Wie bei früheren Versionen enthält Android 16 Verhaltensänderungen, die sich auf Ihre App auswirken können. Die folgenden Verhaltensänderungen gelten ausschließlich für Apps, die auf Android 16 oder höher ausgerichtet sind. Wenn Ihre App auf Android 16 oder höher ausgerichtet ist, sollten Sie sie gegebenenfalls so anpassen, dass sie diese Verhaltensweisen unterstützt.
Sehen Sie sich auch die Liste der Verhaltensänderungen an, die sich auf alle Apps auswirken, die unter Android 16 ausgeführt werden, unabhängig vom targetSdkVersion Ihrer App.
Nutzererfahrung und System-UI
Android 16 (API‑Level 36) enthält die folgenden Änderungen, die für eine einheitlichere, intuitivere Nutzererfahrung sorgen sollen.
Deaktivierung von Edge-to-Edge-Anzeigen wird eingestellt
Android 15: Edge-to-Edge-Anzeige für Apps, die auf Android 15 ausgerichtet sind (API-Level 35): Für Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind, wird die Edge-to-Edge-Anzeige erzwungen. Ihre App kann jedoch deaktiviert werden, indem Sie R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement auf true setzen. Bei Apps, die auf Android 16 (API-Level 36) ausgerichtet sind, ist R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement eingestellt und deaktiviert. Deine App kann nicht deaktivieren, dass sie randlos angezeigt wird.
- Wenn Ihre App auf Android 16 (API-Level 36) ausgerichtet ist und auf einem Android 15-Gerät ausgeführt wird, funktioniert
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementweiterhin. - Wenn Ihre App auf Android 16 (API-Level 36) ausgerichtet ist und auf einem Android 16-Gerät ausgeführt wird, ist
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementdeaktiviert.
Wenn Sie Ihre App unter Android 16 testen, muss sie Edge-to-Edge unterstützen. Entfernen Sie alle Verwendungen von R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement, damit Ihre App auch auf einem Android 15-Gerät Edge-to-Edge unterstützt. Informationen zur Unterstützung von Edge-to-Edge finden Sie in den Anleitungen zu Compose und Views.
Migration oder Deaktivierung für die Funktion „Vorhersagende Zurück-Geste“ erforderlich
Bei Apps, die auf Android 16 (API‑Level 36) oder höher ausgerichtet sind und auf einem Gerät mit Android 16 oder höher ausgeführt werden, sind die Systemanimationen für das vorhersagbare Zurückgehen (Zurück zum Startbildschirm, Aufgabenübergang und Aktivitätsübergang) standardmäßig aktiviert.
Außerdem wird onBackPressed nicht aufgerufen und KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK wird nicht mehr gesendet.
Wenn Ihre App das Zurück-Ereignis abfängt und Sie noch nicht auf die Vorhersage für „Zurück“ migriert haben, aktualisieren Sie Ihre App, damit sie unterstützte APIs für die Zurück-Navigation verwendet, oder deaktivieren Sie die Vorhersage vorübergehend, indem Sie das Attribut android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback in der <application>- oder <activity>-Kennzeichnung der AndroidManifest.xml-Datei Ihrer App auf false festlegen.
Elegant Font APIs eingestellt und deaktiviert
Bei Apps, die auf Android 15 (API‑Level 35) ausgerichtet sind, ist das Attribut elegantTextHeight
TextView standardmäßig auf true gesetzt. Dadurch wird die kompakte Schriftart durch eine Schriftart ersetzt, die viel besser lesbar ist. Sie können dies überschreiben, indem Sie das Attribut elegantTextHeight auf false festlegen.
In Android 16 wird das Attribut elegantTextHeight eingestellt. Es wird ignoriert, sobald Ihre App auf Android 16 ausgerichtet ist. Die von diesen APIs gesteuerten „UI-Schriftarten“ werden eingestellt. Sie sollten daher alle Layouts anpassen, um eine konsistente und zukunftssichere Textwiedergabe in Arabisch, Laotisch, Birmanisch, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu oder Thailändisch zu gewährleisten.
