Device targeting gives you finer control over which parts of your app bundle are delivered to specific devices. For example, you could ensure that a large asset is only delivered to devices with high RAM, or you could deliver different versions of an asset to different devices.
You can target device properties such as:
- Device model
- Device RAM
- System features
- System on chip (for devices with API level at least 31)
Overview of required steps
The following steps are required to enable device targeting:
- Define your device groups in a device targeting configuration file.
- Specify which parts of your bundle should go to which device groups.
- Optional: Test your configuration locally.
- Upload your bundle (containing the configuration file) to Google Play.
Android Gradle Plugin versus Play Unity Plugin
The exact steps required are different depending on whether you are building your app with the Android Gradle Plugin or with the Play Unity Plugin. Before proceeding, select your build setup:
Check Android Gradle Plugin version
To use device targeting, ensure that your Android Gradle Plugin (AGP) version is at least 8.10.0-alpha01. This is packaged with Android Studio Meerkat 2 and higher.
Enable device targeting in Android Gradle Plugin
Device targeting must be enabled explicitly in your gradle.properties file:
android.experimental.enableDeviceTargetingConfigApi=true
Create a device targeting configuration XML file
The device targeting configuration file is an XML file in which you define your
custom device groups. For example, you could define a device group called
high_ram that contains all devices with at least 8GB of RAM:
<config:device-targeting-config
xmlns:config="http://schemas.android.com/apk/config">
<config:device-group name="high_ram">
<config:device-selector ram-min-bytes="8000000000"/>
</config:device-group>
</config:device-targeting-config>
A device group is composed of up to 5 device selectors. A device is included in a device group if it satisfies any of its device selectors.
A device selector can have one or more device properties. A device is selected if it matches all of the selector's device properties.
Available device properties
- device_ram: Device RAM requirements
- min_bytes (inclusive): Minimum required RAM (in bytes)
- max_bytes (exclusive): Maximum required RAM (in bytes)
- included_device_ids: Device models to be included in this selector
(max of 10000 device_ids per group). This property is satisfied if the
device matches any device_id in the list.
- build_brand: Device manufacturer
- build_device: Device model code
- excluded_device_ids: Device models to be excluded in this selector
(max of 10000 device_ids per group). This property is satisfied if the
device matches no device_id in the list.
- build_brand: Device manufacturer
- build_device: Device model code
required_system_features: Features that a device needs to have to be included by this selector (max of 100 features per group). A device needs to have all system features in this list to satisfy this property.
System feature reference
- name: A system feature
forbidden_system_features: Features that a device mustn't have to be included by this selector (max of 100 features per group). If a device has any of the system features in this list it doesn't satisfy this property.
System feature reference
- name: A system feature
system-on-chip: System on chips to be included in this selector. A device needs to have any chip in this list to satisfy this property. System on chips can only be targeted on devices with API level at least 31.
- manufacturer: System on chip manufacturer
- model: System on chip model
