Dokumen ini menunjukkan langkah-langkah penyiapan dasar dan alur kerja untuk alat Batterystats dan skrip Battery Historian. Untuk mempelajari cara menggunakan Battery Historian guna memeriksa pola penggunaan baterai, baca Menganalisis penggunaan daya dengan Battery Historian.
Batterystats adalah alat yang disertakan dalam framework Android yang mengumpulkan data
baterai di perangkat. Anda dapat menggunakan adb untuk menghapus
data baterai yang dikumpulkan ke mesin pengembangan dan membuat laporan yang dapat
dianalisis menggunakan Battery Historian. Battery Historian mengonversi laporan dari
Batterystats menjadi visualisasi dalam bentuk HTML yang dapat Anda lihat di browser.
Batterystats dan Battery Historian berguna untuk hal berikut:
- Menunjukkan cara proses menggunakan daya dari baterai dan juga tempat berlangsungnya proses tersebut.
- Mengidentifikasi tugas di aplikasi Anda yang dapat ditangguhkan atau dihapus untuk meningkatkan daya tahan baterai.
Menginstal Battery Historian
Anda dapat menggunakan Docker untuk menginstal Battery Historian. Untuk metode penginstalan alternatif, termasuk membangun dari sumber, lihat README di halaman GitHub project. Untuk menginstal menggunakan Docker, lakukan hal berikut:
Instal Docker dengan mengikuti petunjuk di situs Docker. Semua jenis langganan dapat digunakan, termasuk langganan Personal yang gratis.
Untuk memastikan Docker telah terinstal dengan benar, buka command line dan masukkan perintah berikut:
docker run hello-worldJika Docker sudah terinstal dengan benar, Docker akan menampilkan output seperti ini:
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 78445dd45222: Pull complete Digest: sha256:c5515758d4c5e1e838e9cd307f6c6a0d620b5e07e6f927b07d05f6d12a1ac8d7 Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminalLuncurkan aplikasi Docker Desktop—yang merupakan frontend GUI untuk Docker—sebelum menjalankan image Battery Historian. Jika image Battery Historian dijalankan, alat Docker akan diinisialisasi. Battery Historian tidak akan berjalan sebelum Anda melakukannya setidaknya satu kali.
Jalankan Battery Historian dari command line saat menjalankannya untuk pertama kali. Aplikasi Docker Desktop tidak mengizinkan Anda menentukan port yang akan digunakan untuk menjalankan server web. Anda dapat melakukannya dari command line. Namun, setelah Anda berhasil menjalankan container dari command line, entri akan dibuat di Docker Desktop. Kemudian, Anda dapat meluncurkannya menggunakan port pemroses yang sama dari Desktop Docker.
Jalankan image Battery Historian menggunakan perintah berikut:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Battery Historian menggunakan port pilihan Anda, seperti yang ditentukan dengan menggunakan
port_number.Buka Battery Historian di browser Anda untuk memastikannya sedang berjalan atau tidak. Alamat dapat bervariasi tergantung sistem operasi Anda:
- Untuk Linux dan Mac
- Battery Historian tersedia di
http://localhost:port_number. - Untuk Windows
- Docker akan memberi tahu alamat IP dari mesin yang digunakannya setelah Docker
dimulai. Misalnya, jika alamat IP adalah 123.456.78.90, Battery
Historian akan tersedia di
http://123.456.78.90:port_number.
Kemudian, halaman awal Battery Historian akan ditampilkan, tempat Anda dapat mengupload dan melihat statistik baterai.
Gambar 1. Halaman awal Battery Historian.
Mengumpulkan data dengan Batterystats
Untuk mengumpulkan data dari perangkat menggunakan Batterystats dan membukanya di Battery Historian, lakukan hal berikut:
Hubungkan perangkat seluler ke komputer.
