Bu sayfa, üçüncü taraf SDK'ların Google Play için yeni bir test özelliği olan ve Google Play uygulama ürün ayrıntılarını yarım sayfalık bir arayüzde sunan satır içi yüklemeyi nasıl entegre edebileceğini açıklamaktadır. Satır içi kurulum, kullanıcıların uygulama bağlamından ayrılmadan kesintisiz bir uygulama yükleme akışı deneyimlemelerini sağlar.
Üçüncü taraf SDK geliştiricileri, SDK'larına satır içi yükleme özelliğini entegre ederek bu SDK'ları kullanan uygulama geliştiricilerinin uygulamaları için satır içi yüklemelere erişebilmelerini sağlayabilir.
Şartlar
Uygulamada satır içi kurulum yarım sayfa arayüzünün görünmesi için:
- Minimum Google Play sürümü 40.4 olmalıdır.
- Android API düzeyi 23 veya daha yüksek olmalıdır.
Süreç mimarisi
Satır içi kurulum süreci mimarisi aşağıdaki şekilde gösterilmiştir:
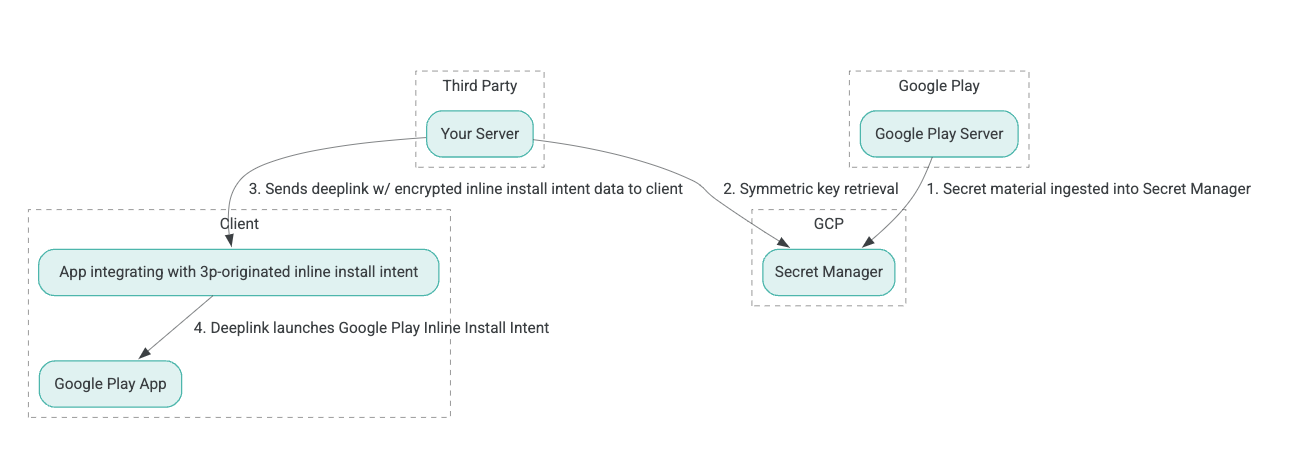
- Google Play sunucuları, İlişkili Verilerle Kimlik Doğrulanmış Şifreleme (AEAD) şifreleme anahtarları üretir ve anahtarları bir Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Gizli Yönetici örneğine aktarır.
- Üçüncü taraf entegratör, AEAD anahtarını GCP Secret Manager'dan alır.
- Üçüncü taraf entegratör, satır içi yükleme
Intentverilerini şifreler, satır içi yükleme amacını çağırmak için kullanılan derin bağlantıda iletilen şifreli metni oluşturur ve yanıt olarak istemciye derin bağlantılar gönderir. - Derin bağlantı takip edildiğinde, Google Play uygulaması amacı yönetir.
Üçüncü taraf bir SDK'yı satır içi yükleme sürecini kullanacak şekilde yapılandırmak için aşağıdaki adımları tamamlayın.
Google Cloud Project'te hizmet hesapları oluşturun
Bu adımda, Google Cloud Console'u kullanarak bir hizmet hesabı kurarsınız.
