您可以通过 Battery Historian 工具了解设备随时间的耗电情况。在系统级别,该工具以 HTML 的形式可视化来自系统日志的电源相关事件。在具体应用级别,该工具可提供各种数据,帮助您识别耗电的应用行为。
本文档介绍了使用 Battery Historian 了解耗电模式的一些方法。文档首先介绍如何读取 Battery Historian 报告的系统级数据,然后讨论如何使用 Battery Historian 诊断和排查与电池消耗相关的应用行为,最后提供了一些有关特别适合使用 Battery Historian 的场景的提示。
使用系统级视图
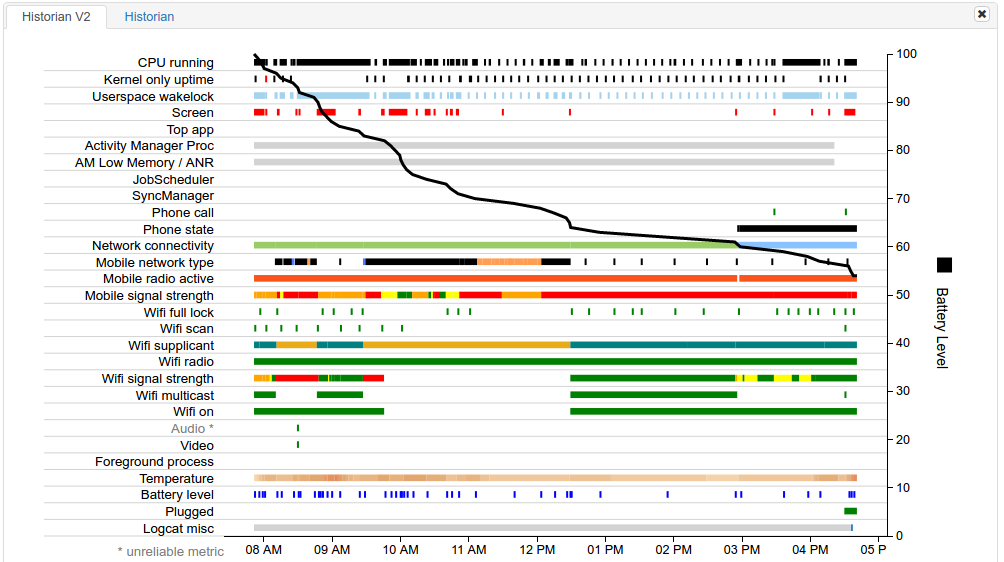
Battery Historian 工具提供各种应用和系统行为的系统级可视化结果,以及它们随时间推移与耗电量的相关性。如图 1 所示,此视图可帮助您诊断和识别应用存在的耗电问题。
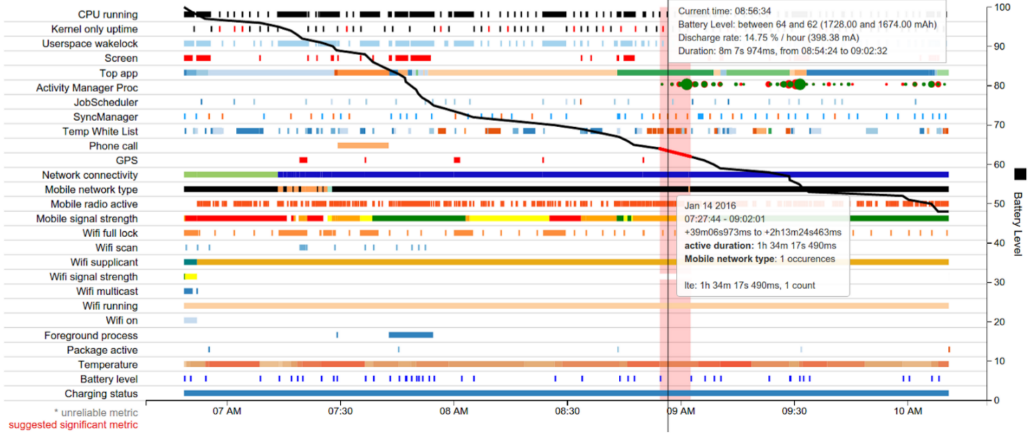
该图中特别值得注意的是表示电池电量的黑色水平下降趋势线(在 y 轴上进行测量)。例如,在电池电量线的最开始处,大约早上 6:50 时,该图表显示电量出现较为急剧的下降。
图 2 为该部分显示画面的特写图。
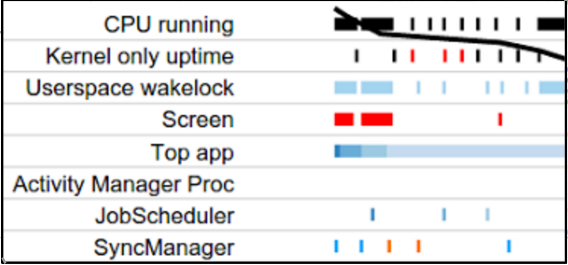
在电池电量线的最开始处,随着电池电量的急剧下降,显示画面上显示有三件事正在发生:CPU 正在运行,应用已获取唤醒锁定,且屏幕已打开。通过这种方式,Battery Historian 可帮助您了解耗电量高时正在发生什么事件。然后,您可以针对应用中的这些行为,研究是否可以进行相关优化。