Dari jendela Terminal, matikan server
adbyang sedang berjalan dengan menjalankan perintah berikut:adb kill-serverMulai ulang
adbdan periksa semua perangkat terhubung dengan menjalankan perintah berikut.adb devicesPerintah ini mencantumkan perangkat Anda, mirip dengan contoh output berikut.

Gambar 2. Output adb devices, menunjukkan satu perangkat terhubungJika halaman tersebut tidak mencantumkan perangkat apa pun, pastikan ponsel terhubung dan proses debug USB diaktifkan, lalu hentikan dan mulai ulang
adb.Reset pengumpulan data baterai dengan menjalankan perintah berikut:
adb shell dumpsys batterystats --resetPerangkat selalu mengumpulkan Batterystats dan informasi proses debug lainnya di latar belakang. Reset akan menghapus data pengumpulan baterai sebelumnya. Jika Anda tidak melakukan reset, outputnya dapat menjadi sangat besar.
Putuskan koneksi perangkat dari komputer sehingga Anda hanya menggunakan daya dari baterai perangkat.
Gunakan aplikasi Anda dan lakukan tindakan yang datanya ingin Anda kumpulkan. Misalnya, putuskan koneksi dari Wi-Fi dan kirim data ke cloud.
Hubungkan kembali ponsel Anda.
Pastikan ponsel Anda dikenali dan jalankan perintah berikut:
adb devicesHapus semua data baterai dengan menjalankan perintah berikut. Proses ini mungkin memerlukan waktu beberapa saat:
adb shell dumpsys batterystats > [path/]batterystats.txt
File
batterystats.txtdibuat di direktori yang Anda tentukan menggunakan argumen jalur opsional. Jika Anda tidak menentukan jalur, file akan dibuat di direktori utama.Buat laporan dari data mentah.
- Untuk perangkat yang menjalankan Android 7.0 dan yang lebih baru:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.zip
- Untuk perangkat yang menjalankan Android 6.0 dan yang lebih lama:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.txt
Laporan bug dapat memerlukan waktu beberapa menit untuk menyelesaikan prosesnya. Jangan memutuskan koneksi perangkat atau membatalkan prosesnya, tunggu sampai selesai.
Seperti halnya
batterystats.txt, file-file ini dibuat di direktori yang Anda tentukan dengan menggunakan argumenpathopsional. Jika Anda tidak menentukan jalur, file akan dibuat di direktori utama.Jika belum berjalan, jalankan Battery Historian menggunakan perintah berikut:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Untuk melihat data Anda di Battery Historian, buka Battery Historian di browser. Untuk Mac dan Linux, Battery Historian berjalan di
http://localhost:port_number. Untuk Windows, Battery Historian berjalan dihttp://your_IP_address:port_number.Klik Browse, lalu pilih file laporan bug yang Anda buat.
Klik Submit. Battery Historian membuka diagram yang dibuat dari data Batterystats Anda.
Melihat data dengan diagram Battery Historian
Diagram Battery Historian menampilkan peristiwa yang terkait dengan daya dari waktu ke waktu.
Setiap baris menampilkan segmen batang berwarna ketika komponen sistem aktif dan menggunakan daya dari baterai. Diagram tidak menunjukkan banyaknya daya baterai yang digunakan oleh komponen tersebut—hanya menunjukan apakah aplikasi aktif atau tidak. Diagram disusun berdasarkan kategori, dengan menampilkan batang untuk setiap kategori dari waktu ke waktu, seperti yang ditampilkan di sumbu X diagram.
