Trang này mô tả cách SDK của bên thứ ba có thể tích hợp cài đặt nội tuyến, một tính năng thử nghiệm mới cho Google Play, hiển thị thông tin chi tiết về sản phẩm ứng dụng Google Play trong giao diện nửa trang tính. Cài đặt nội tuyến cho phép người dùng trải nghiệm quy trình cài đặt ứng dụng liền mạch mà không cần thoát khỏi bối cảnh của ứng dụng.
Các nhà phát triển SDK bên thứ ba có thể tích hợp tính năng cài đặt trực tuyến vào SDK của họ để cho phép các nhà phát triển ứng dụng sử dụng SDK đó truy cập vào tính năng cài đặt trực tuyến cho ứng dụng của họ.
Yêu cầu
Để giao diện nửa trang cài đặt nội tuyến xuất hiện trong ứng dụng:
- Phiên bản Google Play tối thiểu phải là 40.4.
- Mức API Android phải là 23 trở lên.
Kiến trúc quy trình
Kiến trúc quy trình cài đặt nội tuyến được thể hiện trong hình sau:
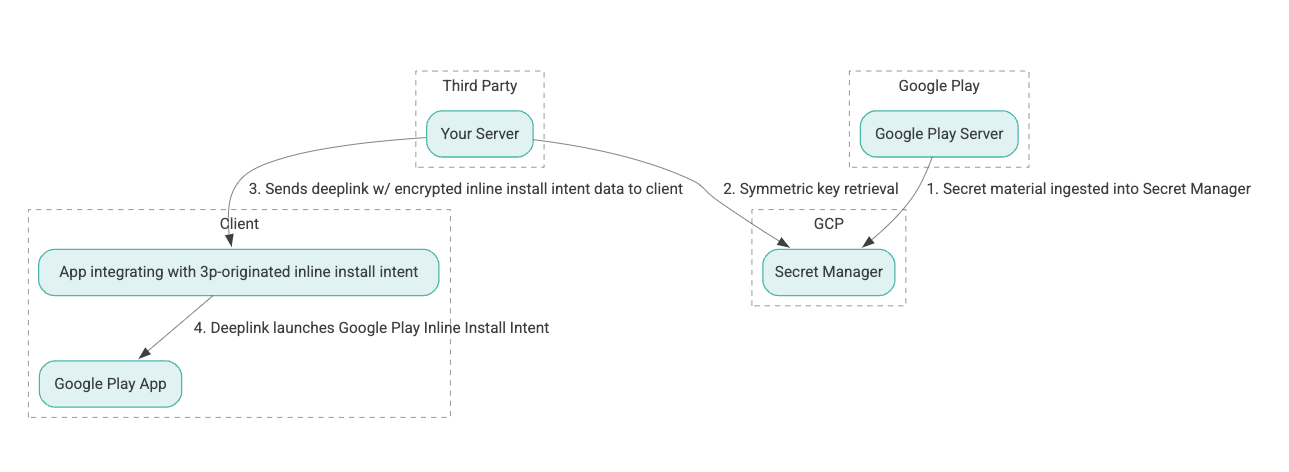
- Máy chủ Google Play tạo khóa mã hóa Mã hóa được xác thực với dữ liệu liên kết (AEAD) và nhập khóa vào phiên bản Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Secret Manager.
- Bên tích hợp thứ ba sẽ lấy khóa AEAD từ GCP Secret Manager.
- Trình tích hợp bên thứ ba mã hoá dữ liệu
Intentcài đặt trong dòng, tạo văn bản mã hoá được truyền trong đường liên kết sâu dùng để gọi ý định cài đặt trong dòng và gửi đường liên kết sâu đến ứng dụng trong các phản hồi. - Khi liên kết sâu được theo dõi, ứng dụng Google Play sẽ xử lý mục đích đó.
Để cấu hình SDK của bên thứ ba để sử dụng quy trình cài đặt nội tuyến, hãy hoàn thành các bước sau.
Tạo tài khoản dịch vụ trong Google Cloud Project
Ở bước này, bạn thiết lập tài khoản dịch vụ bằng Google Cloud Console.
