Credential Manager refers to a set of APIs introduced in Android 14 that support multiple sign-in methods such as username-password, passkeys, and federated sign-in solutions (such as Sign-in with Google). When the Credential Manager API is invoked, the Android system aggregates credentials from all credential providers installed on the device. This document describes the set of APIs that provide integration endpoints for these credential providers.
Setup
Before you implement functionality in your credential provider, complete the setup steps shown in the following sections.
Declare dependencies
Add the following dependencies to your app module's build script, to use the latest version of the Credential Manager library:
Kotlin
dependencies { implementation("androidx.credentials:credentials:1.6.0-rc01") }
Groovy
dependencies { implementation "androidx.credentials:credentials:1.6.0-rc01" }
Declare service element in manifest file
In your app's manifest file AndroidManifest.xml, include a <service>
declaration for a service class that extends the
CredentialProviderService class from the androidx.credentials library, as
shown in the following example.
<service android:name=".MyCredentialProviderService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"
android:label="My Credential Provider"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_CREDENTIAL_PROVIDER_SERVICE"
tools:targetApi="upside_down_cake">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.service.credentials.CredentialProviderService"/>
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.credentials.provider"
android:resource="@xml/provider"/>
</service>
The permission and the intent filter shown in the previous example are integral for the Credential Manager flow to work as expected. The permission is needed so that only the Android system can bind to this service. The intent filter is used for discoverability of this service as a credential provider to be used by Credential Manager.
Declare supported credential types
In your res/xml directory, create a new file called provider.xml. In this
file, declare the credential types your service supports, through constants
defined for each credential type in the library. In the following example, the
service supports traditional passwords as well as passkeys, constants for which
are defined as TYPE_PASSWORD_CREDENTIAL and
TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY_CREDENTIAL:
<credential-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<capabilities>
<capability name="android.credentials.TYPE_PASSWORD_CREDENTIAL" />
<capability name="androidx.credentials.TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY_CREDENTIAL" />
</capabilities>
</credential-provider>
On previous API levels, credential providers integrate with APIs like autofill for passwords and other data. These providers can use the same internal infrastructure to store the existing credential types, while expanding it to support others, including passkeys.
Two-phased approach to provider interaction
Credential Manager interacts with credential providers in two phases:
- The first phase is the begin/query phase whereby the system binds to
credential provider services and invokes
onBeginGetCredentialRequest(),onBeginCreateCredentialRequest(), oronClearCredentialStateRequest()methods withBegin…requests. Providers must process these requests and respond withBegin…responses, populating them with entries that represent visual options to be shown on the account selector. Each entry must have aPendingIntentset. - Once the user selects an entry, the selection phase commences and the
PendingIntentassociated with the entry gets fired, bringing up the corresponding provider activity. Once the user is done interacting with this activity, the credential provider must set the response to the result of the activity before ending it. This response is then sent to the client app that invoked Credential Manager.
Handle passkey creation
Handle queries for passkey creation
When a client app wishes to create a passkey and store it with a
credential provider, they call the createCredential API. To handle this
request in your credential provider service such that the passkey is actually
stored in your storage, complete the steps shown in the following sections.
- Override the
onBeginCreateCredentialRequest()method in your service extended fromCredentialProviderService. - Handle the
BeginCreateCredentialRequestby constructing a correspondingBeginCreateCredentialResponseand passing it through the callback. - While constructing the
BeginCreateCredentialResponse, add the requiredCreateEntries. EachCreateEntryshould correspond to an account where the credential can be saved, and must have aPendingIntentset along with other required metadata.
The following example illustrates how to implement these steps.
override fun onBeginCreateCredentialRequest(
request: BeginCreateCredentialRequest,
cancellationSignal: CancellationSignal,
callback: OutcomeReceiver<BeginCreateCredentialResponse, CreateCredentialException>,
) {
val response: BeginCreateCredentialResponse? = processCreateCredentialRequest(request)
if (response != null) {
callback.onResult(response)
} else {
callback.onError(CreateCredentialUnknownException())
}
}
fun processCreateCredentialRequest(request: BeginCreateCredentialRequest): BeginCreateCredentialResponse? {
when (request) {
is BeginCreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest -> {
// Request is passkey type
return handleCreatePasskeyQuery(request)
}
}
// Request not supported
return null
}
private fun handleCreatePasskeyQuery(
request: BeginCreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest
): BeginCreateCredentialResponse {
// Adding two create entries - one for storing credentials to the 'Personal'
// account, and one for storing them to the 'Family' account. These
// accounts are local to this sample app only.
