Swipe views let you navigate between sibling screens, such as tabs, with a horizontal finger gesture, or swipe. This navigation pattern is also referred to as horizontal paging.
This topic teaches you how to create a tab layout with swipe views for switching between tabs and how to show a title strip instead of tabs.
Implement swipe views
You can create swipe views using AndroidX's
ViewPager2 widget.
To use ViewPager2 and tabs, you need to add a dependency on
ViewPager2 and Material
Components
to your project.
To set up your layout with ViewPager2, add the <ViewPager2> element to your
XML layout. For example, if each page in the swipe view consumes the entire
layout, then your layout looks like this:
<androidx.viewpager2.widget.ViewPager2
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/pager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
To insert child views that represent each page, hook this layout to a
FragmentStateAdapter.
Here's how you might use it to swipe across a collection of Fragment objects:
Kotlin
class CollectionDemoFragment : Fragment() { // When requested, this adapter returns a DemoObjectFragment, // representing an object in the collection. private lateinit var demoCollectionAdapter: DemoCollectionAdapter private lateinit var viewPager: ViewPager2 override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View? { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.collection_demo, container, false) } override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { demoCollectionAdapter = DemoCollectionAdapter(this) viewPager = view.findViewById(R.id.pager) viewPager.adapter = demoCollectionAdapter } } class DemoCollectionAdapter(fragment: Fragment) : FragmentStateAdapter(fragment) { override fun getItemCount(): Int = 100 override fun createFragment(position: Int): Fragment { // Return a NEW fragment instance in createFragment(int). val fragment = DemoObjectFragment() fragment.arguments = Bundle().apply { // The object is just an integer. putInt(ARG_OBJECT, position + 1) } return fragment } } private const val ARG_OBJECT = "object" // Instances of this class are fragments representing a single // object in the collection. class DemoObjectFragment : Fragment() { override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_collection_object, container, false) } override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { arguments?.takeIf { it.containsKey(ARG_OBJECT) }?.apply { val textView: TextView = view.findViewById(android.R.id.text1) textView.text = getInt(ARG_OBJECT).toString() } } }
Java
public class CollectionDemoFragment extends Fragment { // When requested, this adapter returns a DemoObjectFragment, // representing an object in the collection. DemoCollectionAdapter demoCollectionAdapter; ViewPager2 viewPager; @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.collection_demo, container, false); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { demoCollectionAdapter = new DemoCollectionAdapter(this); viewPager = view.findViewById(R.id.pager); viewPager.setAdapter(demoCollectionAdapter); } } public class DemoCollectionAdapter extends FragmentStateAdapter { public DemoCollectionAdapter(Fragment fragment) { super(fragment); } @NonNull @Override public Fragment createFragment(int position) { // Return a NEW fragment instance in createFragment(int). Fragment fragment = new DemoObjectFragment(); Bundle args = new Bundle(); // The object is just an integer. args.putInt(DemoObjectFragment.ARG_OBJECT, position + 1); fragment.setArguments(args); return fragment; } @Override public int getItemCount() { return 100; } } // Instances of this class are fragments representing a single // object in the collection. public class DemoObjectFragment extends Fragment { public static final String ARG_OBJECT = "object"; @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_collection_object, container, false); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { Bundle args = getArguments(); ((TextView) view.findViewById(android.R.id.text1)) .setText(Integer.toString(args.getInt(ARG_OBJECT))); } }
The following sections show how you can add tabs to help facilitate navigation between pages.
Add tabs using a TabLayout
A TabLayout provides
a way to display tabs horizontally. When used together with a ViewPager2, a
TabLayout can provide a familiar interface for navigating between pages in a
swipe view.