- Thiết lập Dự án Google Cloud:
- Tạo một tổ chức Google Cloud. Khi bạn tạo tài khoản Google Workspace hoặc Cloud Identity và liên kết tài khoản đó với tên miền của mình, tài nguyên tổ chức sẽ tự động được tạo. Để biết chi tiết, hãy tham khảo Tạo và quản lý tài nguyên tổ chức.
- Đăng nhập vào GCP Console bằng tài khoản Google Cloud đã tạo ở bước trước, sau đó tạo một dự án Google Cloud. Để biết chi tiết, hãy tham khảo Tạo dự án Google Cloud.
- Tạo tài khoản dịch vụ trong dự án Google Cloud đã tạo. Tài khoản dịch vụ được sử dụng làm Google Cloud Identity để truy cập khóa đối xứng thay mặt cho máy chủ của bạn. Để biết chi tiết, hãy tham khảo Tạo tài khoản dịch vụ.
- Sử dụng cùng một Mã khách hàng Google Workspace (GWCID) / Mã Dasher đã nhập vào biểu mẫu quan tâm.
- Tạo và tải xuống khóa riêng của tài khoản dịch vụ đó.
- Tạo khóa cho tài khoản dịch vụ đó. Để biết chi tiết, hãy xem Tạo khóa tài khoản dịch vụ.
- Tải xuống khóa tài khoản dịch vụ và giữ khóa này có thể truy cập được trên máy chủ của bạn vì khóa này được sử dụng để xác thực truy cập tài nguyên Google Cloud cho các khóa đối xứng. Để biết chi tiết, hãy xem Nhận khóa tài khoản dịch vụ.
Truy xuất thông tin đăng nhập
Ở bước này, bạn sẽ lấy khóa đối xứng từ Secret Manager và lưu trữ nó một cách an toàn (ví dụ: trong tệp JSON) trên máy chủ lưu trữ của riêng bạn. Khóa này được sử dụng để tạo mã hóa dữ liệu cài đặt nội tuyến.
Giá trị secret_id/secretId tham chiếu đến tên bí mật bên trong Trình quản lý bí mật; tên này được tạo bằng cách thêm hsdp-3p-key- vào giá trị do Play cung cấp sdk_id. Ví dụ: nếu sdk_id là abc, tên bí mật sẽ là hsdp-3p-key-abc.
Phiên bản bí mật được cập nhật hàng tuần vào thứ Ba lúc 2 giờ chiều UTC. Những chìa khóa mới thứ hai sẽ tiếp tục hoạt động cho đến lần thay tiếp theo và vật liệu chìa khóa phải được lấy mới và lưu trữ hàng tuần.
Ví dụ về Python
Ví dụ về mã sau đây sử dụng mã truy cập được lưu trữ trong tệp JSON để truy cập vào tài liệu khoá trong Trình quản lý bí mật của GCP và in tài liệu đó ra bảng điều khiển.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
from google.cloud import secretmanager
from google.oauth2 import service_account
import google_crc32c
# Create a service account key file.
service_account_key_file = "<json key file of the service account>"
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(service_account_key_file)
# Create the Secret Manager client.
client = secretmanager.SecretManagerServiceClient(
credentials=credentials
)
# Build the resource name of the secret version.
name = f"projects/prod-play-hsdp-3p-caller-auth/secrets/<secret_id>/versions/latest"
# Access the secret version.
response = client.access_secret_version(request={"name": name})
# Verify payload checksum.
crc32c = google_crc32c.Checksum()
crc32c.update(response.payload.data)
if response.payload.data_crc32c != int(crc32c.hexdigest(), 16):
print("Data corruption detected.")
# A keyset created with "tinkey create-keyset --key-template=AES256_GCM". Note
# that this keyset has the secret key information in cleartext.
keyset = response.payload.data.decode("UTF-8")
# WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment. Please store it
# in a secure storage.
with open('<key file name>', 'w') as f:
f.write(keyset)
Ví dụ Java
Ví dụ mã sau đây sử dụng mã truy cập được lưu trữ trong tệp JSON để truy cập tài liệu quan trọng trong GCP Secret Manager và ghi vào tệp JSON.