系统级可视化还可以提供其他线索。例如,如果它显示移动无线装置频繁关闭和开启,则可能有机会通过智能调度 API(如 JobScheduler 或 Firebase Job Dispatcher 等)优化此行为。
下一部分将介绍如何调查特定于您自己的应用的行为和事件。
查看具体应用的数据
除了系统级数据视图提供的宏观数据外,Battery Historian 还提供特定于您设备上运行的每个应用的数据表格和部分可视化内容。表格数据包括:
- 应用在设备上的估计耗电量。
- 网络信息。
- 唤醒锁定次数。
- 服务。
- 进程信息。
表格提供了关于您的应用的两个数据维度。首先,您可以查找应用的耗电量与其他应用相比的排名位置。为此,请点击“Tables”下的“Device Power Estimates”表格。本示例研究了一款名为“Pug Power”的虚构应用。
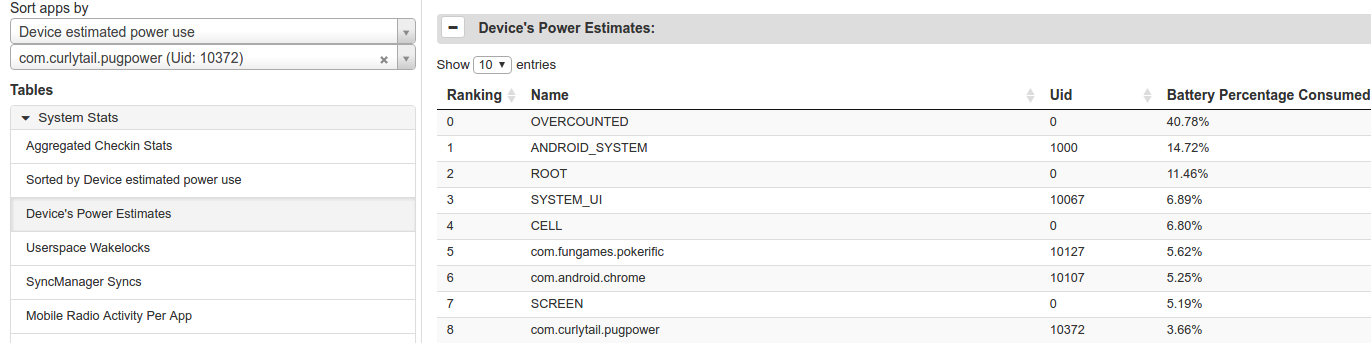
图 3 中的表格显示,Pug Power 在此设备上的耗电量排名第九,在不属于操作系统的应用中排名第三。这些数据表明,需要对此应用进行更深入的研究。
如需查找特定应用的数据,在可视化图表左侧下方,在“App Selection”下方的第二个下拉菜单中输入应用的软件包名称。
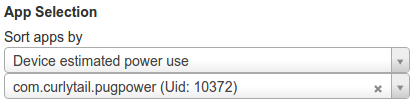
当您选择特定应用时,以下数据可视化类别将更改为显示具体应用数据,而不是系统级数据:
- SyncManager。
- 前台进程。
- 用户空间唤醒锁定。
- 热门应用。
- JobScheduler。
- Activity Manager Proc。
