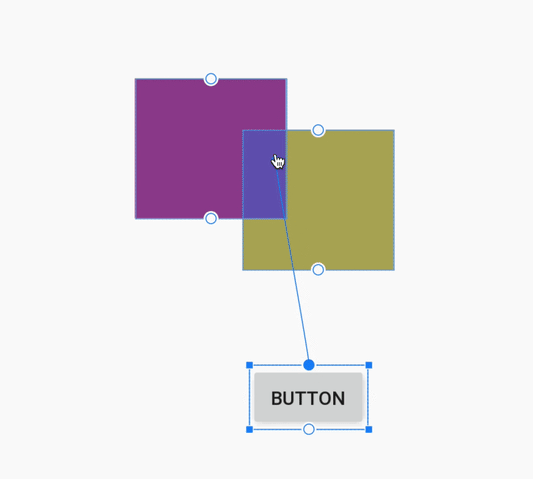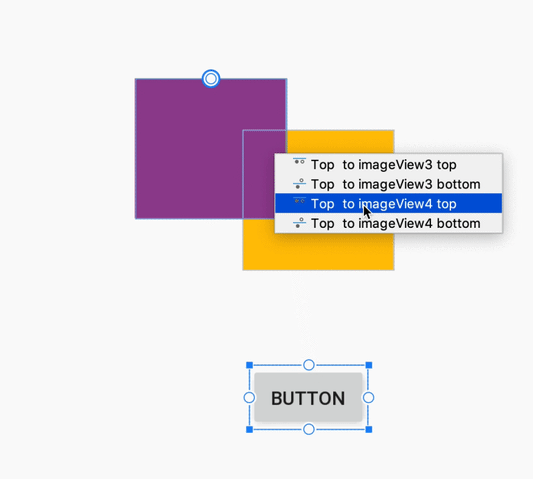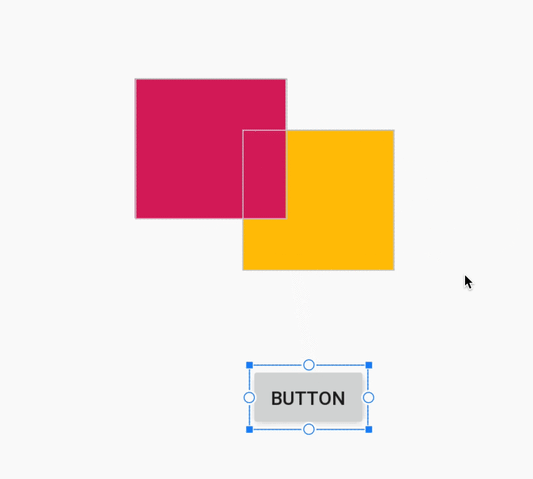
ایجاد محدودیت برای یک کامپوننت همپوشانی در اندروید استودیو ۳.۵
علاوه بر بهروزرسانیهای فوق، اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ شامل بهبودهای زیر در ویرایشگر طرحبندی نیز میشود:
- ویجت محدودیت و منوی کشویی حاشیه پیشفرض اکنون به شما امکان میدهند از منابع ابعاد برای حاشیهها استفاده کنید.
- در نوار ابزار ویرایشگر طرحبندی، فهرست دستگاههایی که اندازه سطح طراحی را تعیین میکنند، بهروزرسانی شده است. علاوه بر این، رفتار snapping هنگام تغییر اندازه بهبود یافته است و دستگیرههای تغییر اندازه روی سطح طراحی اکنون همیشه قابل مشاهده هستند. هنگام تغییر اندازه، پوششهای جدیدی ظاهر میشوند که اندازههای رایج دستگاهها را نشان میدهند.
- ویرایشگر طرحبندی (Layout Editor) طرح رنگی جدیدی دارد که هماهنگی را بهبود میبخشد و تضاد بین اجزا، متن و محدودیتها را کاهش میدهد.
- حالت Blueprint اکنون شامل پشتیبانی از متن برای برخی از اجزایی است که متن در آنها نمایش داده نمیشد.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد این تغییرات، به Android Studio Project Marble: Layout Editor مراجعه کنید.
اتصال داده
علاوه بر افزودن پشتیبانی از پردازش حاشیهنویسی افزایشی برای اتصال داده، این IDE ویژگیهای ویرایشگر هوشمند و عملکرد را هنگام ایجاد عبارات اتصال داده در XML بهبود میبخشد.
عملکرد ویرایشگر کد در اندروید استودیو ۳.۴.۱
بهبود عملکرد ویرایش کد در اندروید استودیو ۳.۵.
پشتیبانی بهبود یافته برای پروژههای C/C++
اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ شامل چندین تغییر است که پشتیبانی از پروژههای C/C++ را بهبود میبخشد.
بهبودهای پنل گزینههای ساخت برای همگامسازی تک متغیره
اکنون میتوانید هم نوع ساخت فعال و هم ABI فعال را در پنل Build Variants مشخص کنید. این ویژگی پیکربندی ساخت را برای هر ماژول ساده میکند و همچنین میتواند عملکرد همگامسازی Gradle را بهبود بخشد.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به تغییر نوع ساخت مراجعه کنید.
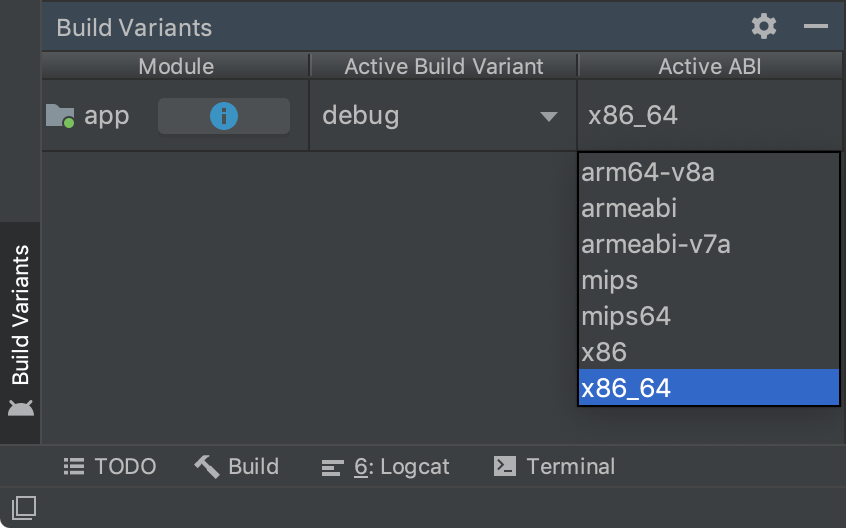
پنل گزینههای ساخت با انتخاب تک متغیره توسط ABI.
نسخههای کنار هم NDK
اکنون میتوانید از چندین نسخه NDK در کنار هم استفاده کنید. این ویژگی به شما انعطافپذیری بیشتری در پیکربندی پروژههایتان میدهد - برای مثال، اگر پروژههایی دارید که از نسخههای مختلف NDK در یک دستگاه استفاده میکنند.
اگر پروژه شما از افزونه Android Gradle نسخه 3.5.0 یا بالاتر استفاده میکند، میتوانید نسخه NDK مورد استفاده هر ماژول در پروژه خود را نیز مشخص کنید. میتوانید از این ویژگی برای ایجاد نسخههای قابل تکرار و کاهش ناسازگاری بین نسخههای NDK و افزونه Android Gradle استفاده کنید.
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، به نصب و پیکربندی NDK، CMake و LLDB مراجعه کنید.
پشتیبانی از سیستم عامل کروم
اندروید استودیو اکنون رسماً از دستگاههای ChromeOS مانند HP Chromebook x360 14، Acer Chromebook 13/Spin 13 و سایر دستگاههایی که میتوانید در بخش نیازمندیهای سیستم در مورد آنها مطالعه کنید، پشتیبانی میکند. برای شروع، اندروید استودیو را روی دستگاه ChromeOS سازگار خود دانلود کنید و دستورالعملهای نصب را دنبال کنید.
توجه: اندروید استودیو در ChromeOS در حال حاضر فقط از استقرار برنامه شما در یک دستگاه سختافزاری متصل پشتیبانی میکند. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، اجرای برنامهها روی یک دستگاه سختافزاری را مطالعه کنید.
تحویل مشروط برای ماژولهای ویژگی
تحویل مشروط به شما امکان میدهد الزامات پیکربندی خاصی را برای دستگاه تعیین کنید تا ماژولهای ویژگی به طور خودکار در حین نصب برنامه دانلود شوند. به عنوان مثال، میتوانید یک ماژول ویژگی را که شامل قابلیتهای واقعیت افزوده (AR) است، طوری پیکربندی کنید که در هنگام نصب برنامه فقط برای دستگاههایی که از AR پشتیبانی میکنند، در دسترس باشد.
این مکانیزم تحویل در حال حاضر از کنترل دانلود یک ماژول در زمان نصب برنامه بر اساس پیکربندیهای دستگاه زیر پشتیبانی میکند:
- ویژگیهای سختافزاری و نرمافزاری دستگاه، شامل نسخه OpenGL ES
- کشور کاربر
- سطح API
اگر دستگاهی تمام الزاماتی را که شما مشخص کردهاید، برآورده نکند، ماژول در زمان نصب برنامه دانلود نمیشود. با این حال، برنامه شما ممکن است بعداً با استفاده از کتابخانه Play Core درخواست دانلود ماژول را داشته باشد. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، پیکربندی تحویل مشروط را مطالعه کنید.
اینتلیجی آیدیا ۲۰۱۹.۱
محیط توسعه یکپارچه اندروید استودیو (Android Studio IDE) با بهبودهایی از IntelliJ IDEA تا نسخه ۲۰۱۹.۱ ، مانند سفارشیسازی تم، بهروزرسانی شده است.
آخرین نسخه IntelliJ که با اندروید استودیو همراه بود، نسخه 2018.3.4 بود. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد بهبودهای سایر نسخههای IntelliJ که به صورت تجمعی با این نسخه از اندروید استودیو همراه شدهاند، به بهروزرسانیهای رفع اشکال زیر مراجعه کنید:
- IntelliJ IDEA 2018.3.6 {: .external-link}
- IntelliJ IDEA 2018.3.5 {: .external-link}
بهروزرسانیهای افزونهی اندروید Gradle نسخه ۳.۵.۰
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد ویژگیهای جدید افزونه Android Gradle نسخه ۳.۵.۰، مانند پشتیبانی بهبود یافته از پردازش حاشیهنویسی افزایشی و تستهای واحد قابل ذخیره، به یادداشتهای انتشار آن مراجعه کنید.
مشارکتکنندگان جامعه
از همه مشارکتکنندگان جامعه ما که به ما در کشف اشکالات و راههای دیگر برای بهبود اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ کمک کردهاند، سپاسگزاریم. به طور خاص، مایلیم از افراد زیر که اشکالات P0 و P1 را گزارش کردند، تشکر کنیم:
|
|
|
۳.۴ (آوریل ۲۰۱۹)
اندروید استودیو ۳.۴ یک نسخه اصلی است که شامل مجموعهای از ویژگیها و بهبودهای جدید میشود.
۳.۴.۲ (ژوئیه ۲۰۱۹)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلف و بهبود عملکرد است. برای مشاهدهی فهرست رفع اشکالات قابل توجه، پست مرتبط را در وبلاگ بهروزرسانیهای انتشار مطالعه کنید.
۳.۴.۱ (مه ۲۰۱۹)
این بهروزرسانی جزئی شامل رفع اشکالات مختلف و بهبود عملکرد است. برای مشاهدهی فهرست رفع اشکالات قابل توجه، پست مرتبط را در وبلاگ بهروزرسانیهای انتشار مطالعه کنید.
۳.۴.۰ مشکلات شناختهشده
هنگام استقرار برنامه شما در دستگاهی که اندروید Q بتا را اجرا میکند، پروفایلینگ غیرفعال است.
- هنگام استفاده از کتابخانه اتصال داده، ممکن است
LiveDataListener.onChanged()با NPE از کار بیفتد. راه حلی برای این مشکل در اندروید استودیو ۳.۴.۱ ارائه خواهد شد و در حال حاضر در آخرین نسخه پیشنمایش اندروید استودیو ۳.۵ موجود است. ( به شماره ۱۲۲۰۶۶۷۸۸ مراجعه کنید)
اینتلیجی آیدیا ۲۰۱۸.۳.۴
محیط توسعه یکپارچه (IDE) اندروید استودیو (Android Studio) با بهبودهایی از IntelliJ IDEA تا نسخه 2018.3.4 بهروزرسانی شده است.
بهروزرسانیهای افزونهی اندروید Gradle نسخه ۳.۴.۰
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد ویژگیهای جدید افزونه Android Gradle نسخه ۳.۴.۰، به یادداشتهای انتشار آن مراجعه کنید.
پنجره ساختار پروژه جدید
پنجره جدید ساختار پروژه (PSD) بهروزرسانی وابستگیها و پیکربندی جنبههای مختلف پروژه شما، مانند ماژولها، انواع ساخت، امضای پیکربندیها و متغیرهای ساخت را آسانتر میکند.
میتوانید PSD را با انتخاب File > Project Structure از نوار منو باز کنید. همچنین میتوانید PSD را با فشار دادن Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S در ویندوز و لینوکس یا Command+; (نقطه ویرگول) در macOS باز کنید. میتوانید توضیحات برخی از بخشهای جدید و بهروز شده PSD را در زیر بیابید.
متغیرها
بخش متغیرهای جدید PSD به شما امکان میدهد متغیرهای ساخت را ایجاد و مدیریت کنید، مانند متغیرهایی که برای ثابت نگه داشتن شماره نسخه وابستگیها در سراسر پروژه شما استفاده میشوند.
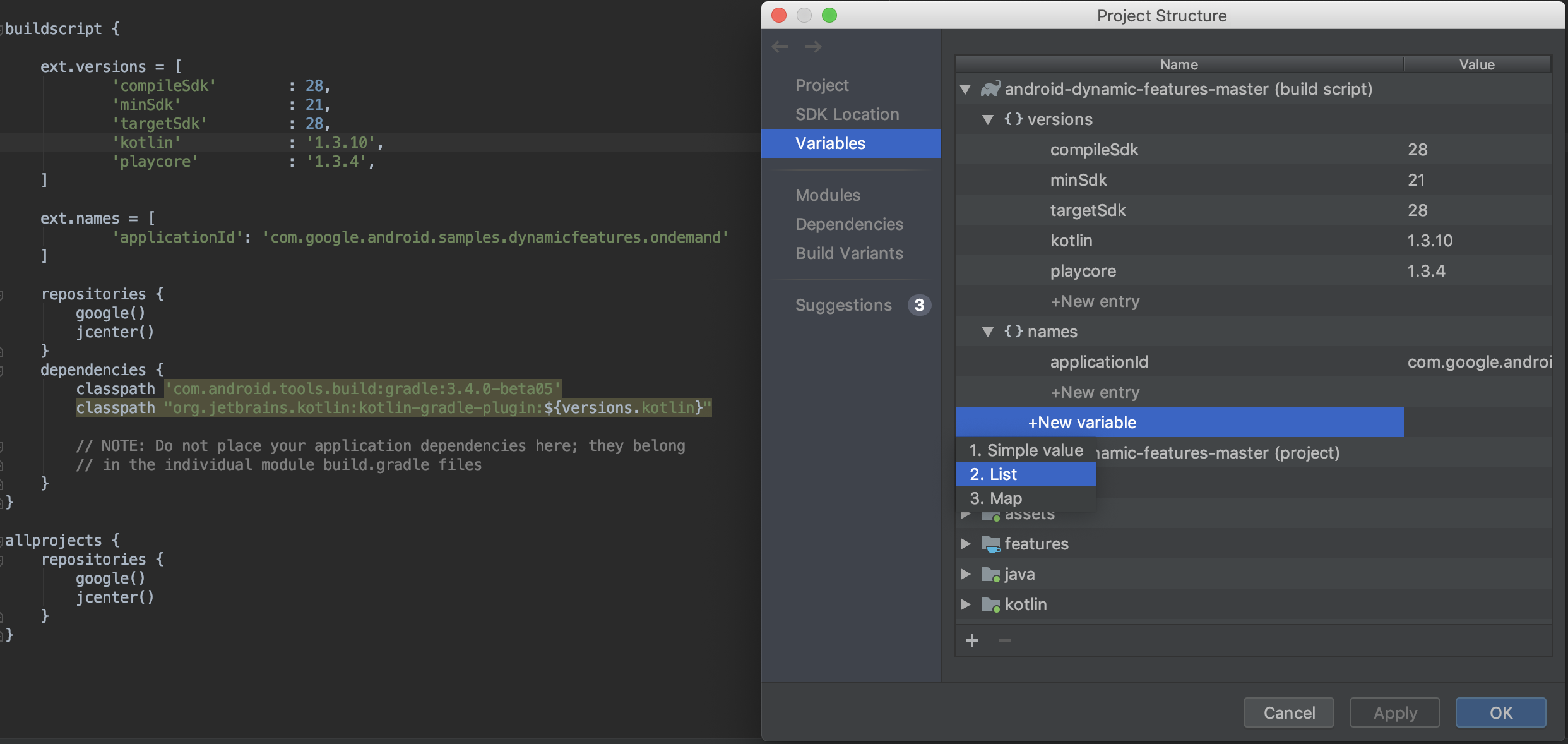
- متغیرهای ساختی که از قبل در اسکریپتهای ساخت Gradle پروژه شما وجود دارند را به سرعت مشاهده و ویرایش کنید.
- متغیرهای ساخت جدید را در سطح پروژه یا ماژول مستقیماً از PSD اضافه کنید.
توجه: اگر فایلهای پیکربندی ساخت موجود شما مقادیر را از طریق اسکریپتهای پیچیده Groovy اختصاص میدهند، ممکن است نتوانید آن مقادیر را از طریق PSD ویرایش کنید. علاوه بر این، نمیتوانید فایلهای ساخت نوشته شده در Kotlin را با استفاده از PSD ویرایش کنید.
ماژولها
ویژگیهایی را که برای همه نسخههای ساخت در یک ماژول موجود اعمال میشوند، پیکربندی کنید یا ماژولهای جدیدی را از بخش ماژولها به پروژه خود اضافه کنید. به عنوان مثال، در اینجا میتوانید ویژگیهای defaultConfig را پیکربندی کنید یا پیکربندیهای امضا را مدیریت کنید.
وابستگیها
با دنبال کردن مراحل زیر، هر وابستگی را در نمودار وابستگی پروژه خود، همانطور که توسط Gradle در حین همگامسازی پروژه حل شده است، بررسی و تجسم کنید:
- در پنل سمت چپ PSD، گزینه Dependencies را انتخاب کنید.
- در پنل ماژولها ، ماژولی را که میخواهید وابستگیهای حلشدهی آن را بررسی کنید، انتخاب کنید.
- در سمت راست PSD، پنل Resolved Dependencies را که در زیر نشان داده شده است، باز کنید.
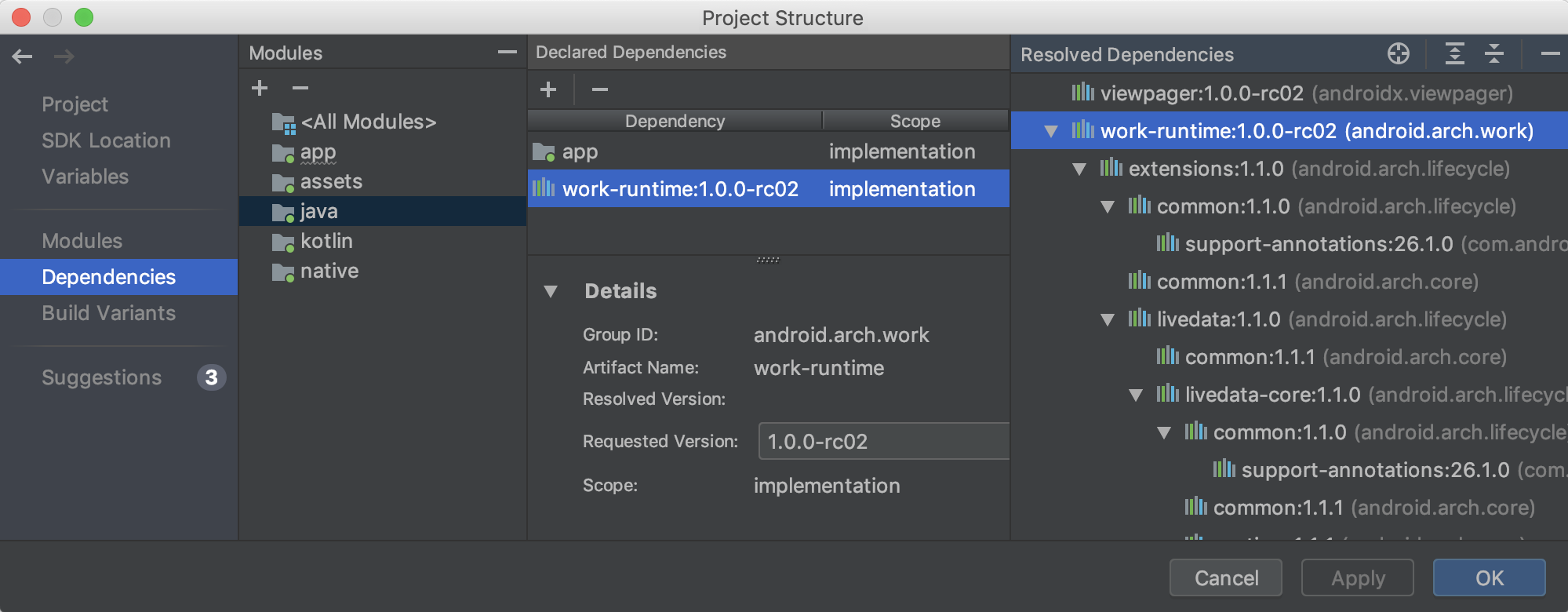
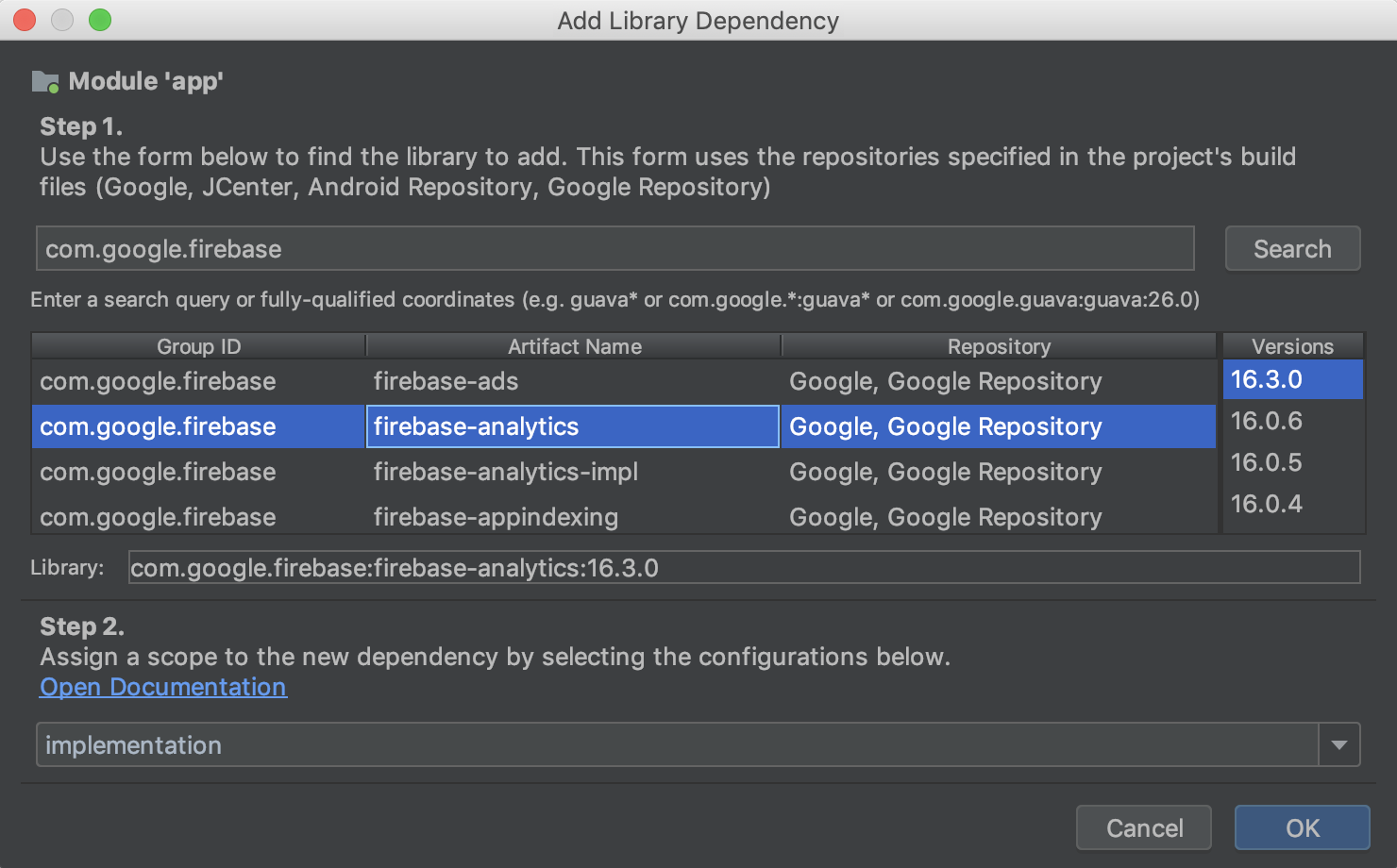
همچنین میتوانید با انتخاب یک ماژول از بخش وابستگیهای PSD، کلیک بر روی دکمه (+) در بخش وابستگیهای اعلامشده و انتخاب نوع وابستگی که میخواهید اضافه کنید، به سرعت وابستگیها را جستجو و به پروژه خود اضافه کنید.
Depending on the type of dependency you select, you should see a dialog, similar to the one below, that helps you add the dependency to the module.
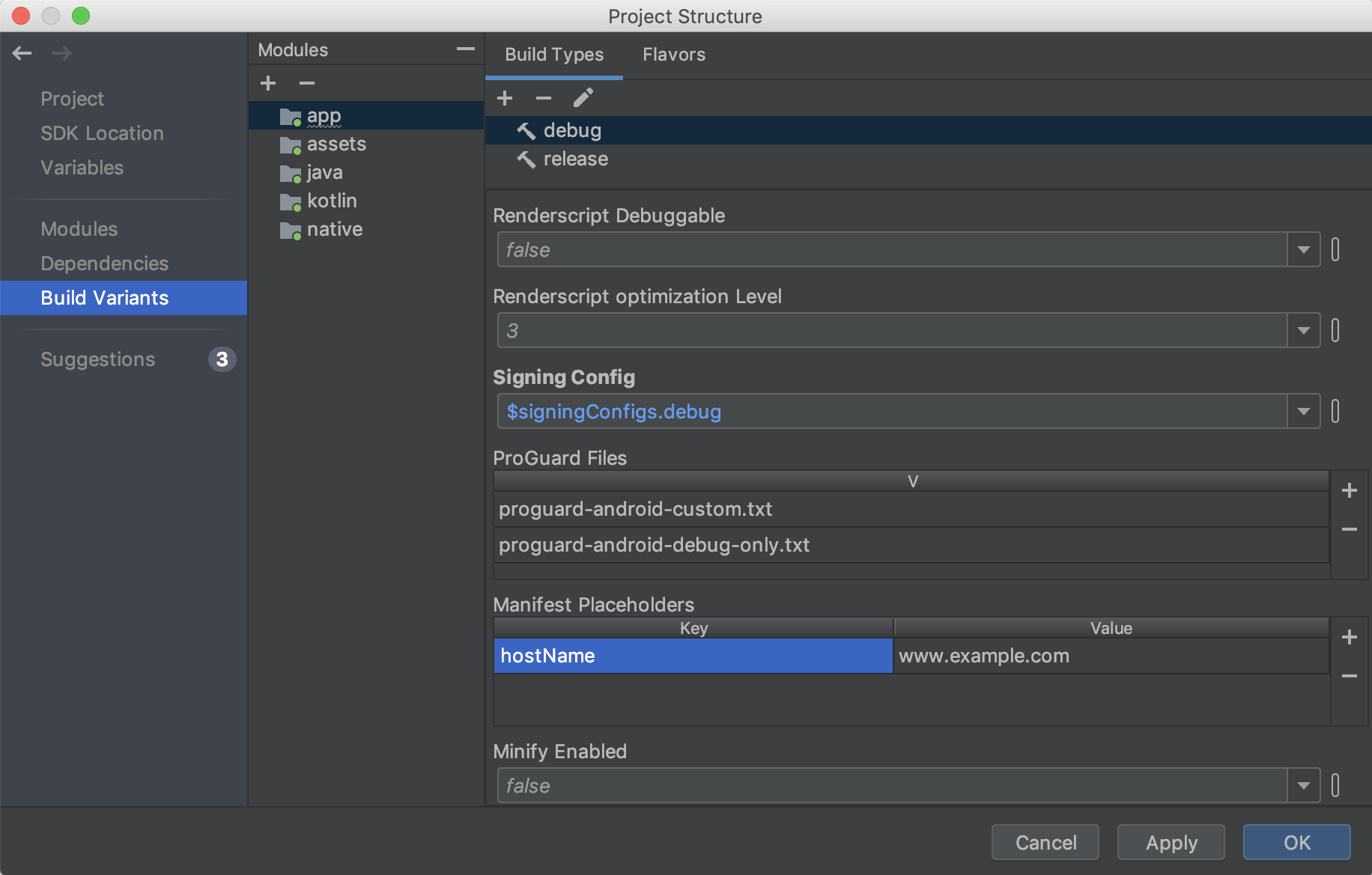
Build Variants
In this section of the PSD, create and configure build variants and product flavors for each module in your project. You can add manifest placeholders, add ProGuard files, and assign signing keys, and more.