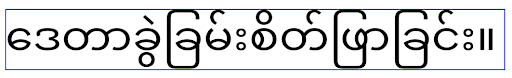
elegantTextHeight-Verhalten für Apps, die auf Android 14 (API-Level 34) oder niedriger ausgerichtet sind, oder für Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind und den Standardwert durch Festlegen des Attributs elegantTextHeight auf false überschrieben haben.
elegantTextHeight-Verhalten für Apps, die auf Android 16 (API-Level 36) ausgerichtet sind, oder für Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind und den Standard nicht überschrieben haben, indem sie das Attribut elegantTextHeight auf false gesetzt haben.Hauptfunktion
Android 16 (API‑Level 36) umfasst die folgenden Änderungen, die verschiedene Kernfunktionen des Android-Systems modifizieren oder erweitern.
Optimierung der Arbeitsplanung mit festem Tarif
Vor der Ausrichtung auf Android 16 wurde bei scheduleAtFixedRate eine Aufgabenausführung verpasst, wenn sich die App nicht in einem gültigen Prozesslebenszyklus befand. In diesem Fall wurden alle verpassten Ausführungen sofort ausgeführt, sobald die App zu einem gültigen Lebenszyklus zurückkehrte.
Wenn Sie Ihre App auf Android 16 ausrichten, wird bei einer verpassten Ausführung von scheduleAtFixedRate höchstens eine Ausführung sofort ausgeführt, wenn die App zu einem gültigen Lebenszyklus zurückkehrt. Durch diese Verhaltensänderung soll sich die App-Leistung verbessern. Testen Sie dieses Verhalten in Ihrer App, um festzustellen, ob sie davon betroffen ist.
Sie können auch das App-Kompatibilitäts-Framework verwenden und das STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS-Kompatibilitätsflag aktivieren.
Formfaktoren von Geräten
Android 16 (API‑Level 36) enthält die folgenden Änderungen für Apps, die auf Geräten mit großem Bildschirm angezeigt werden.
Adaptive Layouts
Android-Apps laufen jetzt auf einer Vielzahl von Geräten (z. B. Smartphones, Tablets, faltbare Geräte, Computer, Autos und Fernseher) und in verschiedenen Fenstermodi auf großen Bildschirmen (z. B. Split-Screen und Desktop-Fenster). Entwickler sollten Android-Apps entwickeln, die sich unabhängig von der Geräteausrichtung an jede Bildschirm- und Fenstergröße anpassen. Paradigmen wie die Einschränkung der Ausrichtung und Größenänderung sind in der heutigen Welt mit mehreren Geräten zu restriktiv.
Einschränkungen in Bezug auf Ausrichtung, Anpassbarkeit der Größe und Seitenverhältnis ignorieren
Bei Apps, die auf Android 16 (API-Level 36) ausgerichtet sind, gelten Einschränkungen für Ausrichtung, Größenänderung und Seitenverhältnis nicht mehr auf Displays mit einer Mindestbreite von mindestens 600 dp. Apps füllen das gesamte Displayfenster aus, unabhängig vom Seitenverhältnis oder der bevorzugten Ausrichtung des Nutzers. Pillarboxing wird nicht verwendet.
Diese Änderung führt zu einem neuen Standardverhalten der Plattform. Android entwickelt sich zu einem Modell, bei dem Apps an verschiedene Ausrichtungen, Displaygrößen und Seitenverhältnisse angepasst werden müssen. Einschränkungen wie eine feste Ausrichtung oder eine begrenzte Anpassbarkeit der Größe beeinträchtigen die Anpassungsfähigkeit von Apps. Gestalten Sie Ihre App adaptiv, um eine optimale Nutzererfahrung zu bieten.
Sie können dieses Verhalten auch mit dem App-Kompatibilitäts-Framework testen und das Kompatibilitäts-Flag UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT aktivieren.
Häufige wichtige Änderungen
Wenn Sie die Einschränkungen für Ausrichtung, Anpassbarkeit und Seitenverhältnis ignorieren, kann sich das auf die Benutzeroberfläche Ihrer App auf einigen Geräten auswirken, insbesondere auf Elemente, die für kleine Layouts im Hochformat entwickelt wurden. Beispiele sind gestreckte Layouts sowie Animationen und Komponenten, die nicht auf dem Bildschirm angezeigt werden. Annahmen zum Seitenverhältnis oder zur Ausrichtung können zu visuellen Problemen in Ihrer App führen. Weitere Informationen dazu, wie Sie diese Probleme vermeiden und das adaptive Verhalten Ihrer App verbessern können.