val createEntries: MutableList<CreateEntry> = mutableListOf()
createEntries.add(
CreateEntry(
PERSONAL_ACCOUNT_ID,
createNewPendingIntent(PERSONAL_ACCOUNT_ID, CREATE_PASSKEY_INTENT)
)
)
createEntries.add(
CreateEntry(
FAMILY_ACCOUNT_ID,
createNewPendingIntent(FAMILY_ACCOUNT_ID, CREATE_PASSKEY_INTENT)
)
)
return BeginCreateCredentialResponse(createEntries)
}
private fun createNewPendingIntent(accountId: String, action: String): PendingIntent {
val intent = Intent(action).setPackage(PACKAGE_NAME)
// Add your local account ID as an extra to the intent, so that when
// user selects this entry, the credential can be saved to this
// account
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_KEY_ACCOUNT_ID, accountId)
return PendingIntent.getActivity(
applicationContext, UNIQUE_REQ_CODE,
intent,
(
PendingIntent.FLAG_MUTABLE
or PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT
)
)
}
Your PendingIntent construction should adhere to the following:
- The corresponding Activity should be set up to surface any required Biometric prompt, confirmation or selection required.
- Any required data that the provider needs when the corresponding activity is
invoked should be set as an extra on the intent that's used to create your
PendingIntent, such as anaccountIdin the creation flow. - Your
PendingIntentmust be constructed with the flagPendingIntent.FLAG_MUTABLEso that the system can append the final request to the intent extra. - Your
PendingIntentmust not be constructed with the flagPendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOTas the user may select an entry, go back and reselect it which would cause thePendingIntentto fire twice. - Your
PendingIntentmust be constructed with a unique request code so that each entry can have its own correspondingPendingIntent.
Handle entry selection for passkey creation requests
- When the user selects a previously populated
CreateEntry, the correspondingPendingIntentis invoked and the associated providerActivityis created. - After the
onCreatemethod of your Activity is invoked, access the associated intent and pass it into thePendingIntentHanderclass to get theProviderCreateCredentialRequest. - Extract the
requestJson,callingAppInfoandclientDataHashfrom the request. - Extract the local
accountIdfrom the intent extra. This is a sample app specific implementation and is not required. This account ID can be used to store this credential against this particular account ID. - Validate the
requestJson. The example below uses local data classes likePublicKeyCredentialCreationOptionsto convert the input JSON to a structured class as per the WebAuthn spec. As a credential provider, you can replace this with your own parser. - Check the asset-link for the calling app if the call originates from a native Android app.
- Surface an authentication prompt. The example below uses the Android Biometric API.
- When authentication is successful, generate a
credentialIdand a key pair. - Save the private key in your local database against
callingAppInfo.packageName. - Construct a Web Authentication API JSON response that
consists of the public key and the
credentialId. The example below uses local utility classes likeAuthenticatorAttestationResponseandFidoPublicKeyCredentialthat help construct a JSON based on the earlier mentioned spec.As a credential provider, you can replace these classes with your own builders. - Construct a
CreatePublicKeyCredentialResponsewith the JSON generated above. - Set
CreatePublicKeyCredentialResponseas an extra on anIntentthroughPendingIntentHander.setCreateCredentialResponse(), and set that intent to the result of the Activity. - Finish the Activity.
The code example below illustrates these steps. This code needs to be handled in
your Activity class once onCreate() is invoked.
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?, persistentState: PersistableBundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState, persistentState)
// ...
val request =
PendingIntentHandler.retrieveProviderCreateCredentialRequest(intent)
val accountId = intent.getStringExtra(CredentialsRepo.EXTRA_KEY_ACCOUNT_ID)
if (request != null && request.callingRequest is CreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest) {
val publicKeyRequest: CreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest =
request.callingRequest as CreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest
createPasskey(
publicKeyRequest.requestJson,
request.callingAppInfo,
publicKeyRequest.clientDataHash,
accountId
)
}
}
@SuppressLint("RestrictedApi")
fun createPasskey(
requestJson: String,
callingAppInfo: CallingAppInfo?,
clientDataHash: ByteArray?,
accountId: String?
