Às vezes, pode ser necessário consultar um conjunto de três ou mais tabelas relacionadas entre si. Nesse caso, é preciso definir relações aninhadas entre as tabelas.
Suponha que, no exemplo do app de streaming de música, você queira consultar todos os usuários, todas as playlists de cada usuário e todas as músicas em cada playlist de cada usuário. Os usuários têm uma relação de um para muitos com playlists, e as playlists têm uma relação de muitos para muitos com músicas. O exemplo de código abaixo mostra as classes que representam essas entidades, bem como a tabela de referência cruzada para a relação de muitos para muitos entre listas de reprodução e músicas:
Kotlin
@Entity
data class User(
@PrimaryKey val userId: Long,
val name: String,
val age: Int
)
@Entity
data class Playlist(
@PrimaryKey val playlistId: Long,
val userCreatorId: Long,
val playlistName: String
)
@Entity
data class Song(
@PrimaryKey val songId: Long,
val songName: String,
val artist: String
)
@Entity(primaryKeys = ["playlistId", "songId"])
data class PlaylistSongCrossRef(
val playlistId: Long,
val songId: Long
)
Java
@Entity
public class User {
@PrimaryKey public long userId;
public String name;
public int age;
}
@Entity
public class Playlist {
@PrimaryKey public long playlistId;
public long userCreatorId;
public String playlistName;
}
@Entity
public class Song {
@PrimaryKey public long songId;
public String songName;
public String artist;
}
@Entity(primaryKeys = {"playlistId", "songId"})
public class PlaylistSongCrossRef {
public long playlistId;
public long songId;
}
Primeiro, modele a relação entre duas tabelas no seu conjunto como faria
normalmente, com uma classe de dados e a anotação @Relation. O
exemplo abaixo mostra uma classe PlaylistWithSongs que modela uma relação de muitos para muitos
entre as classes de entidade Playlist e Song:
Kotlin
data class PlaylistWithSongs(
@Embedded val playlist: Playlist,
@Relation(
parentColumn = "playlistId",
entityColumn = "songId",
associateBy = Junction(PlaylistSongCrossRef::class)
)
val songs: List<Song>
)
Java
public class PlaylistWithSongs {
@Embedded public Playlist playlist;
@Relation(
parentColumn = "playlistId",
entityColumn = "songId",
associateBy = Junction(PlaylistSongCrossRef.class)
)
public List<Song> songs;
}
Depois de definir uma classe de dados que representa essa relação, crie outra
classe que modele a relação entre outra tabela do conjunto e
a classe de relação primária, "aninhando" a relação existente com a
nova. O exemplo abaixo mostra uma classe UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs que modela
uma relação de um para muitos entre a classe de entidade User e a
classe de relação PlaylistWithSongs:
Kotlin
data class UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs(
@Embedded val user: User
@Relation(
entity = Playlist::class,
parentColumn = "userId",
entityColumn = "userCreatorId"
)
val playlists: List<PlaylistWithSongs>
)
Java
public class UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs {
@Embedded public User user;
@Relation(
entity = Playlist.class,
parentColumn = "userId",
entityColumn = "userCreatorId"
)
public List<PlaylistWithSongs> playlists;
}
A classe UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs modela indiretamente as relações
entre as três classes de entidade: User, Playlist e Song. Isso é
ilustrado na figura 1.
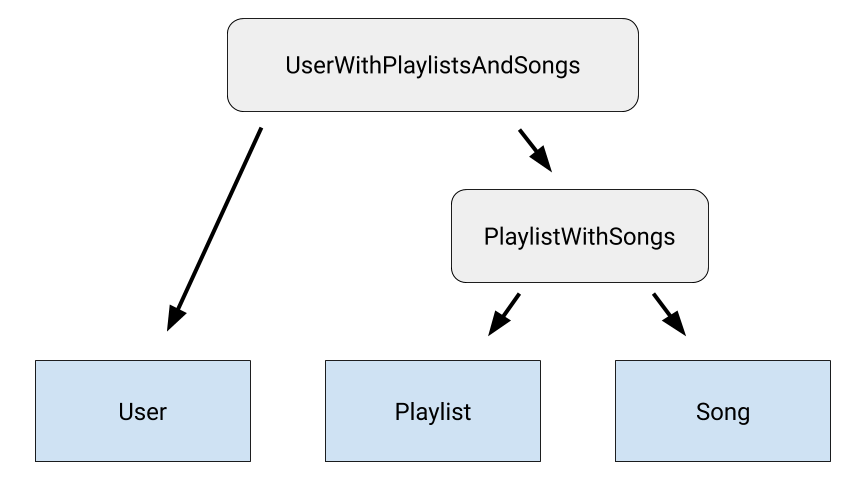
Se houver mais tabelas no seu conjunto, crie uma classe para modelar a relação entre cada tabela restante e a classe de relação que modela as relações entre todas as tabelas anteriores. Isso cria uma cadeia de relações aninhadas entre todas as tabelas que você quer consultar.
Por fim, adicione um método à classe DAO para expor a função de consulta de que
o app precisa. Esse método exige que o Room execute várias consultas. Portanto, adicione a
anotação @Transaction para garantir que toda a operação seja realizada
atomicamente:
Kotlin
@Transaction
@Query("SELECT * FROM User")
fun getUsersWithPlaylistsAndSongs(): List<UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs>
Java
@Transaction
@Query("SELECT * FROM User")
public List<UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs> getUsersWithPlaylistsAndSongs();