Wenn Sie die Geräteausrichtung zulassen, wird die Aktivität häufiger neu erstellt. Das kann dazu führen, dass der Nutzerstatus verloren geht, wenn er nicht richtig beibehalten wird. Informationen zum korrekten Speichern des UI-Zustands finden Sie unter UI-Zustände speichern.
Details zur Implementierung
Die folgenden Manifestattribute und Laufzeit-APIs werden auf Geräten mit großem Display im Vollbild- und Mehrfenstermodus ignoriert:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
Die folgenden Werte für screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() und getRequestedOrientation() werden ignoriert:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Die Größenanpassung des Displays wird durch android:resizeableActivity="false", android:minAspectRatio und android:maxAspectRatio nicht beeinflusst.
Bei Apps, die auf Android 16 (API-Level 36) ausgerichtet sind, werden die Ausrichtung, die Anpassbarkeit der Größe und die Einschränkungen des Seitenverhältnisses auf großen Bildschirmen standardmäßig ignoriert. Jede App, die noch nicht vollständig bereit ist, kann dieses Verhalten jedoch vorübergehend überschreiben, indem sie die Funktion deaktiviert. Dadurch wird das vorherige Verhalten aktiviert, bei dem die App im Kompatibilitätsmodus ausgeführt wird.
Ausnahmen
Die Einschränkungen für Ausrichtung, Größenänderung und Seitenverhältnis unter Android 16 gelten in den folgenden Situationen nicht:
- Spiele (basierend auf der
android:appCategory-Kennzeichnung) - Nutzer, die das Standardverhalten der App in den Einstellungen für das Seitenverhältnis des Geräts explizit aktivieren
- Bildschirme, die kleiner als
sw600dpsind
Vorübergehend deaktivieren
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Aktivität deaktivieren möchten, deklarieren Sie die Manifest-Eigenschaft PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
Wenn zu viele Teile Ihrer App nicht für Android 16 bereit sind, können Sie die Funktion vollständig deaktivieren, indem Sie dieselbe Property auf Anwendungsebene anwenden:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Gesundheit und Fitness
Android 16 (API‑Level 36) enthält die folgenden Änderungen in Bezug auf Gesundheits- und Fitnessdaten.
Berechtigungen für Gesundheit und Fitness
Für Apps, die auf Android 16 (API‑Level 36) oder höher ausgerichtet sind, werden für BODY_SENSORS-Berechtigungen detailliertere Berechtigungen unter android.permissions.health verwendet, die auch von Health Connect genutzt werden. Ab Android 16 ist für alle APIs, für die bisher BODY_SENSORS oder BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND erforderlich war, stattdessen die entsprechende android.permissions.health-Berechtigung erforderlich. Dies betrifft die folgenden Datentypen, APIs und Arten von Vordergrunddiensten:
HEART_RATE_BPMaus den Gesundheitsdiensten unter Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEaus dem Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyundheartRateBpmausProtoLayoutunter Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH, wobei die entsprechende Berechtigungandroid.permission.healthanstelle vonBODY_SENSORSerforderlich ist
Wenn Ihre App diese APIs verwendet, sollte sie die entsprechenden detaillierten Berechtigungen anfordern:
- Für die Überwachung von Herzfrequenz, SpO2 oder Hauttemperatur während der Nutzung: Fordern Sie die detaillierte Berechtigung unter
android.permissions.healthan, z. B.READ_HEART_RATEanstelle vonBODY_SENSORS. - Für den Zugriff auf Sensoren im Hintergrund: Fordern Sie
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDanstelle vonBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDan.
Diese Berechtigungen sind dieselben, die den Zugriff auf das Lesen von Daten aus Health Connect, dem Android-Datenspeicher für Gesundheits‑, Fitness- und Wellnessdaten, schützen.