- Bir Google Cloud Projesi Kurun:
- Bir Google Cloud kuruluşu oluşturun. Bir Google Workspace veya Cloud Identity hesabı oluşturup bunu alan adınızla ilişkilendirdiğinizde, kuruluş kaynağı otomatik olarak oluşturulur. Ayrıntılar için Kuruluş kaynaklarını oluşturma ve yönetme konusuna bakın.
- Önceki adımda oluşturduğunuz Google Cloud hesabını kullanarak GCP Konsoluna giriş yapın ve ardından bir Google Cloud projesi oluşturun. Ayrıntılar için Google Cloud projesi oluşturma konusuna bakın.
- Oluşturulan Google Cloud projesinde bir servis hesabı oluşturun. Hizmet hesabı, sunucularınız adına simetrik anahtara erişmek için bir Google Cloud Kimliği olarak kullanılır. Ayrıntılar için Hizmet hesabı oluşturma konusuna bakın.
- İlgi formuna girilen Google Workspace Müşteri Kimliğini (GWCID) / Dasher Kimliğini kullanın.
- Bu servis hesabının özel anahtarını oluşturun ve indirin.
- Bu servis hesabı için bir anahtar oluşturun. Ayrıntılar için Hizmet hesabı anahtarı oluşturma bölümüne bakın.
- Hizmet hesabı anahtarını indirin ve sunucunuzda erişilebilir tutun; bu, simetrik anahtarlar için Google Cloud kaynaklarına erişimde kimlik doğrulaması amacıyla kullanılır. Ayrıntılar için Hizmet hesabı anahtarı alma konusuna bakın.
Kimlik bilgilerini al
Bu adımda, simetrik anahtarı Secret Manager'dan alıp güvenli bir şekilde (örneğin bir JSON dosyasında) kendi sunucu depolamanızda saklarsınız. Bu anahtar, satır içi kurulum veri şifre metnini oluşturmak için kullanılır.
secret_id/secretId değerleri, Secret Manager içindeki gizli adı ifade eder; bu ad, Play tarafından sağlanan sdk_id değerine hsdp-3p-key- eklenerek oluşturulur. Örneğin, sdk_id abc ise gizli ad hsdp-3p-key-abc olur.
Gizli sürümler her hafta Salı günü saat 14:00 UTC'de güncellenir. İkinci en yeni anahtarlar bir sonraki rotasyona kadar çalışmaya devam eder ve anahtar materyali haftalık olarak yenilenmeli ve saklanmalıdır.
Python örneği
Aşağıdaki kod örneği, GCP Secret Manager'daki anahtar materyale erişmek ve bunu konsola yazdırmak için bir JSON dosyasında saklanan bir erişim belirtecini kullanır.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
from google.cloud import secretmanager
from google.oauth2 import service_account
import google_crc32c
# Create a service account key file.
service_account_key_file = "<json key file of the service account>"
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(service_account_key_file)
# Create the Secret Manager client.
client = secretmanager.SecretManagerServiceClient(
credentials=credentials
)
# Build the resource name of the secret version.
name = f"projects/prod-play-hsdp-3p-caller-auth/secrets/<secret_id>/versions/latest"
# Access the secret version.
response = client.access_secret_version(request={"name": name})
# Verify payload checksum.
crc32c = google_crc32c.Checksum()
crc32c.update(response.payload.data)
if response.payload.data_crc32c != int(crc32c.hexdigest(), 16):
print("Data corruption detected.")
# A keyset created with "tinkey create-keyset --key-template=AES256_GCM". Note
# that this keyset has the secret key information in cleartext.
keyset = response.payload.data.decode("UTF-8")
# WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment. Please store it
# in a secure storage.
with open('<key file name>', 'w') as f:
f.write(keyset)
Java örneği
Aşağıdaki kod örneği, GCP Secret Manager'daki anahtar materyale erişmek ve bunu bir JSON dosyasına yazmak için bir JSON dosyasında saklanan bir erişim belirtecini kullanır.