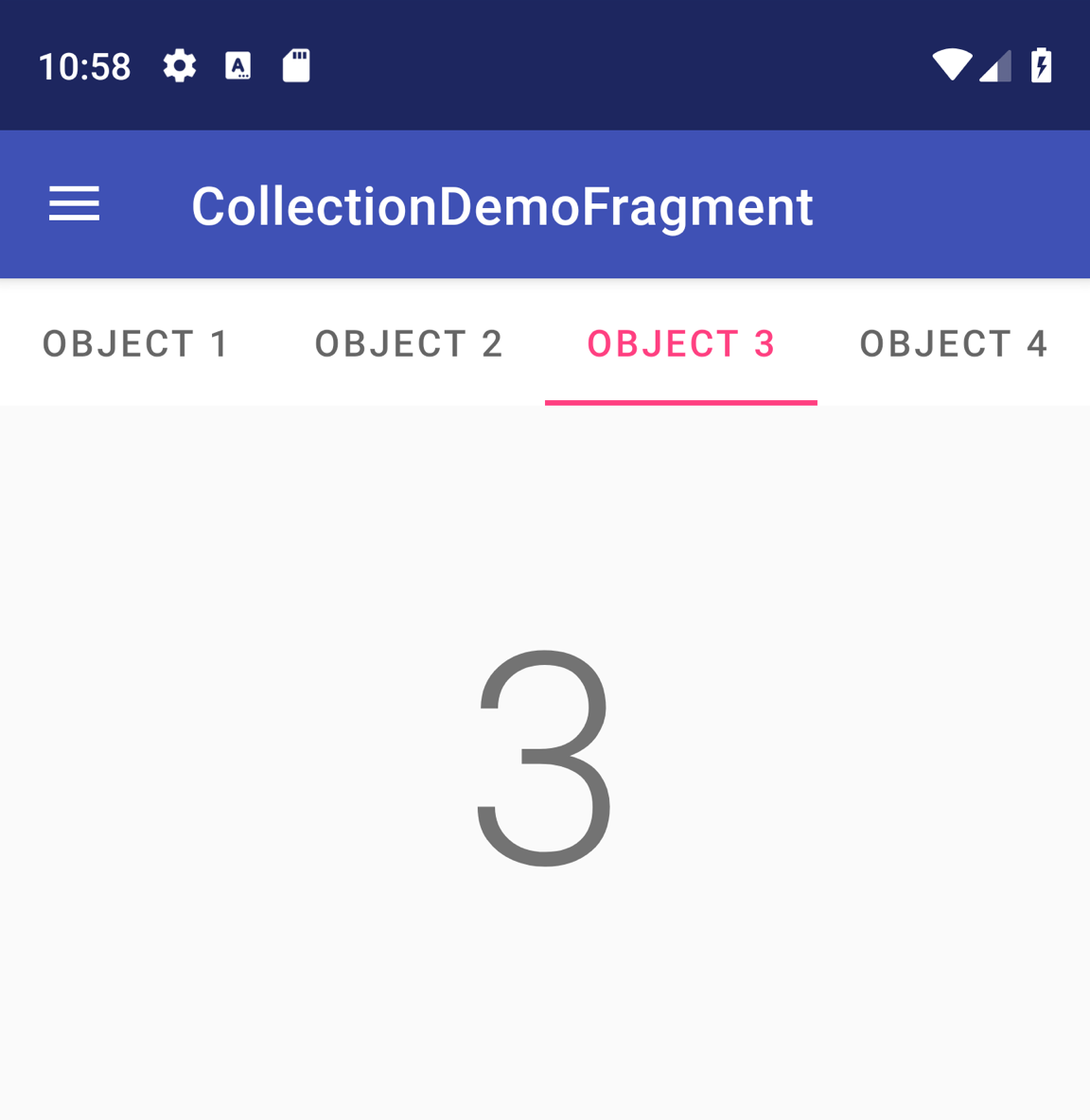
TabLayout with four tabs.
To include a TabLayout in a ViewPager2, add a <TabLayout> element above
the <ViewPager2> element:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<androidx.viewpager2.widget.ViewPager2
android:id="@+id/pager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
Next, create a
TabLayoutMediator
to link the TabLayout to the ViewPager2 and attach it, as follows:
Kotlin
class CollectionDemoFragment : Fragment() { ... override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { val tabLayout = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_layout) TabLayoutMediator(tabLayout, viewPager) { tab, position -> tab.text = "OBJECT ${(position + 1)}" }.attach() } ... }
Java
public class CollectionDemoFragment extends Fragment { ... @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { TabLayout tabLayout = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_layout); new TabLayoutMediator(tabLayout, viewPager, (tab, position) -> tab.setText("OBJECT " + (position + 1)) ).attach(); } ... }
For additional design guidance for tab layouts, see the Material Design documentation for tabs.
Additional resources
To learn more about ViewPager2, see the following additional resources.
Samples
- ViewPager2 samples on GitHub