Mobile Apps
Mobile Apps, die zur Verwendung von READ_HEART_RATE und anderen detaillierten Berechtigungen migriert werden, müssen auch eine Aktivität deklarieren, um die Datenschutzerklärung der App anzuzeigen. Das ist dieselbe Anforderung wie bei Health Connect.
Konnektivität
Android 16 (API-Level 36) enthält die folgenden Änderungen am Bluetooth-Stack, um die Verbindung mit Peripheriegeräten zu verbessern.
Neue Intents für den Umgang mit Verlust der Bindung und Änderungen an der Verschlüsselung
Im Rahmen der Verbesserten Verarbeitung von Verbindungsverlusten werden in Android 16 außerdem zwei neue Intents eingeführt, um Apps besser über Verbindungsverluste und Verschlüsselungsänderungen zu informieren.
Für Apps, die auf Android 16 ausgerichtet sind, ist jetzt Folgendes möglich:
- Sie erhalten eine
ACTION_KEY_MISSING-Intent, wenn ein Verlust der Remote-Bindung erkannt wird. So können Sie Nutzern informativeres Feedback geben und entsprechende Maßnahmen ergreifen. - Sie erhalten eine
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE-Intent, wenn sich der Verschlüsselungsstatus des Links ändert. Dazu gehören Änderungen des Verschlüsselungsstatus, des Verschlüsselungsalgorithmus und der Größe des Verschlüsselungsschlüssels. Apps müssen davon ausgehen, dass die Verknüpfung wiederhergestellt wurde, wenn die Verknüpfung nach Erhalt derACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE-Intent erfolgreich verschlüsselt wurde.
Anpassung an unterschiedliche OEM-Implementierungen
Diese neuen Intents werden in Android 16 eingeführt, ihre Implementierung und Übertragung kann jedoch je nach Gerätehersteller (OEM) variieren. Damit Ihre App auf allen Geräten einheitlich und zuverlässig funktioniert, sollten Entwickler die Verarbeitung von Verbindungsverlusten so gestalten, dass sie sich an diese potenziellen Abweichungen anpasst.
Wir empfehlen folgende App-Verhaltensweisen:
Wenn die
ACTION_KEY_MISSING-Intent gesendet wird:Die ACL-Verbindung (Asynchronous Connectionless) wird vom System getrennt, die Informationen zur Bindung für das Gerät bleiben jedoch erhalten (wie hier beschrieben).
Ihre App sollte diese Intent als primäres Signal für die Erkennung von Verbindungsverlusten verwenden und den Nutzer auffordern, zu bestätigen, dass sich das Remotegerät in Reichweite befindet, bevor das Gerät vergessen oder neu gekoppelt wird.
Wenn die Verbindung eines Geräts nach dem Empfang von
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGgetrennt wird, sollte deine App vorsichtig sein, bevor sie eine neue Verbindung herstellt, da das Gerät möglicherweise nicht mehr mit dem System verbunden ist.Wenn die
ACTION_KEY_MISSING-Intent NICHT gesendet wird:Die ACL-Verbindung bleibt bestehen und die Informationen zur Kopplung des Geräts werden vom System entfernt, genau wie bei Android 15.
In diesem Fall sollte Ihre App die vorhandenen Mechanismen zur Verarbeitung von Verbindungsverlusten wie in früheren Android-Releases fortsetzen, um Verbindungsverluste zu erkennen und zu verwalten.
Neue Möglichkeit zum Entfernen einer Bluetooth-Verbindung
Alle Apps, die auf Android 16 ausgerichtet sind, können jetzt Bluetooth-Geräte über eine öffentliche API in CompanionDeviceManager entkoppeln. Wenn ein Companion-Gerät als CDM-Verknüpfung verwaltet wird, kann die App die Entfernung der Bluetooth-Verknüpfung über die neue removeBond(int) API auf dem verknüpften Gerät auslösen. Die App kann die Änderungen des Kopplungsstatus überwachen, indem sie das Bluetooth-Geräte-Broadcast-Ereignis ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED überwacht.
Sicherheit
Android 16 (API‑Level 36) enthält die folgenden Sicherheitsänderungen.