) {
val request = PublicKeyCredentialCreationOptions(requestJson)
val biometricPrompt = BiometricPrompt(
this,
{ }, // Pass in your own executor
object : AuthenticationCallback() {
override fun onAuthenticationError(errorCode: Int, errString: CharSequence) {
super.onAuthenticationError(errorCode, errString)
finish()
}
override fun onAuthenticationFailed() {
super.onAuthenticationFailed()
finish()
}
@RequiresApi(VERSION_CODES.P)
override fun onAuthenticationSucceeded(
result: AuthenticationResult
) {
super.onAuthenticationSucceeded(result)
// Generate a credentialId
val credentialId = ByteArray(32)
SecureRandom().nextBytes(credentialId)
// Generate a credential key pair
val spec = ECGenParameterSpec("secp256r1")
val keyPairGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("EC")
keyPairGen.initialize(spec)
val keyPair = keyPairGen.genKeyPair()
// Save passkey in your database as per your own implementation
// Create AuthenticatorAttestationResponse object to pass to
// FidoPublicKeyCredential
val response = AuthenticatorAttestationResponse(
requestOptions = request,
credentialId = credentialId,
credentialPublicKey = getPublicKeyFromKeyPair(keyPair),
origin = appInfoToOrigin(callingAppInfo!!),
up = true,
uv = true,
be = true,
bs = true,
packageName = callingAppInfo.packageName
)
val credential = FidoPublicKeyCredential(
rawId = credentialId,
response = response,
authenticatorAttachment = "", // Add your authenticator attachment
)
val result = Intent()
val createPublicKeyCredResponse =
CreatePublicKeyCredentialResponse(credential.json())
// Set the CreateCredentialResponse as the result of the Activity
PendingIntentHandler.setCreateCredentialResponse(
result,
createPublicKeyCredResponse
)
setResult(RESULT_OK, result)
finish()
}
}
)
val promptInfo = BiometricPrompt.PromptInfo.Builder()
.setTitle("Use your screen lock")
.setSubtitle("Create passkey for ${request.rp.name}")
.setAllowedAuthenticators(
BiometricManager.Authenticators.BIOMETRIC_STRONG
/* or BiometricManager.Authenticators.DEVICE_CREDENTIAL */
)
.build()
biometricPrompt.authenticate(promptInfo)
}
@RequiresApi(VERSION_CODES.P)
fun appInfoToOrigin(info: CallingAppInfo): String {
val cert = info.signingInfo.apkContentsSigners[0].toByteArray()
val md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256")
val certHash = md.digest(cert)
// This is the format for origin
return "android:apk-key-hash:${b64Encode(certHash)}"
}
Handle queries for password creation requests
To handle queries for password creation requests, do the following:
- Inside your
processCreateCredentialRequest()method mentioned in the previous section, add another case inside the switch block for handling password requests. - While constructing the
BeginCreateCredentialResponse, add the requiredCreateEntries. - Each
CreateEntryshould correspond to an account where the credential can be saved, and must have aPendingIntentset on it along with other metadata.
The following example illustrates how to implement these steps:
fun processCreateCredentialRequest(
request: BeginCreateCredentialRequest
): BeginCreateCredentialResponse? {
when (request) {
is BeginCreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest -> {
// Request is passkey type
return handleCreatePasskeyQuery(request)
}
is BeginCreatePasswordCredentialRequest -> {
// Request is password type
return handleCreatePasswordQuery(request)
}
}
return null
}
@RequiresApi(VERSION_CODES.M)
private fun handleCreatePasswordQuery(
request: BeginCreatePasswordCredentialRequest
): BeginCreateCredentialResponse {
val createEntries: MutableList<CreateEntry> = mutableListOf()
// Adding two create entries - one for storing credentials to the 'Personal'
// account, and one for storing them to the 'Family' account. These
// accounts are local to this sample app only.
createEntries.add(
CreateEntry(
PERSONAL_ACCOUNT_ID,
createNewPendingIntent(PERSONAL_ACCOUNT_ID, CREATE_PASSWORD_INTENT)
)
)
createEntries.add(
CreateEntry(
FAMILY_ACCOUNT_ID,
createNewPendingIntent(FAMILY_ACCOUNT_ID, CREATE_PASSWORD_INTENT)
)
)
return BeginCreateCredentialResponse(createEntries)
}
Handle entry selection for password creation requests
When the user selects a populated CreateEntry, the corresponding
PendingIntent executes and brings up the associated Activity. Access the
associated intent passed in onCreate and pass it into the
PendingIntentHander class to get the ProviderCreateCredentialRequest method.