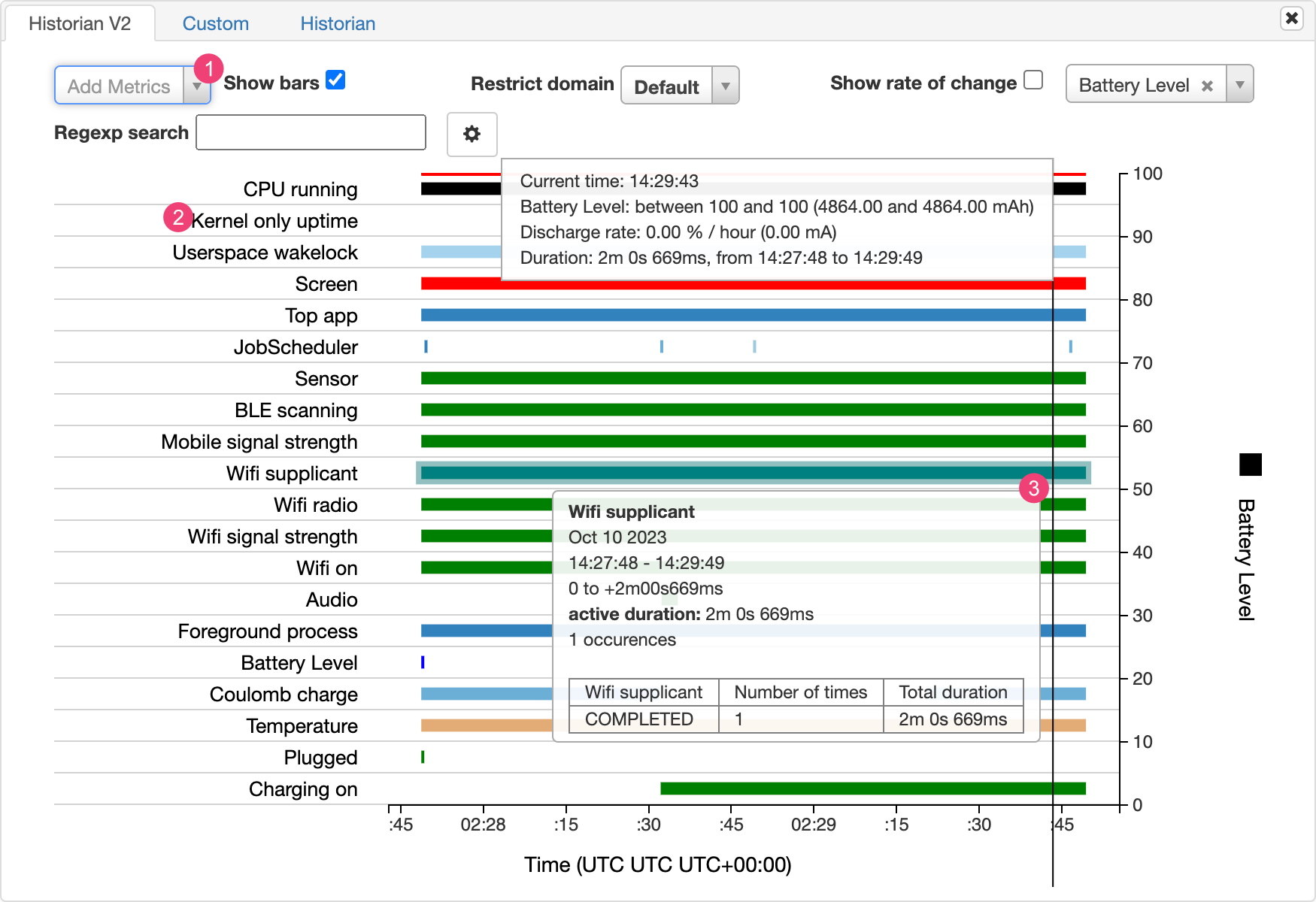
- Tambahkan metrik tambahan dari menu drop-down.
- Tahan kursor ke nama metrik untuk melihat informasi selengkapnya tentang setiap metrik, termasuk kunci untuk warna yang digunakan pada diagram.
- Tahan kursor saat fokus pada batang untuk melihat informasi yang lebih mendetail tentang metrik tersebut dan statistik baterainya di titik tertentu di linimasa.