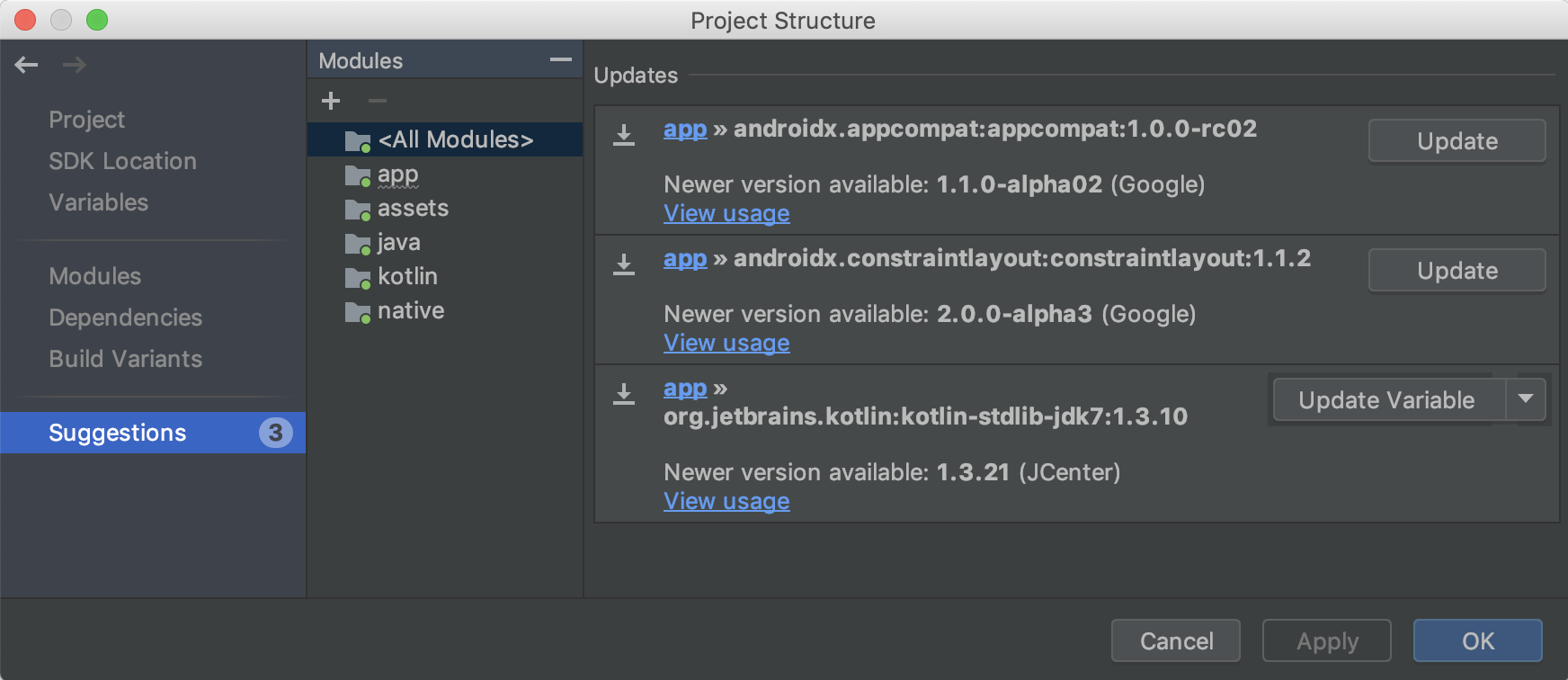
پیشنهادات
See suggested updates for project dependencies and build variables in the Suggestions section, as shown below.
New Resource Manager
Resource Manager is a new tool window for importing, creating, managing, and using resources in your app. You can open the tool window by selecting View > Tool Windows > Resource Manager from the menu bar. The Resource Manager allows you to do the following:
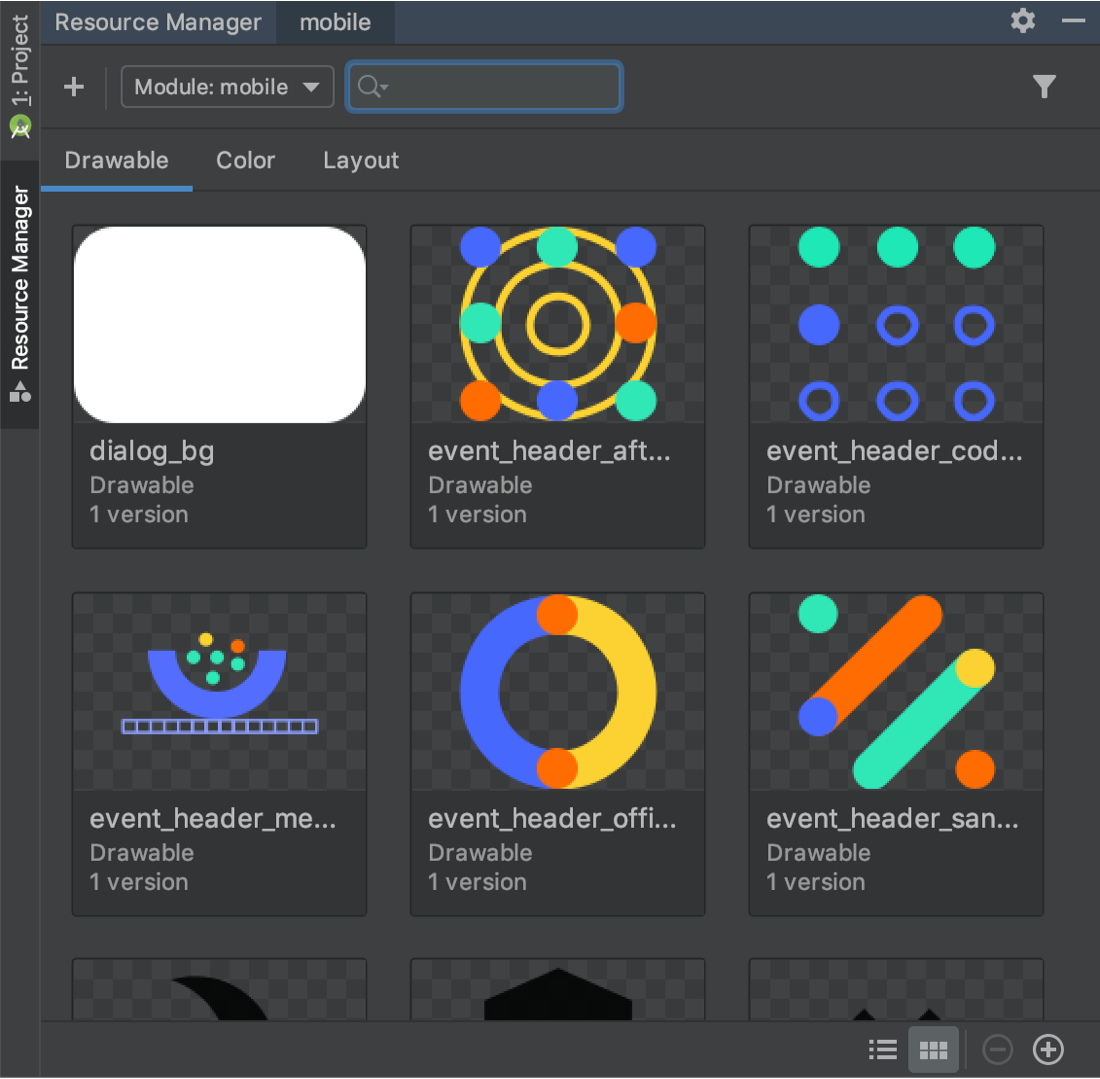
- Visualize resources: You can preview drawables, colors, and layouts to quickly find the resources you need.
- Bulk import: You can import multiple drawable assets at once by either dragging and dropping them into the Resource Manager tool window or by using the Import drawables wizard. To access the wizard, select the (+) button at the top-left corner of the tool window, and then select Import Drawables from the drop down menu.
- Convert SVGs into
VectorDrawableobjects: You can use the Import Drawables wizard to convert your SVG images intoVectorDrawableobjects. - Drag and drop assets: From the Resource Manager tool window, you can drag and drop drawables onto both the design and XML views of the Layout Editor.
- View alternative versions: You can now view alternative versions of your resources by double-clicking a resource within the Tool window. This view shows the different versions you have created and the qualifiers that were included.
- Tile and list views: You can change the view within the tool window to visualize your resources in different arrangements.
To learn more, read the guide about how to Manage app resources .
Checking build IDs when profiling and debugging APKs
When you provide debugging symbol files for the .so shared libraries inside your APK, Android Studio verifies that the build ID of the provided symbol files match the build ID of the .so libraries inside the APK.
If you build the native libraries in your APK with a build ID, Android Studio checks whether the build ID in your symbol files matches the build ID in your native libraries and rejects the symbol files if there is a mismatch. If you did not build with a build ID, then providing incorrect symbol files may cause problems with debugging.
R8 enabled by default
R8 integrates desugaring, shrinking, obfuscating, optimizing, and dexing all in one step—resulting in noticeable build performance improvements . R8 was introduced in Android Gradle plugin 3.3.0 and is now enabled by default for both app and Android library projects using plugin 3.4.0 and higher.
The image below provides a high-level overview of the compile process before R8 was introduced.
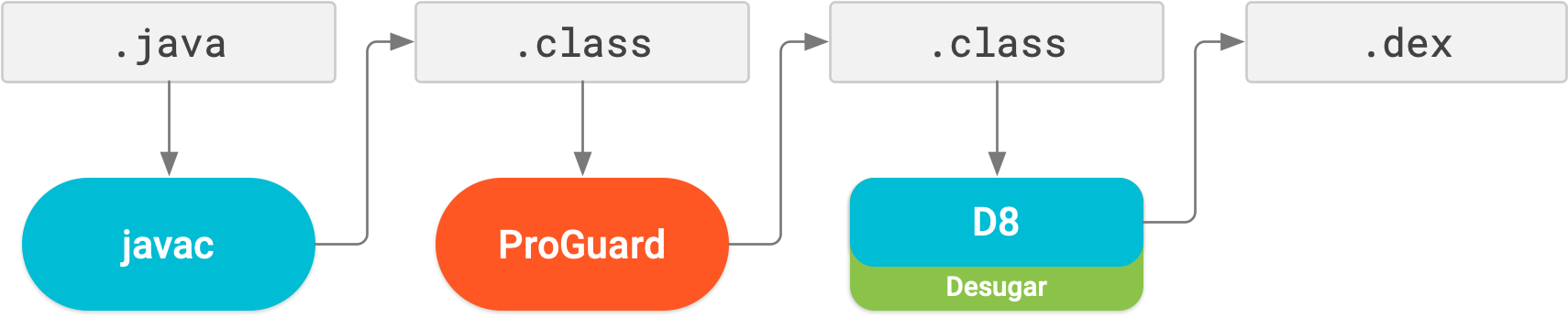
Now, with R8, desugaring, shrinking, obfuscating, optimizing, and dexing (D8) are all completed in one step, as illustrated below.
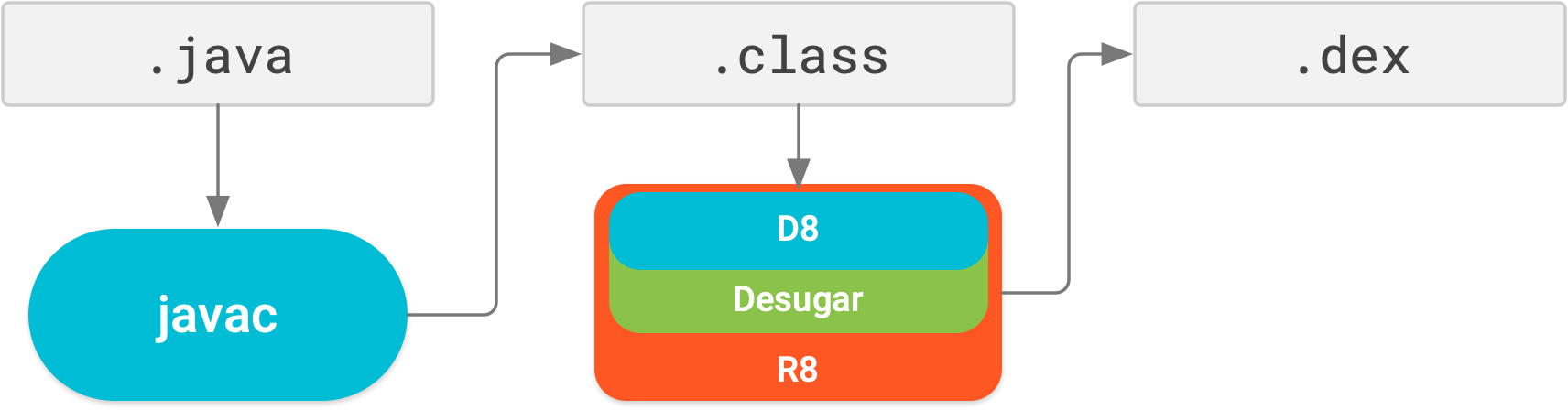
Keep in mind, R8 is designed to work with your existing ProGuard rules, so you'll likely not need to take any actions to benefit from R8. However, because it's a different technology to ProGuard that's designed specifically for Android projects, shrinking and optimization may result in removing code that ProGuard may have not. So, in this unlikely situation, you might need to add additional rules to keep that code in your build output.
If you experience issues using R8, read the R8 compatibility FAQ to check if there's a solution to your issue. If a solution isn't documented, please report a bug . You can disable R8 by adding one of the following lines to your project's gradle.properties file:
# Disables R8 for Android Library modules only.
android.enableR8.libraries = false
# Disables R8 for all modules.
android.enableR8 = false
Note: For a given build type, if you set useProguard to false in your app module's build.gradle file, the Android Gradle plugin uses R8 to shrink your app's code for that build type, regardless of whether you disable R8 in your project's gradle.properties file.
Navigation Editor now supports all argument types
All argument types supported by the Navigation component are now supported in the Navigation Editor. For more information on supported types, see Pass data between destinations .
Layout Editor improvements {:#layout-editor}
The Attributes pane in the Layout Editor has been streamlined into a single page with sections you can expand to reveal attributes you can configure. The Attributes pane also includes the following updates:
- A new Declared Attributes section lists the attributes the layout file specifies and allows you to quickly add new ones.
- The Attributes pane now also features indicators next to each attribute that are solid when the attribute's value is a resource reference and empty otherwise.
- Attributes with errors or warnings are now highlighted. Red highlights indicate errors (for example, when you use invalid layout values) and orange highlights indicate warnings (for example, when you use hard-coded values).
New intention action to quickly import dependencies
If you start using certain Jetpack and Firebase classes in your code, a new intention action suggests adding the required Gradle library dependency to your project, if you haven't already done so. For example, if you reference the WorkManager class without first importing the required android.arch.work:work-runtime dependency, an intention action lets you do so easily in a single click, as shown below.
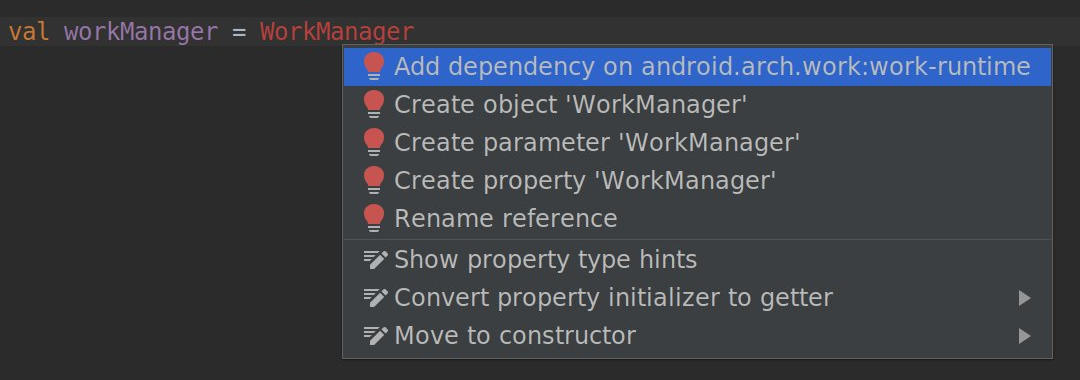
In particular, because Jetpack repackaged the support library into discrete packages that are easier to manage and update, this intention action helps you quickly add only the dependencies you need for the Jetpack components you want to use.
3.3 (January 2019)
Android Studio 3.3 is a major release that includes a variety of new features and improvements.
3.3.2 (March 2019)
This minor update includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of notable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog .
3.3.1 (February 2019)
This minor update includes various bug fixes and performance improvements.
IntelliJ IDEA 2018.2.2
The core Android Studio IDE has been updated with improvements from IntelliJ IDEA through the 2018.2.2 release .
Android Gradle plugin updates
For information on what's new in the Android Gradle plugin, see its release notes .
Navigation Editor
The Navigation Editor lets you quickly visualize and build navigation into your app by using the Navigation Architecture Component .
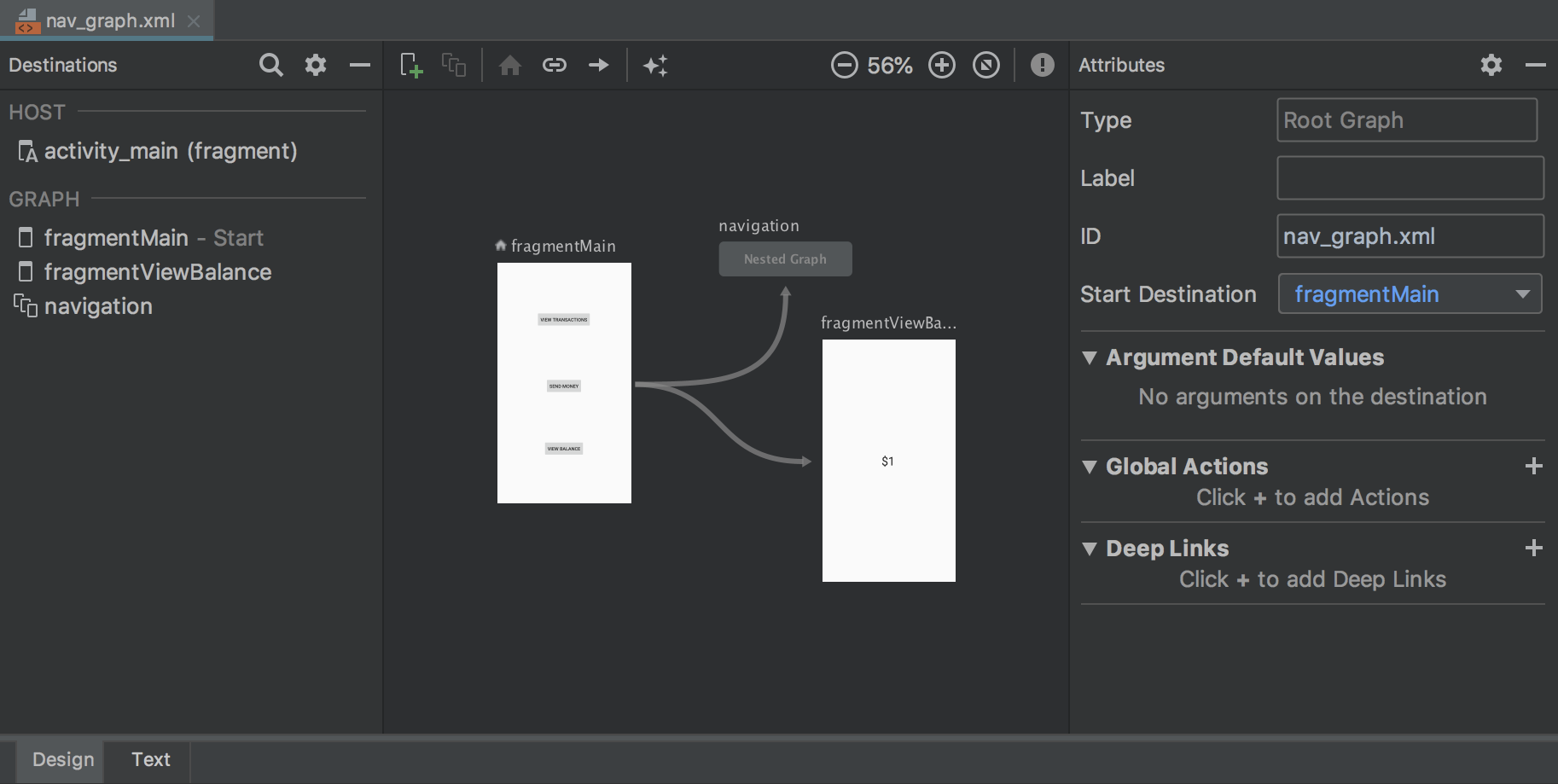
For more information, see Implement navigation with the Navigation Architecture Component .
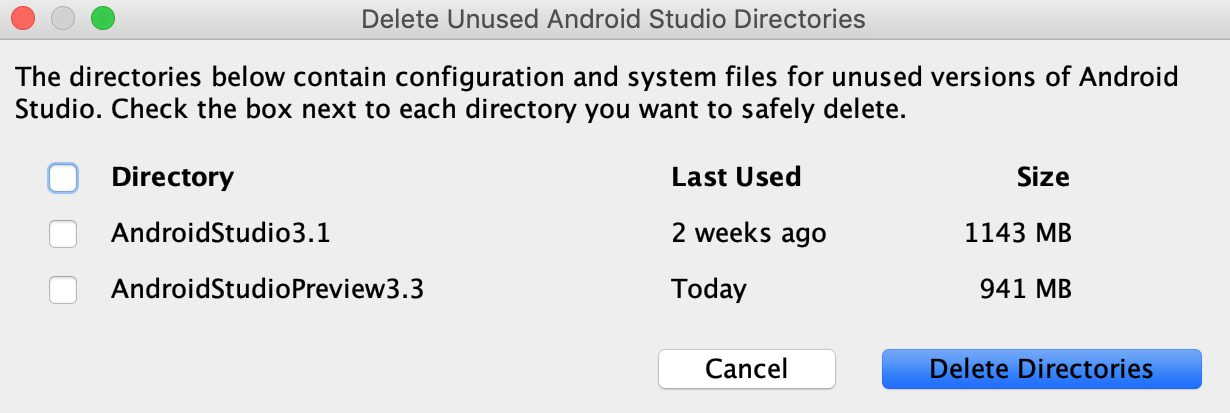
Delete unused Android Studio directories
When you run a major version of Android Studio for the first time, it looks for directories containing caches, settings, indices, and logs for versions of Android Studio for which a corresponding installation can't be found. The Delete Unused Android Studio Directories dialog then displays locations, sizes, and last-modified times of these unused directories and provides an option to delete them.
The directories Android Studio considers for deletion are listed below:
- Linux:
~/.AndroidStudio[Preview] XY - Mac:
~/Library/{Preferences, Caches, Logs, Application Support}/AndroidStudio[Preview] XY - Windows:
%USER%.AndroidStudio[Preview] XY
Lint improvements
Lint, when invoked from Gradle, is significantly faster—larger projects can expect lint to run up to four times faster.
Create New Project wizard
The Create New Project wizard has a new look and contains updates that help streamline the creation of new Android Studio projects.
For more information, see Create a project .
Profiler updates
Android Studio 3.3 includes updates to several of the individual profilers.
Improved performance
Based on user feedback, rendering performance while using the profilers has been greatly improved. Please continue to provide feedback , especially if you continue to see performance issues.
Profiler memory allocation tracking options
To improve app performance while profiling, the Memory Profiler now samples memory allocations periodically by default. If desired, you can change this behavior by using the Allocation Tracking dropdown when testing on devices running Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher.
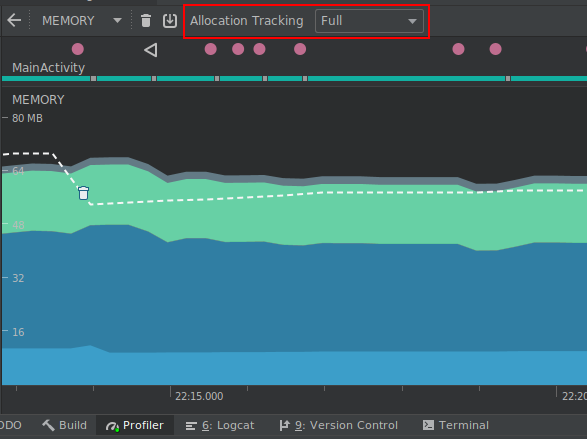
Using the Allocation Tracking dropdown, you can choose from the following modes:
Full: captures all object memory allocations. Note that if you have an app that allocates a lot of objects, you might see significant performance issues while profiling.
Sampled: captures a periodic sample of object memory allocations. This is the default behavior and has less impact on app performance while profiling. You might encounter some performance issues with apps that allocate a lot of objects within a short time period.
Off: turns memory allocation off. If not already selected, this mode is enabled automatically while taking a CPU recording and then returned to the previous setting when the recording is finished. You can change this behavior in the CPU recording configuration dialog.
The tracking affects both Java objects and JNI references.
Inspect frame rendering data
In the CPU Profiler , you can now inspect how long it takes your Java app to render each frame on the main UI thread and RenderThread. This data might be useful when investigating bottlenecks that cause UI jank and low framerates. For example, each frame that takes longer than the 16ms required to maintain a smooth framerate is displayed in red.
To see frame rendering data, record a trace using a configuration that allows you to Trace System Calls . After recording the trace, look for info about each frame along the timeline for the recording under the section called FRAMES , as shown below.
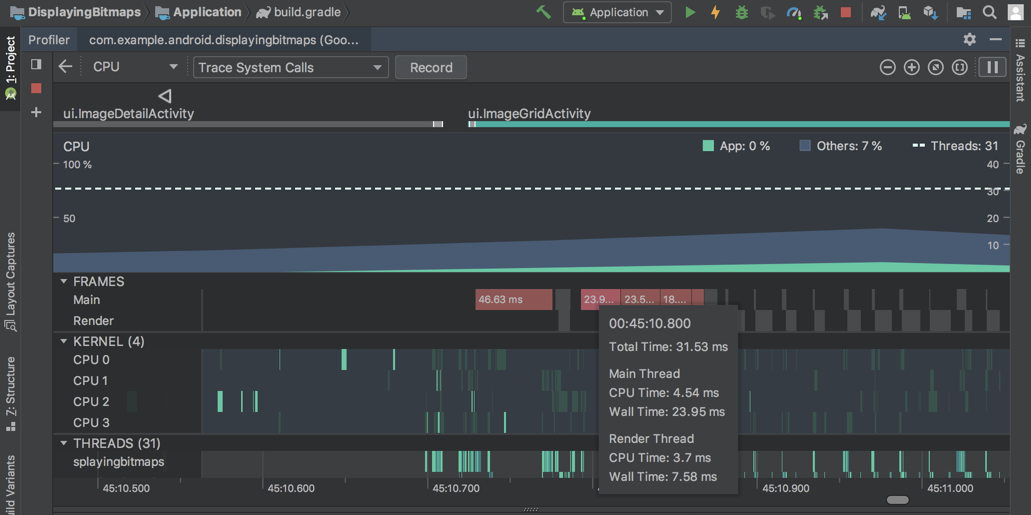
To learn more about investigating and fixing framerate issues, read Slow rendering .