The example below illustrates how to implement this process. This code needs to
be handled in your Activity's onCreate() method.
val createRequest = PendingIntentHandler.retrieveProviderCreateCredentialRequest(intent)
val accountId = intent.getStringExtra(CredentialsRepo.EXTRA_KEY_ACCOUNT_ID)
if (createRequest == null) {
return
}
val request: CreatePasswordRequest = createRequest.callingRequest as CreatePasswordRequest
// Fetch the ID and password from the request and save it in your database
mDatabase.addNewPassword(
PasswordInfo(
request.id,
request.password,
createRequest.callingAppInfo.packageName
)
)
// Set the final response back
val result = Intent()
val response = CreatePasswordResponse()
PendingIntentHandler.setCreateCredentialResponse(result, response)
setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, result)
finish()
Handle user sign-in
User sign-in is handled with the following steps:
- When a client app tries to sign in a user, it prepares a
GetCredentialRequestinstance. - The Android framework propagates this request to all applicable credential providers by binding to these services.
- The provider service then receives a
BeginGetCredentialRequestthat contains a list ofBeginGetCredentialOption, each of which contains parameters that can be used to retrieve matching credentials.
To handle this request in your credential provider service, complete the following steps:
Override the
onBeginGetCredentialRequest()method to handle the request. Note that if your credentials are locked, you can immediately set anAuthenticationActionon the response and invoke the callback.private val unlockEntryTitle = "Authenticate to continue" override fun onBeginGetCredentialRequest( request: BeginGetCredentialRequest, cancellationSignal: CancellationSignal, callback: OutcomeReceiver<BeginGetCredentialResponse, GetCredentialException>, ) { if (isAppLocked()) { callback.onResult( BeginGetCredentialResponse( authenticationActions = mutableListOf( AuthenticationAction( unlockEntryTitle, createUnlockPendingIntent() ) ) ) ) return } try { response = processGetCredentialRequest(request) callback.onResult(response) } catch (e: GetCredentialException) { callback.onError(GetCredentialUnknownException()) } }Providers that require unlocking the credentials before returning any
credentialEntries, must set up a pending intent that navigates the user to the app's unlock flow:private fun createUnlockPendingIntent(): PendingIntent { val intent = Intent(UNLOCK_INTENT).setPackage(PACKAGE_NAME) return PendingIntent.getActivity( applicationContext, UNIQUE_REQUEST_CODE, intent, ( PendingIntent.FLAG_MUTABLE or PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT ) ) }Retrieve credentials from your local database and set them up using
CredentialEntriesto be shown on the selector. For passkeys, you can setcredentialIdas an extra on the intent so as to know which credential it maps to when the user selects this entry.companion object { // These intent actions are specified for corresponding activities // that are to be invoked through the PendingIntent(s) private const val GET_PASSKEY_INTENT_ACTION = "PACKAGE_NAME.GET_PASSKEY" private const val GET_PASSWORD_INTENT_ACTION = "PACKAGE_NAME.GET_PASSWORD" } fun processGetCredentialRequest( request: BeginGetCredentialRequest ): BeginGetCredentialResponse { val callingPackageInfo = request.callingAppInfo val callingPackageName = callingPackageInfo?.packageName.orEmpty() val credentialEntries: MutableList<CredentialEntry> = mutableListOf() for (option in request.beginGetCredentialOptions) { when (option) { is BeginGetPasswordOption -> { credentialEntries.addAll( populatePasswordData( callingPackageName, option ) ) } is BeginGetPublicKeyCredentialOption -> { credentialEntries.addAll( populatePasskeyData( callingPackageInfo, option ) ) } else -> { Log.i(TAG, "Request not supported") } } } return BeginGetCredentialResponse(credentialEntries) }Query credentials from your database, create passkey and password entries to populate.