Including multiple properties in a single selector creates a logical AND, for example:
<config:device-selector ram-min-bytes="7000000000">
<config:included-device-id brand="google" device="flame"/>
</config:device-selector>
will create the condition for all devices with > 7GB of RAM AND it is a Pixel 4, also written as follows:
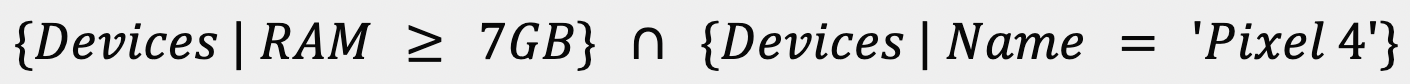
If you want an OR condition, create separate selectors in a single device group, for example:
<config:device-selector ram-min-bytes="7000000000"/>
<config:device-selector>
<config:included-device-id brand="google" device="flame"/>
</config:device-selector>
will create the condition for all devices with > 7GB of RAM OR it is a Pixel 4, also written as follows:
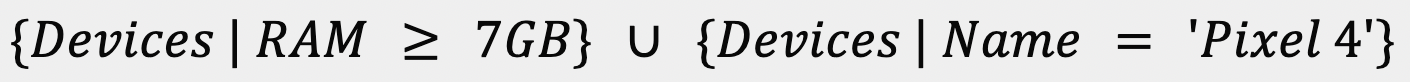
Here is an example showing all possible device properties:
<config:device-targeting-config
xmlns:config="http://schemas.android.com/apk/config">
<config:device-group name="myCustomGroup1">
<config:device-selector ram-min-bytes="8000000000">
<config:included-device-id brand="google" device="redfin"/>
<config:included-device-id brand="google" device="sailfish"/>
<config:included-device-id brand="good-brand"/>
<config:excluded-device-id brand="google" device="caiman"/>
<config:system-on-chip manufacturer="Sinclair" model="ZX80"/>
<config:system-on-chip manufacturer="Commodore" model="C64"/>
</config:device-selector>
<config:device-selector ram-min-bytes="16000000000"/>
</config:device-group>
<config:device-group name="myCustomGroup2">
<config:device-selector ram-min-bytes="4000000000" ram-max-bytes="8000000000">
<config:required-system-feature name="android.hardware.bluetooth"/>
<config:required-system-feature name="android.hardware.location"/>
<config:forbidden-system-feature name="android.hardware.camera"/>
<config:forbidden-system-feature name="mindcontrol.laser"/>
</config:device-selector>
</config:device-group>
</config:device-targeting-config>
Official device manufacturer and device model codes
You can find the correct formatting for the device manufacturer and model code by using the Device Catalog on the Google Play Console, by either:
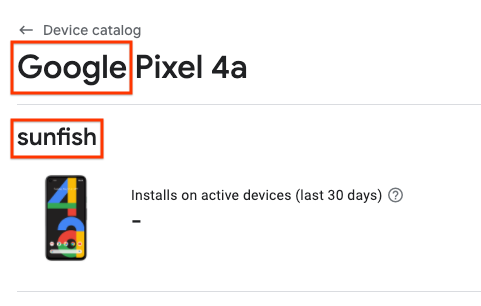
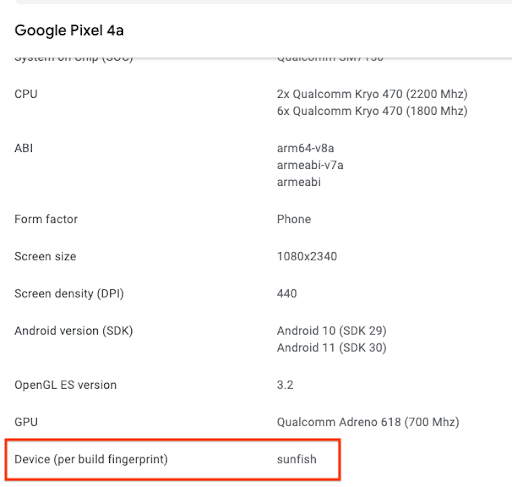
Inspecting individual devices using the Device Catalog, and finding the manufacturer and model code in the locations as shown in the example below (For a Google Pixel 4a, the manufacturer is "Google" and the model code is "sunfish"):
Downloading a CSV of supported devices, and using the Manufacturer and Model Code for the build_brand and build_device fields, respectively.
Include your device targeting configuration file in your app bundle
Add the following to your main module'sbuild.gradle file:
android {
...
bundle {
deviceTargetingConfig = file('device_targeting_config.xml')
deviceGroup {
enableSplit = true // split bundle by #group
defaultGroup = "other" // group used for standalone APKs
}
}
...
}
device_targeting_config.xml is the path of your configuration file relative to
the main module. This ensures that your configuration file is packaged with your
app bundle.
The deviceGroup clause ensures that the APKs generated from your bundle are
split by device groups.
Device targeting for Play Feature Delivery
To use device targeting with Play Feature Delivery, see the documentation for conditional delivery.
Device targeting for Play Asset Delivery
To use device targeting with Play Asset Delivery, see the documentation for asset packs.
Device targeting for on-device AI model delivery
To use device targeting with Play for on-device AI, see the documentation for AI packs.
Report bugs
Report any bugs on the public Issue Tracker.