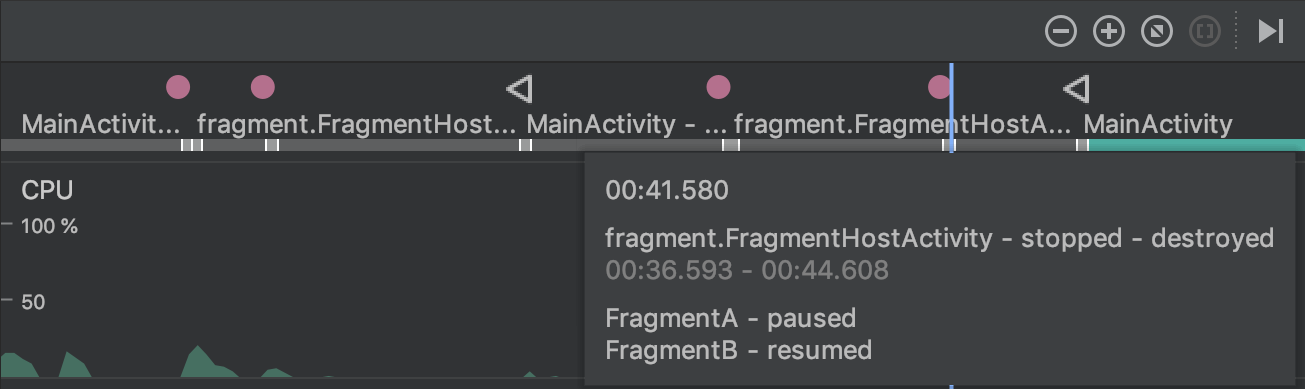
Fragments in the event timeline
The event timeline now shows when fragments are attached and detached. Additionally, when you hover over a fragment, a tooltip shows you the fragment status.
View formatted text for connection payloads in the Network profiler
Previously, the Network profiler displayed only raw text from connection payloads. Android Studio 3.3 now formats certain text types by default, including JSON, XML, and HTML. In the Response and Request tabs, click the View Parsed link to display formatted text, and click the View Source link to display raw text.
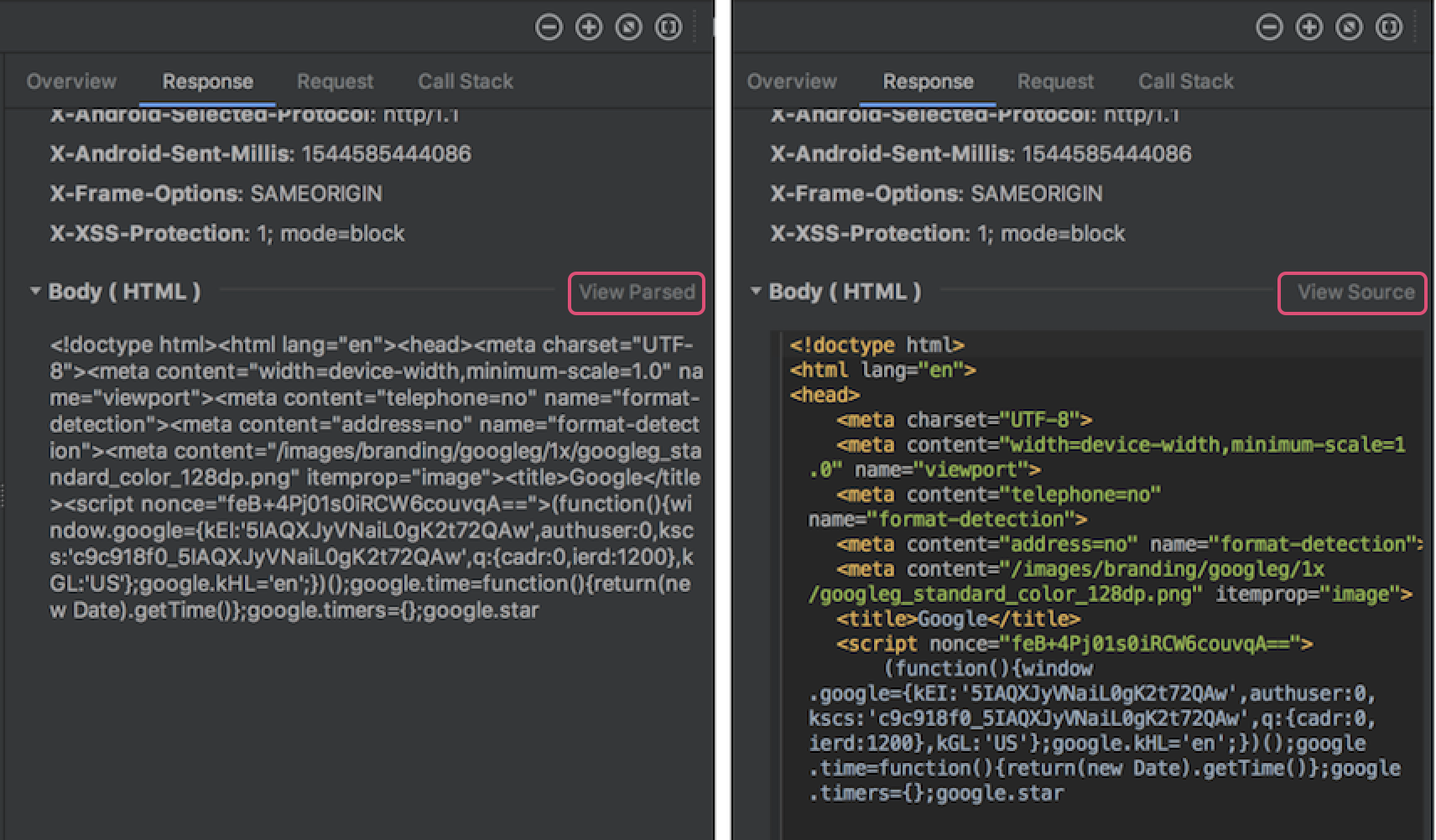
For more information, see Inspect network traffic with Network Profiler .
Automatic downloading of SDK components
When your project needs an SDK component from the SDK platforms, NDK, or CMake, Gradle now attempts to automatically download the required packages as long as you've previously accepted any related license agreements using the SDK Manager.
For more information, see Auto-download missing packages with Gradle .
Support for Clang-Tidy
Android Studio now includes support for static code analysis using Clang-Tidy for projects that include native code. To enable support for Clang-Tidy, update your NDK to r18 or higher.
You can then enable or re-enable the inspections by opening the Settings or Preferences dialog and navigating to Editor > Inspections > C/C++ > General > Clang-Tidy . When selecting this inspection in the Settings or Preferences dialog, you can also see the list of Clang-Tidy checks that are enabled and disabled under the Option section of the right-most panel. To enable additional checks , add them to the list and click Apply .
To configure Clang-Tidy with additional options , click Configure Clang-Tidy Checks Options and add them in the dialog that opens.
Removal of options for C++ customization
The following options have been removed from the Customize C++ Support dialog:
- Exceptions Support (-fexceptions)
- Runtime Type Information Support (-ftti)
The respective behaviors are enabled for all projects created through Android Studio.
CMake version 3.10.2
CMake version 3.10.2 is now included with SDK Manager. Note that Gradle still uses version 3.6.0 by default.
To specify a CMake version for Gradle to use, add the following to your module's build.gradle file:
android {
...
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
...
version "3.10.2"
}
}
}
For more information on configuring CMake in build.gradle , see Manually configure Gradle .
New “+” syntax to specify minimum CMake versions
When specifying a version of CMake in your main module's build.gradle file, you can now append a “+” to match the behavior of CMake's cmake_minimum_required() command.
Caution: Using "+" syntax with other build dependencies is discouraged, as dynamic dependencies can cause unexpected version updates and difficulty resolving version differences.
Android App Bundles now support Instant Apps
Android Studio now lets you build Android App Bundles with full support for Google Play Instant . In other words, you can now build and deploy both installed app and instant experiences from a single Android Studio project and include them in a single Android App Bundle.
If you're creating a new Android Studio project using the Create New Project dialog, make sure you check the box next to Configure your project > This project will support instant apps . Android Studio then creates a new app project as it normally would, but includes the following properties in your manifest to add Instant app support to your app's base module:
<manifest ... xmlns:dist="http://schemas.android.com/apk/distribution">
<dist:module dist:instant="true" />
...
</manifest>
You can then create an instant-enabled feature module by selecting File > New > New Module from the menu bar and then selecting Instant Dynamic Feature Module from the Create New Module dialog. Keep in mind, creating this module also instant-enables your app's base module.
To deploy your app to a local device as an instant experience, edit your run configuration and check the box next to General > Deploy as instant app .
Single-variant project sync
Syncing your project with your build configuration is an important step in letting Android Studio understand how your project is structured. However, this process can be time-consuming for large projects. If your project uses multiple build variants, you can now optimize project syncs by limiting them to only the variant you have currently selected.
You need to use Android Studio 3.3 or higher with Android Gradle plugin 3.3.0 or higher to enable this optimization. When you meet these requirements, the IDE prompts you to enable this optimization when you sync your project. The optimization is also enabled by default on new projects.
To enable this optimization manually, click File > Settings > Experimental > Gradle ( Android Studio > Preferences > Experimental > Gradle on a Mac) and select the Only sync the active variant checkbox.
Note: This optimization currently supports projects that include only the Java programming language. If, for example, the IDE detects Kotlin or C++ code in your project, it does not automatically enable this optimization, and you should not enable it manually.
For more information, see Enable single-variant project sync .
Provide quick feedback
If you've opted into sharing usage statistics to help improve Android Studio, you'll see these two new icons in the status bar at the bottom of the IDE window:


Simply click the icon that best represents your current experience with the IDE. When you do so, the IDE sends usage statistics that allow the Android Studio team to better understand your sentiment. In some cases, such as when you indicate a negative experience with the IDE, you'll have an opportunity to provide additional feedback.
If you haven't already done so, you can enable sharing usage statistics by opening the Settings dialog Preferences on a Mac), navigating to Appearance & Behavior > System Settings > Data Sharing and checking Send usage statistics to Google .
3.2 (September 2018)
Android Studio 3.2 is a major release that includes a variety of new features and improvements.
3.2.1 (October 2018)
This update to Android Studio 3.2 includes the following changes and fixes:
- The bundled Kotlin version is now 1.2.71.
- The default build tools version is now 28.0.3.
- In the Navigation library, argument types have been renamed from
typetoargType. - The following bugs have been fixed:
- When using the Data Binding library, variable names with underscores were causing compilation errors.
- CMake was causing IntelliSense and other CLion features to fail.
- Adding a
SliceProviderwas causing compilation errors in projects that did not useandroidx.*libraries. - Some Kotlin unit tests were not being run.
- An issue with data binding was causing a
PsiInvalidElementAccessException. -
<merge>elements were sometimes causing the Layout Editor to crash.
3.2.0 known issues
Note: These issues have been resolved in Android Studio 3.2.1
We strongly recommend against using Kotlin version 1.2.70.
Kotlin version 1.2.61 fixes a bug that can cause Android Studio to hang, but Kotlin 1.2.70 does not include this fix .
Kotlin versions 1.2.71 and later, however, do include this fix.
Although you typically don't need to specify the build tools version, when using Android Gradle plugin 3.2.0 with
renderscriptSupportModeEnabledset totrue, you need to include the following in each module'sbuild.gradlefile:android.buildToolsVersion "28.0.3"
What's New Assistant
A new assistant informs you about the latest changes in Android Studio.
The assistant opens when you start Android Studio after a fresh installation or update if it detects that there is new information to show. You can also open the assistant by choosing Help > What's new in Android Studio .
Android Jetpack
Android Jetpack helps to accelerate Android development with components, tools, and guidance that eliminate repetitive tasks and enable you to more quickly and easily build high-quality, testable apps. Android Studio includes the following updates to support Jetpack. For more information, see the Jetpack documentation .
Navigation Editor
The new Navigation Editor integrates with the navigation components of Android Jetpack to provide a graphical view for creating the navigation structure of your app. The Navigation Editor simplifies the design and implementation of navigation between in-app destinations.
In Android Studio 3.2, the Navigation Editor is an experimental feature. To enable the Navigation Editor, click File > Settings ( Android Studio > Preferences on Mac), select the Experimental category in the left pane, check the box next to Enable Navigation Editor , and restart Android Studio.
To learn more, read the Navigation Editor documentation .
AndroidX migration
As part of Jetpack, we are migrating the Android Support Libraries to a new Android extension library using the androidx namespace. For more information, see the AndroidX overview .
Android Studio 3.2 helps you through this process with a new migration feature.
To migrate an existing project to AndroidX, choose Refactor > Migrate to AndroidX . If you have any Maven dependencies that have not migrated to the AndroidX namespace, the Android Studio build system also automatically converts those project dependencies.
The Android Gradle plugin provides the following global flags that you can set in your gradle.properties file:
-
android.useAndroidX: When set totrue, this flag indicates that you want to start using AndroidX from now on. If the flag is absent, Android Studio behaves as if the flag were set tofalse. -
android.enableJetifier: When set totrue, this flag indicates that you want to have tool support (from the Android Gradle plugin) to automatically convert existing third-party libraries as if they were written for AndroidX. If the flag is absent, Android Studio behaves as if the flag were set tofalse.
Both flags are set to true when you use the Migrate to AndroidX command.
If you want to start using AndroidX libraries immediately and don't need to convert existing third-party libraries, you can set the android.useAndroidX flag to true and the android.enableJetifier flag to false .
بسته نرمافزاری اندروید
Android App Bundle is a new upload format that includes all of your app's compiled code and resources, but defers APK generation and signing to the Google Play Store.
Google Play's new app serving model then uses your app bundle to generate and serve optimized APKs for each user's device configuration, so each user downloads only the code and resources they need to run your app. You no longer need to build, sign, and manage multiple APKs, and users get smaller, more optimized downloads.
Additionally, you can add feature modules to your app project and include them in your app bundle. Your users can then download and install your app's features on demand.
To build a bundle, choose Build > Build Bundle(s) / APK(s) > Build Bundle(s) .
For more information, including instructions for building and analyzing an Android App Bundle, see Android App Bundle .
Sample data in Layout Editor
Many Android layouts have runtime data that can make it difficult to visualize the look and feel of a layout during the design stage of app development. You can now easily see a preview of your view in the Layout Editor filled with sample data. When you add a view, a button appears below the view in the Design window. Click this button to set the design-time view attributes. You can choose from a variety of sample data templates and specify the number of sample items with which to populate the view.
appears below the view in the Design window. Click this button to set the design-time view attributes. You can choose from a variety of sample data templates and specify the number of sample items with which to populate the view.
To try using sample data, add a RecyclerView to a new layout, click the design-time attributes button below the view, and choose a selection from the carousel of sample data templates.
below the view, and choose a selection from the carousel of sample data templates.
Slices
Slices provide a new way to embed portions of your app's functionality in other user interface surfaces on Android. For example, Slices make it possible to show app functionality and content in Google Search suggestions.
Android Studio 3.2 has a built-in template to help you to extend your app with the new Slice Provider APIs, as well as new lint checks to ensure that you're following best practices when constructing the Slices.
To get started right-click a project folder and choose New > Other > Slice Provider .
To learn more, including how to test your Slice interactions, read the Slices getting started guide .
Kotlin 1.2.61
Android Studio 3.2 bundles Kotlin 1.2.61, and the new Android SDK integrates better with Kotlin. For more information, see the Android Developers blog .
IntelliJ IDEA 2018.1.6
The core Android Studio IDE has been updated with improvements from IntelliJ IDEA through the 2018.1.6 release .
Android profilers
Try the following new Android Profiler features in Android Studio 3.2.
جلسات
You can now save Profiler data as sessions to revisit and inspect later. The profiler keeps your session data until you restart the IDE.
When you record a method trace or capture a heap dump , the IDE adds that data (along with your app's network activity) as a separate entry to the current session, and you can easily switch back and forth between recordings to compare data.
System Trace
In the CPU Profiler , select the new System Trace configuration to inspect your device's system CPU and thread activity. This trace configuration is built on systrace and is useful for investigating system-level issues, such as UI jank.
While using this trace configuration, you can visually mark important code routines in the profiler timeline by instrumenting your C/C++ code with the native tracing API or your Java code with the Trace class.
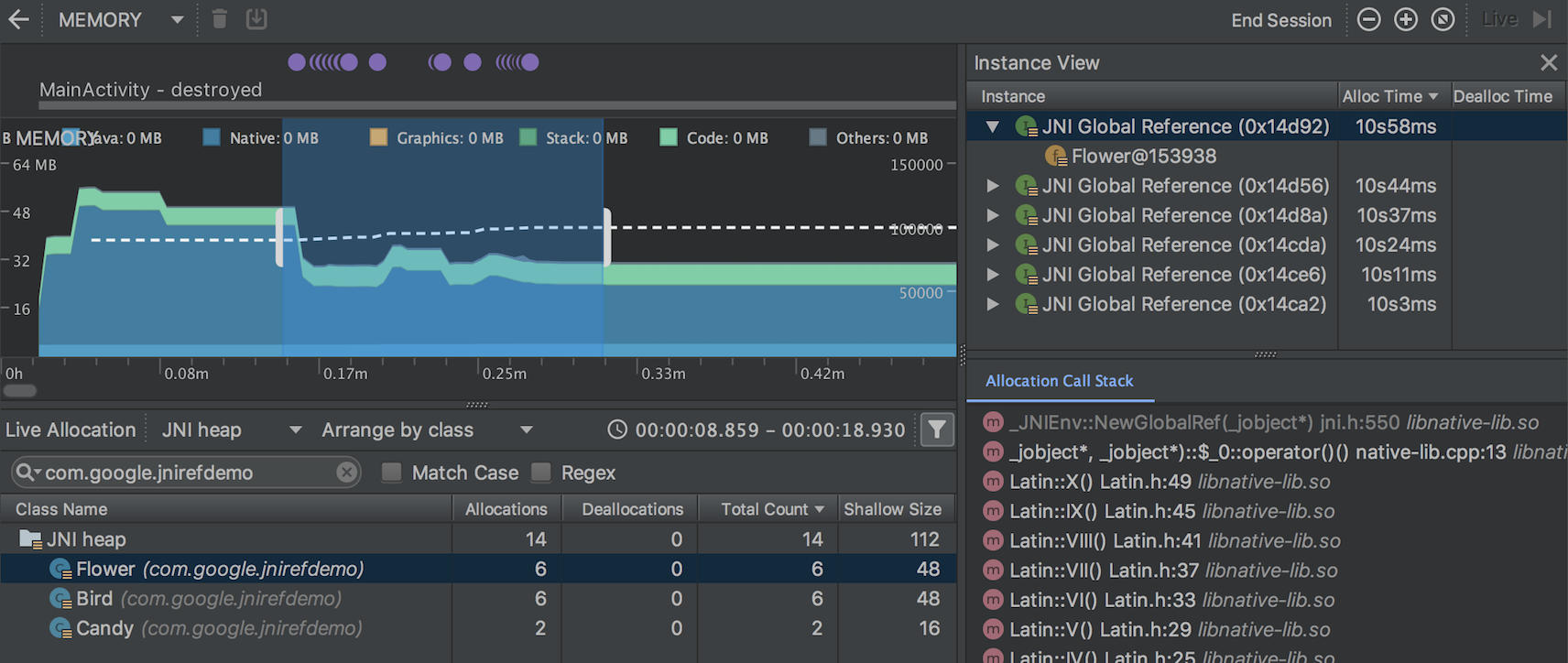
Inspect JNI references in the Memory Profiler
If you deploy your app to a device running Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher, you can now inspect memory allocations for your app's JNI code using the Memory Profiler .
While your app is running, select a portion of the timeline that you want to inspect and select JNI heap from the drop-down menu above the class list, as shown below. You can then inspect objects in the heap as you normally would and double-click objects in the Allocation Call Stack tab to see where the JNI references are allocated and released in your code.
Import, export, and inspect memory heap dump files
You can now import, export, and inspect .hprof memory heap dump files created with the Memory Profiler .
Import your .hprof file by clicking Start new profiler session in the profiler's Sessions pane and then selecting Load from file . You can then inspect its data in the Memory Profiler as you would any other heap dump.
in the profiler's Sessions pane and then selecting Load from file . You can then inspect its data in the Memory Profiler as you would any other heap dump.
To save heap dump data to review later, use the Export Heap Dump button at the right of the Heap Dump entry in the Sessions pane. In the Export As dialog that appears, save the file with the .hprof filename extension.
Record CPU activity during app startup
You can now record CPU activity during your app's startup, as follows:
- Select Run > Edit Configurations from the main menu.
- Under the Profiling tab of your desired run configuration, check the box next to Start recording a method trace on startup .
- Select a CPU recording configuration to use from the dropdown menu.
- Deploy your app to a device running Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher by selecting Run > Profile .
Export CPU traces
After you record CPU activity with the CPU Profiler, you can export the data as a .trace file to share with others or inspect later.
To export a trace after you've recorded CPU activity, do the following:
- Right-click on the recording you want to export from the CPU timeline.
- Select Export trace from the dropdown menu.
- Navigate to where you want to save the file and click Save .
Import and inspect CPU trace files
You can now import and inspect .trace files created with the Debug API or CPU Profiler . (Currently, you can't import System Trace recordings.)
Import your trace file by clicking Start new profiler session in the profiler's Sessions pane and then selecting Load from file . You can then inspect its data in the CPU Profiler similar to how you normally would, with the following exceptions:
in the profiler's Sessions pane and then selecting Load from file . You can then inspect its data in the CPU Profiler similar to how you normally would, with the following exceptions:
- CPU activity is not represented along the CPU timeline.
- The thread activity timeline indicates only where trace data is available for each thread and not actual thread states (such as running, waiting, or sleeping).
Record CPU activity using the Debug API
You can now start and stop recording CPU activity in the CPU Profiler by instrumenting your app with the Debug API . After you deploy your app to a device, the profiler automatically starts recording CPU activity when your app calls startMethodTracing(String tracePath) , and the profiler stops recording when your app calls stopMethodTracing() . While recording CPU activity that's triggered using this API, the CPU Profiler shows Debug API as the selected CPU recording configuration.
Energy Profiler
The Energy Profiler displays a visualization of the estimated energy usage of your app, as well as system events that affect energy usage, such as wakelocks, alarms, and jobs.
The Energy Profiler appears as a new row at the bottom of the Profiler window when you run your app on a connected device or Android Emulator running Android 8.0 (API 26) or higher.
Click the Energy row to maximize the Energy Profiler view. Place your mouse pointer over a bar in the timeline to see a breakdown of energy use by CPU, network, and location (GPS) resources, as well as relevant system events.
System events that affect energy usage are indicated in the System timeline below the Energy timeline. Details of system events within the specified time range are shown in the event pane when you select a time range in the Energy timeline.
To see the call stack and other details for a system event, such as a wakelock, select it in the event pane. To go to the code responsible for a system event, double-click the entry in the call stack.
Lint checking
Android Studio 3.2 includes many new and improved features for lint checking .
The new lint checks help you to find and identify common code problems, ranging from warnings about potential usability issues to high-priority errors regarding potential security vulnerabilities.
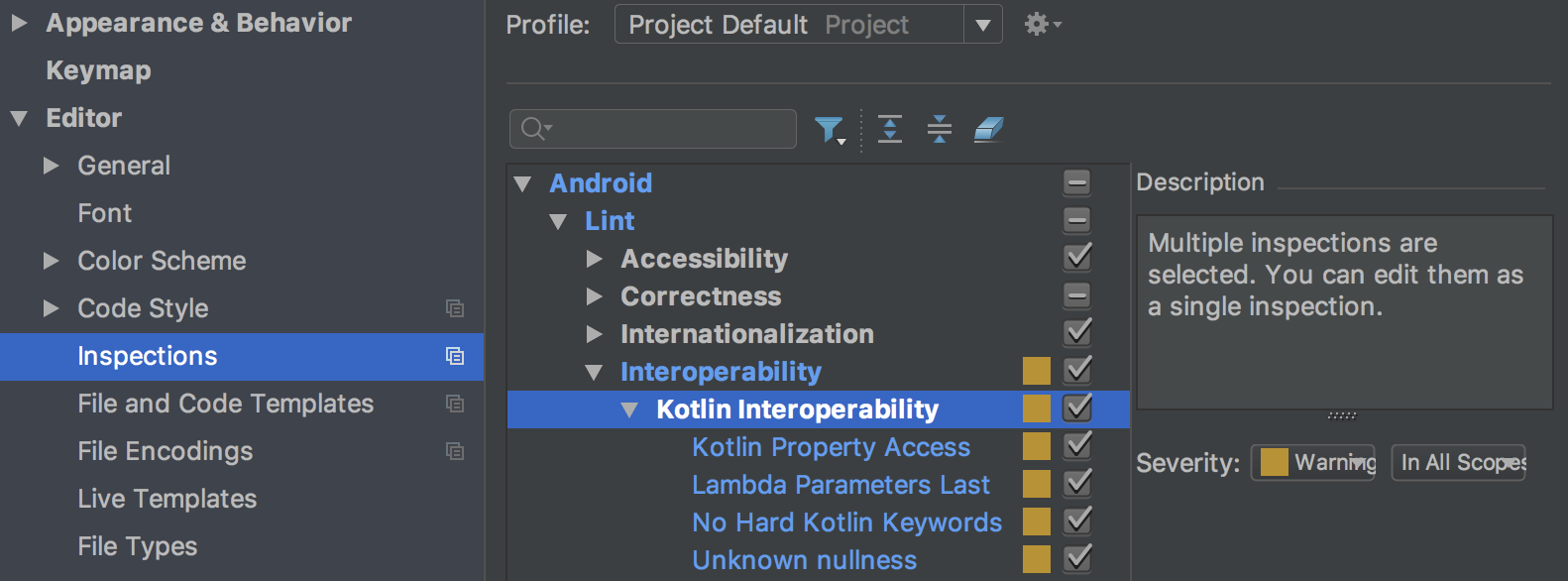
Lint checks for Java/Kotlin interoperability
To make sure that your Java code interoperates well with your Kotlin code, new lint checks enforce the best practices described in the Kotlin Interop Guide . Examples of these checks include looking for the presence of Nullability annotations, use of Kotlin hard keywords, and placing lambda parameters last.
To enable these checks, click File > Settings ( Android Studio > Preferences on Mac) to open the Settings dialog, navigate to the Editor > Inspections > Android > Lint > Interoperability > Kotlin Interoperability section, and select the rules that you want to enable.
To enable these checks for command-line builds, add the following to your build.gradle file:
android {
lintOptions {
check 'Interoperability'
}
}
Lint checks for Slices
New lint checks for Slices help to ensure that you are constructing Slices correctly. For example, lint checks warn you if you have not assigned a primary action to a Slice.
New Gradle target
Use the new lintFix Gradle task to apply all of the safe fixes suggested by the lint check directly to the source code. An example of a lint check that suggests a safe fix to apply is SyntheticAccessor .
Metadata updates
Various metadata, such as the service cast check, have been updated for lint checks to work with Android 9 (API level 28).
Warning if running lint on a new variant
Lint now records which variant and version a baseline is recorded with, and lint warns you if you run it on a different variant than the one with which the baseline was created.
Improvements to existing lint checks
Android Studio 3.2 includes many improvements to existing lint checks. For example, the resource cycle checks now apply to additional resource types, and the translation detector can find missing translations on the fly, in the editor.
Issue IDs more discoverable
Issue IDs are now shown in more places now, including in the Inspection Results window. This makes it easier for you to find the information that you need to enable or disable specific checks through lintOptions in build.gradle .
For more information, see Configure lint options with Gradle .
Data Binding V2
Data Binding V2 is now enabled by default and is compatible with V1. This means that, if you have library dependencies that you compiled with V1, you can use them with projects using Data Binding V2. However, note that projects using V1 cannot consume dependencies that were compiled with V2.
D8 desugaring
In Android Studio 3.1, we integrated the desugaring step into the D8 tool as an experimental feature, reducing overall build time. In Android Studio 3.2, desugaring with D8 is turned on by default.
New code shrinker
R8 is a new tool for code shrinking and obfuscation that replaces ProGuard. You can start using the preview version of R8 by including the following in your project's gradle.properties file:
android.enableR8 = true
Changed default ABIs for multi-APKs
When building multiple APKs that each target a different ABI, the plugin no longer generates APKs for the following ABIs by default: mips , mips64 , and armeabi .