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.api.gax.core.CredentialsProvider;
import com.google.api.gax.core.FixedCredentialsProvider;
import com.google.auth.oauth2.ServiceAccountCredentials;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.AccessSecretVersionResponse;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceClient;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceSettings;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretVersionName;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.zip.CRC32C;
import java.util.zip.Checksum;
/** */
final class ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide {
private ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
accessSecretVersion();
}
public static void accessSecretVersion() throws IOException {
// TODO(developer): Replace these variables before running the sample.
String projectId = "projectId";
String secretId = "secretId";
String versionId = "versionId";
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath = "path/to/credentials.json";
String secretMaterialOutputPath = "path/to/secret.json";
accessSecretVersion(
projectId, secretId, versionId, accessTokenPrivateKeyPath, secretMaterialOutputPath);
}
// Access the payload for the given secret version if one exists. The version
// can be a version number as a string (e.g. "5") or an alias (e.g. "latest").
public static void accessSecretVersion(
String projectId,
String secretId,
String versionId,
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath,
String secretMaterialOutputPath)
throws IOException {
// We can explicitly instantiate the SecretManagerServiceClient (below) from a json file if we:
// 1. Create a CredentialsProvider from a FileInputStream of the JSON file,
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider =
FixedCredentialsProvider.create(
ServiceAccountCredentials.fromStream(new FileInputStream(accessTokenPrivateKeyPath)));
// 2. Build a SecretManagerService Settings object from that credentials provider, and
SecretManagerServiceSettings secretManagerServiceSettings =
SecretManagerServiceSettings.newBuilder()
.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.build();
// 3. Initialize client that will be used to send requests by passing the settings object to
// create(). This client only needs to be created once, and can be reused for multiple requests.
// After completing all of your requests, call the "close" method on the client to safely clean
// up any remaining background resources.
try (SecretManagerServiceClient client =
SecretManagerServiceClient.create(secretManagerServiceSettings)) {
SecretVersionName secretVersionName = SecretVersionName.of(projectId, secretId, versionId);
// Access the secret version.
AccessSecretVersionResponse response = client.accessSecretVersion(secretVersionName);
// Verify checksum. The used library is available in Java 9+.
// If using Java 8, you may use the following:
// https://github.com/google/guava/blob/e62d6a0456420d295089a9c319b7593a3eae4a83/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/Hashing.java#L395
byte[] data = response.getPayload().getData().toByteArray();
Checksum checksum = new CRC32C();
checksum.update(data, 0, data.length);
if (response.getPayload().getDataCrc32C() != checksum.getValue()) {
System.out.printf("Data corruption detected.");
return;
}
String payload = response.getPayload().getData().toStringUtf8();
// Print the secret payload.
//
// WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment - this
// snippet is showing how to access the secret material.
System.out.printf("Plaintext: %s\n", payload);
// Write the JSON secret material payload to a json file
try (PrintWriter out =
new PrintWriter(Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get(secretMaterialOutputPath), UTF_8))) {
out.write(payload);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Đặt thông tin xác thực mặc định của ứng dụng
Nếu bạn không muốn sử dụng CredentialsProvider để truyền khóa riêng tư vào tệp JSON trong triển khai Java, bạn có thể sửa đổi triển khai bằng cách thiết lập Thông tin xác thực mặc định của ứng dụng (ADC):
- Thông báo cho thư viện máy khách nơi tìm khóa tài khoản dịch vụ.
- Thêm các phụ thuộc Maven vào dự án Java.
- Gọi
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()để tự động xác thực (do bước 1).
Các bước này sửa đổi việc triển khai Java bằng cách:
- Loại bỏ nhu cầu tạo các đối tượng
CredentialsProvidervàSecretManagerServiceSettings. - Thay đổi lệnh gọi thành
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()để không bao gồm đối số.
Tạo văn bản mã hóa và tạo liên kết sâu
Ở bước này, bạn sử dụng thư viện mã hóa Tink để tạo enifd (văn bản mã hóa InlineInstallData) từ đối tượng protobuf InlineInstallData.