Output Batterystats tambahan
Anda dapat melihat informasi tambahan dari file batterystats.txt di
bagian statistik di bawah diagram Battery Historian.
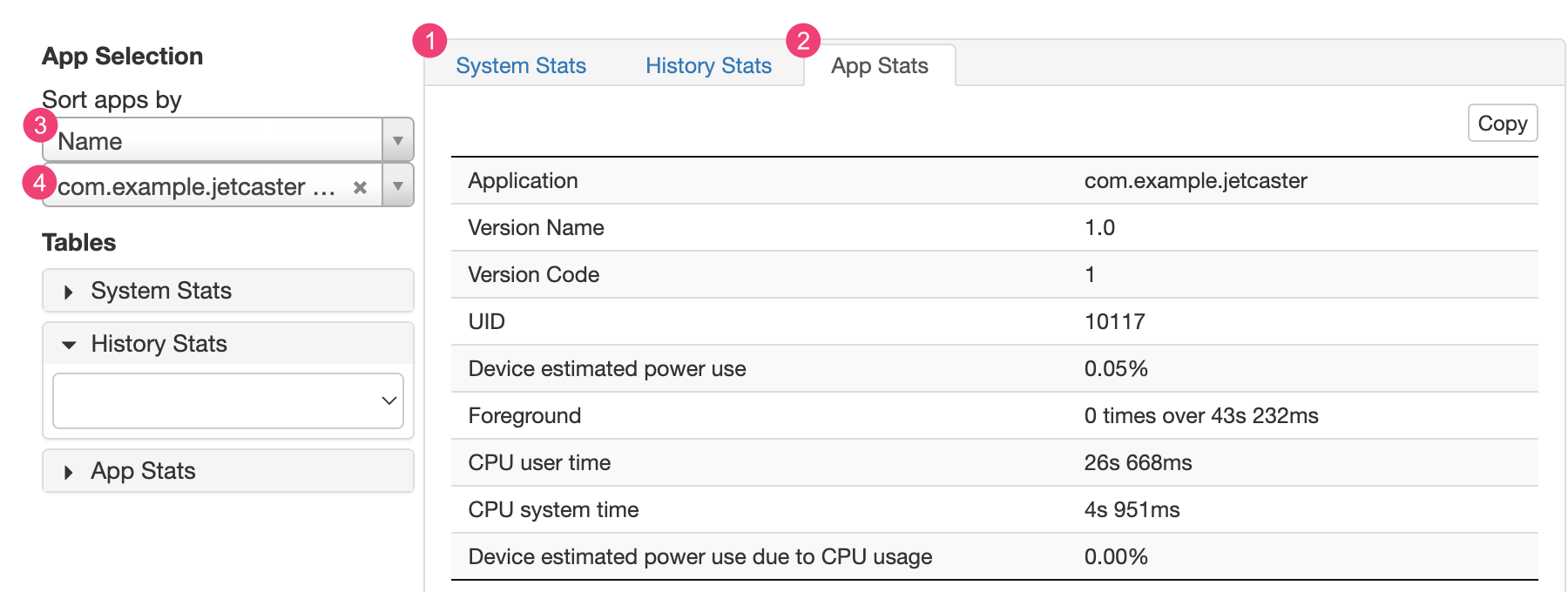
Tab 1 System Stats mencakup statistik seluruh sistem, seperti tingkat sinyal seluler dan kecerahan layar. Informasi ini memberikan gambaran keseluruhan tentang apa yang terjadi pada perangkat. Informasi tersebut sangat berguna untuk memastikan tidak ada peristiwa eksternal yang memengaruhi pengujian Anda.
Tab 2 App Stats mencakup informasi tentang aplikasi tertentu. Urutkan daftar aplikasi menggunakan menu drop-down 3 Sort apps by di panel App Selection. Anda dapat memilih aplikasi tertentu untuk melihat statistiknya menggunakan menu drop-down 4 aplikasi.

