Ce document présente les étapes et le workflow de configuration de base de l'outil Batterystats et du script Battery Historian. Pour savoir comment utiliser Battery Historian pour inspecter des modèles de consommation de batterie, consultez Analyser la consommation d'énergie avec Battery Historian.
Batterystats est un outil inclus dans le framework Android qui collecte les données sur la batterie de votre appareil. Vous pouvez utiliser adb pour vider les données de batterie collectées sur votre ordinateur de développement et créer un rapport que vous pouvez analyser à l'aide de Battery Historian. Battery Historian convertit le rapport de BatteryStats en un code HTML visualisable dans votre navigateur.
Batterystats et Battery Historian sont utiles pour :
- vous montrer où et comment les processus utilisent la batterie ;
- identifier les tâches dans votre application susceptibles d'être différées voire supprimées afin d'améliorer l'autonomie de la batterie.
Installer Battery Historian
Vous pouvez utiliser Docker pour installer Battery Historian. Pour connaître d'autres méthodes d'installation, y compris la compilation à partir de la source, consultez le fichier README sur la page GitHub du projet. Pour effectuer l'installation à l'aide de Docker, procédez comme suit :
Installez Docker en suivant les instructions du site Web de Docker. Tout type d'abonnement fonctionne, y compris un abonnement personnel gratuit.
Pour vérifier que Docker est correctement installé, ouvrez la ligne de commande et saisissez la commande suivante :
docker run hello-worldSi Docker est correctement installé, un résultat semblable à celui-ci s'affiche :
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 78445dd45222: Pull complete Digest: sha256:c5515758d4c5e1e838e9cd307f6c6a0d620b5e07e6f927b07d05f6d12a1ac8d7 Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminalLancez l'application Docker Desktop, qui est une interface IUG pour Docker, avant d'exécuter l'image Battery Historian. Cela initialise les outils Docker. Vous devez effectuer cette opération au moins une fois pour que Battery Historian s'exécute.
Exécutez Battery Historian à partir de la ligne de commande lors de sa première exécution. L'application Docker Desktop ne vous permet pas de spécifier le port sur lequel exécuter le serveur Web. Pour ce faire, vous devez utiliser la ligne de commande. Cependant, une fois que vous avez exécuté avec succès le conteneur à partir de la ligne de commande, une entrée est créée dans Docker Desktop. Vous pouvez ensuite lancer Battery Historian avec le même port d'écouteur depuis Docker Desktop.
Exécutez l'image de Battery Historian à l'aide de la commande suivante :
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Battery Historian utilise le port de votre choix, comme spécifié à l'aide de
port_number.Accédez à Battery Historian dans votre navigateur pour vérifier qu'il est en cours d'exécution. L'adresse varie en fonction de votre système d'exploitation :
- Pour Linux et Mac
- Battery Historian est disponible à l'adresse
http://localhost:port_number. - Pour Windows
- Lorsque vous démarrez Docker, l'adresse IP de la machine utilisée vous est indiquée. Par exemple, si l'adresse IP est 123.456.78.90, Battery Historian est disponible à l'adresse
http://123.456.78.90:port_number.
Vous retrouverez alors la page d'accueil de Battery Historian, d'où vous pouvez importer et consulter des statistiques sur la batterie.
Figure 1. Page d'accueil de Battery Historian
Recueillir des données avec Batterystats
Pour collecter les données de votre appareil à l'aide de Batterystats et les ouvrir dans Battery Historian, procédez comme suit :
Connectez votre appareil mobile à votre ordinateur.
Dans une fenêtre de terminal, arrêtez le serveur
adben cours d'exécution en exécutant la commande suivante :adb kill-serverRedémarrez
adbet vérifiez les appareils connectés en exécutant la commande suivante :adb devicesElle liste votre appareil, comme dans l'exemple de résultat suivant :

Figure 2. Résultat d' adb devices, qui montre un appareil connectéSi aucun appareil ne s'affiche, assurez-vous que votre téléphone est connecté et que le débogage USB est activé, puis arrêtez et redémarrez
adb.Réinitialisez la collecte des données de la batterie en exécutant la commande suivante :
adb shell dumpsys batterystats --resetL'appareil collecte toujours les statistiques de batterie et d'autres informations de débogage en arrière-plan. La réinitialisation efface les précédentes données de collecte de la batterie. Si vous ne réinitialisez pas, le résultat peut être très volumineux.
Déconnectez votre appareil de votre ordinateur afin de n'utiliser que la batterie de l'appareil.
Utilisez votre application et effectuez les actions pour lesquelles vous souhaitez collecter des données. Par exemple, déconnectez-vous du Wi-Fi et envoyez des données dans le cloud.
Reconnectez votre téléphone.
Assurez-vous que votre téléphone est reconnu et exécutez la commande suivante :
adb devicesVidez toutes les données de la batterie en exécutant la commande suivante. Cette opération peut prendre quelques instants.
adb shell dumpsys batterystats > [path/]batterystats.txt
Le fichier
batterystats.txtest créé dans le répertoire que vous indiquez à l'aide de l'argument de chemin facultatif. Si vous ne spécifiez pas de chemin d'accès, le fichier est créé dans votre répertoire d'accueil.Créez un rapport à partir de données brutes.