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.api.gax.core.CredentialsProvider;
import com.google.api.gax.core.FixedCredentialsProvider;
import com.google.auth.oauth2.ServiceAccountCredentials;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.AccessSecretVersionResponse;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceClient;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceSettings;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretVersionName;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.zip.CRC32C;
import java.util.zip.Checksum;
/** */
final class ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide {
private ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
accessSecretVersion();
}
public static void accessSecretVersion() throws IOException {
// TODO(developer): Replace these variables before running the sample.
String projectId = "projectId";
String secretId = "secretId";
String versionId = "versionId";
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath = "path/to/credentials.json";
String secretMaterialOutputPath = "path/to/secret.json";
accessSecretVersion(
projectId, secretId, versionId, accessTokenPrivateKeyPath, secretMaterialOutputPath);
}
// Access the payload for the given secret version if one exists. The version
// can be a version number as a string (e.g. "5") or an alias (e.g. "latest").
public static void accessSecretVersion(
String projectId,
String secretId,
String versionId,
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath,
String secretMaterialOutputPath)
throws IOException {
// We can explicitly instantiate the SecretManagerServiceClient (below) from a json file if we:
// 1. Create a CredentialsProvider from a FileInputStream of the JSON file,
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider =
FixedCredentialsProvider.create(
ServiceAccountCredentials.fromStream(new FileInputStream(accessTokenPrivateKeyPath)));
// 2. Build a SecretManagerService Settings object from that credentials provider, and
SecretManagerServiceSettings secretManagerServiceSettings =
SecretManagerServiceSettings.newBuilder()
.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.build();
// 3. Initialize client that will be used to send requests by passing the settings object to
// create(). This client only needs to be created once, and can be reused for multiple requests.
// After completing all of your requests, call the "close" method on the client to safely clean
// up any remaining background resources.
try (SecretManagerServiceClient client =
SecretManagerServiceClient.create(secretManagerServiceSettings)) {
SecretVersionName secretVersionName = SecretVersionName.of(projectId, secretId, versionId);
// Access the secret version.
AccessSecretVersionResponse response = client.accessSecretVersion(secretVersionName);
// Verify checksum. The used library is available in Java 9+.
// If using Java 8, you may use the following:
// https://github.com/google/guava/blob/e62d6a0456420d295089a9c319b7593a3eae4a83/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/Hashing.java#L395
byte[] data = response.getPayload().getData().toByteArray();
Checksum checksum = new CRC32C();
checksum.update(data, 0, data.length);
if (response.getPayload().getDataCrc32C() != checksum.getValue()) {
System.out.printf("Data corruption detected.");
return;
}
String payload = response.getPayload().getData().toStringUtf8();
// Print the secret payload.
//
// WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment - this
// snippet is showing how to access the secret material.
System.out.printf("Plaintext: %s\n", payload);
// Write the JSON secret material payload to a json file
try (PrintWriter out =
new PrintWriter(Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get(secretMaterialOutputPath), UTF_8))) {
out.write(payload);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Uygulama Varsayılan Kimlik Bilgileri'ni ayarlama
Java uygulamasında özel anahtarı bir JSON dosyasına iletmek için CredentialsProvider kullanmak istemiyorsanız Uygulama Varsayılan Kimlik Bilgileri'ni (ADC) ayarlayarak uygulamayı değiştirebilirsiniz:
- İstemci kitaplıklarına hizmet hesabı anahtarının nerede bulunacağını söyleyin.
- Java projesine Maven bağımlılıklarını ekleyin.
- Adım 1 nedeniyle kimlik doğrulamasını otomatik olarak alan
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()numaralı telefonu arayın.
Bu adımlar Java uygulamasını şu şekilde değiştirir:
CredentialsProviderveSecretManagerServiceSettingsnesnelerini oluşturma gereksinimini ortadan kaldırır.- Çağrıyı hiçbir argüman içermeyecek şekilde
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()olarak değiştiriyorum.
Şifreli metin oluşturun ve derin bağlantı oluşturun
Bu adımda, Tink şifreleme kütüphanesini kullanarak InlineInstallData protobuf nesnesinden enifd (InlineInstallData şifreli metni) oluşturursunuz.
