네이티브 코드로 앱을 디버깅하고 프로파일링할 때 프로세스 시작 시 사용 설정해야 하는 디버깅 도구를 사용하는 것이 유용할 때가 많습니다. 이를 위해서는 zegote에서 복제하는 것보다 새로운 프로세스에서 앱을 실행해야 합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
- strace로 시스템 호출 추적
- malloc debug 또는 Address Sanitizer(ASan)로 메모리 버그 찾기
- Simpleperf로 프로파일링
래핑 셸 스크립트 사용
wrap.sh 사용법은 간단합니다.
- 다음을 패키징하는 디버그 가능한 맞춤 APK를 컴파일합니다.
wrap.sh라는 셸 스크립트 자세한 내용은 래핑 셸 스크립트 만들기 및 wrap.sh 패키징을 참고하세요.- 셸 스크립트에 필요한 추가 도구(예: 자체
strace바이너리)
- 기기에 디버그 가능한 APK를 설치합니다.
- 앱을 실행합니다.
래핑 셸 스크립트 만들기
wrap.sh가 포함된 디버그 가능한 APK를 실행하면 시스템에서 스크립트를 실행하고 명령어를 전달하여 앱을 인수로 시작합니다. 스크립트가 앱을 실행하는데 환경이나 인수가 바뀔 수 있습니다. 스크립트는 MirBSD Korn 셸(mksh) 구문을 따라야 합니다.
다음 스니펫은 앱을 시작하기만 하는 간단한 wrap.sh 파일을 작성하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
#!/system/bin/sh exec "$@"
Malloc 디버그
wrap.sh를 통해 malloc 디버그를 사용하려면 다음 행을 포함하세요.
#!/system/bin/sh LIBC_DEBUG_MALLOC_OPTIONS=backtrace logwrapper "$@"
ASan
ASan 도움말에서 ASan에 대한 실행 방법의 예를 참조하세요.
wrap.sh 패키징
wrap.sh를 활용하려면 APK를 디버깅할 수 있어야 합니다. android:debuggable="true" 설정이 Android 매니페스트의 <application> 요소에 구성되어 있거나 build.gradle 파일에 디버그 빌드를 구성하는 Android 스튜디오를 사용하는지 확인하세요.
또한 앱의 build.gradle 파일에서 useLegacyPackaging을 true로 설정해야 합니다. 대부분의 경우 이 옵션은 false로 기본 설정되어 있으므로 명시적으로 true로 설정하여 예기치 않은 상황의 발생을 방지하는 것이 좋습니다.
앱의 네이티브 라이브러리로 wrap.sh 스크립트를 패키징해야 합니다. 앱에 네이티브 라이브러리가 포함되어 있지 않으면 프로젝트 디렉터리에 lib 디렉터리를 직접 추가해야 합니다. 앱에서 지원하는 각 아키텍처의 경우 해당 네이티브 라이브러리 디렉터리에 셸 스크립트 래핑의 사본을 제공해야 합니다.
다음 예는 ARMv8과 x86-64 아키텍처를 모두 지원하는 파일 레이아웃을 보여줍니다.
# App Directory
|- AndroidManifest.xml
|- …
|- lib
|- arm64-v8a
|- ...
|- wrap.sh
|- x86_64
|- ...
|- wrap.sh
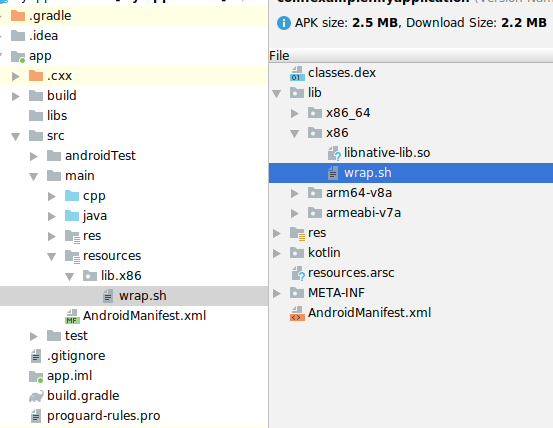
Android 스튜디오는 lib/ 디렉터리에서 .so 파일만 패키징하므로 Android 스튜디오 사용자라면 wrap.sh 파일을 src/main/resources/lib/* 디렉터리에 배치하여 올바르게 패키징해야 합니다.
resources/lib/x86은 UI에 lib.x86으로 표시되지만 실제로는 하위 디렉터리입니다.
wrap.sh 사용 시 디버그
wrap.sh를 사용할 때 디버거를 첨부하려면 셸 스크립트에서 직접 디버깅을 사용 설정해야 합니다. 실행 방법은 출시마다 다르므로 이 예는 wrap.sh를 지원하는 모든 출시에 적절한 옵션을 추가하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
#!/system/bin/sh
cmd=$1
shift
os_version=$(getprop ro.build.version.sdk)
if [ "$os_version" -eq "27" ]; then
cmd="$cmd -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_android_adb,suspend=n,server=y -Xcompiler-option --debuggable $@"
elif [ "$os_version" -eq "28" ]; then
cmd="$cmd -XjdwpProvider:adbconnection -XjdwpOptions:suspend=n,server=y -Xcompiler-option --debuggable $@"
else
cmd="$cmd -XjdwpProvider:adbconnection -XjdwpOptions:suspend=n,server=y $@"
fi
exec $cmd