Sperrung der MediaStore-Version
Bei Apps, die auf Android 16 oder höher ausgerichtet sind, ist MediaStore#getVersion() jetzt für jede App eindeutig. Dadurch werden identifizierende Eigenschaften aus dem Versionsstring entfernt, um Missbrauch und Verwendung für Fingerprinting-Techniken zu verhindern. Apps dürfen keine Annahmen über das Format dieser Version treffen. Apps sollten Versionsänderungen bereits bei der Verwendung dieser API verarbeiten und in den meisten Fällen sollte ihr aktuelles Verhalten nicht geändert werden müssen, es sei denn, der Entwickler hat versucht, zusätzliche Informationen abzuleiten, die über den beabsichtigten Umfang dieser API hinausgehen.
Sicherere Intents
Safer Intents ist eine mehrphasige Sicherheitsinitiative, die darauf abzielt, die Sicherheit des Intent-Auflösungsmechanismus von Android zu verbessern. Ziel ist es, Apps vor schädlichen Aktionen zu schützen, indem während der Verarbeitung von Intents Prüfungen durchgeführt und Intents herausgefiltert werden, die bestimmte Kriterien nicht erfüllen.
In Android 15 lag der Fokus auf der sendenden App. In Android 16 wird die Steuerung nun auf die empfangende App verlagert. Entwickler können die strenge Intent-Auflösung über ihr App-Manifest aktivieren.
Es werden zwei wichtige Änderungen eingeführt:
Explizite Intents müssen mit dem Intent-Filter der Zielkomponente übereinstimmen: Wenn ein Intent explizit auf eine Komponente ausgerichtet ist, muss er mit dem Intent-Filter dieser Komponente übereinstimmen.
Intents ohne Aktion können keinem Intent-Filter entsprechen: Intents, für die keine Aktion angegeben ist, sollten nicht in einen Intent-Filter aufgelöst werden.
Diese Änderungen gelten nur, wenn mehrere Apps beteiligt sind, und haben keine Auswirkungen auf die Verarbeitung von Intents innerhalb einer einzelnen App.
Positiv beeinflussen
Da es sich um eine Opt-in-Funktion handelt, müssen Entwickler sie explizit in ihrem App-Manifest aktivieren, damit sie wirksam wird. Daher beschränkt sich die Wirkung der Funktion auf Apps, deren Entwickler:
- Sie kennen die Funktion „Safer Intents“ und ihre Vorteile.
- Sie entscheiden sich aktiv dafür, strengere Praktiken für die Intent-Verarbeitung in ihre Apps aufzunehmen.
Dieser Opt-in-Ansatz minimiert das Risiko, dass vorhandene Apps, die möglicherweise auf dem aktuellen, weniger sicheren Verhalten bei der Intent-Auflösung basieren, nicht mehr funktionieren.
Die anfänglichen Auswirkungen in Android 16 sind möglicherweise begrenzt, aber die Initiative „Safer Intents“ hat einen Fahrplan für umfassendere Auswirkungen in zukünftigen Android-Releases. Es ist geplant, die strikte Intenterkennung zum Standardverhalten zu machen.
Die Funktion „Safer Intents“ kann die Sicherheit des Android-Ökosystems erheblich verbessern, da sie es böswilligen Apps erschwert, Sicherheitslücken im Mechanismus zur Intent-Auflösung auszunutzen.
Die Umstellung auf die Abmeldung und die obligatorische Durchsetzung muss jedoch sorgfältig verwaltet werden, um potenzielle Kompatibilitätsprobleme mit vorhandenen Apps zu beheben.
Implementierung
Entwickler müssen das strengere Intent-Matching explizit über das Attribut intentMatchingFlags in ihrem App-Manifest aktivieren.
Hier ist ein Beispiel, in dem die Funktion für die gesamte App aktiviert ist, aber auf einem Empfänger deaktiviert bzw. deaktiviert wurde:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
Weitere Informationen zu den unterstützten Flags:
| Name des Parameters | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Erzwingt einen strengeren Abgleich für eingehende Intents |
| Keine | Deaktiviert alle speziellen Abgleichsregeln für eingehende Intents. Wenn Sie mehrere Flags angeben, werden widersprüchliche Werte aufgelöst, indem das Flag „none“ Vorrang erhält. |
| allowNullAction | Die Abgleichsregeln werden gelockert, sodass Intents ohne Aktion abgeglichen werden können. Dieses Flag muss in Verbindung mit „enforceIntentFilter“ verwendet werden, um ein bestimmtes Verhalten zu erzielen. |
Testen und Fehler beheben
Wenn die Erzwingung aktiv ist, sollten Apps ordnungsgemäß funktionieren, sofern der Intent-Aufrufer den Intent richtig ausgefüllt hat.