Giao thức InlineInstallData được định nghĩa như sau:
syntax = "proto2";
package hsdpexperiments;
option java_package = "com.google.hsdpexperiments";
option java_multiple_files = true;
// InlineInstallData is used by 3p auth callers to generate "encrypted inline
// flow data" (enifd) which is decrypted in PGS to verify authenticity and
// freshness.
message InlineInstallData {
// The timestamp which indicates the time encrypted data is generated.
// Used to validate freshness (i.e. generation time in past 4 hours).
// Required.
optional int64 timestamp_ms = 1;
// The docid of the app that we want to open inline install page for.
// This is the package name.
// Required.
optional string target_package_name = 2;
// This is the name of the app requesting the ad from Google Ad Serving
// system.
// Required.
optional string caller_package_name = 3;
// This is the advertising id that will be collected by 3P Ad SDKs.
// Optional.
optional string advertising_id = 4;
// This is used to indicate the network from where the inline install was
// requested.
// Required.
optional string ad_network_id = 5;
}
Trong bước này, bạn cũng tạo URL liên kết sâu bằng các tham số sau:
| Trường | Mô tả | Bắt buộc |
|---|---|---|
| id | Tên gói của ứng dụng sẽ được cài đặt. | Có |
| nội dòng | Đặt thành true nếu yêu cầu cài đặt nội tuyến một nửa trang tính; nếu là false, ý định liên kết sâu đến Google Play. |
Có |
| enifd | Mã định danh được mã hóa cho SDK 3P. | Có |
| lft | Một mã định danh nội bộ. | Có |
| 3pAuthCallerId | Giá trị nhận dạng SDK. | Có |
| trang thông tin | Một tham số không bắt buộc để chỉ định mục tiêu cho một trang thông tin tuỳ chỉnh trên Cửa hàng Play. | Không |
| người giới thiệu | Một chuỗi theo dõi trình giới thiệu không bắt buộc. | Không |
Ví dụ về Python
Lệnh sau đây tạo mã Python từ InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --python_out=.
Mã mẫu Python sau đây xây dựng InlineInstallData và mã hóa nó bằng khóa đối xứng để tạo ra văn bản mã hóa:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
import base64
import time
import inline_install_data_pb2 as InlineInstallData
import tink
from tink import aead
from tink import cleartext_keyset_handle
# Read the stored symmetric key.
with open("example3psecret.json", "r") as f:
keyset = f.read()
"""Encrypt and decrypt using AEAD."""
# Register the AEAD key managers. This is needed to create an Aead primitive later.
aead.register()
# Create a keyset handle from the cleartext keyset in the previous
# step. The keyset handle provides abstract access to the underlying keyset to
# limit access of the raw key material. WARNING: In practice, it is unlikely
# you will want to use a cleartext_keyset_handle, as it implies that your key
# material is passed in cleartext, which is a security risk.
keyset_handle = cleartext_keyset_handle.read(tink.JsonKeysetReader(keyset))
# Retrieve the Aead primitive we want to use from the keyset handle.
primitive = keyset_handle.primitive(aead.Aead)
inlineInstallData = InlineInstallData.InlineInstallData()
inlineInstallData.timestamp_ms = int(time.time() * 1000)
inlineInstallData.target_package_name = "x.y.z"
inlineInstallData.caller_package_name = "a.b.c"
inlineInstallData.ad_network_id = "<sdk_id>"
# Use the primitive to encrypt a message. In this case the primary key of the
# keyset will be used (which is also the only key in this example).
ciphertext = primitive.encrypt(inlineInstallData.SerializeToString(), b'<sdk_id>')
print(f"InlineInstallData Ciphertext: {ciphertext}")
# Base64 Encoded InlineInstallData Ciphertext
enifd = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(ciphertext).decode('utf-8')
print(enifd)
# Deeplink
print(f"https://play.google.com/d?id={inlineInstallData.target_package_name}\&inline=true\&enifd={enifd}\&lft=1\&3pAuthCallerId={inlineInstallData.ad_network_id}")
Thực thi tập lệnh Python bằng cách chạy lệnh sau:
python <file_name>.py
Ví dụ về Java
Lệnh sau đây tạo mã Java từ InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --java_out=.