InlineInstallData protokolü aşağıdaki gibi tanımlanır:
syntax = "proto2";
package hsdpexperiments;
option java_package = "com.google.hsdpexperiments";
option java_multiple_files = true;
// InlineInstallData is used by 3p auth callers to generate "encrypted inline
// flow data" (enifd) which is decrypted in PGS to verify authenticity and
// freshness.
message InlineInstallData {
// The timestamp which indicates the time encrypted data is generated.
// Used to validate freshness (i.e. generation time in past 4 hours).
// Required.
optional int64 timestamp_ms = 1;
// The docid of the app that we want to open inline install page for.
// This is the package name.
// Required.
optional string target_package_name = 2;
// This is the name of the app requesting the ad from Google Ad Serving
// system.
// Required.
optional string caller_package_name = 3;
// This is the advertising id that will be collected by 3P Ad SDKs.
// Optional.
optional string advertising_id = 4;
// This is used to indicate the network from where the inline install was
// requested.
// Required.
optional string ad_network_id = 5;
}
Bu adımda ayrıca şu parametreleri kullanarak derin bağlantı URL'sini de oluşturursunuz:
| Fields'ın oynadığı filmler | Açıklama | Zorunlu |
|---|---|---|
| id | Yüklenecek uygulamanın paket adı. | Evet |
| satır içi | Satır içi yarım sayfa kurulumu isteniyorsa true olarak ayarlayın; false ise amaç Google Play'e derin bağlantılar sağlar. |
Evet |
| enifd | 3P SDK'ları için şifrelenmiş tanımlayıcı. | Evet |
| lft | Dahili bir tanımlayıcı. | Evet |
| 3pAuthCallerId | SDK tanımlayıcısı. | Evet |
| giriş | Özel mağaza listesi için hedefi belirtmek üzere isteğe bağlı bir parametre. | Hayır |
| yönlendiren | İsteğe bağlı bir yönlendiren izleme dizesi. | Hayır |
Python örneği
Aşağıdaki komut InlineInstallData.proto'dan Python kodu üretir:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --python_out=.
Aşağıdaki Python örnek kodu InlineInstallData'ı oluşturur ve şifreli metni oluşturmak için simetrik anahtarla şifreler:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
import base64
import time
import inline_install_data_pb2 as InlineInstallData
import tink
from tink import aead
from tink import cleartext_keyset_handle
# Read the stored symmetric key.
with open("example3psecret.json", "r") as f:
keyset = f.read()
"""Encrypt and decrypt using AEAD."""
# Register the AEAD key managers. This is needed to create an Aead primitive later.
aead.register()
# Create a keyset handle from the cleartext keyset in the previous
# step. The keyset handle provides abstract access to the underlying keyset to
# limit access of the raw key material. WARNING: In practice, it is unlikely
# you will want to use a cleartext_keyset_handle, as it implies that your key
# material is passed in cleartext, which is a security risk.
keyset_handle = cleartext_keyset_handle.read(tink.JsonKeysetReader(keyset))
# Retrieve the Aead primitive we want to use from the keyset handle.
primitive = keyset_handle.primitive(aead.Aead)
inlineInstallData = InlineInstallData.InlineInstallData()
inlineInstallData.timestamp_ms = int(time.time() * 1000)
inlineInstallData.target_package_name = "x.y.z"
inlineInstallData.caller_package_name = "a.b.c"
inlineInstallData.ad_network_id = "<sdk_id>"
# Use the primitive to encrypt a message. In this case the primary key of the
# keyset will be used (which is also the only key in this example).
ciphertext = primitive.encrypt(inlineInstallData.SerializeToString(), b'<sdk_id>')
print(f"InlineInstallData Ciphertext: {ciphertext}")
# Base64 Encoded InlineInstallData Ciphertext
enifd = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(ciphertext).decode('utf-8')
print(enifd)
# Deeplink
print(f"https://play.google.com/d?id={inlineInstallData.target_package_name}\&inline=true\&enifd={enifd}\&lft=1\&3pAuthCallerId={inlineInstallData.ad_network_id}")
Aşağıdaki komutu çalıştırarak Python betiğini çalıştırın:
python <file_name>.py
Java örneği
Aşağıdaki komut InlineInstallData.proto'dan Java kodu üretir:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --java_out=.
