对包含原生代码的应用进行调试和性能剖析时,一些需要在进程启动时便启用的调试工具通常很有用。这要求您以全新的进程来运行应用,而不是从 zygote 克隆。例如:
- 使用 strace 跟踪系统调用。
- 使用 malloc debug 或 Address Sanitizer (ASan) 查找内存错误。
- 使用 Simpleperf 进行性能剖析。
使用封装 Shell 脚本
wrap.sh 的使用非常简单:
- 编译一个打包了以下内容的自定义可调试 APK:
- 一个名为
wrap.sh的 Shell 脚本。如需了解详情,请参阅创建封装 Shell 脚本和打包 wrap.sh。 - 您的 Shell 脚本需要的任何其他工具(例如您自己的
strace二进制文件)。
- 一个名为
- 在设备上安装可调试 APK。
- 启动应用。
创建封装 Shell 脚本
当您启动包含 wrap.sh 的可调试 APK 时,系统会执行该脚本并传递启动应用的命令作为参数。脚本负责启动应用,但可以对环境或参数进行任何更改。脚本应遵循 MirBSD Korn Shell (mksh) 语法。
以下代码段展示了如何编写只用于启动应用的简单 wrap.sh 文件:
#!/system/bin/sh exec "$@"
Malloc 调试
如需通过 wrap.sh 使用 malloc 调试,请添加以下行:
#!/system/bin/sh LIBC_DEBUG_MALLOC_OPTIONS=backtrace logwrapper "$@"
ASan
ASan 文档中包含一个示例,说明了如何为 ASan 执行此操作。
打包 wrap.sh
为了充分利用 wrap.sh,您的 APK 必须是可调试的。请确保在 Android 清单的 <application> 元素中配置了 android:debuggable="true" 设置,如果您使用的是 Android Studio,请确保已在 build.gradle 文件中配置了调试 build。
还需要在应用的 build.gradle 文件中将 useLegacyPackaging 设置为 true。在大多数情况下,此选项默认设置为 false,因此您可能需要将其明确设置为 true 以避免发生任何意外。
必须将 wrap.sh 脚本与应用的各原生库一起打包。如果应用没有原生库,请手动将 lib 目录添加到项目目录中。对于应用支持的每种架构,必须在该原生库目录下提供封装 Shell 脚本的副本。
以下示例展示了同时支持 ARMv8 和 x86-64 架构的文件布局:
# App Directory
|- AndroidManifest.xml
|- …
|- lib
|- arm64-v8a
|- ...
|- wrap.sh
|- x86_64
|- ...
|- wrap.sh
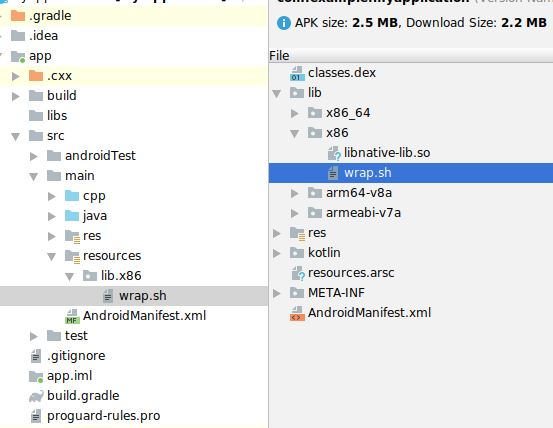
Android Studio 仅打包 lib/ 目录中的 .so 文件,因此如果您是 Android Studio 用户,则需要将 wrap.sh 文件放在 src/main/resources/lib/* 目录中,以便它们得到正确打包。
请注意,resources/lib/x86 在界面中显示为 lib.x86,但实际上它应该是子目录:
使用 wrap.sh 时进行调试
如果您在使用 wrap.sh 时想要附加调试程序,则您的 Shell 脚本将需要手动启用调试。如何执行此操作因版本而异,此示例展示了如何为支持 wrap.sh 的所有版本添加适当的选项:
#!/system/bin/sh
cmd=$1
shift
os_version=$(getprop ro.build.version.sdk)
if [ "$os_version" -eq "27" ]; then
cmd="$cmd -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_android_adb,suspend=n,server=y -Xcompiler-option --debuggable $@"
elif [ "$os_version" -eq "28" ]; then
cmd="$cmd -XjdwpProvider:adbconnection -XjdwpOptions:suspend=n,server=y -Xcompiler-option --debuggable $@"
else
cmd="$cmd -XjdwpProvider:adbconnection -XjdwpOptions:suspend=n,server=y $@"
fi
exec $cmd