private fun populatePasskeyData( callingAppInfo: CallingAppInfo?, option: BeginGetPublicKeyCredentialOption ): List<CredentialEntry> { val passkeyEntries: MutableList<CredentialEntry> = mutableListOf() val request = PublicKeyCredentialRequestOptions(option.requestJson) // Get your credentials from database where you saved during creation flow val creds = getCredentialsFromInternalDb(request.rpId) val passkeys = creds.passkeys for (passkey in passkeys) { val data = Bundle() data.putString("credId", passkey.credId) passkeyEntries.add( PublicKeyCredentialEntry( context = applicationContext, username = passkey.username, pendingIntent = createNewPendingIntent( GET_PASSKEY_INTENT_ACTION, data ), beginGetPublicKeyCredentialOption = option, displayName = passkey.displayName, icon = passkey.icon ) ) } return passkeyEntries } // Fetch password credentials and create password entries to populate to the user private fun populatePasswordData( callingPackage: String, option: BeginGetPasswordOption ): List<CredentialEntry> { val passwordEntries: MutableList<CredentialEntry> = mutableListOf() // Get your password credentials from database where you saved during // creation flow val creds = getCredentialsFromInternalDb(callingPackage) val passwords = creds.passwords for (password in passwords) { passwordEntries.add( PasswordCredentialEntry( context = applicationContext, username = password.username, pendingIntent = createNewPendingIntent( GET_PASSWORD_INTENT ), beginGetPasswordOption = option, displayName = password.username, icon = password.icon ) ) } return passwordEntries } private fun createNewPendingIntent( action: String, extra: Bundle? = null ): PendingIntent { val intent = Intent(action).setPackage(PACKAGE_NAME) if (extra != null) { intent.putExtra("CREDENTIAL_DATA", extra) } return PendingIntent.getActivity( applicationContext, UNIQUE_REQUEST_CODE, intent, (PendingIntent.FLAG_MUTABLE or PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT) ) }Once you query and populate the credentials, now you need to handle the selection phase for the credentials being selected by the user, whether it is a passkey or a password.
Handling user selection for passkeys
- In the
onCreatemethod of the corresponding Activity, retrieve the associated intent, and pass toPendingIntentHandler.retrieveProviderGetCredentialRequest(). - Extract the
GetPublicKeyCredentialOptionfrom the request retrieved above. Subsequently, extract therequestJsonandclientDataHashfrom this option. - Extract the
credentialIdfrom the intent extra, which was populated by the credential provider when the correspondingPendingIntentwas set up. - Extract the passkey from your local database using the request parameters accessed above.
Assert that the passkey is valid with extracted metadata, and user verification.
val getRequest = PendingIntentHandler.retrieveProviderGetCredentialRequest(intent) val publicKeyRequest = getRequest?.credentialOptions?.first() as GetPublicKeyCredentialOption val requestInfo = intent.getBundleExtra("CREDENTIAL_DATA") val credIdEnc = requestInfo?.getString("credId").orEmpty() // Get the saved passkey from your database based on the credential ID from the PublicKeyRequest val passkey = mDatabase.getPasskey(credIdEnc) // Decode the credential ID, private key and user ID val credId = b64Decode(credIdEnc) val privateKey = b64Decode(passkey.credPrivateKey) val uid = b64Decode(passkey.uid) val origin = appInfoToOrigin(getRequest.callingAppInfo) val packageName = getRequest.callingAppInfo.packageName validatePasskey( publicKeyRequest.requestJson, origin, packageName, uid, passkey.username, credId, privateKey )To validate the user, surface a Biometric prompt (or other assertion method). The code snippet below uses the Android Biometric API.
Once the authentication succeeds, construct a JSON response based on the W3 Web Authentication Assertion spec. In the code snippet below, helper data classes like
AuthenticatorAssertionResponseare used to take in structured parameters and convert them into the required JSON format. The response contains a digital signature from the private key of a WebAuthn credential. The relying party's server can verify this signature to authenticate a user before signing in.Construct a
PublicKeyCredentialusing the JSON generated above and set it on a finalGetCredentialResponse. Set this final response on the result of this activity.