Blockierte Intents lösen jedoch Warnmeldungen wie "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" und "Access blocked:" mit dem Tag "PackageManager." aus.
Dies deutet auf ein potenzielles Problem hin, das sich auf die App auswirken könnte und Aufmerksamkeit erfordert.
Logcat-Filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU-Syscall-Filterung
Um die Mali-GPU-Oberfläche zu härten, wurden Mali-GPU-IOCTLs, die eingestellt wurden oder nur für die GPU-Entwicklung vorgesehen sind, in Produktions-Builds blockiert. Außerdem wurden IOCTLs, die für das GPU-Profiling verwendet werden, auf den Shell-Prozess oder debugfähige Anwendungen beschränkt. Weitere Informationen zur Richtlinie auf Plattformebene finden Sie im SAC-Update.
Diese Änderung betrifft Pixel-Geräte mit Mali-GPU (Pixel 6 bis Pixel 9). Arm hat eine offizielle Kategorisierung seiner IOCTLs in Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst seines r54p2-Release bereitgestellt. Diese Liste wird auch in zukünftigen Treiberversionen weitergeführt.
Diese Änderung hat keine Auswirkungen auf unterstützte Grafik-APIs (einschließlich Vulkan und OpenGL) und sollte sich nicht auf Entwickler oder vorhandene Anwendungen auswirken. GPU-Profiling-Tools wie der Streamline Performance Analyzer und der Android GPU Inspector sind davon nicht betroffen.
Testen
Wenn Sie eine SELinux-Verweigerung wie die folgende sehen, ist Ihre Anwendung wahrscheinlich von dieser Änderung betroffen:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
Wenn Ihre Anwendung blockierte IOCTLs verwenden muss, melden Sie bitte einen Fehler und weisen Sie ihn android-partner-security@google.com zu.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Gilt diese Richtlinienänderung für alle OEMs? Diese Änderung ist optional, steht aber allen OEMs zur Verfügung, die diese Härtungsmethode verwenden möchten. Eine Anleitung zur Implementierung der Änderung finden Sie in der Implementierungsdokumentation.
Muss ich Änderungen an der OEM-Codebasis vornehmen, um diese Funktion zu implementieren, oder ist sie standardmäßig in einem neuen AOSP-Release enthalten? Die Änderung auf Plattformebene wird standardmäßig mit einem neuen AOSP-Release eingeführt. Anbieter können diese Änderung in ihrem Code aktivieren, wenn sie sie anwenden möchten.
Sind SoCs dafür verantwortlich, die IOCTL-Liste auf dem neuesten Stand zu halten? Wenn mein Gerät beispielsweise eine ARM Mali-GPU verwendet, muss ich mich wegen der Änderungen an ARM wenden? Einzelne SoCs müssen ihre IOCTL-Listen pro Gerät bei der Veröffentlichung des Treibers aktualisieren. ARM aktualisiert beispielsweise die veröffentlichte IOCTL-Liste bei Treiberupdates. OEMs sollten jedoch darauf achten, dass sie die Updates in ihre SEPolicy aufnehmen und bei Bedarf ausgewählte benutzerdefinierte IOCTLs den Listen hinzufügen.
Wird diese Änderung automatisch auf alle im Handel erhältlichen Pixel angewendet oder ist eine Nutzeraktion erforderlich, um sie zu aktivieren? Diese Änderung gilt für alle im Handel erhältlichen Pixel-Geräte mit Mali-GPU (Pixel 6 bis 9). Es ist keine Nutzeraktion erforderlich, um diese Änderung zu übernehmen.
Hat die Verwendung dieser Richtlinie Auswirkungen auf die Leistung des Kerneltreibers? Diese Richtlinie wurde mit GFXBench auf der Mali-GPU getestet. Es wurde keine messbare Änderung der GPU-Leistung beobachtet.