Aşağıdaki Java örnek kodu InlineInstallData'ı oluşturur ve şifreli metni oluşturmak için simetrik anahtarla şifreler:
package com.google.hsdpexperiments;
import static com.google.common.io.BaseEncoding.base64Url;
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.common.flags.Flag;
import com.google.common.flags.FlagSpec;
import com.google.common.flags.Flags;
import com.google.crypto.tink.Aead;
import com.google.crypto.tink.InsecureSecretKeyAccess;
import com.google.crypto.tink.KeysetHandle;
import com.google.crypto.tink.TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat;
import com.google.crypto.tink.aead.AeadConfig;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.Security;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.conscrypt.Conscrypt;
/** info on encryption in https://github.com/google/tink#learn-more */
final class ThirdPartyEnifdGuide {
@FlagSpec(
name = "third_party_id",
help = "the identifier associated with the 3p for which to generate the enifd")
private static final Flag<String> thirdPartyAuthCallerId = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "package_name", help = "the package name of the target app")
private static final Flag<String> packageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "caller_package_name", help = "the package name of the caller app")
private static final Flag<String> callerPackageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "secret_filename", help = "the path to the json file with the secret material")
private static final Flag<String> secretFilename = Flag.value("");
private ThirdPartyEnifdGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// parse flags
Flags.parse(args);
// File keyFile = new File(args[0]);
Path keyFile = Paths.get(secretFilename.get());
// Create structured inline flow data
InlineInstallData idrp =
InlineInstallData.newBuilder()
.setTargetPackageName(packageName.get())
.setCallerPackageName(callerPackageName.get())
.setTimestampMs(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setAdNetworkId(thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get())
.build();
// we can print this out here to make sure it's well formatted, this will help debug
System.out.println(idrp.toString());
// Register all AEAD key types with the Tink runtime.
Conscrypt.checkAvailability();
Security.addProvider(Conscrypt.newProvider());
AeadConfig.register();
// Read AEAD key downloaded from secretmanager into keysethandle
KeysetHandle handle =
TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat.parseKeyset(
new String(Files.readAllBytes(keyFile), UTF_8), InsecureSecretKeyAccess.get());
// Generate enifd using tink library
Aead aead = handle.getPrimitive(Aead.class);
byte[] plaintext = idrp.toByteArray();
byte[] ciphertext = aead.encrypt(plaintext, thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get().getBytes(UTF_8));
String enifd = base64Url().omitPadding().encode(ciphertext);
// Build deeplink, escaping ampersands (TODO: verify this is necessary while testing e2e)
String deeplink =
"https://play.google.com/d?id="
+ packageName.get()
+ "\\&inline=true\\&enifd="
+ enifd
+ "\\&lft=1\\&3pAuthCallerId="
+ thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get();
System.out.println(deeplink);
}
}
Son olarak, Java programını ikili bir dosyaya dönüştürün ve aşağıdaki kodu kullanarak çağırın:
path/to/binary/ThirdPartyEnifdGuide --secret_filename=path/to/jsonfile/example3psecret.json --package_name=<package_name_of_target_app> --third_party_id=<3p_caller_auth_id>
secret_filenamebayrağı, gizli materyali içeren JSON dosyasının yolunu belirtir.package_namebayrağı hedef uygulamanın belge kimliğidir.third_party_idbayrağı, üçüncü taraf arayan kimlik doğrulama kimliğini (yani<sdk_id>) belirtmek için kullanılır.
Satır İçi Kurulum amacını başlatın
Önceki adımda oluşturulan derin bağlantıyı test etmek için bir Android cihazı (USB hata ayıklamanın etkinleştirildiğinden emin olun) ADB'nin yüklü olduğu bir iş istasyonuna bağlayın ve aşağıdaki komutu çalıştırın:
adb shell am start "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
İstemci kodunda, aşağıdaki yöntemlerden birini (Kotlin veya Java) kullanarak intent'i gönderin.
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
val deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending")
intent.data = Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl)
val packageManager = context.getPackageManager()
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0)
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
String id = "exampleAppToBeInstalledId";
String deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>";
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending");
intent.setData(Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl));
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Ek
Aşağıdaki bölümlerde belirli kullanım durumlarına ilişkin ek rehberlik sağlanmaktadır.