If you want to build APKs that target these ABIs, you must use NDK r16b or lower and specify the ABIs in your build.gradle file, as shown below:
splits { abi { include 'armeabi', 'mips', 'mips64' ... } }
splits { abi { include("armeabi", "mips", "mips64") ... } }
Note: This behavior change is also included in Android Studio 3.1 RC1 and higher.
Improved editor features for CMake build files
If you use CMake to add C and C++ code to your project , Android Studio now includes improved editor features to help you to edit your CMake build scripts, such as the following:
- Syntax highlighting and code completion: The IDE now highlights and suggests code completion for common CMake commands. Additionally, you can navigate to a file by clicking it while pressing the Control key (Command on Mac).
- Code reformatting: You can now use IntelliJ's code reformat option to apply code styles to your CMake build scripts.
- Safe refactoring: The IDE's built-in refactoring tools now also check if you are renaming or deleting files that you reference in your CMake build scripts.
Navigate external header files
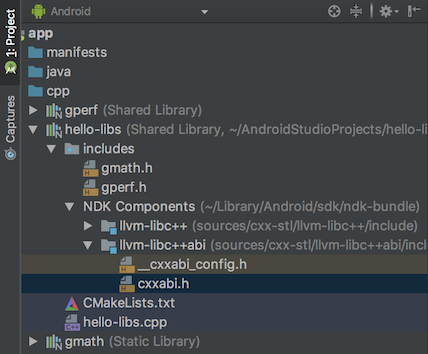
When using the Project window in previous versions of Android Studio, you could navigate and inspect only the header files that belong to libraries you build from a local project. With this release, you can now also view and inspect header files included with external C/C++ library dependencies that you import into your app project.
If you already include C/C++ code and libraries in your project , open the Project window on the left side of the IDE by selecting View > Tool Windows > Project from the main menu and select Android from the drop-down menu. In the cpp directory, all headers that are within the scope of your app project are organized under the include node for each of your local C/C++ library dependencies, as shown below.
Native multidex enabled by default
Previous versions of Android Studio enabled native multidex when deploying the debug version of an app to a device running Android API level 21 or higher. Now, whether you're deploying to a device or building an APK for release, the Android plugin for Gradle enables native multidex for all modules that set minSdkVersion=21 or higher.
AAPT2 moved to Google's Maven repository
Beginning with Android Studio 3.2, the source for AAPT2 (Android Asset Packaging Tool 2) is Google's Maven repository.
To use AAPT2, make sure that you have a google() dependency in your build.gradle file, as shown here:
buildscript { repositories { google() // here jcenter() } dependencies { classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.2.0' } } allprojects { repositories { google() // and here jcenter() } }
buildscript { repositories { google() // here jcenter() } dependencies { classpath("com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.2.0") } } allprojects { repositories { google() // and here jcenter() } }
The new version of AAPT2 fixes many issues, including improved handling of non-ASCII characters on Windows.
Removal of configuration on demand
The Configure on demand preference has been removed from Android Studio.
Android Studio no longer passes the --configure-on-demand argument to Gradle.
ADB Connection Assistant
The new ADB Connection Assistant provides step-by-step instructions to help you set up and use a device over the Android Debug Bridge (ADB) connection.
To start the assistant, choose Tools > Connection Assistant .
The ADB Connection Assistant provides instructions, in-context controls, and a list of connected devices in a series of pages in the Assistant panel.
Emulator improvements
You can now save and load snapshots of an AVD (Android virtual device) at any time in the Android Emulator, making it fast and easy to return an emulated device to a known state for testing. When you edit an AVD using the AVD Manager, you can specify which AVD snapshot to load when the AVD starts.
Controls for saving, loading, and managing AVD snapshots are now in the Snapshots tab in the emulator's Extended controls window.
For details, see Snapshots .
For additional information on what's new and changed in the Emulator, see the Emulator release notes .
3.1 (March 2018)
Android Studio 3.1.0 is a major release that includes a variety of new features and improvements.
3.1.4 (August 2018)
This update to Android Studio 3.1 includes the following changes and fixes:
- The bundled Kotlin is now version 1.2.50.
- New projects are created with
kotlin-stdlib-jdk* artifacts, rather than withkotlin-stdlib-jre*artifacts, which are deprecated. - R8 parsing of ProGuard rules has been improved.
- The following bugs have been fixed:
- Attempting to run the Kotlin Main class failed with an error:
"Error: Could not find or load main class..." - R8 entered an infinite loop while performing certain optimizations.
- Using the Rerun failed tests command in the Run window sometimes incorrectly returned the message "No tests were found".
- D8 did not correctly handle
invoke-virtualinstances, causing a crash with aVerifyError:invoke-super/virtual can't be used on private method - The Data Binding compiler was depending on an old version of
com.android.tools:annotations. The compiler now uses tools annotations from the base project when available. - Android Studio crashed during fragment transitions when using profilers.
- The debugger crashed when debugging a layout with a text box.
- D8 failed to read some ZIP files with special characters.
3.1.3 (June 2018)
This update to Android Studio 3.1 includes fixes for the following bugs:
- Memory leaks caused Android Studio to become slow and unresponsive after you had been using the Layout Editor. This update includes fixes for most of these issues. We intend to release another update soon to address additional memory leaks.
- Some applications built with D8 crashed on some Verizon Ellipsis tablets.
- Installation of applications built with D8 failed with an
INSTALL_FAILED_DEXOPTerror on devices running Android 5.0 or 5.1 (API level 21 or 22). - Some applications that used the OkHttp library and were built with D8 crashed on devices running Android 4.4 (API level 19).
- Android Studio sometimes failed to start, with a
ProcessCanceledExceptionduring class initialization forcom.intellij.psi.jsp.JspElementType.
3.1.2 (April 2018)
This update to Android Studio 3.1 includes fixes for the following bugs:
- In some cases, Android Studio hung indefinitely during exit.
Builds configured with source sets failed with the following message when Instant Run was enabled:
"The SourceSet name is not recognized by the Android Gradle Plugin."- When Instant Run was enabled, builds of new Kotlin projects failed when triggered by the Run command.
- During editing of the
build.gradlefile, there was sometimes a noticeable delay between typing a character and the character appearing on the screen. Build failures occurred during dexing in some projects with large numbers of modules or external dependencies, with the following error message:
"RejectedExecutionException: Thread limit exceeded replacing blocked worker"- The computation of the D8 main DEX list was not taking into account some reflective invocations.
This update also includes changes that make running lint checks from Gradle much faster in some scenarios.
3.1.1 (April 2018)
This update to Android Studio 3.1 includes fixes for the following bugs:
In some cases, when a project created in Android Studio 3.0 was opened for the first time in Android Studio 3.1, the Gradle-aware Make task was removed from the Before launch area in Run/Debug Configurations . The result was that projects did not build when the Run or Debug button was clicked, which in turn caused failures such as deployment of incorrect APKs and crashes when using Instant Run.
To solve this problem, Android Studio 3.1.1 adds the Gradle-aware Make task to the run configuration for projects that are missing this entry. This modification occurs after the first Gradle sync when the project is loaded.
- The debugger crashed when debugging a layout with a text box if advanced profiling was enabled.
- Android Studio froze after you clicked Build Variants .
- AAR (Android archive) files were extracted twice, once during the Gradle sync process and once during the Gradle build process.
- Elements were missing from some vector drawables imported from SVG files.
- The warning regarding the deprecation of the
compiledependency configuration has been updated with better guidance regarding theimplementationandapiconfigurations. For details of migrating away from using thecompileconfiguration, see the documentation for the new dependency configurations .
Coding/IDE
IntelliJ 2017.3.3
The core Android Studio IDE has been updated with improvements from IntelliJ IDEA through the 2017.3.3 release. Improvements include better control flow analysis for collections and strings, improved nullability inference, new quick fixes, and much more.
For details, see the JetBrains release notes for IntelliJ IDEA versions 2017.2 and 2017.3 , as well as the JetBrains release notes for bug-fix updates .
SQL editing improvements with Room
When you use the Room database library , you can take advantage of several improvements to SQL editing:
- Code completion within a
Queryunderstands SQL tables (entities), columns, query parameters, aliases, joins, subqueries, and WITH clauses. - SQL syntax highlighting now works.
- You can right-click a table name in SQL and rename it, which also rewrites the corresponding Java or Kotlin code (including, for example, the return type of the query). Renaming works in the other direction, too, so renaming a Java class or field rewrites the corresponding SQL code.
- SQL usages are shown when using Find usages (right-click and choose Find usages from the context menu).
- To navigate to an SQL entity's declaration in Java or Kotlin code, you can hold Control (Command on Mac) while clicking the entity.
For information on using SQL with Room, see Save data in a local database using Room .
Updates to data binding
This update includes several improvements for data binding :
You can now use a
LiveDataobject as an observable field in data binding expressions. TheViewDataBindingclass now includes a newsetLifecycle()method that you use to observeLiveDataobjects.The
ObservableFieldclass can now accept otherObservableobjects in its constructor.You can preview a new incremental compiler for your data binding classes. For details of this new compiler and instructions for enabling it, see Data Binding Compiler V2 .
Benefits of the new compiler include the following:
-
ViewBindingclasses are generated by the Android Plugin for Gradle before the Java compiler. - Libraries keep their generated binding classes when the app is compiled, rather than being regenerated each time. This can greatly improve performance for multi-module projects.
-
Compiler and Gradle
D8 is the default DEX compiler
The D8 compiler is now used by default for generating DEX bytecode.
This new DEX compiler brings with it several benefits, including the following:
- Faster dexing
- Lower memory usage
- Improved code generation (better register allocation, smarter string tables)
- Better debugging experience when stepping through code
You don't need to make any changes to your code or your development workflow to get these benefits, unless you had previously manually disabled the D8 compiler.
If you set android.enableD8 to false in your gradle.properties , either delete that flag or set it to true :
android.enableD8=true
For details, see New DEX compiler .
Incremental desugaring
For projects that use Java 8 language features , incremental desugaring is enabled by default, which can improve build times.
Desugaring converts syntactic sugar into a form that the compiler can process more efficiently.
You can disable incremental desugaring by specifying the following in your project's gradle.properties file:
android.enableIncrementalDesugaring=false
Simplified output window
The Gradle Console has been replaced with the Build window, which has Sync and Build tabs.
For details about how to use the new, simplified Build window, see Monitor the build process .
Batch updates and indexing concurrency
The Gradle sync and IDE indexing processes are now much more efficient, reducing time wasted on many redundant indexing operations.
C++ and LLDB
We have made many quality and performance improvements in the coding, syncing, building, and debugging phases of C++ development. Improvements include the following:
If you work with large C++ projects, you should notice a significant improvement in the reduction of time spent building symbols. Sync time is also greatly reduced for large projects.
Performance when building and syncing with CMake has been improved through more aggressive reuse of cached results.
The addition of formatters ("pretty printers") for more C++ data structures makes LLDB output easier to read.
LLDB now works with only Android 4.1 (API level 16) and higher.
Note: Native debugging with Android Studio 3.0 or greater does not work on 32-bit Windows. If you are using 32-bit Windows and need to debug native code, use Android Studio 2.3.
کاتلین
Kotlin upgraded to version 1.2.30
Android Studio 3.1 includes Kotlin version 1.2.30 .
Kotlin code now analyzed with command-line lint check
Running lint from the command line now analyzes your Kotlin classes.
For each project that you would like to run lint on, Google's Maven repository must be included in the top-level build.gradle file. The Maven repository is already included for projects created in Android Studio 3.0 and higher.
ابزارهای عملکرد
Sample native C++ processes with CPU Profiler
The CPU Profiler now includes a default configuration to record sampled traces of your app's native threads. You can use this configuration by deploying your app to a device running Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher and then selecting Sampled (Native) from the CPU Profiler's recording configurations dropdown menu. After that, record and inspect a trace as you normally would.
You can change default settings, such as the sampling interval, by creating a recording configuration .
To switch back to tracing your Java threads, select either a Sampled (Java) or Instrumented (Java) configuration.
Filter CPU traces, memory allocation results, and heap dumps
The CPU Profiler and Memory Profiler include a search feature that allows you to filter results from recording a method trace, memory allocations, or heap dump.
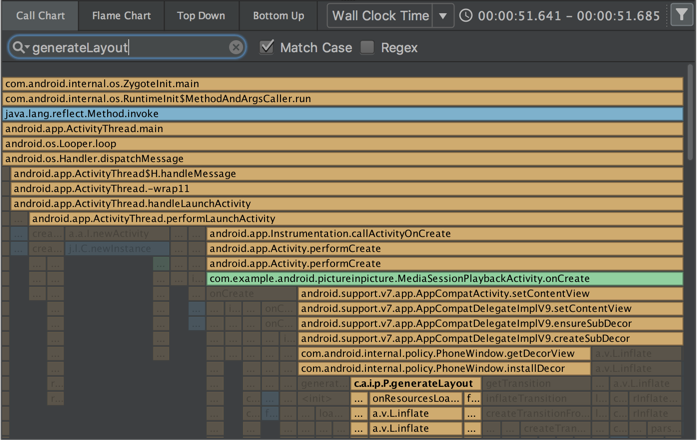
To search, click Filter in the top-right corner of the pane, type your query, and press Enter.
in the top-right corner of the pane, type your query, and press Enter.
Tip: You can also open the search field by pressing Control + F (Command + F on Mac).
In the CPU Profiler's Flame Chart tab, call stacks that include methods related to your search query are highlighted and moved to the left side of the chart.
For more information on filtering by method, class, or package name, see Record and inspect method traces .
Request tab in the Network Profiler
The Network Profiler now includes a Request tab that provides details about network requests during the selected timeline. In previous versions, the Network Profiler only provided information about network responses.
Thread View in the Network Profiler
After selecting a portion of the timeline in the Network Profiler , you can select one of the following tabs to see more detail about the network activity during that timeframe:
- Connection View : Provides the same information as previous versions of Android Studio—it lists files that were sent or received during the selected portion of the timeline across all of your app's CPU threads. For each request, you can inspect the size, type, status, and transmission duration.
- Thread View : Displays network activity of each of your app's CPU threads. This view allows you to inspect which of your app's threads are responsible for each network request.
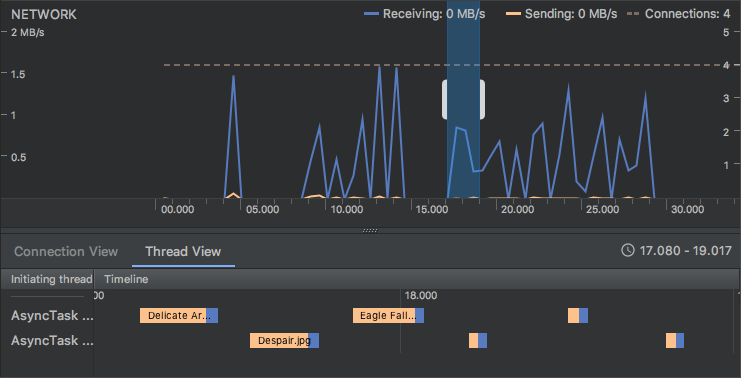
Layout Inspector
The Layout Inspector gained new features, including some functionality previously provided by the deprecated Hierarchy Viewer and Pixel Perfect tools:
- Zoom buttons and keyboard shortcuts for navigating and inspecting layouts
- Reference grid overlay
- Ability to load a reference image and use it as an overlay (useful for comparing your layout with a UI mockup)
- Render subtree preview to isolate a view in a complex layout
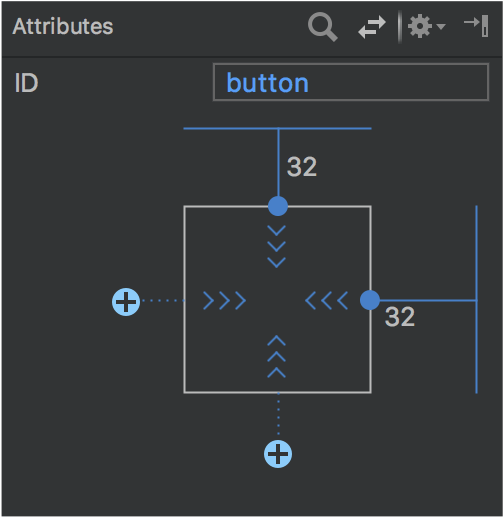
ویرایشگر طرحبندی
The Palette in the Layout Editor has received many improvements:
- Reorganization of categories for views and layouts.
- New Common category for views and layouts, which you can add to with a Favorite command.
- Improved search for views and layouts .
- New commands for opening documentation for a specific view or layout element.
You can use the new Convert view command in the Component tree or design editor to convert a view or layout to another type of view or layout.
You can now easily create constraints to items near the selected view using the new Create a connection![]() buttons in the view inspector at the top of the Attributes window.
buttons in the view inspector at the top of the Attributes window.
Run and Instant Run
The behavior of the Use same selection for future launches option in the Select deployment target dialog has been made more consistent. If the Use same selection option is enabled, then the Select deployment target dialog opens only the first time that you use the Run command until the selected device is no longer connected.
When targeting a device running Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher, Instant Run can deploy changes to resources without causing an application restart. This is possible because the resources are contained in a split APK.
شبیهساز
For details of what's new and changed in the emulator since Android Studio 3.0, see the Android Emulator release notes from version 27.0.2 through version 27.1.12 .
Major improvements include the following:
- Quick Boot snapshots for saving of emulator state and faster start, with the ability to use the Save now command to save a custom start state.
- Windowless emulator screen.
- System images for Android 8.0 (API level 26), Android 8.1 (API level 27), and Android P Developer Preview.
User interface and user experience improvements
More tooltips, keyboard shortcuts, and helpful messages
We have added tooltips and helpful message overlays in many places throughout Android Studio.
To see keyboard shortcuts for many commands, just hold the mouse pointer over a button until the tooltip appears.
Tools > Android menu removed
The Tools > Android menu has been removed. Commands that were previously under this menu have been moved.
- Many commands moved to directly under the Tools menu.
- The Sync project with gradle files command moved to the File menu.
- The Device Monitor command has been removed, as described below.
Device Monitor available from the command line
In Android Studio 3.1, the Device Monitor serves less of a role than it previously did. In many cases, the functionality available through the Device Monitor is now provided by new and improved tools.
See the Device Monitor documentation for instructions for invoking the Device Monitor from the command line and for details of the tools available through the Device Monitor.
3.0 (October 2017)
Android Studio 3.0.0 is a major release that includes a variety of new features and improvements.
macOS users: If you are updating an older version of Android Studio, you may encounter an update error dialog that says "Some conflicts were found in the installation area". Simply ignore this error and click Cancel to resume the installation.
3.0.1 (November 2017)
This is a minor update to Android Studio 3.0 that includes general bug fixes and performance improvements.
Android Plugin for Gradle 3.0.0
The new Android plugin for Gradle includes a variety of improvements and new features, but it primarily improves build performance for projects that have a large number of modules. When using the new plugin with these large projects, you should experience the following:
- Faster build configuration times due to new delayed dependency resolution.
- Variant-aware dependency resolution for only the projects and variants you are building.
- Faster incremental build times when applying simple changes to code or resources.
Note: These improvements required significant changes that break some of the plugin's behaviors, DSL, and APIs. Upgrading to version 3.0.0 might require changes to your build files and Gradle plugins.
This version also includes the following:
- Support for Android 8.0.
- Support for building separate APKs based on language resources.
- Support for Java 8 libraries and Java 8 language features (without the Jack compiler).
- Support for Android Test Support Library 1.0 (Android Test Utility and Android Test Orchestrator ).
- Improved ndk-build and cmake build speeds.
- Improved Gradle sync speed.
- AAPT2 is now enabled by default.
- Using
ndkCompileis now more restricted. You should instead migrate to using either CMake or ndk-build to compile native code that you want to package into your APK. To learn more, read Migrate from ndkcompile .
For more information about what's changed, see the Android Plugin for Gradle release notes .
If you're ready to upgrade to the new plugin, see Migrate to Android Plugin for Gradle 3.0.0 .
Kotlin support
As announced at Google I/O 2017 , the Kotlin programming language is now officially supported on Android. So with this release, Android Studio includes Kotlin language support for Android development.
You can incorporate Kotlin into your project by converting a Java file to Kotlin (click Code > Convert Java File to Kotlin File ) or by creating a new Kotlin- enabled project using the New Project wizard.
To get started, read how to add Kotlin to your project .
Java 8 language features support
You can now use certain Java 8 language features and consume libraries built with Java 8. Jack is no longer required , and you should first disable Jack to use the improved Java 8 support built into the default toolchain.
To update your project to support the new Java 8 language toolchain, update the Source Compatibility and Target Compatibility to 1.8 in the Project Structure dialog (click File > Project Structure ). To learn more, read how to use Java 8 language features .
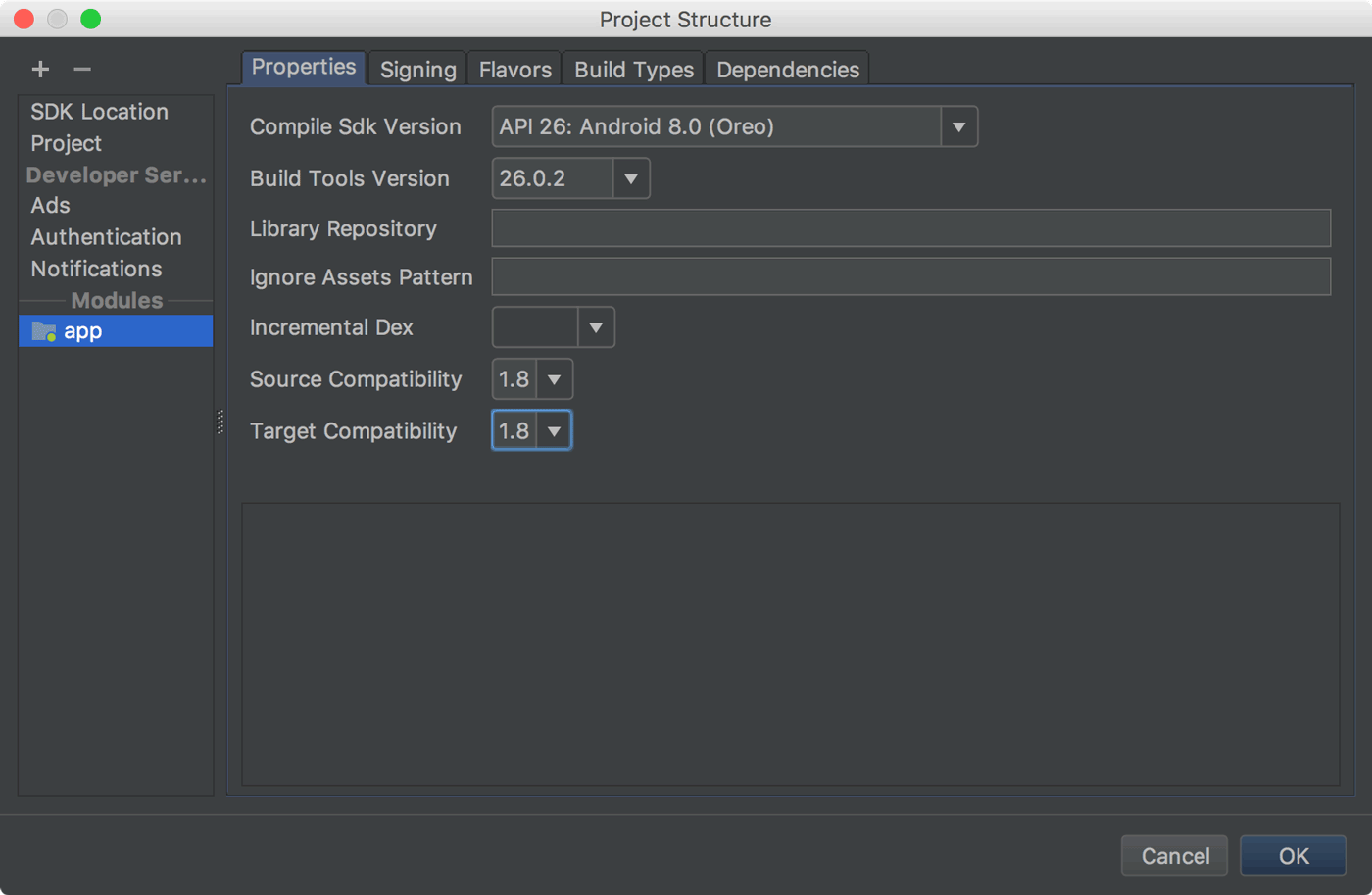
Android Profiler
The new Android Profiler replaces the Android Monitor tool and provides a new suite of tools to measure your app's CPU, memory, and network usage in realtime. You can perform sample-based method tracing to time your code execution, capture heap dumps, view memory allocations, and inspect the details of network-transmitted files.
To open, click View > Tool Windows > Android Profiler (or click Android Profiler in the toolbar).
The event timeline at the top of the window shows touch events, key presses, and activity changes so you have more context to understand other performance events in the timeline.
Note: The Logcat view also moved to a separate window (it was previously inside Android Monitor, which was removed).
From the Android Profiler's overview timeline, click on the CPU , MEMORY , or NETWORK timelines to access the corresponding profiler tools.
CPU Profiler
The CPU Profiler helps you analyze the CPU thread usage of your app by triggering a sample or instrumented CPU trace. Then, you can troubleshoot CPU performance issues using a variety of data views and filters.
For more information, see the CPU Profiler guide .
Memory Profiler
The Memory Profiler helps you identify memory leaks and memory churn that can lead to stutter, freezes, and even app crashes. It shows a realtime graph of your app's memory use, lets you capture a heap dump, force garbage collections, and track memory allocations.
For more information, see the Memory Profiler guide .
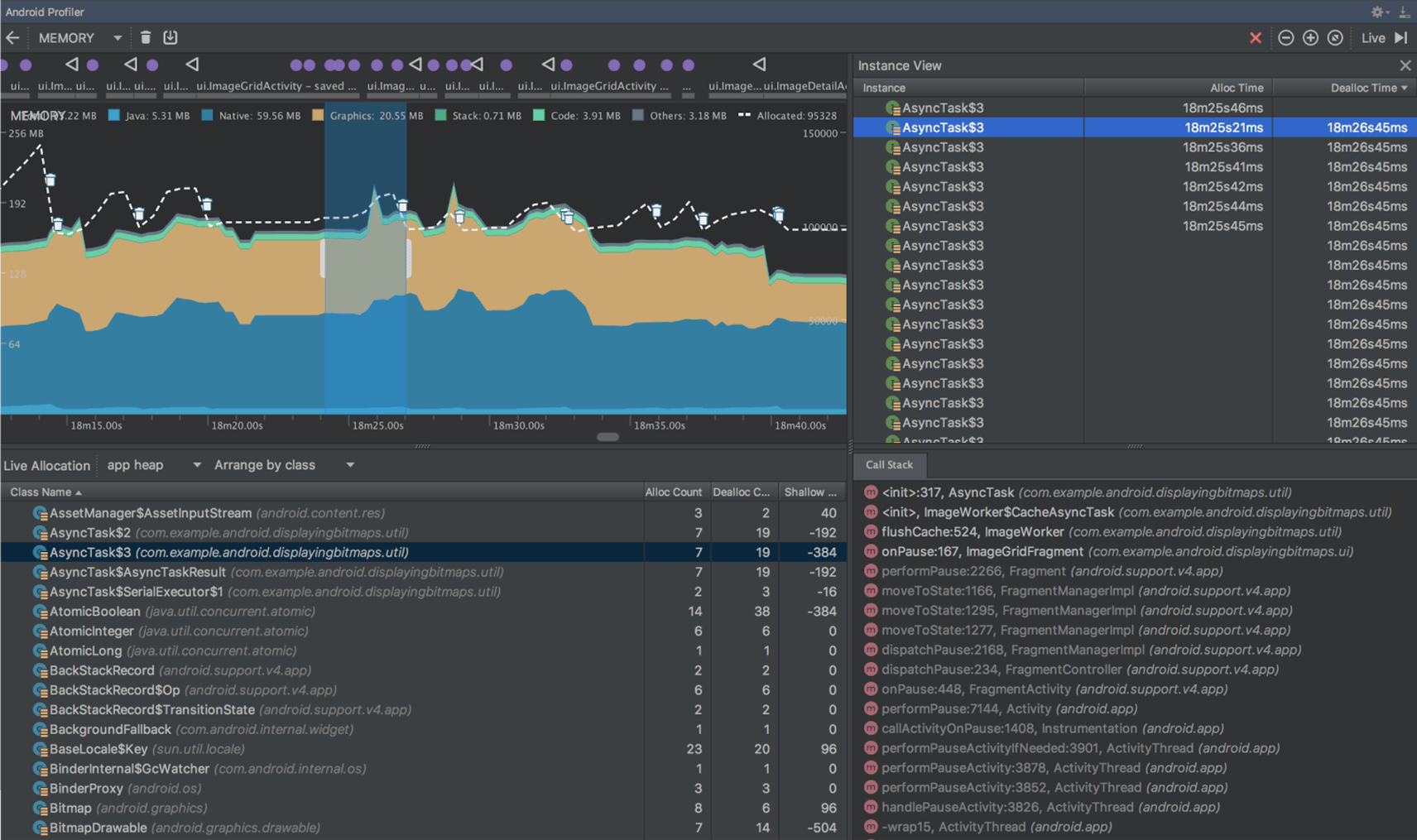
Network Profiler
The Network Profiler allows you to monitor the network activity of your app, inspect the payload of each of your network requests, and link back to the code that generated the network request.