The following example illustrates how these steps can be implemented:
val request = PublicKeyCredentialRequestOptions(requestJson)
val privateKey: ECPrivateKey = convertPrivateKey(privateKeyBytes)
val biometricPrompt = BiometricPrompt(
this,
{ }, // Pass in your own executor
object : BiometricPrompt.AuthenticationCallback() {
override fun onAuthenticationError(
errorCode: Int,
errString: CharSequence
) {
super.onAuthenticationError(errorCode, errString)
finish()
}
override fun onAuthenticationFailed() {
super.onAuthenticationFailed()
finish()
}
override fun onAuthenticationSucceeded(
result: BiometricPrompt.AuthenticationResult
) {
super.onAuthenticationSucceeded(result)
val response = AuthenticatorAssertionResponse(
requestOptions = request,
credentialId = credId,
origin = origin,
up = true,
uv = true,
be = true,
bs = true,
userHandle = uid,
packageName = packageName
)
val sig = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withECDSA")
sig.initSign(privateKey)
sig.update(response.dataToSign())
response.signature = sig.sign()
val credential = FidoPublicKeyCredential(
rawId = credId,
response = response,
authenticatorAttachment = "", // Add your authenticator attachment
)
val result = Intent()
val passkeyCredential = PublicKeyCredential(credential.json())
PendingIntentHandler.setGetCredentialResponse(
result, GetCredentialResponse(passkeyCredential)
)
setResult(RESULT_OK, result)
finish()
}
}
)
val promptInfo = BiometricPrompt.PromptInfo.Builder()
.setTitle("Use your screen lock")
.setSubtitle("Use passkey for ${request.rpId}")
.setAllowedAuthenticators(
BiometricManager.Authenticators.BIOMETRIC_STRONG
/* or BiometricManager.Authenticators.DEVICE_CREDENTIAL */
)
.build()
biometricPrompt.authenticate(promptInfo)
Handling user selection for password authentication
- In your corresponding activity, access the intent passed in to
onCreateand extract theProviderGetCredentialRequestusingPendingIntentHandler. Use
GetPasswordOptionin the request to retrieve password credentials for the incoming package name.val getRequest = PendingIntentHandler.retrieveProviderGetCredentialRequest(intent) val passwordOption = getRequest?.credentialOptions?.first() as GetPasswordOption val username = passwordOption.allowedUserIds.first() // Fetch the credentials for the calling app package name val creds = mDatabase.getCredentials(callingAppInfo.packageName) val passwords = creds.passwords val it = passwords.iterator() var password = "" while (it.hasNext()) { val passwordItemCurrent = it.next() if (passwordItemCurrent.username == username) { password = passwordItemCurrent.password break } }Once retrieved, set the response for the selected password credential.
// Set the response back val result = Intent() val passwordCredential = PasswordCredential(username, password) PendingIntentHandler.setGetCredentialResponse( result, GetCredentialResponse(passwordCredential) ) setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, result) finish()
Handle selection of an authentication action entry
As mentioned earlier, a credential provider can set an
AuthenticationAction if the credentials are locked. If the user selects this
entry, the Activity corresponding to the intent action set in the
PendingIntent is invoked. Credential providers can then surface a biometric
authentication flow or similar mechanism to unlock the credentials. On success,
the credential provider must construct a BeginGetCredentialResponse, similar
to how user sign-in handling is described above, as the credentials are now
unlocked. This response must then be set through the
PendingIntentHandler.setBeginGetCredentialResponse() method before the
prepared intent is set as the result and the Activity is finished.
Clear credential requests
A client app may request that any state maintained for credential selection must
be cleared, such as a credential provider may remember the previously selected
credential and only return that next time. A client app calls this API and
expects that sticky selection to be cleared. Your credential provider service
can handle this request by overriding the
onClearCredentialStateRequest() method:
override fun onClearCredentialStateRequest(
request: ProviderClearCredentialStateRequest,
cancellationSignal: CancellationSignal,
callback: OutcomeReceiver<Void?, ClearCredentialException>
) {
// Delete any maintained state as appropriate.
}
Add capability to link to your provider's settings page
To allow your users to open your provider's settings from the Passwords,
passkeys, & autofill screen, credential provider apps should implement the
credential-provider settingsActivity manifest attribute in
res/xml/provider.xml. This attribute lets you use an intent to open your app's
own settings screen if a user clicks on a provider name in the Passwords,
passkeys, & autofill list of services. Set the value of this attribute to the
name of the activity to be launched from the settings screen.