Muss die IOCTL-Liste mit den aktuellen Userspace- und Kerneltreiberversionen übereinstimmen? Ja, die Liste der zulässigen IOCTLs muss mit den IOCTLs synchronisiert werden, die sowohl von den Userspace- als auch von den Kernel-Treibern unterstützt werden. Wenn die IOCTLs im Userspace oder im Kernel-Treiber aktualisiert werden, muss die SEPolicy-IOCTL-Liste entsprechend aktualisiert werden.
ARM hat IOCTLs als „eingeschränkt“ / „Instrumentierung“ kategorisiert, aber wir möchten einige davon in Produktionsanwendungsfällen verwenden und/oder andere ablehnen. Die einzelnen OEMs/SoCs sind dafür verantwortlich, wie sie die von ihnen verwendeten IOCTLs basierend auf der Konfiguration ihrer Mali-Bibliotheken im Userspace kategorisieren. Die Liste von ARM kann bei der Entscheidung helfen, aber der Anwendungsfall jedes OEM/SoC kann unterschiedlich sein.
Datenschutz
Android 16 (API‑Level 36) umfasst die folgenden Änderungen in Bezug auf den Datenschutz.
Berechtigung für das lokale Netzwerk
Auf Geräte im LAN kann von jeder App zugegriffen werden, die die Berechtigung INTERNET hat.
Dadurch können Apps problemlos eine Verbindung zu lokalen Geräten herstellen. Dies hat jedoch auch Auswirkungen auf den Datenschutz, z. B. in Bezug auf die Erstellung eines Fingerabdrucks des Nutzers und die Verwendung als Proxy für den Standort.
Das Projekt „Local Network Protections“ zielt darauf ab, die Privatsphäre des Nutzers zu schützen, indem der Zugriff auf das lokale Netzwerk durch eine neue Laufzeitberechtigung eingeschränkt wird.
Release-Plan
Diese Änderung wird zwischen zwei Releases bereitgestellt, nämlich 25Q2 und 26Q2. Entwickler müssen diese Anleitung für das 2. Quartal 2025 unbedingt befolgen und Feedback geben, da diese Schutzmaßnahmen in einem späteren Android-Release erzwungen werden. Außerdem müssen sie Szenarien, die auf implizitem lokalen Netzwerkzugriff basieren, gemäß der folgenden Anleitung aktualisieren und sich auf die Ablehnung und den Widerruf der neuen Berechtigung durch Nutzer vorbereiten.
Positiv beeinflussen
Derzeit ist LNP eine Opt-in-Funktion. Das bedeutet, dass nur die Apps betroffen sind, für die sie aktiviert wurde. In der Opt-in-Phase sollen App-Entwickler herausfinden, welche Teile ihrer App auf impliziten Zugriff auf das lokale Netzwerk angewiesen sind, damit sie sich auf die Berechtigungsanforderungen für die nächste Version vorbereiten können.
Apps sind betroffen, wenn sie über folgende Methoden auf das lokale Netzwerk des Nutzers zugreifen:
- Direkte oder bibliotheksbasierte Verwendung von Raw Sockets für lokale Netzwerkadressen (z.B. mDNS- oder SSDP-Diensterkennungsprotokoll)
- Verwendung von Klassen auf Framework-Ebene, die auf das lokale Netzwerk zugreifen (z.B. NsdManager)
Für Traffic zu und von einer lokalen Netzwerkadresse ist die Berechtigung für den Zugriff auf das lokale Netzwerk erforderlich. In der folgenden Tabelle sind einige häufige Fälle aufgeführt:
| Low-Level-Netzwerkbetrieb der App | Berechtigung für das lokale Netzwerk erforderlich |
|---|---|
| Ausgehende TCP-Verbindung herstellen | Ja |
| Eingehende TCP-Verbindungen akzeptieren | Ja |
| Senden eines UDP-Unicast, ‑Multicast oder ‑Broadcast | Ja |
| Eingehendes UDP-Unicast, ‑Multicast oder ‑Broadcast empfangen | Ja |
Diese Einschränkungen sind tief im Netzwerk-Stack implementiert und gelten daher für alle Netzwerk-APIs. Dazu gehören Sockets, die in nativem oder verwaltetem Code erstellt wurden, Netzwerkbibliotheken wie Cronet und OkHttp sowie alle APIs, die darauf basieren. Wenn Sie versuchen, Dienste im lokalen Netzwerk aufzulösen (d.h. Dienste mit dem Suffix „.local“), ist die Berechtigung für das lokale Netzwerk erforderlich.