For more information, see the Network Profiler guide .
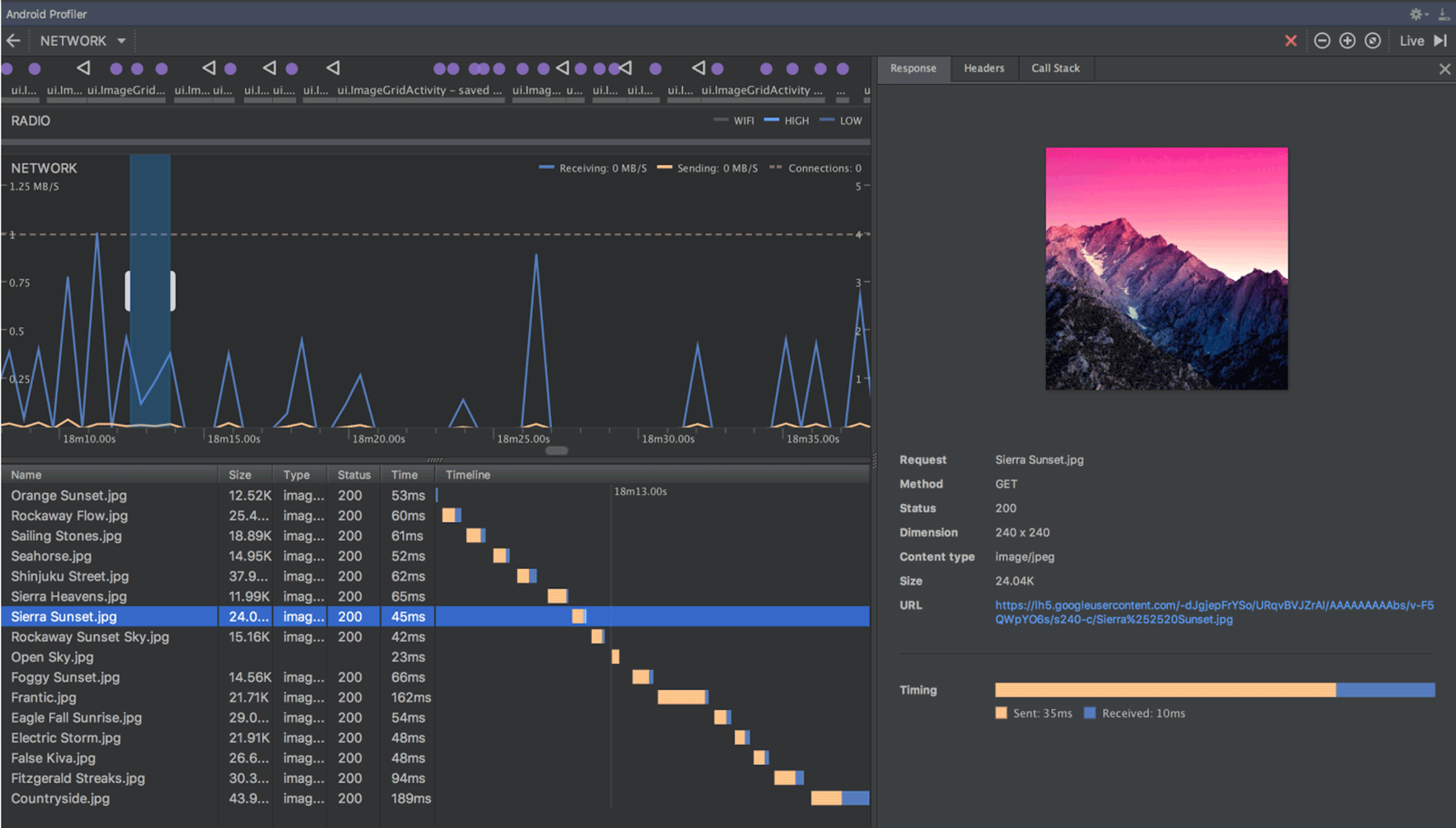
APK profiling and debugging
Android Studio now allows you to profile and debug any APK without having to build it from an Android Studio project—as long as the APK is built to enable debugging and you have access to the debug symbols and source files.
To get started, click Profile or debug APK from the Android Studio Welcome screen. Or, if you already have a project open, click File > Profile or debug APK from the menu bar. This displays the unpacked APK files, but it does not decompile the code. So, to properly add breakpoints and view stack traces, you need to attach Java source files and native debug symbols.
For more information, see Profile and Debug Pre-built APKs .
Device File Explorer
The new Device File Explorer allows you to inspect your connected device's filesystem, and transfer files between the device and your computer. This replaces the filesystem tool available in DDMS.
To open, click View > Tool Windows > Device File Explorer .
For more information, see the Device File Explorer guide .
Instant Apps support
New support for Android Instant Apps allows you to create Instant Apps in your project using two new module types : Instant App modules and Feature modules (these require that you install the Instant Apps Development SDK ).
Android Studio also includes a new modularize refactoring action to help you add support for Instant Apps in an existing project. For example, if you want to refactor your project to place some classes in an Instant App feature module, select the classes in the Project window and click Refactor > Modularize . In the dialog that appears, select the module where the classes should go and click OK .
And when you're ready to test your Instant App, you can build and run your Instant App module on a connected device by specifying the Instant App's URL within the run configuration launch options : Select Run > Edit Configurations , select your Instant App module, and then set the URL under Launch Options .
For more information, see Android Instant Apps .
Android Things modules
New Android Things templates in the New Project and New Module wizards to help you start developing for Android-powered IOT devices.
For more information, see how to create an Android Things project .
Adaptive Icons wizard
Image Asset Studio now supports vector drawables and allows you to create adaptive launcher icons for Android 8.0 while simultaneously creating traditional icons ("Legacy" icons) for older devices.
To start, right-click on the res folder in your project, and then click New > Image Asset . In the Asset Studio window, select Launcher Icons (Adaptive and Legacy) as the icon type.
Note: You must set compileSdkVersion to 26 or higher to use adaptive launcher icons.
For more information, read about Adaptive Icons .
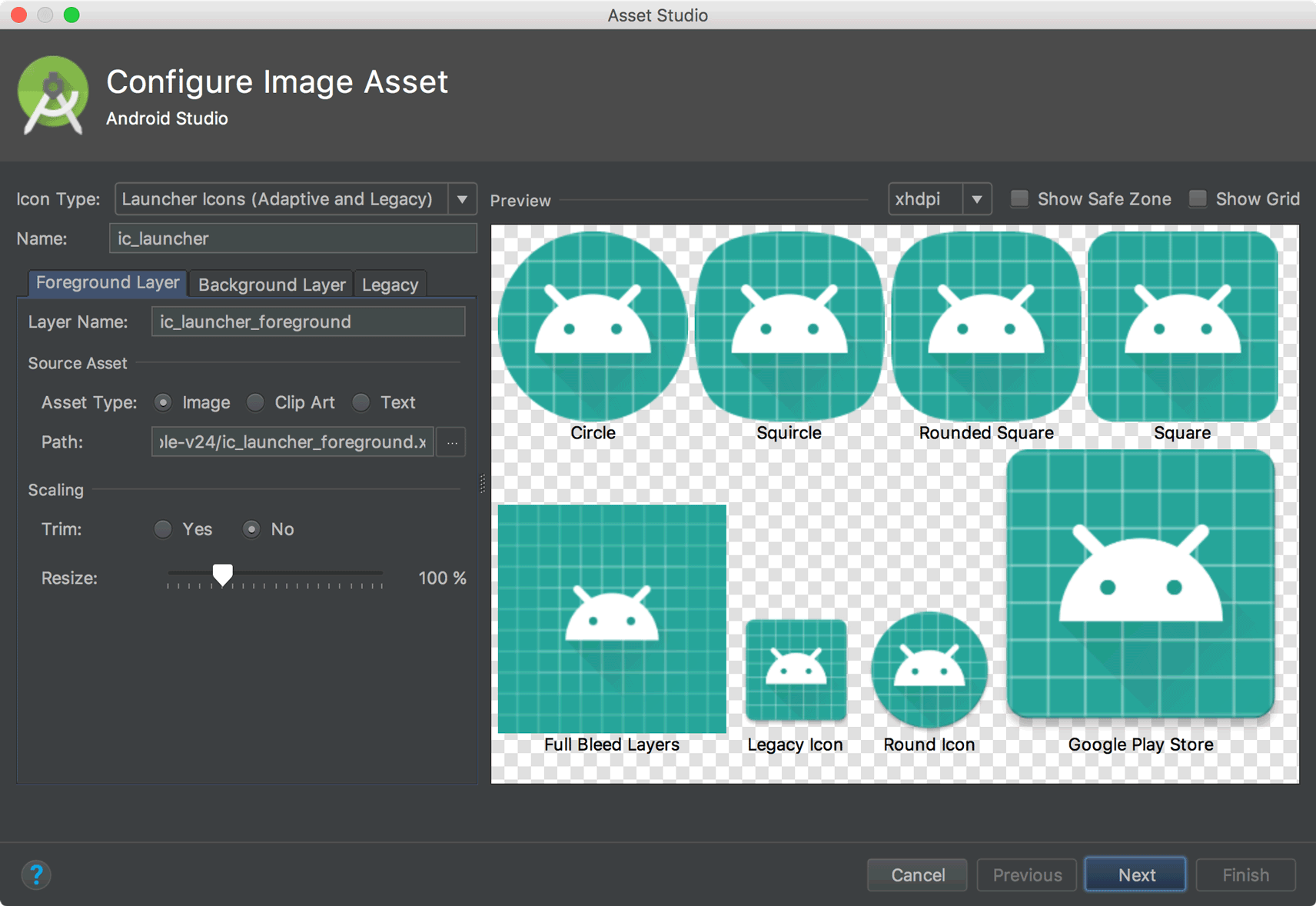
Support for font resources
To support the new font resources in Android 8.0, Android Studio includes a font resources selector to help bundle fonts into your app or configure your project to download the fonts on the device (when available). The layout editor can also preview the fonts in your layout.
To try downloadable fonts, ensure that your device or emulator is running Google Play Services v11.2.63 or higher. For more information, read about Downloadable Fonts .
Firebase App Indexing Assistant
The Firebase Assistant has been updated with a new tutorial to test App Indexing . To open the Assistant, select Tools > Firebase . Then select App Indexing > Test App Indexing .
The tutorial includes new buttons to test your public and personal content indexing:
- In step 2, click Preview search results to verify that your URLs are showing up in Google Search results.
- In step 3, click Check for errors to verify that the indexable objects in your app have been added to the personal content index.
Android App Links Assistant
The App Links Assistant has been updated with the following new capabilities:
Add URL tests for each URL mapping to be sure your intent filters handle real-world URLs.
You can also define these URL tests by hand using the
<tools:validation>tag described below.Create a Digital Asset Links file with the appropriate object entry to support Google Smart Lock , and add the corresponding
asset_statements<meta-data>tag to your manifest file.
URL intent-filter validator
Android Studio now supports a special tag in the manifest file that allows you to test your intent filter URLs . These are the same tags that the App Links Assistant can create for you .
To declare a test URL for an intent filter, add a <tools:validation> element alongside the corresponding <intent-filter> element. For example:
<activity ...>
<intent-filter>
...
</intent-filter>
<tools:validation testUrl="https://www.example.com/recipe/1138" />
</activity>
Be sure to also include xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" in the <manifest> tag.
If any one of the test URLs does not pass the intent filter definition, a lint error appears. Such an error still allows you to build debug variants, but it will break your release builds.
ویرایشگر طرحبندی
The Layout Editor has been updated with a number of enhancements, including the following:
- New toolbar layout and icons.
- Updated layout in the component tree.
- Improved drag-and-drop view insertions.
- New error panel below the editor, showing all issues with suggestions to fix (if available).
- Various UI enhancements for building with
ConstraintLayout, including the following:- New support to create barriers .
- New support to create groups: In the toolbar, select Guidelines > Add Group (requires ConstraintLayout 1.1.0 beta 2 or higher)
- New UI to create chains: Select multiple views, and then right-click and select Chain .
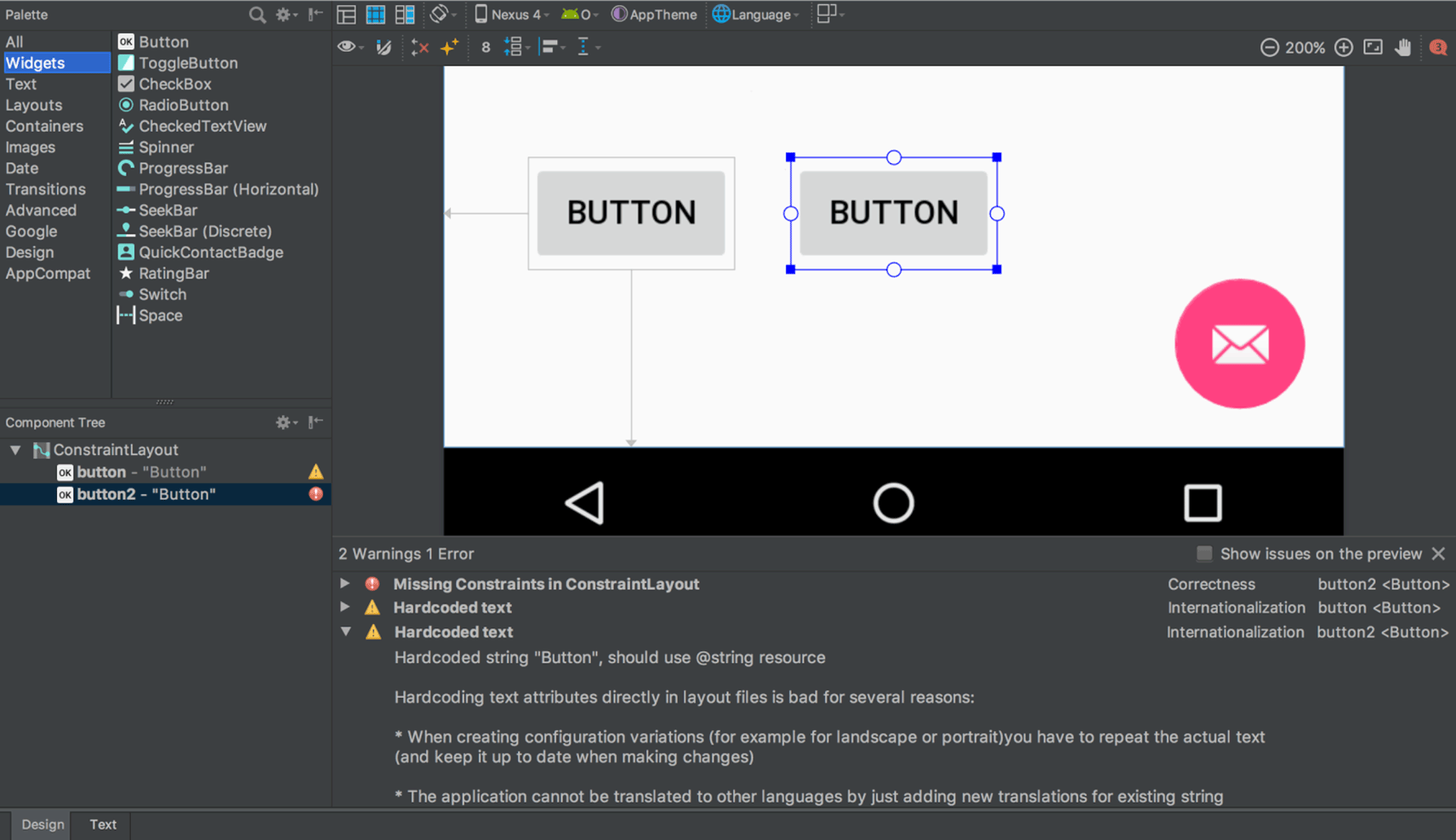
Layout Inspector
The Layout Inspector includes enhancements to make it easier to debug issues with your app layouts, including grouping properties into common categories and new search functionality in both the View Tree and the Properties panes.
APK Analyzer
You can now use the APK Analyzer from the command line with the apkanalyzer tool.
The APK Analyzer has also been updated with the following improvements:
- For APKs built with ProGuard, you can load ProGuard mapping files that add capabilities to the DEX viewer, including:
- Bolded nodes to indicate that the nodes should not be removed when shrinking code.
- A button to show nodes that were removed during the shrinking process.
- A button that restores the original names of nodes in the tree view that were obfuscated by ProGuard.
- The DEX Viewer now shows the estimated size impact of each package, class and method.
- New filtering options at the top to show and hide fields and methods.
- In the tree view, nodes that are references not defined in the DEX file appear in italics.
For more information, see Analyze Your Build with APK Analyzer .
Preview for D8 DEX compiler
Android Studio 3.0 includes an optional new DEX compiler called D8. It will eventually replace the DX compiler, but you can opt-in to use the new D8 compiler now.
DEX compilation directly impacts your app's build time, .dex file size, and runtime performance. And when comparing the new D8 compiler with the current DX compiler, D8 compiles faster and outputs smaller .dex files, while having the same or better app runtime performance.
To try it, set the following in your project's gradle.properties file:
android.enableD8=true
For more information, see the blog post about the D8 compiler .
Google's Maven repository
Android Studio now uses Google's Maven Repository by default instead of depending on the Android SDK Manager to get updates for Android Support Library, Google Play Services, Firebase, and other dependencies. This makes it easier to keep your libraries up to date, especially when using a continuous integration (CI) system.
All new projects now include the Google Maven repository by default. To update your existing project, add google() in the repositories block of the top-level build.gradle file:
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
}
}
Learn more about Google's Maven repository here .
Other changes
- Native debugging with Android Studio no longer supports 32-bit Windows. We've chosen to focus on other platforms because very few developers are using this platform. If you are using 32-bit Windows and you plan to debug native code, you should keep using Android Studio 2.3 .
- Upgraded the base IDE to IntelliJ 2017.1.2 , which adds a number of new features from 2016.3 and 2017.1 , such as Java 8 language refactoring, parameter hints, semantic highlighting, draggable breakpoints, instant results in search, and much more.
- Added many new lint checks.
- Also see the latest Android Emulator updates .
2.3 (March 2017)
Android Studio 2.3.0 is primarily a bug fix and stability release, but it also includes a number of new features.
2.3.3 (June 2017)
This is a minor update to add support for Android O (API level 26).
2.3.2 (April 2017)
This is a minor update to Android Studio 2.3 for the following changes:
- AVD Manager updates to support Google Play in system images.
- Bug fixes for NDK builds when using R14+ of the NDK.
Also see corresponding updates for Android Emulator 26.0.3 .
2.3.1 (April 2017)
This is a minor update to Android Studio 2.3 that fixes an issue where some physical Android devices did not work properly with Instant Run (see Issue #235879 ).
<h3 class="hide-from-toc">
New
</h3>
<div class="video-wrapper-left">
<iframe class="devsite-embedded-youtube-video" data-video-id="VFyKclKBGf0"
data-autohide="1" data-showinfo="0" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen>
</iframe>
</div>
<ul>
<li>Android Studio can now convert PNG, BMP, JPG, and static GIF files to
WebP format. WebP is an image file format from Google that provides lossy
compression (like JPEG) as well as transparency (like PNG) but can provide
better compression than either JPEG or PNG. For more information, see
<a href="/studio/write/convert-webp.html">Convert images to WebP in Android
Studio</a>.
</li>
<li>The new <a href="/studio/write/app-link-indexing.html">App Links
Assistant</a> simplifies the process of adding Android App Links to your app
into a step-by-step wizard. Android App Links are HTTP URLs that bring users
directly to specific content in your Android app.
</li>
<li>The Layout Editor now includes support for two new ConstraintLayout
features:
<ul>
<li>Define a view size based on an aspect ratio.
</li>
<li>Create packed, spread, and weighted linear groups with constraint
chains.
</li>
</ul>
For more information, see <a href=
"/training/constraint-layout/index.html">Build a Responsive UI with
ConstraintLayout</a>.
</li>
<li>The Layout Editor also now lets you create a list of <a href=
"/studio/write/layout-editor.html#edit-properties">favorite attributes</a> so
you don't have to click <b>View all attributes</b> to access the attributes
you use most.
</li>
<li>When adding a material icon using the Vector Import Dialog (<b>File >
New > Vector Asset</b>), you can now filter the list of available icons by
category or by icon name. For more information, see <a href=
"/studio/write/vector-asset-studio.html#materialicon">Adding a material
icon</a>.
</li>
<li>
<a href="/studio/write/annotations.html#accessibility">New and updated
annotations</a>. The new <code>@RestrictTo</code> annotation for methods,
classes, and packages lets you restrict an API. The updated
<code>@VisibleForTesting</code> annotation now has an optional
<code>otherwise</code> argument that lets you designate what the visibility
of a method should be if not for the need to make it visible for testing.
Lint uses the <code>otherwise</code> option to enforce the intended
visibility of the method.
</li>
<li>New <a href="/studio/write/lint.html#snapshot">lint baseline support</a>
allows you to use a snapshot of your project's current set of warnings as a
baseline for future inspection runs so only new issues are reported. The
baseline snapshot lets you start using lint to fail the build for new issues
without having to go back and address all existing issues first.
</li>
<li>New lint checks, including the following:
<ul>
<li>Obsolete <code>SDK_INT</code> Checks: Android Studio removes obsolete
code that checks for SDK versions.
</li>
<li>Object Animator Validation: Lint analyzes your code to make sure that
your <code>ObjectAnimator</code> calls reference valid methods with the
right signatures and checks that those methods are annotated with <code>
@Keep</code> to prevent ProGuard from renaming or removing them during
release builds.
</li>
<li>Unnecessary Item Decorator Copy: Older versions of the
<code>RecyclerView</code> library did not include a divider decorator
class, but one was provided as a sample in the support demos. Recent
versions of the library have a divider decorator class. Lint looks for
the old sample and suggests replacing it with the new one.
</li>
<li>WifiManager Leak: Prior to Android 7.0 (API level 24), initializing
the <code>WifiManager</code> with <code><a href="/reference/android/content/Context.html#getSystemService(java.lang.Class<T>)">Context.getSystemService()</a></code>
can cause a memory leak if the context is not the application context.
Lint looks for these initializations, and if it <em>cannot</em> determine
that the context is the application context, it suggests you use <code><a href="/reference/android/content/Context.html#getApplicationContext()">Context.getApplicationContext()</a></code> to get the proper context for the
initialization.
</li>
<li>Improved Resource Prefix: The existing <code>resourcePrefix</code>
lint check had many limitations. You can now configure your project with
a prefix, such as <code>android { resourcePrefix '<var>my_lib</var>'
}</code>, and lint makes sure that all of your resources are using this
prefix. You can use variations of the name for styles and themes. For
example for the <var>my_lib</var> prefix, you can have themes named
<code>MyLibTheme</code>, <code>myLibAttr</code>,
<code>my_lib_layout</code>, and so on.
</li>
<li>Switch to WebP: This check identifies images in your project that can
be converted to WebP format based on your project’s
<code>minSdkVersion</code> setting. An associated quickfix can
automatically convert the images, or you can <a href=
"/studio/write/convert-webp.html">convert images to WebP</a> manually.
</li>
<li>Unsafe WebP: If your project already includes WebP images, this check
analyzes your project to ensure that your <code>minSdkVersion</code>
setting is high enough to support the included images. For more
information about WebP support in Android and Android Studio, see
<a class="external" href=
"https://developers.google.com/speed/webp/faq#which_web_browsers_natively_support_webp">
Which browsers natively support WebP?</a> and <a href=
"/studio/write/convert-webp.html">Create WebP Images Using Android
Studio</a>.
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
<h3 class="hide-from-toc">
Changes
</h3>
<ul>
<li>A separate button to push changes with Instant Run: After deploying your
app, you now click <b>Apply Changes</b> <img src=
"/studio/images/buttons/toolbar-apply-changes.svg" alt="" class=
"inline-icon"> to quickly push incremental changes to your running app using
Instant Run. The <b>Run</b> <img src="/studio/images/buttons/toolbar-run.png"
alt="" class="inline-icon"> and <b>Debug</b> <img src=
"/studio/images/buttons/toolbar-debug.png" alt="" class="inline-icon">
buttons are always available to you when you want to reliably push your
changes and force an app restart.
<ul>
<li>Instant Run is supported only when deploying your app to a target
device running Android 5.0 (API level 21) or higher.
</li>
<li>Instant Run is no longer disabled for projects that <a href=
"/studio/projects/add-native-code.html">link to external native
projects</a> using CMake or ndk-build. However, you can only use Instant
Run to push incremental changes to your Java code, not your native code.
</li>
<li>Cold swaps (which you can force for a running app by clicking
<strong>Run</strong> <img src="/studio/images/buttons/toolbar-run.png"
alt="" class="inline-icon">) are now more reliable. Forcing a cold swap
also fixes the issue where changes to notification and widget UIs were
not updated on the target device.
</li>
<li>Includes optimizations that make app startup much faster. These
optimizations may affect profiling, so you should temporarily <a href=
"/studio/run/index.html#disable-ir">disable Instant Run</a> whenever
profiling your app.
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<p>
The <b>AVD Manager</b> <img src=
"/studio/images/buttons/toolbar-avd-manager.png" alt="" class=
"inline-icon"> and <b>SDK Manager</b> <img src=
"/studio/images/buttons/toolbar-sdk-manager.png" alt="" class=
"inline-icon"> buttons are now included in the lean Navigation Bar as
well as the full Toolbar. To use the lean Navigation Bar, click
<b>View</b> to open the View menu, then ensure that <b>Navigation Bar</b>
is selected and <b>Toolbar</b> is <em>not</em> selected.
</p>
<img src="/studio/images/releases/navigationbar_sdkavd_2x.png" width="757">
</li>
<li>The "Hybrid" debugger has been renamed to "Dual" debugger.
</li>
<li>In the <a href="/studio/run/rundebugconfig.html">Run/Debug
Configurations</a> dialog, under Defaults in the left pane, the following run
configuration names have changed with no behavior changes:
<ul>
<li>The JUnit name has changed to Android JUnit. If you have a project
that uses JUnit run configurations, those configurations are transformed
to Android JUnit run configurations the first time you open the project
with Android Studio. A dialog appears to inform you of the name change.
</li>
<li>The Android Tests name has changed to Android Instrumented Tests.
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>The <a href="/studio/debug/am-gpu-debugger.html">GPU Debugger</a> has
been removed from Android Studio as of version 2.3. An open-source,
standalone version of the tool is now available on <a href=
"https://github.com/google/gapid" class="external-link">GitHub</a>.
</li>
<li>The Run/Debug option is no longer available when you right-click a <code>
*.gradle build</code> script.
</li>
<li>All templates now use <code>ConstraintLayout</code> as the default
layout.
</li>
<li>The Widgets palette in the Layout Editor has been redesigned.
</li>
</ul>
<p>
This release also includes a number of bug fixes. <a href=
"https://code.google.com/p/android/issues/list?can=1&q=target%3D2.3+status%3DReleased&colspec=ID+Status+Priority+Owner+Summary+Stars+Reporter+Opened&cells=tiles">
See all bug fixes in 2.3.0.</a>
</p>
<p class="note">
<b>Known issue:</b> Some device manufacturers block apps from automatically
launching after being installed on the device. When deploying your app to a
physical device using Android Studio 2.3, this restriction breaks the
intended behavior of Instant Run and causes the following error output:
<code>Error: Not found; no service started</code>. To avoid this issue,
either <a href="/studio/run/emulator.html">use the emulator</a> or enable
automatic launching for your app in your device's settings. The procedure
for doing this is different for each device, so check the instructions
provided by the manufacturer. To learn more about this issue, see
<a href="https://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=235879">Issue
#235879</a>.