- Pour les appareils sous Android version 7.0 ou version ultérieure :
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.zip
- Pour les appareils sous Android version 6.0 ou version antérieure :
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.txt
Bugreport peut prendre plusieurs minutes. Ne déconnectez pas votre appareil et n'annulez pas le processus tant qu'il n'est pas terminé.
Comme pour
batterystats.txt, ces fichiers sont créés dans le répertoire que vous spécifiez à l'aide de l'argument facultatifpath. Si vous ne spécifiez pas de chemin d'accès, ils sont créés dans votre répertoire d'accueil.Si ce n'est pas déjà le cas, exécutez Battery Historian à l'aide de la commande suivante :
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Pour afficher vos données dans Battery Historian, ouvrez-le dans votre navigateur. Pour Mac et Linux, Battery Historian s'exécute sur
http://localhost:port_number. Pour Windows, il s'exécute surhttp://your_IP_address:port_number.Cliquez sur Parcourir, puis sélectionnez le fichier bugreport que vous avez créé.
Cliquez sur Envoyer. Battery Historian ouvre un graphique créé à partir de vos données Batterystats.
Afficher des données avec des graphiques Battery Historian
Les graphiques Battery Historian représentent des événements et l'évolution de leur consommation d'énergie au fil du temps.
Chaque ligne affiche un segment de barre de couleur lorsqu'un composant système est actif et utilise donc l'énergie de la batterie. Le graphique n'indique pas la quantité de batterie utilisée par le composant, mais uniquement si l'application est active. Les graphiques sont organisés par catégorie, avec une barre pour chaque catégorie au fil du temps, comme indiqué sur l'axe X du graphique.
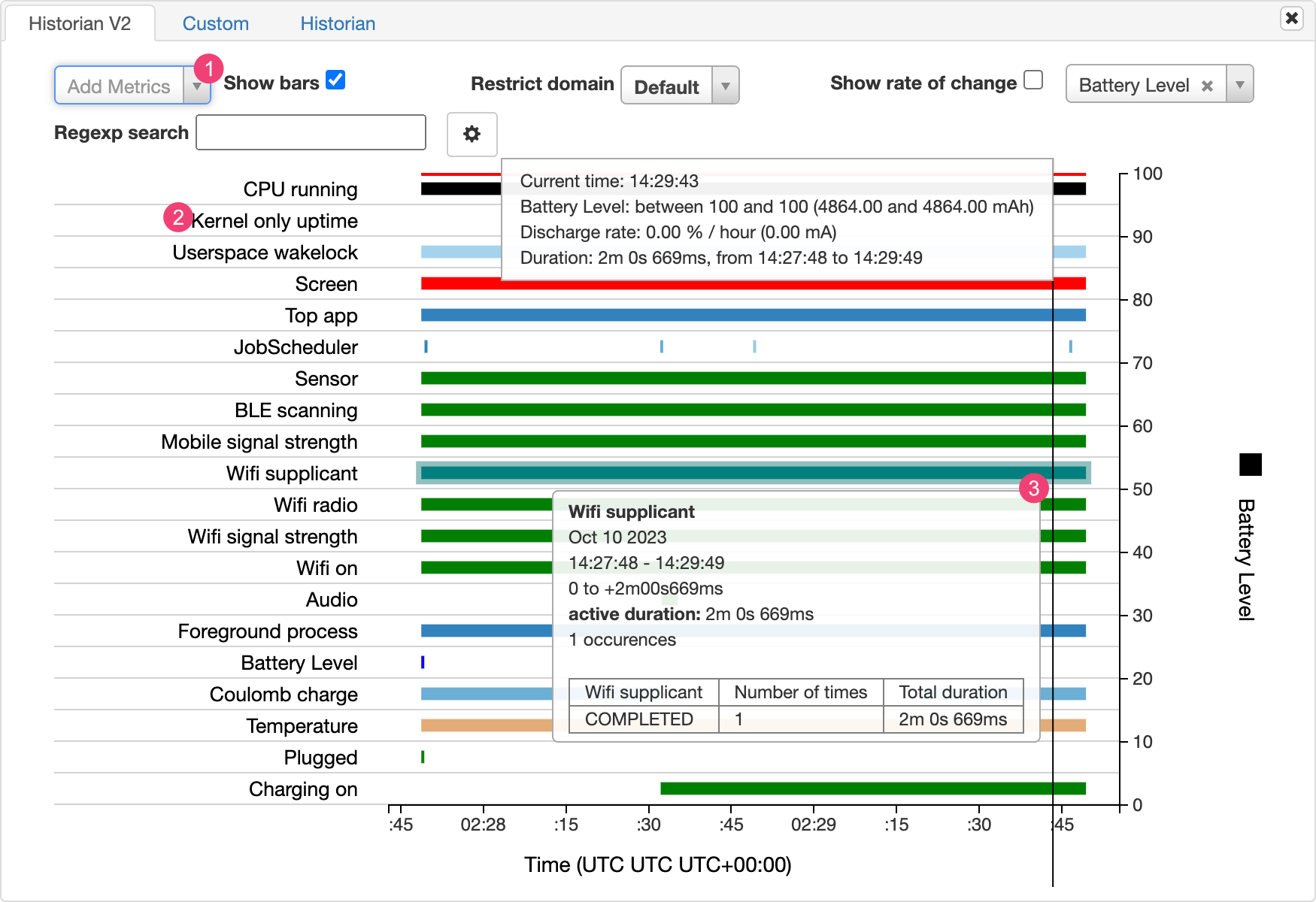
- Ajoutez des métriques supplémentaires à partir de la liste déroulante.