Ausnahmen von den oben genannten Regeln:
- Wenn sich der DNS-Server eines Geräts in einem lokalen Netzwerk befindet, ist für den Traffic zu oder von diesem Gerät (über Port 53) keine Berechtigung für den Zugriff auf das lokale Netzwerk erforderlich.
- Für Apps, die Output Switcher als In-App-Auswahl verwenden, sind keine Berechtigungen für das lokale Netzwerk erforderlich (weitere Informationen folgen im 4. Quartal 2025).
Entwicklerleitfaden (Opt-in)
So aktivieren Sie Einschränkungen für das lokale Netzwerk:
- Flashen Sie das Gerät mit einem Build mit 25Q2 Beta 3 oder höher.
- Installieren Sie die zu testende App.
AppCompat-Flag in adb umschalten:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Gerät neu starten
Der Zugriff Ihrer App auf das lokale Netzwerk ist jetzt eingeschränkt und jeder Versuch, auf das lokale Netzwerk zuzugreifen, führt zu Socket-Fehlern. Wenn Sie APIs verwenden, die lokale Netzwerkoperationen außerhalb Ihres App-Prozesses ausführen (z. B. NsdManager), sind diese während der Opt-in-Phase nicht betroffen.
Wenn Sie den Zugriff wiederherstellen möchten, müssen Sie Ihrer App die Berechtigung für NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES erteilen.
- Die App muss die Berechtigung
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESin ihrem Manifest deklarieren. - Öffnen Sie die Einstellungen > Apps > [Name der App] > Berechtigungen > Geräte in der Nähe > Zulassen.
Der Zugriff Ihrer App auf das lokale Netzwerk sollte jetzt wiederhergestellt sein und alle Ihre Szenarien sollten wie vor der Aktivierung der App funktionieren.
Sobald die Durchsetzung des Schutzes des lokalen Netzwerks beginnt, wirkt sich das auf den Netzwerkverkehr der App aus.
| Berechtigung | Ausgehende LAN-Anfrage | Ausgehende/eingehende Internetanfrage | Eingehende LAN-Anfrage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gewährt | Microsoft Works | Microsoft Works | Microsoft Works |
| Nicht gewährt | Pannen | Microsoft Works | Pannen |
Verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl, um das App-Compat-Flag zu deaktivieren:
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Fehler
Fehler, die durch diese Einschränkungen entstehen, werden an den aufrufenden Socket zurückgegeben, wenn er „send“ oder eine „send“-Variante für eine lokale Netzwerkadresse aufruft.
Beispiele für Fehler:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Definition des lokalen Netzwerks
Ein lokales Netzwerk in diesem Projekt bezieht sich auf ein IP-Netzwerk, das eine für Broadcasts geeignete Netzwerkschnittstelle wie WLAN oder Ethernet verwendet, jedoch keine Mobilfunk- (WWAN) oder VPN-Verbindungen.
Die folgenden Netzwerke gelten als lokale Netzwerke:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-Local
- Direkt verbundene Routen
- Stummelnetzwerke wie Thread
- Mehrere Subnetze (noch nicht festgelegt)
Außerdem werden sowohl Multicast-Adressen (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) als auch die IPv4-Broadcast-Adresse (255.255.255.255) als lokale Netzwerkadressen klassifiziert.
App-eigene Fotos
Wenn Nutzer auf Geräten mit Android 16 oder höher von einer App, die auf SDK 36 oder höher ausgerichtet ist, um Berechtigungen für Fotos und Videos gebeten werden und den Zugriff auf ausgewählte Medien einschränken, werden alle Fotos, die der App gehören, in der Bildauswahl vorab ausgewählt angezeigt. Nutzer können die Auswahl dieser Elemente jederzeit aufheben. Dadurch wird der Zugriff der App auf diese Fotos und Videos widerrufen.