</p>
2.2 (September 2016)
2.2.3 (December 2016)
<p>
This is a minor update to Android Studio 2.2. It includes a bug fixes
focused around gradle, the core IDE, and lint.
</p>
<p>
Highlighted build changes:
</p>
<ul>
<li>ProGuard version rollback. Due to a <a href=
"https://sourceforge.net/p/proguard/bugs/625/">correctness issue</a>
discovered in ProGuard 5.3.1, we have rolled back to ProGuard 5.2.1. We
have worked with the ProGuard team on getting a fix quickly, and we expect
to roll forward to ProGuard 5.3.2 in Android Studio 2.3 Canary 3.
</li>
<li>Bug fix for <code>aaptOptions</code> <code>IgnoreAssetsPattern</code>
not working properly (<a href="http://b.android.com/224167">issue
224167</a>)
</li>
<li>Bug fix for Gradle autodownload for Constraint Layout library
(<a href="https://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=212128">issue
212128</a>)
</li>
<li>Bug fix for a JDK8/Kotlin compiler + dx issue (<a href=
"http://b.android.com/227729">issue 227729</a>)
</li>
</ul>
<p>
<a href=
"https://code.google.com/p/android/issues/list?can=1&q=target%3D2.2.3+status%3AReleased+&colspec=ID+Status+Priority+Owner+Summary+Stars+Reporter+Opened&cells=tiles">
See all bug fixes in 2.2.3</a>.
</p>
2.2.2 (October 2016)
<p>
This is a minor update to Android Studio 2.2. It includes a number of small
changes and bug fixes, including:
</p>
<ul>
<li>When reporting Instant Run issues through the IDE, the report now also
includes logcat output for <code>InstantRun</code> events. To help us
improve Instant Run, please <a href=
"/studio/run/index.html#submit-feedback">enable extra logging and report
any issues</a>.
</li>
<li>A number of small bug fixes for Gradle.
</li>
<li>A fix for problems with generating multiple APKs.
</li>
</ul>
2.2.1 (October 2016)
<p>
This is a minor update to Android Studio 2.2. It includes several bug fixes
and a new feature to enable extra logging to help us troubleshoot Instant
Run issues—to help us improve Instant Run, please <a href=
"/studio/run/index.html#submit-feedback">enable extra logging and report
any issues</a>.
</p>
جدید
- All new Layout Editor with tools custom-built to support ConstraintLayout .
<li>New <strong><a href=
"http://tools.android.com/tech-docs/layout-inspector">Layout
Inspector</a></strong> lets you examine snapshots of your layout hierarchy
while your app is running on the emulator or a device.
</li>
<li>New <strong><a href="/studio/write/firebase.html">Assistant</a></strong>
window to help you integrate Firebase services into your app.
</li>
<li>New <strong><a href="/studio/debug/apk-analyzer.html">APK
Analyzer</a></strong> tool so you can inspect the contents of your packaged
app.
</li>
<li>New <strong><a href=
"http://tools.android.com/tech-docs/test-recorder">Espresso Test
Recorder</a></strong> tool (currently in beta) to help you create UI tests by
recording your own interactions.
</li>
<li>New <strong><a href=
"http://tools.android.com/tech-docs/build-cache">build cache</a></strong>
(currently experimental) to speed up build performance.
</li>
<li>New <strong>C/C++ build integration with CMake and ndk-build</strong>.
Compile and build new or existing native code into libraries packaged into
your APK, and debug using lldb. For new projects, Android Studio uses CMake
by default, but also supports ndk-build for existing projects. To learn how
to include native code in your Android application, read <a href=
"/studio/projects/add-native-code.html">Add C and C++ Code to Your
Project</a>. To learn how to debug native code with lldb, see <a href=
"/studio/debug/index.html#debug-native">Debug Native Code</a>.
</li>
<li>New <strong><a href="/studio/intro/index.html#sample-code">Samples
Browser</a></strong> so you can easily look up Google Android sample code
from within Android Studio to jump start app development.
</li>
<li>New <strong>Merged Manifest Viewer</strong> to help you diagnose how your
manifest file merges with your app dependencies across project build
variants.
</li>
<li>The <strong>Run</strong> window now contains log messages for the current
running app. Note that you can configure the <a href=
"/studio/debug/am-logcat.html">logcat Monitor</a> display, but not the
<strong>Run</strong> window.
</li>
<li>New <strong><a href="/studio/run/emulator.html">Android
Emulator</a></strong> features:
<ul>
<li>Added new <strong>Virtual</strong> <strong>Sensors</strong> and
<strong>Cellular</strong> > <strong>Signal Strength</strong> controls.
</li>
<li>Added an <strong>LTE</strong> option to the <strong>Cellular</strong>
> <strong>Network type</strong> control.
</li>
<li>Added simulated vertical swipes for scrolling through vertical menus
with a mouse wheel.
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>New <strong><a href="/studio/run/rundebugconfig.html">Run/Debug
Configuration</a></strong> features:
<ul>
<li>The <strong>Debugger</strong> tab of the Android App and Android
Tests templates now contain several new options for debugging with LLDB.
</li>
<li>The <strong>Profiling</strong> tab of the Android App and Android
Tests templates now contain a <strong>Capture GPU Commands</strong>
option for enabling GPU tracing. You can display GPU traces in the GPU
Debugger (a beta feature).
</li>
<li>The Android Tests template now has a <strong>Firebase Test Lab Device
Matrix</strong> option for the <strong>Deployment Target</strong>.
</li>
<li>The Native Application template has been deprecated. If you use this
template in a project, Android Studio automatically converts it to the
Android App template.
</li>
<li>The Android Application template has been renamed to Android App.
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Improved installation, configuration, performance, and UI features in the
<strong><a href="/studio/debug/am-gpu-debugger.html">GPU
Debugger</a></strong> (currently in beta).
</li>
<li>Android Studio now comes bundled with <strong>OpenJDK 8</strong>.
Existing projects still use the JDK specified in <strong>File > Project
Structure > SDK Location</strong>. You can switch to use the new bundled
JDK by clicking <strong>File > Project Structure > SDK
Location</strong> and checking the <strong>Use embedded JDK</strong>
checkbox.
</li>
<li>Added new <strong>help menus and buttons</strong> in the UI so you can
more easily find the online documentation.
</li>
تغییرات
- Updated the IDE codebase from IntelliJ 15 to IntelliJ 2016.1
- Instant Run now requires the platform SDK corresponding to the target device API level to be installed.
- Instant Run will automatically disabled if user is running the app under a work profile or as a secondary user.
- Fixed many reliability issues for Instant Run where changes were not getting deployed or the app would crash:
- Some app assets were not deployed to your running app. ( Bug: #213454 )
- App crashes when user transitions between Instant Run and non Instant Run sessions where a Serializable class does not have serialVersionUID defined. ( Bug: #209006 )
- Style changes aren't reflected with Instant Run. ( Bug: #210851 )
- Instant Run session is unreliable and causes FileNotFoundException. ( Bug: #213083 )
- Changes to drawables not reflected until full rebuild is performed for KitKat. ( Bug: #21530 )
- Resource changes aren't reflected with Instant Run when custom sourceSets contain nested paths. ( Bug: #219145 )
- Hot and warm swap don't work if changed class contains annotation with enum value. ( Bug: #209047 )
- Changes to annotation data not reflected with Instant Run. ( Bug: #210089 )
- Instant Run doesn't pick up code changes if you make changes outside the IDE. ( Bug: #213205 )
- Instant Run session is unreliable due to mismatch security token. ( Bug: #211989
- Cold swap fails for devices that doesn't properly support run-as. ( Bug: #210875 )
- App crash after instant run restart. ( Bug: #219744 )
- ClassNotFoundException observed when switching from Instant Run to Instant Debug. ( Bug: #215805 )
<li>Improved performance for <strong>Gradle sync</strong> within the IDE,
especially for large projects.
</li>
<li>Improved build times for both full and incremental builds with new app
packaging code.
</li>
<li>Improved <strong>Jack compiler performance and features</strong>,
including support for annotation processors and dexing in process. To learn
more, read the <a href=
"/studio/releases/gradle-plugin.html#revisions">Android plugin for Gradle
2.2.0 release notes</a>.
</li>
<li>Removed the <strong>Scale</strong> AVD property from the AVD Manager.
</li>
<li>The Android Emulator <strong>-port</strong> and <strong>-ports</strong>
command-line options now report which ports and serial number the emulator
instance is using, and warn if there are any issues with the values you
provided.
</li>
<li>Improved the <strong><a href=
"/studio/write/create-java-class.html">Create New Class dialog</a></strong>
and the corresponding file templates. <strong>Note:</strong> If you've
previously customized the <strong>AnnotationType</strong>,
<strong>Class</strong>, <strong>Enum</strong>, <strong>Interface</strong>, or
<strong>Singleton</strong> file templates, you need to modify your templates
to comply with the new templates or you won’t be able to use the new fields
in the <strong>Create New Class</strong> dialog.
</li>
<li>Improved the <strong><a href=
"/studio/write/vector-asset-studio.html">Vector Asset Studio</a></strong>
user interface and added support for Adobe Photoshop Document (PSD) files.
</li>
<li>Improved the <strong><a href=
"/studio/write/image-asset-studio.html">Image Asset Studio</a></strong> user
interface.
</li>
<li>Improved the <strong>Theme Editor</strong>'s Resource Picker.
</li>
<li>Fixed memory leaks and reduced overall memory usage in Android Studio.
</li>
<li>Added a <strong>Background</strong> button in the <strong><a href=
"/studio/intro/update.html#sdk-manager">SDK Manager</a></strong> so you can
get back to work and install your packages in the background.
</li>
<li>Improved <strong><a href="/studio/intro/accessibility.html">Accessibility
features</a></strong>, including support for screen readers and keyboard
navigation.
</li>
<li>Enhanced <strong>Code Analysis</strong> includes code quality checks for
Java 8 language usage and more cross-file analysis.
</li>
<li>Several toolbar icons have changed.
</li>
2.1 (April 2016)
The primary changes in this update provide support for development with the Android N Preview.
2.1.3 (August 2016)
This update adds compatibility with Gradle 2.14.1, which includes performance improvements, new features, and an important security fix . For more details, see the Gradle release notes .
By default, new projects in Android Studio 2.1.3 use Gradle 2.14.1. For existing projects, the IDE prompts you to upgrade to Gradle 2.14.1 and Android plugin for Gradle 2.1.3 , which is required when using Gradle 2.14.1 and higher.
2.1.2 (June 2016)
This update includes a number of small changes and bug fixes:
- Instant Run updates and bug fixes.
- Improvements to LLDB performance and crash notifications.
- Fixed a regression in the Android Studio 2.1.1 security update that caused
git rebaseto fail.
2.1.1 (May 2016)
Security release update.
The Android N platform adds support for Java 8 language features , which require a new experimental compiler called Jack. The latest version of Jack is currently supported only in Android Studio 2.1. So if you want to use Java 8 language features, you need to use Android Studio 2.1 to build your app.
Note: Instant Run is disabled when you enable the Jack compiler because they currently are not compatible.
Although Android Studio 2.1 is now stable, the Jack compiler is still experimental and you must enable it with the jackOptions property in your build.gradle file.
Other than the changes to support the N Preview, Android Studio 2.1 includes minor bug fixes and the following enhancements:
- The Java-aware C++ debugger is now enabled by default when you're using an N device or emulator and select Native debugger mode (in the Debugger tab for your run/debug configuration).
For other build enhancements, including incremental Java compilation and dexing-in-process,update your Android plugin for Gradle to version 2.1.0.
2.0 (April 2016)
Note: If you are developing for the N Developer Preview, you should use Android Studio 2.1 Preview. Android Studio 2.0 does not support all the features required to target the N Preview.
Instant Run :
- Android Studio now deploys clean builds faster than ever before. Additionally, pushing incremental code changes to the emulator or a physical device is now almost instantaneous. Review your updates without redeploying a new debug build or, in many cases, without restarting the app.
- Instant Run supports pushing the following changes to a running app:
- Changes to the implementation of an existing instance method or static method
- Changes to an existing app resource
- Changes to structural code, such as a method signature or a static field (requires a target device running API level 21 or higher).
- Read the documentation to learn more about Instant Run .
Note: Instant Run is supported only when you deploy the debug build variant, use Android plugin for Gradle version 2.0.0 or higher, and configure your app's module-level
build.gradlefile forminSdkVersion 15or higher. For the best performance, configure your app forminSdkVersion 21or higher.
New additions to Lint:
- Inspection of
switchstatements using@IntDefannotated integers to make sure all constants are handled. To quickly add any missing statements, use the intention action drop-down menu and select Add Missing @IntDef Constants . - Flags for incorrect attempts to use string interpolation to insert version numbers in the
build.gradlefile. - Flags for anonymous classes that extend the
Fragmentclass. - Flags for native code in unsafe locations, such as the
res/andasset/folders. This flag encourages storing native code in thelibs/folder, which is then securely packaged into the application'sdata/app-lib/folder at install time. AOSP: #169950 - Flags for unsafe calls to
Runtime.load()andSystem.load()calls. AOSP: #179980 - Find and remove any unused resources by selecting Refactor > Remove Unused Resources from the menu bar. Unused resource detection now supports resources only referenced by unused resources, references in raw files such as
.htmlimage references, andtools:keepandtools:discardattributes used by the Gradle resource shrinker, while considering inactive source sets (such as resources used in other build flavors) and properly handling static field imports. - Checks that implicit API references are supported on all platforms targeted by
minSdkVersion. - Flags improper usage of
RecyclerViewandParcelable. -
@IntDef,@IntRange, and@Sizeinspections are now also checked forintarrays and varargs.
Additional Improvements :
- Optimized for Android Emulator 2.0, which is faster than ever before, supports a wider range of virtual devices, and features a drastically improved UI. To learn more about the new emulator, read the SDK Tools release notes .
- Improvements to the Android Virtual Device Manager :
- System images are now categorized under the following tabs: Recommended , x86 , and Other .
- Under advanced settings, you can enable multi-core support and specify the number of cores the emulator can use.
- Under advanced settings, you can determine how graphics are rendered on the emulator by selecting one of the following options:
- Hardware: use you computer's graphics card for faster rendering.
- Software: use software-based rendering.
- Auto: let the emulator decide the best option. This is the default setting.
- Improved AAPT packaging times by specifying deploy target before the app is built. This allows Android Studio to efficiently package only the resources required by the specified device.
- Added Cloud Test Lab integration to provide on-demand app testing with the convenience and scalability of a cloud service. Learn more about how you can use Cloud Test Lab with Android Studio .
- Added a preview of the new GPU Debugger . For graphics intensive applications, you can now visually step through your OpenGL ES code to optimize your app or game.
- Added Google App Indexing Test. Add support for URLs, app indexing, and search functionality to your apps to help drive more traffic to your app, discover which app content is used most, and attract new users. Test and validate URLs in your app all within Android Studio. See Supporting URLs and App Indexing in Android Studio .
- Upgrades from the latest IntelliJ 15 release, including improved code analysis and performance. See What's New in IntelliJ for a complete description of the new features and enhancements.
- XML editor auto-complete now adds quotations marks when completing attributes. To check if this option is enabled, open the Setting or Preferences dialogue, navigate to Editor > General > Smart Keys , and check the box next to Add quotes for attribute value on attribute completion . Issue: 195113
- The XML editor now supports code completion for data binding expressions.
Android Studio v1.5.1 (December 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Fixed a rendering failure issue in the Layout Editor. Issue: 194612
- Added the ability to vary
descriptionmanifest attributes by configuration. Issue: 194705 - Improved the contrast of the Android Studio Darcula appearance theme in Vector Asset Studio. Issue: 191819
- Added Help button support to Vector Asset Studio.
- Added support for the
%operator for data binding. Issue: 194045 - Fixed a case where launching an app for debugging resulted in the debugger connecting to the wrong device. Issue: 195167
- Fixed a null pointer exception that could occur when attempting to run an app in certain scenarios.
Android Studio v1.5.0 (November 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Added new Memory Monitor analysis abilities to Android Monitor. When you view an HPROF file captured from this monitor, the display is now more helpful so you can more quickly locate problems, such as memory leaks. To use this monitor, click Android Monitor at the bottom of the main window. In Android Monitor, click the Memory tab. While the monitor is running, click the Dump Java Heap icon, and then click Captures in the main window and double-click the file to view it. Click Capture Analysis on the right. (The Android Device Monitor can't be running at the same time as Android Monitor.)
- Added new deep link and app link support. The Code Editor can automatically create an intent filter for deep linking in the
AndroidManifest.xmlfile. It can also generate code to help you integrate with the App Indexing API in an activity in a Java file. A deep link testing feature helps you verify that a specified deep link can launch an app. In the General tab of the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, you can specify deep link launch options. You can also test App Indexing API calls in an activity by using the Android Monitor logcat display. The Androidlinttool now has warnings for certain issues involving deep links and the App Indexing API. - Added the ability to use short names when code-completing custom views in the Code Editor.
- Added support for more
VectorDrawableelements to Vector Asset Studio for backward-compatibility. Vector Asset Studio can use these elements to convert vector drawables into PNG raster images to use with Android 4.4 (API level 20) and lower. - Added new
lintchecks for Android TV and Android Auto to give you immediate, actionable feedback in Android Studio, along with several quick fixes. For example, for Android TV, it can report and provide a quick fix for permissions, unsupported hardware,uses-featureelement, and missing banner issues. For Android Auto, it can validate the correct usage in the descriptor file referred from yourAndroidManifest.xmlfile, report if there isn't an intent filter for theMediaBrowserServiceclass, and identify certain voice actions issues. - Added new
lintchecks for insecure broadcast receivers,SSLCertificateSocketFactoryandHostnameVerifierclass uses, andFile.setReadable()andFile.setWritable()calls. It also detects invalid manifest resource lookups, especially for resources that vary by configuration. - Fixed a number of stability issues.
Android Studio v1.4.1 (October 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Fixed a Gradle model caching issue that could lead to excessive Gradle syncing when the IDE was restarted.
- Fixed a native debugging deadlock issue.
- Fixed an issue blocking users of the Subversion 1.9 version control system.
- Fixed a Device Chooser dialog problem where after connecting a device that was unauthorized you could no longer select the emulator. Issue: 189658
- Fixed incorrect translation error reporting for locales that have a region qualifier and a translation in the region (but not in the base locale). Issue: 188577
- Fixed a deadlock issue in the Theme Editor related to its interaction with the Layout Editor. Issue: 188070
- Fixed a Theme Editor reload and edit conflict causing attributes to not properly update. Issue: 187726
- Improved Theme Editor performance.
- Fixed an issue where the
android:requiredattribute was ignored in the manifest. Issue: 187665
Android Studio v1.4.0 (September 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Added the Vector Asset Studio tool for importing vector graphics, such as material icons and SVG files. To use this tool, in the Android view of the Project window, right-click the res folder and select New > Vector Asset .
- Added new Android Monitor functions, GPU and Network. To use these monitors, click Android Monitor at the bottom of the main window. The Android Device Monitor can't be running at the same time as Android Monitor.
- Added an early preview of the new Theme Editor. To use this feature, select Tools > Android > Theme Editor .
- Updated the Android templates for the Design Support Library. Templates now include support for the Material Design specification, as well as the
appcompatSupport Library for backwards compatibility.
Android Studio v1.3.2 (August 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Added support for Android 6.0 (API level 23), including new icons and AVD Manager support for creating devices with new screen densities.
- Fixed an exception that was occurring during update checks. Issue: 183068
- Fixed problem where unresolved view coordinates could cause the layout editor to crash. Issue: 178690
- Fixed issue with invalid resource type warnings. Issue: 182433
- Fixed lint check that was incorrectly flagging resources as private. Issue: 183120
Android Studio v1.3.1 (August 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Fixed support for creating an Android Wear Android Virtual Device (AVD) on Windows.
- Updated the Project Wizard to use the entered project name.
- Added support to allow the Android SDK to be stored in a read-only directory.
- Updated Android plugin for Gradle version to 1.3.0.
- Fixed issues with launching a debug session from the Android Debug Bridge (adb) Unix shell.
- Fixed the Java package renaming message to show the correct package name.
Android Studio v1.3.0 (July 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Added options to enable developer services , such as Google AdMob and Analytics , in your app from within Android Studio.
- Added additional annotations , such as
@RequiresPermission,@CheckResults, and@MainThread. - Added the capability to generate Java heap dumps and analyze thread allocations from the Memory Monitor . You can also convert Android-specific HPROF binary format files to standard HPROF format from within Android Studio.
- Integrated the SDK Manager into Android Studio to simplify package and tools access and provide update notifications.
Note: The standalone SDK Manager is still available from the command line, but is recommended for use only with standalone SDK installations.
- Added the
fingercommand in the emulator console to simulate fingerprint authentication. - Added a
<public>resource declaration to designate library resources as public and private resources.Note: Requires Android plugin for Gradle version 1.3 or higher.
- Added data binding support to create declarative layouts that bind your application logic to layout elements.
- Added support for a separate test APK module to build test APKs in Android Studio.
- Updated the AVD Manager with HAXM optimizations and improved notifications.
- Added 64-bit ARM and MIPS emulator support for QEMU 2.1.
- Simplified the resolution of Lint warnings by adding quick fixes, such as the automatic generation of Parcelable implementation.
- Added live template support for quick insertion of code snippets.
Android Studio v1.2.2(June 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Fixed build issues that were blocking builds from completing.
Android Studio v1.2.1 (May 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Fixed minor performance and feature issues.
Android Studio v1.2.0 (April 2015)
Fixes and enhancements:
- Updated the Android runtime window to include the Memory Monitor tool and added a tab for CPU performance monitoring.
- Added a Captures tab in the left margin to display the captured memory and CPU performance data files, such as CPU method tracking and memory heap snapshots.
- Expanded annotation support with additional metadata annotations and inferred nullability.
- Enhanced the Translations Editor with additional support for Best Current Practice (BCP) 47, which uses 3-letter language and region codes.
- Integrated IntelliJ 14 and 14.1 features for improved code analysis and performance:
- Enhanced debugging to show inline values for variables and referring objects, as well as perform inline evaluation of lambda and operator expressions.
- Added code style detection for tab and indent sizes.
- Added scratch files for code experiments and prototyping without project files.
- Added the simultaneous insertion of opening and closing tags in HTML and XML files.
- Added a built-in Java class decompiler so you can look at what's inside a library for which the source code is not available.
See What's New in IntelliJ for a complete description of the new features and enhancements.
- Added additional Project Views for Scratches , Project Files , Problems , Production , and Tests to enhance project management and access.
- Enhanced the File > Settings menu and dialogs for improved settings access and management.
- Added support for high-density displays for Windows and Linux.
- Added support for 280 dpi resources in the
res/drawable-280dpi/folder.
Android Studio v1.1.0 (February 2015)
Various fixes and enhancements:
- Added support for the Android Wear watch template.
- Modified new project and module creation to include
res/mipmapfolders for density-specific launcher icons. Theseres/mipmapfolders replace theres/drawablefolders for launcher icons. - Updated launcher icons to have a Material Design look and added an
xxxhdpilauncher icon. - Added and enhanced Lint checks for region and language combinations, launcher icons, resource names, and other common code problems.
- Added support for Best Current Practice (BCP) language tag 47.
Android Studio v1.0.1 (December 2014)
Various fixes and enhancements:
- Fixed AVD Manager and device.xml file lock issue.
- Fixed the emulator log on Windows systems.
- Fixed issue with creating AVDs with Android Studio and Android SDK installed on different drives on Windows systems.
- Sets the default update channel for new downloads to Stable . If you installed the 1.0.0 version of Android Studio and would like stable, production-ready version updates, use File > Settings > Updates to change to the Stable update channel.
Android Studio v1.0 (December 2014)
Initial release of Android Studio.
Android Studio v0.8.14 (October 2014)
See tools.android.com for a full list of changes.
Android Studio v0.8.6 (August 2014)
See tools.android.com for a full list of changes.
Android Studio v0.8.0 (June 2014)
Added support for Android Wear projects.
See tools.android.com for a full list of changes.
Android Studio v0.5.2 (May 2014)
- See tools.android.com for a full list of changes.
Android Studio v0.4.6 (March 2014)
- See tools.android.com for a full list of changes.
Android Studio v0.4.2 (Jan 2014)
- See tools.android.com for a full list of changes.
Android Studio v0.3.2 (Oct 2013)
- See tools.android.com for a full list of changes.
Android Studio v0.2.x (July 2013)
- Merged in the latest IntelliJ codebase changes. Includes fixes for issues reported by Studio users such as tweaks to Linux font sizes and font rendering.
- Android Gradle plug-in updated to 0.5.0.
Caution: This new version is not backwards compatible. When opening a project that uses an older version of the plug-in, Studio will show an error stating Gradle <project_name> project refresh failed.
The updated Gradle plug-in includes the following changes:
- Fixed IDE model to contain the output file even if it's customized through the DSL. Also fixed the DSL to get/set the output file on the variant object so that it's not necessary to use
variant.packageApplication or variant.zipAlign - Fixed dependency resolution so that we resolved the combination of (default config, build types, flavor(s)) together instead of separately.
- Fixed dependency for tests of library project to properly include all the dependencies of the library itself.
- Fixed case where two dependencies have the same leaf name.
- Fixed issue where Proguard rules file cannot be applied on flavors.
All Gradle plugin release notes are available are here: http://tools.android.com/tech-docs/new-build-system .
- Fixed IDE model to contain the output file even if it's customized through the DSL. Also fixed the DSL to get/set the output file on the variant object so that it's not necessary to use
- Gradle errors from aapt no longer point to merged output files in the build/ folder, they point back to the real source locations.
- Parallel Builds. It's now possible to use Gradle's parallel builds. Please be aware that parallel builds are in "incubation" (see Gradle's documentation .) This feature is off by default. To enable it, go to Preferences > Compiler and check the box Compile independent modules in parallel .
- Further work on the new resource repository used for layout rendering, resource folding in the editor, and more:
- Basic support for .aar library dependencies (eg using a library without a local copy of the sources). Still not working for resource XML validation and navigation in source editors.
- Cycle detection in resource references.
- Quick Documentation (F1), which can show all translations of the string under the caret, will now also show all resource overlays from the various Gradle flavors and build types, as well as libraries. They are listed in reverse resource overlay order, with strikethrough on the versions of the string that are masked.
- Fixes to handle updating the merged resources when the set of module dependencies change.
- XML rendering fixes to properly handle character entity declarations and XML and unicode escapes.
- Save screenshot support for the layout preview and layout editor windows.
- Template bug fixes.
- Lint bug fixes.
- Various fixes for crash reports. Thank you, and keep filing crash reports!
Android Studio v0.1.x (May 2013)
- Various bug fixes, including a fix for a common Windows installation issue.
Older releases of Android Gradle Plugin
3.6.0 (February 2020)
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
Gradle 5.6.4 . To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
SDK Build Tools 28.0.3 or higher.
3.6.4 (July 2020)
This minor update supports compatibility with new default settings and features for package visibility in Android 11 .
See the 4.0.1 release notes for details.
New features
This version of the Android Gradle plugin includes the following new features.
View Binding
View binding provides compile-time safety when referencing views in your code. You can now replace findViewById() with the auto-generated binding class reference. To start using View binding, include the following in each module's build.gradle file:
android { viewBinding.enabled = true }
android { viewBinding.enabled = true }
To learn more, read the View Binding documentation .
Support for the Maven Publish plugin
The Android Gradle plugin includes support for the Maven Publish Gradle plugin , which allows you to publish build artifacts to an Apache Maven repository. The Android Gradle plugin creates a component for each build variant artifact in your app or library module that you can use to customize a publication to a Maven repository.
To learn more, go to the page about how to use the Maven Publish plugin .
New default packaging tool
When building the debug version of your app, the plugin uses a new packaging tool, called zipflinger , to build your APK. This new tool should provide build speed improvements. If the new packaging tool doesn't work as you expect, please report a bug . You can revert to using the old packaging tool by including the following in your gradle.properties file:
android.useNewApkCreator=false
Native build attribution
You can now determine the length of time it takes Clang to build and link each C/C++ file in your project. Gradle can output a Chrome trace that contains timestamps for these compiler events so you can better understand the time required to build your project. To output this build attribution file, do the following:
Add the flag
-Pandroid.enableProfileJson=truewhen running a Gradle build. For example:gradlew assembleDebug -Pandroid.enableProfileJson=trueOpen the Chrome browser and type
chrome://tracingin the search bar.Click the Load button and navigate to
<var>project-root</var>/build/android-profileto find the file. The file is namedprofile-<var>timestamp</var>.json.gz.