- Maintenez le pointeur sur le nom d'une métrique pour afficher plus d'informations à son sujet, y compris une légende pour les couleurs utilisées dans le graphique.
- Maintenez le pointeur sur une barre pour afficher plus de détails sur cette métrique et sur les statistiques de la batterie à un moment précis de la chronologie.
Résultats Batterystats supplémentaires
Vous pouvez afficher d'autres informations à partir du fichier batterystats.txt dans la section des statistiques après le graphique Battery Historian.
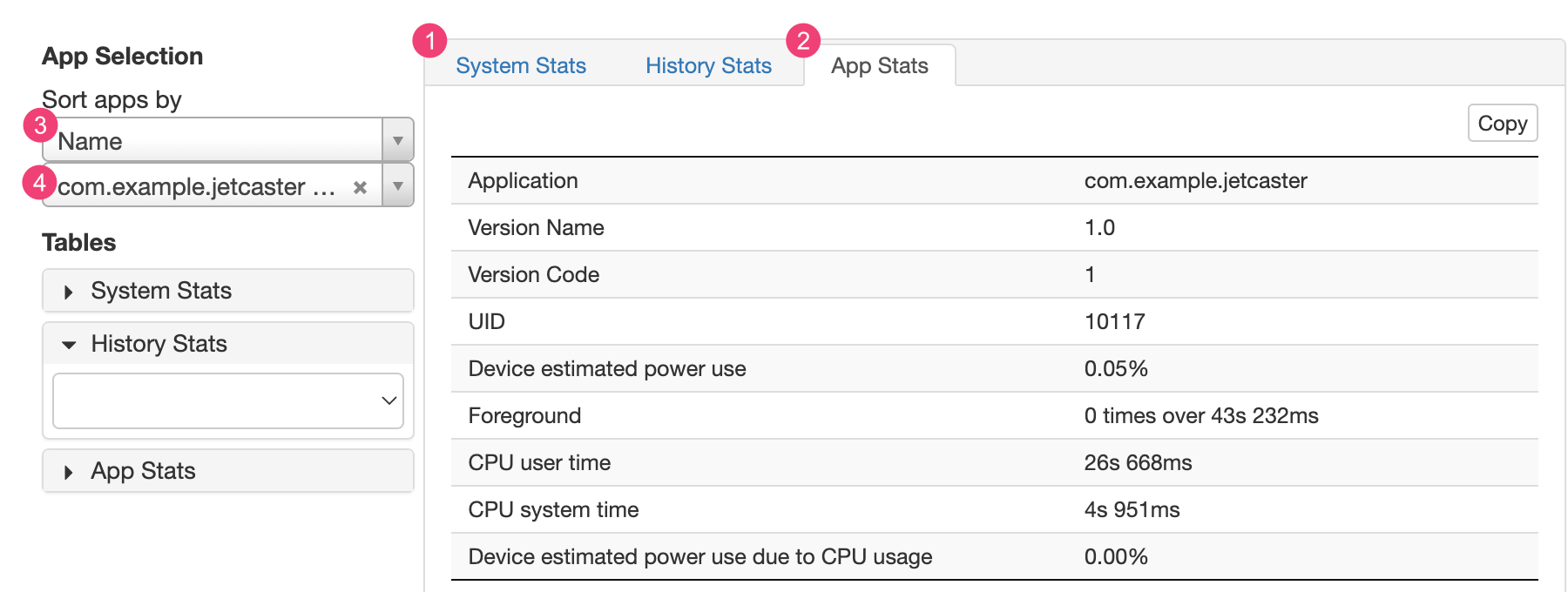
L'onglet 1, System Stats (Statistiques système), inclut des statistiques relatives au système, telles que le niveau de signal cellulaire et la luminosité de l'écran. Ces informations offrent une vue d'ensemble de l'activité de l'appareil. Elles sont particulièrement utiles pour vous assurer qu'aucun événement externe n'affecte votre test.
L'onglet 2, App Stats (Statistiques de l'application), contient des informations sur des applications spécifiques. Triez la liste des applications à l'aide de la liste déroulante 3 Sort apps by (Trier les applications par) du volet App Selection (Sélection des applications). Vous pouvez sélectionner une application spécifique pour afficher les statistiques correspondantes à l'aide de la liste déroulante 4.