Python ortamını hazırlama
Python örnek kodunu çalıştırmak için iş istasyonunuzda Python ortamını kurun ve gerekli bağımlılıkları yükleyin.
Python ortamını kurun:
Python3.11'i yükleyin (eğer zaten yüklüyse, bu adımı atlayın):
sudo apt install python3.11Pip'i kurun:
sudo apt-get install pipvirtualenvyükleyin:sudo apt install python3-virtualenvSanal bir ortam oluşturun (Tink bağımlılığı için gereklidir):
virtualenv inlineinstall --python=/usr/bin/python3.11
Sanal ortama girin:
source inlineinstall/bin/activatePip'i güncelle:
python -m pip install --upgrade pipGerekli bağımlılıkları kurun:
Tink'i yükleyin:
pip install tinkGoogle crc32c'yi yükleyin:
pip install google-crc32cSecret Manager'ı yükleyin:
pip install google-cloud-secret-managerProtobuf derleyicisini kurun:
sudo apt install protobuf-compiler
C++ enifd üretimi
Aşağıda enifd üretmek için yazdığımız ve dahili olarak doğruladığımız bir C++ örneği bulunmaktadır.
enifd oluşturma işlemi, aşağıdaki C++ kodu kullanılarak gerçekleştirilebilir:
// A command-line example for using Tink AEAD w/ key template aes128gcmsiv to
// encrypt an InlineInstallData proto.
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "<path_to_protoc_output>/inline_install_data.proto.h"
#include "absl/flags/flag.h"
#include "absl/flags/parse.h"
#include "absl/strings/escaping.h"
#include "absl/strings/string_view.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_config.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_key_templates.h"
#include "tink/cc/config/global_registry.h"
#include "tink/cc/examples/util/util.h"
#include "tink/cc/keyset_handle.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/status.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/statusor.h"
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, keyset_filename, "",
"Keyset file (downloaded from secretmanager) in JSON format");
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, associated_data, "",
"Associated data for AEAD (default: empty");
namespace {
using ::crypto::tink::Aead;
using ::crypto::tink::AeadConfig;
using ::crypto::tink::KeysetHandle;
using ::crypto::tink::util::Status;
using ::crypto::tink::util::StatusOr;
} // namespace
namespace tink_cc_examples {
// AEAD example CLI implementation.
void AeadCli(const std::string& keyset_filename,
absl::string_view associated_data) {
Status result = AeadConfig::Register();
if (!result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to register AeadConfig";
return;
}
// Read the keyset from file.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<KeysetHandle>> keyset_handle =
ReadJsonCleartextKeyset(keyset_filename);
if (!keyset_handle.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to read json keyset";
return;
}
// Get the primitive.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<Aead>> aead =
(*keyset_handle)
->GetPrimitive<crypto::tink::Aead>(
crypto::tink::ConfigGlobalRegistry());
if (!aead.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to get primitive";
return;
}
// Instantiate the enifd.
hsdpexperiments::InlineInstallData iid;
iid.set_timestamp_ms(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch())
.count());
iid.set_target_package_name("<TARGET_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_caller_package_name("<CALLER_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_ad_network_id("<SDK_ID>");
// Compute the output.
StatusOr<std::string> encrypt_result =
(*aead)->Encrypt(iid.SerializeAsString(), associated_data);
if (!encrypt_result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to encrypt Inline Install Data";
return;
}
const std::string& output = encrypt_result.value();
std::string enifd;
absl::WebSafeBase64Escape(output, &enifd);
std::clog << "enifd: " << enifd << '\n';
}
} // namespace tink_cc_examples
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
absl::ParseCommandLine(argc, argv);
std::string keyset_filename = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_keyset_filename);
std::string associated_data = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_associated_data);
std::clog << "Using keyset from file " << keyset_filename
<< " to AEAD-encrypt inline install data with associated data '"
<< associated_data << "'." << '\n';
tink_cc_examples::AeadCli(keyset_filename, associated_data);
return 0;
}
Bu kod, Tink belgelerinde bulunabilen bir örnekten uyarlanmıştır.