You can see the native build attribution data near the top of the viewer:
Behavior changes
When using this version of the plugin, you might encounter the following changes in behavior.
Native libraries packaged uncompressed by default
When you build your app, the plugin now sets extractNativeLibs to "false" by default. That is, your native libraries are page aligned and packaged uncompressed. While this results in a larger upload size, your users benefit from the following:
- Smaller app install size because the platform can access the native libraries directly from the installed APK, without creating a copy of the libraries.
- Smaller download size because Play Store compression is typically better when you include uncompressed native libraries in your APK or Android App Bundle.
If you want the Android Gradle plugin to instead package compressed native libraries, include the following in your app's manifest:
<application
android:extractNativeLibs="true"
... >
</application>
Note: The extractNativeLibs manifest attribute has been replaced by the useLegacyPackaging DSL option. For more information, see the release note Use the DSL to package compressed native libraries .
Default NDK version
If you download multiple versions of the NDK, the Android Gradle plugin now selects a default version to use in compiling your source code files. Previously, the plugin selected the latest downloaded version of the NDK. Use the android.ndkVersion property in the module's build.gradle file to override the plugin-selected default.
Simplified R class generation
The Android Gradle plugin simplifies the compile classpath by generating only one R class for each library module in your project and sharing those R classes with other module dependencies. This optimization should result in faster builds, but it requires that you keep the following in mind:
- Because the compiler shares R classes with upstream module dependencies, it's important that each module in your project uses a unique package name.
- The visibility of a library's R class to other project dependencies is determined by the configuration used to include the library as a dependency. For example, if Library A includes Library B as an 'api' dependency, Library A and other libraries that depend on Library A have access to Library B's R class. However, other libraries might not have access to Library B's R class. If Library A uses the
implementationdependency configuration. To learn more, read about dependency configurations .
Remove resources missing from default configuration
For Library modules, if you include a resource for a language that you do not include in the default set of resources—for example, if you include hello_world as a string resource in /values-es/strings.xml but you don't define that resource in /values/strings.xml —the Android Gradle plugin no longer includes that resource when compiling your project. This behavior change should result in fewer Resource Not Found runtime exceptions and improved build speed.
D8 now respects CLASS retention policy for annotations
When compiling your app, D8 now respects when annotations apply a CLASS retention policy, and those annotations are no longer available at runtime. This behavior also exists when setting the app's target SDK to API level 23, which previously allowed access to these annotations during runtime when compiling your app using older versions of the Android Gradle plugin and D8.
Other behavior changes
-
aaptOptions.noCompressis no longer case sensitive on all platforms (for both APK and bundles) and respects paths that use uppercase characters. Data binding is now incremental by default. To learn more, see issue #110061530 .
All unit tests, including Roboelectric unit tests, are now fully cacheable. To learn more, see issue #115873047 .
رفع اشکالات
This version of the Android Gradle plugin includes the following bug fixes:
- Robolectric unit tests are now supported in library modules that use data binding. To learn more, see issue #126775542 .
- You can now run
connectedAndroidTesttasks across multiple modules while Gradle's parallel execution mode is enabled.
مشکلات شناخته شده
This section describes known issues that exist in Android Gradle plugin 3.6.0.
Slow performance of Android Lint task
Android Lint can take much longer to complete on some projects due to a regression in its parsing infrastructure, resulting in slower computation of inferred types for lambdas in certain code constructs.
The issue is reported as a bug in IDEA and will be fixed in Android Gradle Plugin 4.0.
Missing Manifest class {:#agp-missing-manifest}
If your app defines custom permissions in its manifest, the Android Gradle plugin typically generates a Manifest.java class that includes your custom permissions as string constants. The plugin packages this class with your app, so you can more easily reference those permissions at runtime.
Generating the manifest class is broken in Android Gradle plugin 3.6.0. If you build your app with this version of the plugin, and it references the manifest class, you might see a ClassNotFoundException exception. To resolve this issue, do one of the following:
Reference your custom permissions by their fully-qualified name. For example,
"com.example.myapp.permission.DEADLY_ACTIVITY".Define your own constants, as shown below:
public final class CustomPermissions { public static final class permission { public static final String DEADLY_ACTIVITY="com.example.myapp.permission.DEADLY_ACTIVITY"; } }
3.5.0 (August 2019)
Android Gradle plugin 3.5.0, along with Android Studio 3.5 , is a major release and a result of Project Marble, which is a focus on improving three main areas of the Android developer tools: system health, feature polish, and fixing bugs. Notably, improving project build speed was a main focus for this update.
For information about these and other Project Marble updates, read the Android Developers blog post or the sections below.
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
Gradle 5.4.1 . To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
SDK Build Tools 28.0.3 or higher.
3.5.4 (July 2020)
This minor update supports compatibility with new default settings and features for package visibility in Android 11 .
See the 4.0.1 release notes for details.
3.5.3 (December 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.5.3 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements.
3.5.2 (November 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.5.2 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of noteable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog .
3.5.1 (October 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.5.1 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of noteable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog .
Incremental annotation processing
The Data Binding annotation processor supports incremental annotation processing if you set android.databinding.incremental=true in your gradle.properties file. This optimization results in improved incremental build performance. For a full list of optimized annotation processors, refer to the table of incremental annotation processors .
Additionally, KAPT 1.3.30 and higher also support incremental annotation processors, which you can enable by including kapt.incremental.apt=true in your gradle.properties file.
Cacheable unit tests
When you enable unit tests to use Android resources, assets, and manifests by setting includeAndroidResources to true , the Android Gradle plugin generates a test config file containing absolute paths, which breaks cache relocatability. You can instruct the plugin to instead generate the test config using relative paths, which allows the AndroidUnitTest task to be fully cacheable, by including the following in your gradle.properties file:
android.testConfig.useRelativePath = true
مشکلات شناخته شده
When using Kotlin Gradle plugin 1.3.31 or earlier, you might see the following warning when building or syncing your project:
WARNING: API 'variant.getPackageLibrary()' is obsolete and has been replaced with 'variant.getPackageLibraryProvider()'.To resolve this issue , upgrade the plugin to version 1.3.40 or higher.
3.4.0 (April 2019)
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
Gradle 5.1.1 or higher. To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
Note: When using Gradle 5.0 and higher, the default Gradle daemon memory heap size decreases from 1 GB to 512 MB. This might result in a build performance regression. To override this default setting, specify the Gradle daemon heap size in your project's
gradle.propertiesfile.SDK Build Tools 28.0.3 or higher.
3.4.3 (July 2020)
This minor update supports compatibility with new default settings and features for package visibility in Android 11 .
See the 4.0.1 release notes for details.
3.4.2 (July 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.4.2 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of noteable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog .
3.4.1 (May 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.4.1 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of noteable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog .
New features
New lint check dependency configurations: The behavior of
lintCheckshas changed and a new dependency configuration,lintPublish, has been introduced to give you more control over which lint checks are packaged in your Android libraries.-
lintChecks: This is an existing configuration that you should use for lint checks you want to only run when building your project locally. If you were previously using thelintChecksdependency configuration to include lint checks in the published AAR, you need to migrate those dependencies to instead use the newlintPublishconfiguration described below. -
lintPublish: Use this new configuration in library projects for lint checks you want to include in the published AAR, as shown below. This means that projects that consume your library also apply those lint checks.
The following code sample uses both dependency configurations in a local Android library project.
dependencies { // Executes lint checks from the ':lint' project at build time. lintChecks project(':lint') // Packages lint checks from the ':lintpublish' in the published AAR. lintPublish project(':lintpublish') }
dependencies { // Executes lint checks from the ':lint' project at build time. lintChecks(project(":lint")) // Packages lint checks from the ':lintpublish' in the published AAR. lintPublish(project(":lintpublish")) }
In general, packaging and signing tasks should see an overall build speed improvement. If you notice a performance regression related to these tasks, please report a bug .
-
Behavior changes
Android Instant Apps Feature plugin deprecation warning: If you're still using the
com.android.featureplugin to build your instant app, Android Gradle plugin 3.4.0 will give throw you a deprecation warning. To make sure you can still build you instant app on future versions of the plugin, migrate your instant app to using the dynamic feature plugin , which also allows you to publish both your installed and instant app experiences from a single Android App Bundle.R8 enabled by default: R8 integrates desugaring, shrinking, obfuscating, optimizing, and dexing all in one step—resulting in noticeable build performance improvements . R8 was introduced in Android Gradle plugin 3.3.0 and is now enabled by default for both app and Android library projects using plugin 3.4.0 and higher.
The image below provides a high-level overview of the compile process before R8 was introduced.

Now, with R8, desugaring, shrinking, obfuscating, optimizing, and dexing (D8) are all completed in one step, as illustrated below.

Keep in mind, R8 is designed to work with your existing ProGuard rules, so you'll likely not need to take any actions to benefit from R8. However, because it's a different technology to ProGuard that's designed specifically for Android projects, shrinking and optimization may result in removing code that ProGuard may have not. So, in this unlikely situation, you might need to add additional rules to keep that code in your build output.
If you experience issues using R8, read the R8 compatibility FAQ to check if there's a solution to your issue. If a solution isn't documented, please report a bug . You can disable R8 by adding one of the following lines to your project's gradle.properties file:
# Disables R8 for Android Library modules only.
android.enableR8.libraries = false
# Disables R8 for all modules.
android.enableR8 = false
Note: For a given build type, if you set useProguard to false in your app module's build.gradle file, the Android Gradle plugin uses R8 to shrink your app's code for that build type, regardless of whether you disable R8 in your project's gradle.properties file.
-
ndkCompileis deprecated: You now get a build error if you try to usendkBuildto compile your native libraries. You should instead use either CMake or ndk-build to Add C and C++ code to your project .
مشکلات شناخته شده
The correct usage of unique package names are currently not enforced but will become more strict on later versions of the plugin. On Android Gradle plugin version 3.4.0, you can opt-in to check whether your project declares acceptable package names by adding the line below to your
gradle.propertiesfile.android.uniquePackageNames = trueTo learn more about setting a package name through the Android Gradle plugin, see Set the application ID .
3.3.0 (January 2019)
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
Gradle 4.10.1 or higher. To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
Note: When using Gradle 5.0 and higher, the default Gradle daemon memory heap size decreases from 1 GB to 512 MB. This might result in a build performance regression. To override this default setting, specify the Gradle daemon heap size in your project's
gradle.propertiesfile.SDK Build Tools 28.0.3 or higher.
3.3.3 (July 2020)
This minor update supports compatibility with new default settings and features for package visibility in Android 11 .
See the 4.0.1 release notes for details.
3.3.2 (March 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.3.2 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements. To see a list of noteable bug fixes, read the related post on the Release Updates blog .
3.3.1 (February 2019)
This minor update supports Android Studio 3.3.1 and includes various bug fixes and performance improvements.
New features
Improved classpath synchronization: When resolving dependencies on your runtime and compile time classpaths, the Android Gradle plugin attempts to fix certain downstream version conflicts for dependencies that appear across multiple classpaths.
For example, if the runtime classpath includes Library A version 2.0 and the compile classpath includes Library A version 1.0, the plugin automatically updates the dependency on the compile classpath to Library A version 2.0 to avoid errors.
However, if the runtime classpath includes Library A version 1.0 and the compile includes Library A version 2.0, the plugin does not downgrade the dependency on the compile classpath to Library A version 1.0, and you will get an error. To learn more, see Fix conflicts between classpaths .
Improved incremental Java compilation when using annotation processors: This update decreases build time by improving support for incremental Java compilation when using annotation processors.
Note: This feature is compatible with Gradle 4.10.1 and higher, except Gradle 5.1 due to Gradle issue 8194 .
For projects using Kapt (most Kotlin-only projects and Kotlin-Java hybrid projects): Incremental Java compilation is enabled, even when you use data binding or the retro-lambda plugin. Annotation processing by the Kapt task is not yet incremental.
For projects not using Kapt (Java-only projects): If the annotation processors you use all support incremental annotation processing , incremental Java compilation is enabled by default. To monitor incremental annotation processor adoption, watch Gradle issue 5277 .
If, however, one or more annotation processors do not support incremental builds, incremental Java compilation is not enabled. Instead, you can include the following flag in your
gradle.propertiesfile:android.enableSeparateAnnotationProcessing=trueWhen you include this flag, the Android Gradle plugin executes the annotation processors in a separate task and allows the Java compilation task to run incrementally.
Better debug info when using obsolete API: When the plugin detects that you're using an API that's no longer supported, it can now provide more-detailed information to help you determine where that API is being used. To see the additional info, you need to include the following in your project's
gradle.propertiesfile:android.debug.obsoleteApi=trueYou can also enable the flag by passing
-Pandroid.debug.obsoleteApi=truefrom the command line.You can run instrumentation tests on feature modules from the command line.
Behavior changes
Lazy task configuration: The plugin now uses Gradle's new task creation API to avoid initializing and configuring tasks that are not required to complete the current build (or tasks not on the execution task graph). For example, if you have multiple build variants, such as “release” and “debug” build variants, and you're building the “debug” version of your app, the plugin avoids initializing and configuring tasks for the “release” version of your app.
Calling certain older methods in the Variants API, such as
variant.getJavaCompile(), might still force task configuration. To make sure that your build is optimized for lazy task configuration, invoke new methods that instead return a TaskProvider object, such asvariant.getJavaCompileProvider().If you execute custom build tasks, learn how to adapt to Gradle's new task-creation API .
For a given build type, when setting
useProguard false, the plugin now uses R8 instead of ProGuard to shrink and obfuscate your app's code and resources. To learn more about R8, read this blog post from the Android Developer's Blog.Faster R class generation for library projects: Previously, the Android Gradle plugin would generate an
R.javafile for each of your project's dependencies and then compile those R classes alongside your app's other classes. The plugin now generates a JAR containing your app's compiled R class directly, without first building intermediateR.javaclasses. This optimization may significantly improve build performance for projects that include many library subprojects and dependencies, and improve the indexing speed in Android Studio.When building an Android App Bundle , APKs generated from that app bundle that target Android 6.0 (API level 23) or higher now include uncompressed versions of your native libraries by default. This optimization avoids the need for the device to make a copy of the library and thus reduces the on-disk size of your app. If you'd rather disable this optimization, add the following to your
gradle.propertiesfile:android.bundle.enableUncompressedNativeLibs = falseThe plugin enforces minimum versions of some third-party plugins.
Single-variant project sync : Syncing your project with your build configuration is an important step in letting Android Studio understand how your project is structured. However, this process can be time-consuming for large projects. If your project uses multiple build variants, you can now optimize project syncs by limiting them to only the variant you have currently selected.
You need to use Android Studio 3.3 or higher with Android Gradle Plugin 3.3.0 or higher to enable this optimization. When you meet these requirements, the IDE prompts you to enable this optimization when you sync your project. The optimization is also enabled by default on new projects.
To enable this optimization manually, click File > Settings > Experimental > Gradle ( Android Studio > Preferences > Experimental > Gradle on a Mac) and select the Only sync the active variant checkbox.
Note : This optimization fully supports projects that include Java and C++ languages, and has some support for Kotlin. When enabling the optimization for projects with Kotlin content, Gradle sync falls back to using full variants internally.
Automatic downloading of missing SDK packages : This functionality has been expanded to support NDK. To learn more, read Auto-download missing packages with Gradle .
Bug Fixes
Android Gradle plugin 3.3.0 fixes the following issues:
- The build process calling
android.support.v8.renderscript.RenderScriptinstead of the AndroidX version, despite Jetifier being enabled - Clashes due to
androidx-rs.jarincluding statically bundledannotation.AnyRes - When using RenderScript, you no longer have to manually set the Build Tools version in your
build.gradlefiles
- The build process calling
3.2.0 (September 2018)
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
- Gradle 4.6 or higher. To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
- SDK Build Tools 28.0.3 or higher.
3.2.1 (October 2018)
With this update, you no longer need to specify a version for the SDK Build Tools. The Android Gradle plugin now uses version 28.0.3 by default.
New features
Support for building Android App Bundles: The app bundle is a new upload format that includes all your app's compiled code and resources while deferring APK generation and signing to the Google Play Store. You no longer have to build, sign, and manage multiple APKs, and users get smaller downloads that are optimized for their device. To learn more, read About Android App Bundles .
Support for improved incremental build speeds when using annotation processors: The
AnnotationProcessorOptionsDSL now extendsCommandLineArgumentProvider, which enables either you or the annotation processor author to annotate arguments for the processor using incremental build property type annotations . Using these annotations improves the correctness and performance of incremental and cached clean builds. To learn more, read Pass arguments to annotation processors .Migration tool for AndroidX: When using Android Gradle plugin 3.2.0 with Android 3.2 and higher, you can migrate your project's local and Maven dependencies to use the new AndroidX libraries by selecting Refactor > Migrate to AndroidX from the menu bar. Using this migration tool also sets the following flags to
truein yourgradle.propertiesfile:android.useAndroidX: When set totrue, the Android plugin uses the appropriate AndroidX library instead of a Support Library. When this flag is not specified, the plugin sets it tofalseby default.android.enableJetifier: When set totrue, the Android plugin automatically migrates existing third-party libraries to use AndroidX by rewriting their binaries. When this flag is not specified, the plugin sets it tofalseby default. You can set this flag totrueonly whileandroid.useAndroidXis also set totrue, otherwise you get a build error.To learn more, read the AndroidX overview .
New code shrinker, R8: R8 is a new tool for code shrinking and obfuscation that replaces ProGuard. You can start using the preview version of R8 by including the following in your project's
gradle.propertiesfile:android.enableR8 = true
android.enableR8 = true
Behavior changes
Desugaring with D8 is now enabled by default.
AAPT2 is now on Google's Maven repo. To use AAPT2, make sure that you have the
google()dependency in yourbuild.gradlefile, as shown below:buildscript { repositories { google() // here jcenter() } dependencies { classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.2.0' } } allprojects { repositories { google() // and here jcenter() }
buildscript { repositories { google() // here jcenter() } dependencies { classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.2.0' } } allprojects { repositories { google() // and here jcenter() }
Native multidex is now enabled by default. Previous versions of Android Studio enabled native multidex when deploying the debug version of an app to a device running Android API level 21 or higher. Now, whether you're deploying to a device or building an APK for release, the Android Gradle plugin enables native multidex for all modules that set
minSdkVersion=21or higher.The plugin now enforces a minimum version of the protobuf plugin (0.8.6), Kotlin plugin (1.2.50), and Crashlytics plugin (1.25.4).
The feature module plugin,
com.android.feature, now enforces the use of only letters, digits, and underscores when specifying a module name. For example, if your feature module name includes dashes, you get a build error. This behavior matches that of the dynamic feature plugin.
رفع اشکالات
- JavaCompile is now cacheable in projects with data binding. ( Issue #69243050 )
- Better compile avoidance for library modules with data binding. ( Issue #77539932 )
- You can now re-enable configure-on-demand if you've disable it in earlier versions due to some unpredictable build errors. ( Issue #77910727 )
3.1.0 (March 2018)
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
Gradle 4.4 or higher.
To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
Build Tools 27.0.3 or higher.
Keep in mind, you no longer need to specify a version for the build tools using the
android.buildToolsVersionproperty—the plugin uses the minimum required version by default.
New DEX compiler, D8
By default, Android Studio now uses a new DEX compiler called D8. DEX compilation is the process of transforming .class bytecode into .dex bytecode for the Android Runtime (or Dalvik, for older versions of Android). Compared to the previous compiler, called DX, D8 compiles faster and outputs smaller DEX files, all while having the same or better app runtime performance.
D8 shouldn't change your day-to-day app development workflow. However, if you experience any issues related to the new compiler, please report a bug . You can temporarily disable D8 and use DX by including the following in your project's gradle.properties file:
android.enableD8=false
For projects that use Java 8 language features , incremental desugaring is enabled by default. You can disable it by specifying the following in your project's gradle.properties file:
android.enableIncrementalDesugaring=false.
Preview users: If you're already using a preview version of D8, note that it now compiles against libraries included in the SDK build tools —not the JDK. So, if you are accessing APIs that exist in the JDK but not in the SDK build tools libraries, you get a compile error.
Behavior changes
When building multiple APKs that each target a different ABI, the no longer generates APKs for the following ABIs by default:
mips,mips64, andarmeabi.If you want to build APKs that target these ABIs, you must use NDK r16b or lower and specify the ABIs in your
build.gradlefile, as shown below:splits { abi { include 'armeabi', 'mips', 'mips64' ... } }
splits { abi { include("armeabi", "mips", "mips64") ... } }
The Android plugin's build cache now evicts cache entries that are older than 30 days.
Passing
"auto"toresConfigno longer automatically picks string resources to package into your APK. If you continue to use"auto", the plugin packages all string resources your app and its dependencies provide. So, you should instead specify each locale that you want the plugin to package into your APK.Because local modules can't depend on your app's test APK, adding dependencies to your instrumented tests using the
androidTestApiconfiguration, instead ofandroidTestImplementation, causes Gradle to issue the following warning:WARNING: Configuration 'androidTestApi' is obsolete and has been replaced with 'androidTestImplementation'
WARNING: Configuration 'androidTestApi' is obsolete and has been replaced with 'androidTestImplementation'
رفع اشکالات
- Fixes an issue where Android Studio doesn't properly recognize dependencies in composite builds.
- Fixes an issue where you get a project sync error when loading the Android plugin multiple times in a single build–for example, when multiple subprojects each include the Android plugin in their buildscript classpath.
3.0.0 (October 2017)
Android Gradle plugin 3.0.0 includes a variety of changes that aim to address performance issues of large projects.
For example, on a sample skeleton project with ~130 modules and a large number of external dependencies (but no code or resources), you can experience performance improvements similar to the following:
| Android plugin version + Gradle version | Android plugin 2.2.0 + Gradle 2.14.1 | Android plugin 2.3.0 + Gradle 3.3 | Android plugin 3.0.0 + Gradle 4.1 |
|---|---|---|---|
Configuration (eg running ./gradlew --help ) | ~2 mins | ~9 s | ~2.5 s |
| 1-line Java change (implementation change) | ~2 mins 15 s | ~29 s | ~6.4 s |
Some of these changes break existing builds. So, you should consider the\ effort of migrating your project before using the new plugin.
If you don't experience the performance improvements described above, please file a bug and include a trace of your build using the Gradle Profiler .
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
- Gradle 4.1 or higher. To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
- Build Tools 26.0.2 or higher. With this update, you no longer need to specify a version for the build tools—the plugin uses the minimum required version by default. So, you can now remove the
android.buildToolsVersionproperty.
3.0.1 (November 2017)
This is a minor update to support Android Studio 3.0.1, and includes general bug fixes and performance improvements.
بهینهسازیها
- Better parallelism for multi-module projects through a fine grained task graph.
- When making changes to dependency, Gradle performs faster builds by not re-compiling modules that do not have access to that dependency's API. You should restrict which dependencies leak their APIs to other modules by using Gradle's new dependency configurations :
implementation,api,compileOnly, andruntimeOnly. - Faster incremental build speed due to per-class dexing. Each class is now compiled into separate DEX files, and only the classes that are modified are re-dexed. You should also expect improved build speeds for apps that set
minSdkVersionto 20 or lower, and use legacy multi-dex . - Improved build speeds by optimizing certain tasks to use chached outputs. To benefit from this optimization, you need to first enable the Gradle build cache .
- Improved incremental resource processing using AAPT2, which is now enabled by default. If you are experiencing issues while using AAPT2, please report a bug . You can also disable AAPT2 by setting
android.enableAapt2=falsein yourgradle.propertiesfile and restarting the Gradle daemon by running./gradlew --stopfrom the command line.
New features
- Variant-aware dependency management . When building a certain variant of a module, the plugin now automatically matches variants of local library module dependencies to the variant of the module you are building.
- Includes a new Feature module plugin to support Android Instant Apps and the Android Instant Apps SDK (which you can download using the SDK manager ). To learn more about creating Feature modules with the new plugin, read Structure of an instant app with multiple features .
- Built-in support for using certain Java 8 language features and Java 8 libraries. Jack is now deprecated and no longer required , and you should first disable Jack to use the improved Java 8 support built into the default toolchain. For more information, read Use Java 8 language features .
Added support for running tests with Android Test Orchestrator , which allows you to run each of your app's tests within its own invocation of Instrumentation. Because each test runs in its own Instrumentation instance, any shared state between tests doesn't accumulate on your device's CPU or memory. And, even if one test crashes, it takes down only its own instance of Instrumentation, so your other tests still run.
- Added
testOptions.executionto determine whether to use on-device test orchestration. If you want to use Android Test Orchestrator , you need to specifyANDROID_TEST_ORCHESTRATOR, as shown below. By default, this property is set toHOST, which disables on-device orchestration and is the standard method of running tests.
Groovy
android { testOptions { execution 'ANDROID_TEST_ORCHESTRATOR' } }
کاتلین
android { testOptions { execution = "ANDROID_TEST_ORCHESTRATOR" } }
- Added
New
androidTestUtildependency configuration allows you to install another test helper APK before running your instrumentation tests, such as Android Test Orchestrator:Groovy
dependencies { androidTestUtil 'com.android.support.test:orchestrator:1.0.0' ... }
کاتلین
dependencies { androidTestUtil("com.android.support.test:orchestrator:1.0.0") ... }
Added
testOptions.unitTests.includeAndroidResourcesto support unit tests that require Android resources, such as Roboelectric . When you set this property totrue, the plugin performs resource, asset, and manifest merging before running your unit tests. Your tests can then inspectcom/android/tools/test_config.propertieson the classpath for the following keys:android_merged_assets: the absolute path to the merged assets directory.Note: For library modules, the merged assets do not contain the assets of dependencies (see issue #65550419 ).
android_merged_manifest: the absolute path to the merged manifest file.android_merged_resources: the absolute path to the merged resources directory, which contains all the resources from the module and all its dependencies.android_custom_package: the package name of the final R class. If you dynamically modify the application ID, this package name may not match thepackageattribute in the app's manifest.
- Support for fonts as resources (which is a new feature introduced in Android 8.0 (API level 26) ).
- Support for language-specific APKs with Android Instant Apps SDK 1.1 and higher.
You can now change the output directory for your external native build project, as shown below:
Groovy
android { ... externalNativeBuild { // For ndk-build, instead use the ndkBuild block. cmake { ... // Specifies a relative path for outputs from external native // builds. You can specify any path that's not a subdirectory // of your project's temporary build/ directory. buildStagingDirectory "./outputs/cmake" } } }
کاتلین
android { ... externalNativeBuild { // For ndk-build, instead use the ndkBuild block. cmake { ... // Specifies a relative path for outputs from external native // builds. You can specify any path that's not a subdirectory // of your project's temporary build/ directory. buildStagingDirectory = "./outputs/cmake" } } }
- You can now use CMake 3.7 or higher when building native projects from Android Studio.
New
lintChecksdependency configuration allows you to build a JAR that defines custom lint rules, and package it into your AAR and APK projects.Your custom lint rules must belong to a separate project that outputs a single JAR and includes only
compileOnlydependencies. Other app and library modules can then depend on your lint project using thelintChecksconfiguration:Groovy
dependencies { // This tells the Gradle plugin to build ':lint-checks' into a lint.jar file // and package it with your module. If the module is an Android library, // other projects that depend on it automatically use the lint checks. // If the module is an app, lint includes these rules when analyzing the app. lintChecks project(':lint-checks') }
کاتلین
dependencies { // This tells the Gradle plugin to build ':lint-checks' into a lint.jar file // and package it with your module. If the module is an Android library, // other projects that depend on it automatically use the lint checks. // If the module is an app, lint includes these rules when analyzing the app. lintChecks(project(":lint-checks")) }
Behavior changes
- Android plugin 3.0.0 removes certain APIs, and your build will break if you use them. For example, you can no longer use the Variants API to access
outputFile()objects or useprocessManifest.manifestOutputFile()to get the manifest file for each variant. To learn more, read API changes . - You no longer need to specify a version for the build tools (so, you can now remove the
android.buildToolsVersionproperty). By default, the plugin automatically uses the minimum required build tools version for the version of Android plugin you're using. - You now enable/disable PNG crunching in the
buildTypesblock, as shown below. PNG crunching is enabled by default for all builds except debug builds because it increases build times for projects that include many PNG files. So, to improve build times for other build types, you should either disable PNG crunching or convert your images to WebP .Groovy
android { buildTypes { release { // Disables PNG crunching for the release build type. crunchPngs false } } }
کاتلین
android { buildTypes { release { // Disables PNG crunching for the release build type. isCrunchPngs = false } } }
- The Android plugin now automatically builds executable targets that you configure in your external CMake projects.
