Thành phần Dialog hiển thị thông báo bật lên hoặc yêu cầu người dùng nhập dữ liệu trên một lớp phía trên nội dung chính của ứng dụng. Điều này tạo ra trải nghiệm giao diện người dùng bị gián đoạn để thu hút sự chú ý của người dùng.
Sau đây là một số trường hợp sử dụng hộp thoại:
- Xác nhận hành động của người dùng, chẳng hạn như khi xoá tệp.
- Yêu cầu người dùng nhập dữ liệu, chẳng hạn như trong ứng dụng danh sách việc cần làm.
- Trình bày danh sách các tuỳ chọn để người dùng lựa chọn, chẳng hạn như chọn quốc gia trong quá trình thiết lập hồ sơ.
Chủ đề này cung cấp các cách triển khai sau:
Khả năng tương thích của phiên bản
Phương thức triển khai này yêu cầu bạn phải đặt minSDK của dự án thành API cấp 21 trở lên.
Phần phụ thuộc
Tạo hộp thoại Cảnh báo
Thành phần kết hợp AlertDialog cung cấp một API thuận tiện để tạo hộp thoại theo chủ đề Material Design. Ví dụ sau đây triển khai hai nút trong hộp thoại cảnh báo, một nút đóng hộp thoại và một nút xác nhận yêu cầu của hộp thoại:
Cách triển khai này ngụ ý một thành phần kết hợp mẹ truyền đối số đến thành phần kết hợp con theo cách sau:
Kết quả
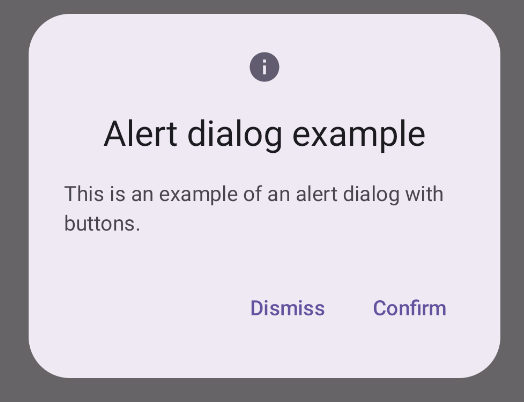
Điểm chính
AlertDialog có các tham số cụ thể để xử lý các phần tử cụ thể của hộp thoại. Trong đó có:
title: Văn bản xuất hiện ở đầu hộp thoại.text: Văn bản xuất hiện ở giữa hộp thoại.icon: Hình ảnh xuất hiện ở đầu hộp thoại.onDismissRequest: Hàm được gọi khi người dùng đóng hộp thoại, chẳng hạn như bằng cách nhấn vào bên ngoài hộp thoại.dismissButton: Một thành phần kết hợp đóng vai trò là nút đóng.confirmButton: Một thành phần kết hợp đóng vai trò là nút xác nhận.Khi người dùng nhấp vào một trong các nút, hộp thoại sẽ đóng lại. Khi người dùng nhấp vào xác nhận, thao tác này sẽ gọi một hàm cũng xử lý xác nhận. Trong ví dụ này, các hàm đó là
onDismissRequest()vàonConfirmRequest().Trong trường hợp hộp thoại của bạn yêu cầu một nhóm nút phức tạp hơn, bạn có thể sử dụng thành phần kết hợp
Dialogvà điền vào hộp thoại theo cách linh hoạt hơn.
Tạo hộp thoại
Dialog là một thành phần kết hợp cơ bản không cung cấp bất kỳ kiểu nào hoặc các vị trí được xác định trước cho nội dung. Đây là một vùng chứa đơn giản mà bạn nên điền sẵn bằng một vùng chứa như Card. Sau đây là một số tham số chính của hộp thoại:
onDismissRequest: Hàm lambda được gọi khi người dùng đóng hộp thoại.properties: Một thực thể củaDialogPropertiescung cấp một số phạm vi bổ sung để tuỳ chỉnh.
Tạo hộp thoại cơ bản
Ví dụ sau đây là cách triển khai cơ bản của thành phần kết hợp Dialog. Xin lưu ý rằng lớp này sử dụng Card làm vùng chứa phụ. Nếu không có Card, thành phần Text sẽ xuất hiện riêng lẻ phía trên nội dung chính của ứng dụng.
Kết quả
Xin lưu ý rằng khi hộp thoại đang mở, nội dung chính của ứng dụng bên dưới hộp thoại sẽ xuất hiện màu tối và màu xám:

Tạo hộp thoại nâng cao
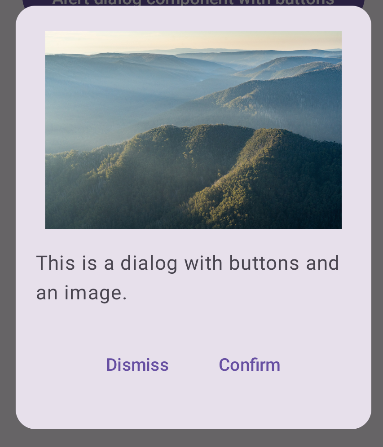
Sau đây là cách triển khai nâng cao hơn của thành phần kết hợp Dialog. Trong trường hợp này, thành phần triển khai theo cách thủ công một giao diện tương tự như ví dụ AlertDialog trước đó.
Kết quả
Các bộ sưu tập chứa hướng dẫn này
Hướng dẫn này là một phần của các bộ sưu tập Hướng dẫn nhanh được tuyển chọn này, bao gồm các mục tiêu phát triển Android rộng hơn:
Văn bản hiển thị

Yêu cầu người dùng nhập dữ liệu