如果您的应用以不必要的频率执行同步和执行作业,SyncManager 和 JobScheduler 可视化图表会立即突出显示这种情况。这样,它们能快速展露出优化应用行为以提升电池性能的机会。
您还可以再获取具体应用的一条可视化数据,即用户空间唤醒锁定。如需将此信息包含在 bug 报告中,请在终端窗口中输入以下命令:
$ adb shell dumpsys batterystats --enable full-wake-history
图 5 和图 6 显示了 Pug Power 的数据:图 5 显示了具体应用数据的可视化图表,图 6 显示了相应的表格数据。
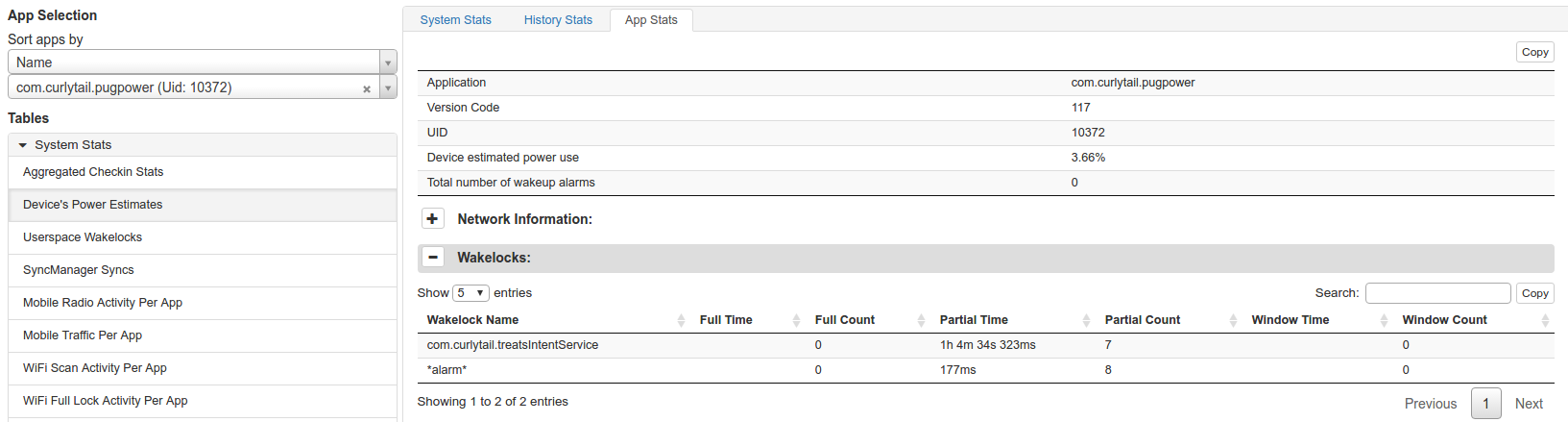
查看可视化图表并没有发现任何显而易见的问题。JobScheduler 行显示应用没有调度作业。SyncManager 行显示应用尚未执行任何同步操作。
不过,查看表格数据的 Wakelocks 部分发现,Pug Power 获取了 1 个小时内的唤醒锁定总时间。这种代价高昂的异常行为可能是应用耗电量较高的原因。这条信息有助于开发者专攻优化后可能会大大获益的方面。在此情况下,为什么应用会获得如此多的唤醒锁定时间,开发者又如何改善这种行为呢?
Battery Historian 的其他功能
在很多其他情况下,Battery Historian 也可帮助您找出改善电池行为的机会。例如,Battery Historian 可以显示应用是否具有以下行为:
- 过于频繁地触发唤醒闹钟(至少每 10 秒钟一次)。
- 持续保留 GPS 锁定。
- 至少每 30 秒调度一次作业。
- 至少每 30 秒调度一次同步。
- 使用手机无线装置的频率高于预期。