Mã mẫu Java sau đây tạo InlineInstallData và mã hoá bằng khoá đối xứng để tạo văn bản mã hoá:
package com.google.hsdpexperiments;
import static com.google.common.io.BaseEncoding.base64Url;
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.common.flags.Flag;
import com.google.common.flags.FlagSpec;
import com.google.common.flags.Flags;
import com.google.crypto.tink.Aead;
import com.google.crypto.tink.InsecureSecretKeyAccess;
import com.google.crypto.tink.KeysetHandle;
import com.google.crypto.tink.TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat;
import com.google.crypto.tink.aead.AeadConfig;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.Security;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.conscrypt.Conscrypt;
/** info on encryption in https://github.com/google/tink#learn-more */
final class ThirdPartyEnifdGuide {
@FlagSpec(
name = "third_party_id",
help = "the identifier associated with the 3p for which to generate the enifd")
private static final Flag<String> thirdPartyAuthCallerId = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "package_name", help = "the package name of the target app")
private static final Flag<String> packageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "caller_package_name", help = "the package name of the caller app")
private static final Flag<String> callerPackageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "secret_filename", help = "the path to the json file with the secret material")
private static final Flag<String> secretFilename = Flag.value("");
private ThirdPartyEnifdGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// parse flags
Flags.parse(args);
// File keyFile = new File(args[0]);
Path keyFile = Paths.get(secretFilename.get());
// Create structured inline flow data
InlineInstallData idrp =
InlineInstallData.newBuilder()
.setTargetPackageName(packageName.get())
.setCallerPackageName(callerPackageName.get())
.setTimestampMs(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setAdNetworkId(thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get())
.build();
// we can print this out here to make sure it's well formatted, this will help debug
System.out.println(idrp.toString());
// Register all AEAD key types with the Tink runtime.
Conscrypt.checkAvailability();
Security.addProvider(Conscrypt.newProvider());
AeadConfig.register();
// Read AEAD key downloaded from secretmanager into keysethandle
KeysetHandle handle =
TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat.parseKeyset(
new String(Files.readAllBytes(keyFile), UTF_8), InsecureSecretKeyAccess.get());
// Generate enifd using tink library
Aead aead = handle.getPrimitive(Aead.class);
byte[] plaintext = idrp.toByteArray();
byte[] ciphertext = aead.encrypt(plaintext, thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get().getBytes(UTF_8));
String enifd = base64Url().omitPadding().encode(ciphertext);
// Build deeplink, escaping ampersands (TODO: verify this is necessary while testing e2e)
String deeplink =
"https://play.google.com/d?id="
+ packageName.get()
+ "\\&inline=true\\&enifd="
+ enifd
+ "\\&lft=1\\&3pAuthCallerId="
+ thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get();
System.out.println(deeplink);
}
}
Cuối cùng, xây dựng chương trình Java thành tệp nhị phân và gọi nó bằng đoạn mã sau:
path/to/binary/ThirdPartyEnifdGuide --secret_filename=path/to/jsonfile/example3psecret.json --package_name=<package_name_of_target_app> --third_party_id=<3p_caller_auth_id>
- Cờ
secret_filenamechỉ định đường dẫn đến tệp JSON chứa tài liệu bí mật. - Cờ
package_namelà ID tài liệu của ứng dụng mục tiêu. - Cờ
third_party_idđược sử dụng để chỉ định ID xác thực của bên thứ ba (tức là<sdk_id>).
Khởi chạy ý định Cài đặt nội tuyến
Để kiểm tra liên kết sâu được tạo trong bước trước, hãy kết nối thiết bị Android (đảm bảo bật gỡ lỗi USB) với máy trạm đã cài đặt ADB và chạy lệnh sau:
adb shell am start "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
Trong mã máy khách, hãy gửi ý định bằng một trong các phương pháp sau (Kotlin hoặc Java).
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
val deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending")
intent.data = Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl)
val packageManager = context.getPackageManager()
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0)
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
String id = "exampleAppToBeInstalledId";
String deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>";
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending");
intent.setData(Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl));
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Phụ lục
Các phần sau cung cấp hướng dẫn bổ sung về một số trường hợp sử dụng nhất định.