<credential-provider
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:settingsSubtitle="Example settings provider name"
android:settingsActivity="com.example.SettingsActivity">
<capabilities>
<capability name="android.credentials.TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY_CREDENTIAL" />
</capabilities>
</credential-provider>
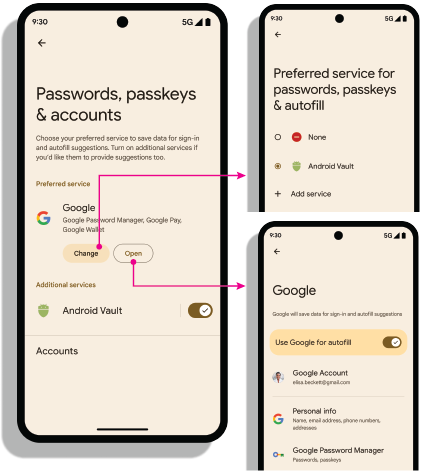
Settings intents
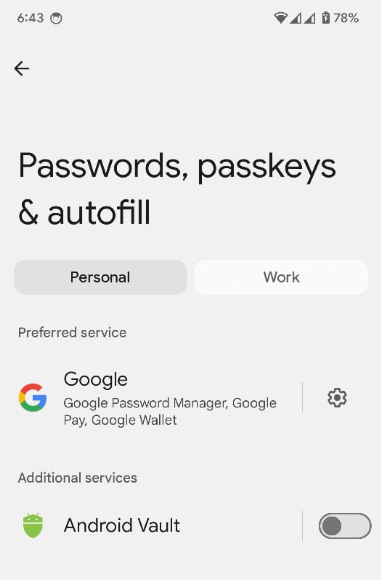
Open settings: The android.settings.CREDENTIAL_PROVIDER intent
brings up a settings screen where the user can select their preferred and
additional credential providers.
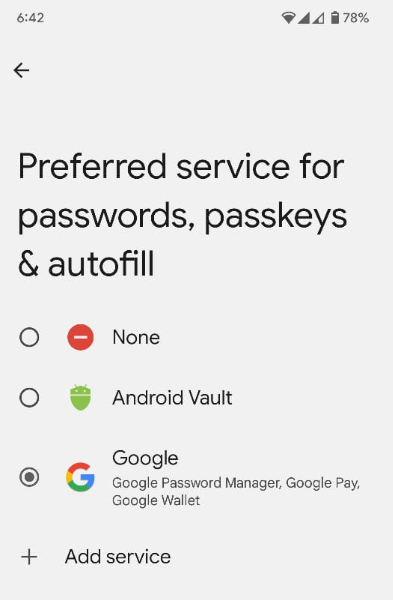
Preferred credential service: The
ACTION_REQUEST_SET_AUTOFILL_SERVICE intent redirects your user to the
preferred provider selection screen. The selected provider on this screen
becomes the preferred credentials and autofill provider.
Obtain an allowlist of privileged apps
Privileged apps such as web browsers make Credential Manager calls on behalf of
other relying parties by setting the origin parameter in the Credential
Manager GetCredentialRequest() and
CreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest() methods. To process these requests,
the credential provider retrieves the origin using the getOrigin()
API.
To retrieve the origin, the credential provider app needs to pass in a list of
privileged and trusted callers to the
androidx.credentials.provider.CallingAppInfo's getOrigin() API. This allowlist
must be a valid JSON object. The origin is returned if the packageName and
the certificate fingerprints obtained from signingInfo match those of an app
found in the privilegedAllowlist passed to the getOrigin() API. After the
origin value is obtained, the provider app should consider this a privileged
call and set this origin on the client data
in the AuthenticatorResponse, instead of computing the
origin using the calling app's signature.
If you retrieve an origin, use the clientDataHash that's provided directly
in CreatePublicKeyCredentialRequest() or
GetPublicKeyCredentialOption() instead of assembling and hashing
clientDataJSON during the signature request. To avoid JSON parsing issues, set
a placeholder value for clientDataJSON in the attestation and assertion
response. Google Password Manager uses an openly-available
allowlist for calls to getOrigin(). As a credential
provider, you can use this list or provide your own in the JSON format described
by the API. It is up to the provider to select which list is used. To get
privileged access with third party credential providers, refer to the
documentation provided by the third party.
Enable providers on a device
Users must enable the provider through device settings > Passwords & Accounts > Your Provider > Enable or Disable.
fun createSettingsPendingIntent(): PendingIntent