- You must now add annotation processors to the processor classpath using the
annotationProcessordependency configuration. - Using the deprecated
ndkCompileis now more restricted. You should instead migrate to using either CMake or ndk-build to compile native code that you want to package into your APK. To learn more, read Migrate from ndkcompile .
3.0.0 (October 2017)
Android Gradle plugin 3.0.0 includes a variety of changes that aim to address performance issues of large projects.
For example, on a sample skeleton project with ~130 modules and a large number of external dependencies (but no code or resources), you can experience performance improvements similar to the following:
| Android plugin version + Gradle version | Android plugin 2.2.0 + Gradle 2.14.1 | Android plugin 2.3.0 + Gradle 3.3 | Android plugin 3.0.0 + Gradle 4.1 |
|---|---|---|---|
Configuration (eg running ./gradlew --help ) | ~2 mins | ~9 s | ~2.5 s |
| 1-line Java change (implementation change) | ~2 mins 15 s | ~29 s | ~6.4 s |
Some of these changes break existing builds. So, you should consider the\ effort of migrating your project before using the new plugin.
If you don't experience the performance improvements described above, please file a bug and include a trace of your build using the Gradle Profiler .
This version of the Android plugin requires the following:
- Gradle 4.1 or higher. To learn more, read the section about updating Gradle .
- Build Tools 26.0.2 or higher. With this update, you no longer need to specify a version for the build tools—the plugin uses the minimum required version by default. So, you can now remove the
android.buildToolsVersionproperty.
3.0.1 (November 2017)
This is a minor update to support Android Studio 3.0.1, and includes general bug fixes and performance improvements.
بهینهسازیها
- Better parallelism for multi-module projects through a fine grained task graph.
- When making changes to dependency, Gradle performs faster builds by not re-compiling modules that do not have access to that dependency's API. You should restrict which dependencies leak their APIs to other modules by using Gradle's new dependency configurations :
implementation,api,compileOnly, andruntimeOnly. - Faster incremental build speed due to per-class dexing. Each class is now compiled into separate DEX files, and only the classes that are modified are re-dexed. You should also expect improved build speeds for apps that set
minSdkVersionto 20 or lower, and use legacy multi-dex . - Improved build speeds by optimizing certain tasks to use chached outputs. To benefit from this optimization, you need to first enable the Gradle build cache .
- Improved incremental resource processing using AAPT2, which is now enabled by default. If you are experiencing issues while using AAPT2, please report a bug . You can also disable AAPT2 by setting
android.enableAapt2=falsein yourgradle.propertiesfile and restarting the Gradle daemon by running./gradlew --stopfrom the command line.
New features
- Variant-aware dependency management . When building a certain variant of a module, the plugin now automatically matches variants of local library module dependencies to the variant of the module you are building.
- Includes a new Feature module plugin to support Android Instant Apps and the Android Instant Apps SDK (which you can download using the SDK manager ). To learn more about creating Feature modules with the new plugin, read Structure of an instant app with multiple features .
- Built-in support for using certain Java 8 language features and Java 8 libraries. Jack is now deprecated and no longer required , and you should first disable Jack to use the improved Java 8 support built into the default toolchain. For more information, read Use Java 8 language features .
Added support for running tests with Android Test Orchestrator , which allows you to run each of your app's tests within its own invocation of Instrumentation. Because each test runs in its own Instrumentation instance, any shared state between tests doesn't accumulate on your device's CPU or memory. And, even if one test crashes, it takes down only its own instance of Instrumentation, so your other tests still run.
- Added
testOptions.executionto determine whether to use on-device test orchestration. If you want to use Android Test Orchestrator , you need to specifyANDROID_TEST_ORCHESTRATOR, as shown below. By default, this property is set toHOST, which disables on-device orchestration and is the standard method of running tests.
Groovy
android { testOptions { execution 'ANDROID_TEST_ORCHESTRATOR' } }
کاتلین
android { testOptions { execution = "ANDROID_TEST_ORCHESTRATOR" } }
- Added
New
androidTestUtildependency configuration allows you to install another test helper APK before running your instrumentation tests, such as Android Test Orchestrator:Groovy
dependencies { androidTestUtil 'com.android.support.test:orchestrator:1.0.0' ... }
کاتلین
dependencies { androidTestUtil("com.android.support.test:orchestrator:1.0.0") ... }
Added
testOptions.unitTests.includeAndroidResourcesto support unit tests that require Android resources, such as Roboelectric . When you set this property totrue, the plugin performs resource, asset, and manifest merging before running your unit tests. Your tests can then inspectcom/android/tools/test_config.propertieson the classpath for the following keys:android_merged_assets: the absolute path to the merged assets directory.Note: For library modules, the merged assets do not contain the assets of dependencies (see issue #65550419 ).
android_merged_manifest: the absolute path to the merged manifest file.android_merged_resources: the absolute path to the merged resources directory, which contains all the resources from the module and all its dependencies.android_custom_package: the package name of the final R class. If you dynamically modify the application ID, this package name may not match thepackageattribute in the app's manifest.
- Support for fonts as resources (which is a new feature introduced in Android 8.0 (API level 26) ).
- Support for language-specific APKs with Android Instant Apps SDK 1.1 and higher.
You can now change the output directory for your external native build project, as shown below:
Groovy
android { ... externalNativeBuild { // For ndk-build, instead use the ndkBuild block. cmake { ... // Specifies a relative path for outputs from external native // builds. You can specify any path that's not a subdirectory // of your project's temporary build/ directory. buildStagingDirectory "./outputs/cmake" } } }
کاتلین
android { ... externalNativeBuild { // For ndk-build, instead use the ndkBuild block. cmake { ... // Specifies a relative path for outputs from external native // builds. You can specify any path that's not a subdirectory // of your project's temporary build/ directory. buildStagingDirectory = "./outputs/cmake" } } }
- You can now use CMake 3.7 or higher when building native projects from Android Studio.
New
lintChecksdependency configuration allows you to build a JAR that defines custom lint rules, and package it into your AAR and APK projects.Your custom lint rules must belong to a separate project that outputs a single JAR and includes only
compileOnlydependencies. Other app and library modules can then depend on your lint project using thelintChecksconfiguration:Groovy
dependencies { // This tells the Gradle plugin to build ':lint-checks' into a lint.jar file // and package it with your module. If the module is an Android library, // other projects that depend on it automatically use the lint checks. // If the module is an app, lint includes these rules when analyzing the app. lintChecks project(':lint-checks') }
کاتلین
dependencies { // This tells the Gradle plugin to build ':lint-checks' into a lint.jar file // and package it with your module. If the module is an Android library, // other projects that depend on it automatically use the lint checks. // If the module is an app, lint includes these rules when analyzing the app. lintChecks(project(":lint-checks")) }
Behavior changes
- Android plugin 3.0.0 removes certain APIs, and your build will break if you use them. For example, you can no longer use the Variants API to access
outputFile()objects or useprocessManifest.manifestOutputFile()to get the manifest file for each variant. To learn more, read API changes . - You no longer need to specify a version for the build tools (so, you can now remove the
android.buildToolsVersionproperty). By default, the plugin automatically uses the minimum required build tools version for the version of Android plugin you're using. - You now enable/disable PNG crunching in the
buildTypesblock, as shown below. PNG crunching is enabled by default for all builds except debug builds because it increases build times for projects that include many PNG files. So, to improve build times for other build types, you should either disable PNG crunching or convert your images to WebP .Groovy
android { buildTypes { release { // Disables PNG crunching for the release build type. crunchPngs false } } }
کاتلین
android { buildTypes { release { // Disables PNG crunching for the release build type. isCrunchPngs = false } } }
- The Android plugin now automatically builds executable targets that you configure in your external CMake projects.
- You must now add annotation processors to the processor classpath using the
annotationProcessordependency configuration. - Using the deprecated
ndkCompileis now more restricted. You should instead migrate to using either CMake or ndk-build to compile native code that you want to package into your APK. To learn more, read Migrate from ndkcompile .
2.3.0 (February 2017)
2.3.3 (June 2017)
This is a minor update that adds compatibility with Android Studio 2.3.3 .
2.3.2 (May 2017)
This is a minor update that adds compatibility with Android Studio 2.3.2 .
2.3.1 (April 2017)
This is a minor update to Android plugin 2.3.0 that fixes an issue where some physical Android devices did not work properly with Instant Run (see Issue #235879 ).
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 3.3 or higher.
- Build Tools 25.0.0 or higher.
- New:
- Uses Gradle 3.3, which includes performance improvements and new features. For more details, see the Gradle release notes .
- Build cache : stores certain outputs that the Android plugin generates when building your project (such as unpackaged AARs and pre-dexed remote dependencies). Your clean builds are much faster while using the cache because the build system can simply reuse those cached files during subsequent builds, instead of recreating them. Projects using Android plugin 2.3.0 and higher use the build cache by default. To learn more, read Improve Build Speed with Build Cache .
- Includes a
cleanBuildCachetask that clears the build cache . - If you are using the experimental version of build cache (included in earlier versions of the plugin), you should update your plugin to the latest version.
- Includes a
- Changes:
- Supports changes to Instant Run included in Android Studio 2.3 .
- Configuration times for very large projects should be significantly faster.
- Fixed issues with auto-downloading for the constraint layout library .
- Plugin now uses ProGuard version 5.3.2 .
- Includes many fixes for reported bugs . Please continue to file bug reports when you encounter issues.
2.2.0 (September 2016)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.14.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 23.0.2 or higher.
- New:
- Uses Gradle 2.14.1, which includes performance improvements and new features, and fixes a security vulnerability that allows local privilege escalation when using the Gradle daemon. For more details, see the Gradle release notes .
- Using the
externalNativeBuild {}DSL, Gradle now lets you link to your native sources and compile native libraries using CMake or ndk-build. After building your native libraries, Gradle packages them into your APK. To learn more about using CMake and ndk-build with Gradle, read Add C and C++ Code to Your Project . - When you run a build from the command line , Gradle now attempts to auto-download any missing SDK components or updates that your project depends on. To learn more, read Auto-download missing packages with Gradle .
- A new experimental caching feature lets Gradle speed up build times by pre-dexing, storing, and reusing the pre-dexed versions of your libraries. To learn more about using this experimental feature, read the Build Cache guide.
- Improves build performance by adopting a new default packaging pipeline which handles zipping, signing, and zipaligning in one task. You can revert to using the older packaging tools by adding
android.useOldPackaging=trueto yourgradle.propertiesfile. While using the new packaging tool, thezipalignDebugtask is not available. However, you can create one yourself by calling thecreateZipAlignTask(String taskName, File inputFile, File outputFile)method. - APK signing now uses APK Signature Scheme v2 in addition to traditional JAR signing. All Android platforms accept the resulting APKs. Any modification to these APKs after signing invalidates their v2 signatures and prevents installation on a device. To disable this feature, add the following to your module-level
build.gradlefile:Groovy
android { ... signingConfigs { config { ... v2SigningEnabled false } } }
کاتلین
android { ... signingConfigs { create("config") { ... v2SigningEnabled = false } } }
- For multidex builds, you can now use ProGuard rules to determine which classes Gradle should compile into your app's main DEX file. Because the Android system loads the main DEX file first when starting your app, you can prioritize certain classes at startup by compiling them into the main DEX file. After you create a ProGuard configuration file specifically for your main DEX file, pass the configuration file's path to Gradle using
buildTypes.multiDexKeepProguard. Using this DSL is different from usingbuildTypes.proguardFiles, which provides general ProGuard rules for your app and does not specify classes for the main DEX file. - Adds support for the
android:extractNativeLibsflag, which can reduce the size of your app when you install it on a device. When you set this flag tofalsein the<application>element of your app manifest, Gradle packages uncompressed and aligned versions of your native libraries with your APK. This preventsPackageManagerfrom copying out your native libraries from the APK to the device's file system during installation and has the added benefit of making delta updates of your app smaller. - You can now specify
versionNameSuffixandapplicationIdSuffixfor product flavors. ( Issue 59614 )
- Changes:
-
getDefaultProguardFilenow returns the default ProGuard files that Android plugin for Gradle provides and no longer uses the ones in the Android SDK. - Improved Jack compiler performance and features:
- Jack now supports Jacoco test coverage when setting
testCoverageEnabledtotrue. - Improved support for annotation processors. Annotation processors on your classpath, such as any
compiledependencies, are automatically applied to your build. You can also specify an annotation processor in your build and pass arguments by using thejavaCompileOptions.annotationProcessorOptions {}DSL in your module-levelbuild.gradlefile:Groovy
android { ... defaultConfig { ... javaCompileOptions { annotationProcessorOptions { className 'com.example.MyProcessor' // Arguments are optional. arguments = [ foo : 'bar' ] } } } }
کاتلین
android { ... defaultConfig { ... javaCompileOptions { annotationProcessorOptions { className = "com.example.MyProcessor" // Arguments are optional. arguments(mapOf(foo to "bar")) } } } }
If you want to apply an annotation processor at compile time but not include it in your APK, use the
annotationProcessordependency scope:Groovy
dependencies { compile 'com.google.dagger:dagger:2.0' annotationProcessor 'com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:2.0' // or use buildVariantAnnotationProcessor to target a specific build variant }
کاتلین
dependencies { implementation("com.google.dagger:dagger:2.0") annotationProcessor("com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:2.0") // or use buildVariantAnnotationProcessor to target a specific build variant }
- By default, if the Gradle daemon's heap size is at least 1.5 GB, Jack now runs in the same process as Gradle. To adjust the daemon heap size, add the following to your
gradle.propertiesfile:# This sets the daemon heap size to 1.5GB. org.gradle.jvmargs=-Xmx1536M
For a list of parameters you can set, run the following from the command line:
java -jar /build-tools/jack.jar --help-properties
- Jack now supports Jacoco test coverage when setting
-
2.1.0 (April 2016)
2.1.3 (August 2016)
This update requires Gradle 2.14.1 and higher. Gradle 2.14.1 includes performance improvements, new features, and an important security fix . For more details, see the Gradle release notes .
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.10 or higher.
- Build Tools 23.0.2 or higher.
- New:
- Added support for the N Developer Preview, JDK 8, and Java 8 language features using the Jack toolchain. To find out more, read the N Preview guide .
Note: Instant Run does not currently work with Jack and will be disabled while using the new toolchain. You only need to use Jack if you are developing for the N Preview and want to use the supported Java 8 language features.
- Added default support for incremental Java compilation to reduce compilation time during development. It does this by only recompiling portions of the source that have changed or need to be recompiled. To disable this feature, add the following code to your module-level
build.gradlefile:Groovy
android { ... compileOptions { incremental false } }
کاتلین
android { ... compileOptions { incremental = false } }
Added support for dexing-in-process which performs dexing within the build process rather than in a separate, external VM processes. This not only makes incremental builds faster, but also speeds up full builds. The feature is enabled by default for projects that have set the Gradle daemon's maximum heap size to at least 2048 MB. You can do this by including the following in your project's
```none org.gradle.jvmargs = -Xmx2048m ```gradle.propertiesfile:If you have defined a value for
```none org.gradle.jvmargs = -Xmx3072m ```javaMaxHeapSizein your module-levelbuild.gradlefile, you need to setorg.gradle.jvmargsto the value ofjavaMaxHeapSize+ 1024 MB. For example, if you have setjavaMaxHeapSizeto "2048m", you need to add the following to your project'sgradle.propertiesfile:To disable dexing-in-process, add the following code to your module-level
build.gradlefile:Groovy
android { ... dexOptions { dexInProcess false } }
کاتلین
android { ... dexOptions { dexInProcess = false } }
- Added support for the N Developer Preview, JDK 8, and Java 8 language features using the Jack toolchain. To find out more, read the N Preview guide .
2.0.0 (April 2016)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.10 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- New:
- Enables Instant Run by supporting bytecode injection, and pushing code and resource updates to a running app on the emulator or a physical device.
- Added support for incremental builds, even when the app isn't running. Full build times are improved by pushing incremental changes through the Android Debug Bridge to the connected device.
- Added
maxProcessCountto control how many worker dex processes can be spawned concurrently. The following code, in the module-levelbuild.gradlefile, sets the maximum number of concurrent processes to 4:Groovy
android { ... dexOptions { maxProcessCount = 4 // this is the default value } }
کاتلین
android { ... dexOptions { maxProcessCount = 4 // this is the default value } }
</li> <li>Added an experimental code shrinker to support pre-dexing and reduce re-dexing of dependencies, which are not supported with Proguard. This improves the build speed of your debug build variant. Because the experimental shrinker does not support optimization and obfuscation, you should enable Proguard for your release builds. To enable the experimental shrinker for your debug builds, add the following to your module-level <code>build.gradle</code> file:Groovy
android { ... buildTypes { debug { minifyEnabled true useProguard false } release { minifyEnabled true useProguard true // this is a default setting } } }
کاتلین
android { ... buildTypes { getByName("debug") { minifyEnabled = true useProguard = false } getByName("release") { minifyEnabled = true useProguard = true // this is a default setting } } }
</li> <li>Added logging support and improved performance for the resource shrinker. The resource shrinker now logs all of its operations into a <code>resources.txt</code> file located in the same folder as the Proguard log files. </li> </ul>
- Changed behavior:
- When
minSdkVersionis set to 18 or higher, APK signing uses SHA256.
<li>DSA and ECDSA keys can now sign APK packages. <p class="note"> <strong>Note:</strong> The <a href= "/training/articles/keystore.html">Android keystore</a> provider no longer supports <a href= "/about/versions/marshmallow/android-6.0-changes.html#behavior-keystore"> DSA keys on Android 6.0</a> (API level 23) and higher. </p> </li> </ul>- When
- Fixed issues:
- Fixed an issue that caused duplicate AAR dependencies in both the test and main build configurations.
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.5.0 (November 2015)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Integrated the Data Binding plugin into the Android plugin for Gradle. To enable it, add the following code to each per-project
build.gradlefile that uses the plugin: - Added a new Transform API to allow third-party plugins to manipulate compiled
.classfiles before they're converted to.dexfiles. The Transform API simplifies injecting custom class manipulations while offering more flexibility regarding what you can manipulate. To insert a transform into a build, create a new class implementing one of theTransforminterfaces, and register it withandroid.registerTransform(theTransform)orandroid.registerTransform(theTransform, dependencies). There's no need to wire tasks together. Note the following about the Transform API: - A transform can apply to one or more of the following: the current project, subprojects, and external libraries.
- A transform must be registered globally, which applies them to all variants.
- Internal code processing, through the Java Code Coverage Library (JaCoCo), ProGuard, and MultiDex, now uses the Transform API. However, the Java Android Compiler Kit (Jack) doesn't use this API: only the
javac/dxcode path does. - Gradle executes the transforms in this order: JaCoCo, third-party plugins, ProGuard. The execution order for third-party plugins matches the order in which the transforms are added by the third party plugins; third-party plugin developers can't control the execution order of the transforms through an API.
- Deprecated the
dexgetter from theApplicationVariantclass. You can't access theDextask through the variant API anymore because it's now accomplished through a transform. There's currently no replacement for controlling the dex process. - Fixed incremental support for assets.
- Improved MultiDex support by making it available for test projects, and tests now automatically have the
com.android.support:multidex-instrumentationdependency. - Added the ability to properly fail a Gradle build and report the underlying error cause when the Gradle build invokes asynchronous tasks and there's a failure in the worker process.
- Added support for configuring a specific Application Binary Interface (ABI) in variants that contain multiple ABIs.
- Added support for a comma-separated list of device serial numbers for the
ANDROID_SERIALenvironment variable when installing or running tests. - Fixed an installation failure on devices running Android 5.0 (API level 20) and higher when the APK name contains a space.
- Fixed various issues related to the Android Asset Packaging Tool (AAPT) error output.
- Added JaCoCo incremental instrumentation support for faster incremental builds. The Android plugin for Gradle now invokes the JaCoCo instrumenter directly. To force a newer version of the JaCoCo instrumenter, you need to add it as a build script dependency.
- Fixed JaCoCo support so it ignores files that aren't classes.
- Added vector drawable support for generating PNGs at build time for backward-compatibility. Android plugin for Gradle generates PNGs for every vector drawable found in a resource directory that doesn't specify an API version or specifies an
android:minSdkVersionattribute of 20 or lower in the<uses-sdk>element in the app manifest. You can set PNG densities by using thegeneratedDensitiesproperty in thedefaultConfigorproductFlavorsections of abuild.gradlefile. - Added sharing of the mockable
android.jar, which the plugin generates only once and uses for unit testing. Multiple modules, such asappandlib, now share it. Delete$rootDir/buildto regenerate it. - Changed the processing of Java resources to occur before the obfuscation tasks instead of during the packaging of the APK. This change allows the obfuscation tasks to have a chance to adapt the Java resources following packages obfuscation.
- Fixed an issue with using Java Native Interface (JNI) code in the experimental library plugin.
- Added the ability to set the platform version separately from the
android:compileSdkVersionattribute in the experimental library plugin.
android { dataBinding { enabled = true } }
android { dataBinding { enabled = true } }
- Integrated the Data Binding plugin into the Android plugin for Gradle. To enable it, add the following code to each per-project
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.3.1 (August 2015)
Dependencies:- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- Fixed the ZipAlign task to properly consume the output of the previous task when using a customized filename.
- Fixed Renderscript packaging with the NDK .
- Maintained support for the
createDebugCoverageReportbuild task. - Fixed support for customized use of the
archiveBaseNameproperty in thebuild.gradlebuild file. - Fixed the
Invalid ResourceTypelint warning caused by parameter method annotation lookup when running lint outside of Android Studio.
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.3.0 (July 2015)
Dependencies:- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
Added support for the
com.android.build.threadPoolSizeproperty to control theAndroidtask thread pool size from thegradle.propertiesfile or the command line. The following example sets this property to 4.-Pcom.android.build.threadPoolSize=4- Set the default build behavior to exclude
LICENSEandLICENSE.txtfiles from APKs. To include these files in an APK, remove these files from thepackagingOptions.excludesproperty in thebuild.gradlefile. For example:android { packagingOptions.excludes = [] }
android { packagingOptions.excludes.clear() }
- Added the
sourceSetstask to inspect the set of all available source sets. - Enhanced unit test support to recognize multi-flavor and build variant source folders. For example, to test an app with multi-flavors
flavor1andflavorAwith theDebugbuild type, the test source sets are:- آزمون
- testFlavor1
- testFlavorA
- testFlavor1FlavorA
- testFlavor1FlavorADebug
Android tests already recognized multi-flavor source folders.
- Improved unit test support to:
- Run
javacon main and test sources, even if theuseJackproperty is set totruein your build file. - Correctly recognize dependencies for each build type.
- Run
- Added support for specifying instrumentation test-runner arguments from the command line. For example:
./gradlew connectedCheck \ -Pandroid.testInstrumentationRunnerArguments.size=medium \ -Pandroid.testInstrumentationRunnerArguments.class=TestA,TestB Added support for arbitrary additional Android Asset Packaging Tool (AAPT) parameters in the
build.gradlefile. For example:android { aaptOptions { additionalParameters "--custom_option", "value" } }
android { aaptOptions { additionalParameters += listOf("--custom_option", "value") } }
- Added support for a test APK module as a separate test module, using the
targetProjectPathandtargetVariantproperties to set the APK path and target variant.Note: A test APK module does not support product flavors and can only target a single variant. Also, Jacoco is not supported yet.
- Added resource name validation before merging resources.
- When building an AAR (Android ARchive) package for library modules, do not provide an automatic
@{applicationId}placeholder in the manifest merger settings. Instead, use a different placeholder, such as@{libApplicationId}and provide a value for it if you want to include application Ids in the archive library.
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.2.0 (April 2015)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Enhanced support for running unit tests with Gradle.
- Added support to include Java-style resources in the classpath when running unit tests directly from Gradle.
- Added unit test dependency support for Android Archive (AAR) artifacts.
- Added support for the
unitTestVariantsproperty so unit test variants can be manipulated using thebuild.gradlefile. - Added the
unitTest.allcode block undertestOptionsto configure customized tasks for unit test. The following sample code shows how to add unit test configuration settings using this new option:android { testOptions { unitTest.all { jvmArgs '-XX:MaxPermSize=256m' // Or any other gradle option. } } }
android { testOptions { unitTest.all { jvmArgs += listOf("-XX:MaxPermSize=256m") // Or any other gradle option. } } }
- Fixed the handling of enums and public instance fields in the packaging of the
mockable-android.jarfile. - Fixed library project task dependencies so test classes recompile after changes.
- Added the
testProguardFileproperty to apply ProGuard files when minifying a test APK. - Added the
timeOutproperty to theadbOptionscode block for setting the maximum recording time for Android Debug Bridge screen recording. - Added support for 280 dpi resources.
- Improved performance during project evaluation.
- Enhanced support for running unit tests with Gradle.
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.1.3 (March 2015)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Fixed issue with duplicated dependencies on a test app that triggered a ProGuard failure.
- Fixed Comparator implementation which did not comply with the JDK Comparator contract and generated a JDK 7 error.
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.1.2 (February 2015)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Normalized path when creating a mockable JAR for unit testing.
- Fixed the
archivesBaseNamesetting in thebuild.gradlefile. - Fixed the unresolved placeholder failure in manifest merger when building a library test application.
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.1.1 (February 2015)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Modified build variants so only variants that package a Wear app trigger Wear-specific build tasks.
- Changed dependency related issues to fail at build time rather than at debug time. This behavior allows you to run diagnostic tasks (such as 'dependencies') to help resolve the conflict.
- Fixed the
android.getBootClasspath()method to return a value.
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.1.0 (February 2015)
- Dependencies:
- Gradle 2.2.1 or higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Added new unit test support
- Enabled unit tests to run on the local JVM against a special version of the
android.jarfile that is compatible with popular mocking frameworks, for example Mockito. - Added new test tasks
testDebug,testRelease, andtestMyFlavorDebugwhen using product flavors. - Added new source folders recognized as unit tests:
src/test/java/,src/testDebug/java/,src/testMyFlavor/java/. - Added new configurations in the
build.gradlefile for declaring test-only dependencies, for example,testCompile 'junit:junit:4.11',testMyFlavorCompile 'some:library:1.0'.Note: Test-only dependencies are not currently compatible with Jack (Java Android Compiler Kit).
- Added the
android.testOptions.unitTests.returnDefaultValuesoption to control the behaviour of the mockable android.jar. - Replaced
Testin test task names withAndroidTest. For example, theassembleDebugTesttask is nowassembleDebugAndroidTesttask. Unit test tasks still haveUnitTestin the task name, for exampleassembleDebugUnitTest. - Modified ProGuard configuration files to no longer apply to the test APK. If minification is enabled, ProGuard processes the test APK and applies only the mapping file that is generated when minifying the main APK.
- Updated dependency management
- Fixed issues using
providedandpackagescopes.Note: These scopes are incompatible with AAR (Android ARchive) packages and will cause a build with AAR packages to fail.
- Modified dependency resolution to compare the dependencies of an app under test and the test app. If an artifact with the same version is found for both apps, it's not included with the test app and is packaged only with the app under test. If an artifact with a different version is found for both apps, the build fails.
- Fixed issues using
- Added support for
anyDpiresource qualifier in resource merger. - Improved evaluation and IDE sync speeds for projects with a large number of Android modules .
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.0.1 (January 2015)
- Dependencies:
Gradle 2.2.1 up to 2.3.x.
Note: This version of the Android plugin for Gradle is not compatible with Gradle 2.4 and higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Fixed issue with Gradle build failure when accessing the
extractReleaseAnnotationsmodule. ( Issue 81638 ). - Fixed issue with
Disablepassing the--no-optimizesetting to the Dalvik Executable (dex) bytecode. ( Issue 82662 ). - Fixed manifest merger issues when importing libraries with a
targetSdkVersionless than 16. - Fixed density ordering issue when using Android Studio with JDK 8.
- Fixed issue with Gradle build failure when accessing the
Android plugin for Gradle, revision 1.0.0 (December 2014)
- Dependencies:
Gradle 2.2.1 up to 2.3.x.
Note: This version of the Android plugin for Gradle is not compatible with Gradle 2.4 and higher.
- Build Tools 21.1.1 or higher.
- General Notes:
- Initial plugin release.