Chuẩn bị môi trường Python
Để chạy mã mẫu Python, hãy thiết lập môi trường Python trên máy trạm của bạn và cài đặt các phụ thuộc cần thiết.
Thiết lập môi trường Python:
Cài đặt python3.11 (nếu đã cài đặt, bỏ qua bước này):
sudo apt install python3.11Cài đặt pip:
sudo apt-get install pipCài đặt
virtualenv:sudo apt install python3-virtualenvTạo môi trường ảo (bắt buộc đối với sự phụ thuộc vào Tink):
virtualenv inlineinstall --python=/usr/bin/python3.11
Vào môi trường ảo:
source inlineinstall/bin/activateCập nhật pip:
python -m pip install --upgrade pipCài đặt các phụ thuộc cần thiết:
Cài đặt Tink:
pip install tinkCài đặt Google crc32c:
pip install google-crc32cCài đặt Secret Manager:
pip install google-cloud-secret-managerCài đặt trình biên dịch protobuf:
sudo apt install protobuf-compiler
C++ enifd generation
Sau đây là một ví dụ C++ mà chúng tôi đã viết và xác thực nội bộ để tạo enifd.
Việc tạo enifd có thể được thực hiện bằng mã C++ như sau:
// A command-line example for using Tink AEAD w/ key template aes128gcmsiv to
// encrypt an InlineInstallData proto.
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "<path_to_protoc_output>/inline_install_data.proto.h"
#include "absl/flags/flag.h"
#include "absl/flags/parse.h"
#include "absl/strings/escaping.h"
#include "absl/strings/string_view.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_config.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_key_templates.h"
#include "tink/cc/config/global_registry.h"
#include "tink/cc/examples/util/util.h"
#include "tink/cc/keyset_handle.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/status.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/statusor.h"
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, keyset_filename, "",
"Keyset file (downloaded from secretmanager) in JSON format");
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, associated_data, "",
"Associated data for AEAD (default: empty");
namespace {
using ::crypto::tink::Aead;
using ::crypto::tink::AeadConfig;
using ::crypto::tink::KeysetHandle;
using ::crypto::tink::util::Status;
using ::crypto::tink::util::StatusOr;
} // namespace
namespace tink_cc_examples {
// AEAD example CLI implementation.
void AeadCli(const std::string& keyset_filename,
absl::string_view associated_data) {
Status result = AeadConfig::Register();
if (!result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to register AeadConfig";
return;
}
// Read the keyset from file.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<KeysetHandle>> keyset_handle =
ReadJsonCleartextKeyset(keyset_filename);
if (!keyset_handle.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to read json keyset";
return;
}
// Get the primitive.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<Aead>> aead =
(*keyset_handle)
->GetPrimitive<crypto::tink::Aead>(
crypto::tink::ConfigGlobalRegistry());
if (!aead.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to get primitive";
return;
}
// Instantiate the enifd.
hsdpexperiments::InlineInstallData iid;
iid.set_timestamp_ms(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch())
.count());
iid.set_target_package_name("<TARGET_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_caller_package_name("<CALLER_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_ad_network_id("<SDK_ID>");
// Compute the output.
StatusOr<std::string> encrypt_result =
(*aead)->Encrypt(iid.SerializeAsString(), associated_data);
if (!encrypt_result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to encrypt Inline Install Data";
return;
}
const std::string& output = encrypt_result.value();
std::string enifd;
absl::WebSafeBase64Escape(output, &enifd);
std::clog << "enifd: " << enifd << '\n';
}
} // namespace tink_cc_examples
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
absl::ParseCommandLine(argc, argv);
std::string keyset_filename = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_keyset_filename);
std::string associated_data = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_associated_data);
std::clog << "Using keyset from file " << keyset_filename
<< " to AEAD-encrypt inline install data with associated data '"
<< associated_data << "'." << '\n';
tink_cc_examples::AeadCli(keyset_filename, associated_data);
return 0;
}
Mã này được điều chỉnh từ một mẫu có trong tài liệu Tink.
