내장 인텐트 (BII)를 사용하면 앱에서 처리 기능을 표현할 수 있습니다. Google에 문의하기 shortcuts.xml 파일에서 기능을 선언하고 매핑함으로써 인텐트 매개변수를 fulfillment에 매핑하면 Google 어시스턴트가 응답하여 특정 화면에 앱을 실행하도록 사용자가 작업을 완료할 수 있습니다.
내장 인텐트는 앱 카테고리에 따라 그룹화됩니다. 각 카테고리는 사용자가 앱에서 자주 실행하려는 일련의 일반적인 작업을 나타냅니다. 사용 가능한 BII, 매개변수, 예시의 전체 목록 테스트에 사용할 수 있는 쿼리는 내장 인텐트 참조에 있습니다.
많은 BII에는 특정 배포 요구사항이 있으며 추천을 제공합니다 이러한 요구사항과 권장사항은 앱이 다음과 같은 이점을 제공하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 최상의 경험을 할 수 있도록 돕는 것입니다.
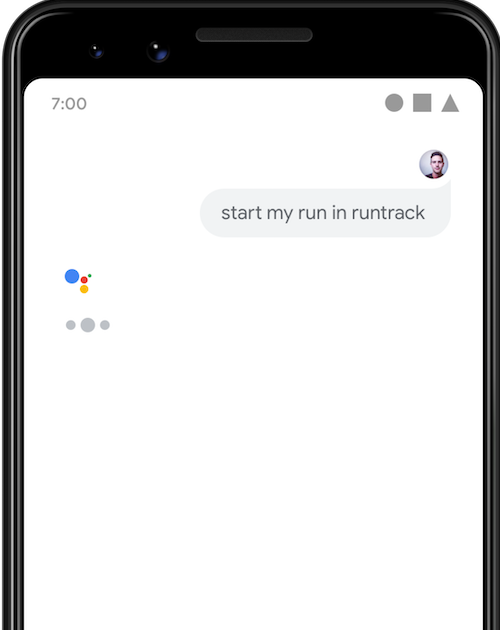
START_EXERCISE BII 호출
어시스턴트에 쿼리를 요청해 보세요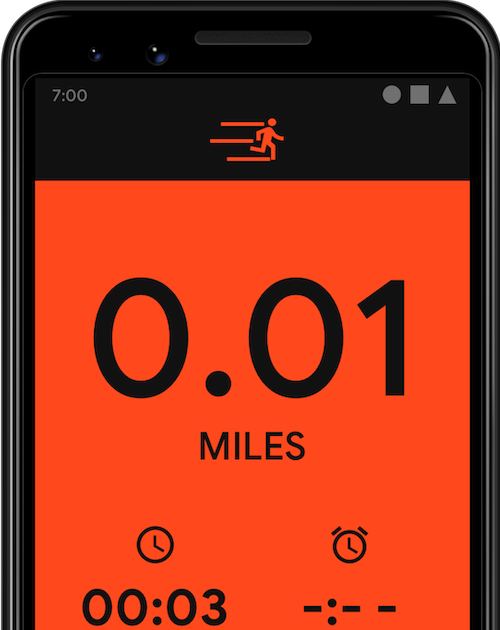
START_EXERCISE 작업을 시작합니다.
BII 구현 및 인텐트 매개변수 처리
앱 작업의 경우 기능을 선언하고 BII 매개변수를 처리합니다. shortcuts.xml 파일에 추가합니다. BII를 구현하고 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 선택한 BII를 사용하여
capability를 선언합니다. - 추가하려는 각 BII 필드에 중첩된
parameter요소를 추가합니다.targetClass또는targetPackage를 사용하는 경우 Android에 매핑합니다.extras인텐트를 가져옵니다.- 딥 링크 URL을 사용하는 경우 쿼리에 이름이 지정된 매개변수를 사용합니다. URL 템플릿의 문자열입니다.
BII 매개변수를 처리하려면 BII 매개변수를
capability에 있는 명시적 Android 인텐트의 상응하는 매개변수입니다.
그런 다음 앱에서 그 가치를 사용할 수 있습니다. 앱에서
BII 매개변수 하지만 '권장됨'으로 표시된 데이터 필드를 처리하세요.
내장 인텐트 참조에서 확인하세요.
각각 고유한 세트의 집합을 갖는 여러 인텐트 처리를 정의할 수 있습니다. 권장 매개변수입니다. Google은 다음에 따라 적절한 처리를 선택합니다. 기능 매개변수를 사용하여 사용자의 쿼리와 선언된 인텐트에 포함됩니다.
예를 들면 다음과 같습니다. actions.intent.START_EXERCISE
인텐트는 앱에서 exercise.name BII 매개변수를 처리하도록 권장하지만
매개변수 없이 앱에서 BII를 구현할 수 있습니다.
이 작업을 수행하면 구체적인
운동 이름(예: "Example App에 운동 추적을 시작하도록 요청")
이 다음 스니펫에는 필수 매개변수가 없는 처리로의 대체가 있습니다. 매개변수가 사용자의 쿼리에 포함되지 않은 경우:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shortcuts xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<capability android:name="actions.intent.START_EXERCISE">
<intent
android:action="android.intent.action.VIEW"
android:targetClass="com.example.myapplication.Activity1"
android:targetPackage="com.example.myapplication">
<parameter
android:name="exercise.name"
android:key="exerciseType"
android:required="true"
/>
</intent>
<intent
android:action="android.intent.action.VIEW"
android:targetClass="com.example.myapplication.Activity2">
</intent>
</capability>
</shortcuts>
Google 어시스턴트는 사용자에게 가장 관련성 높은 정보를 제공하기 위해 앱에 매개변수 값을 반환할 때 사용자에게 적용됩니다. 예를 들어 예시 레스토랑의 모바일 앱에서 피자를 주문할 때 볼 수 있습니다 사용자에게 더 나은 서비스를 제공하기 위해 어시스턴트가 위도를 제공할 수 있습니다. 앱에 가장 가까운 Example Restaurant의 경도 값을 반환합니다.
추가 요구사항으로, 앱에서 직접 실행되는 사용자의 실제 상태를 수정하는 작업 (예: 송금, 주문, 메시지 전송)이 있으면 먼저 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
명확성
<url-parameter> 또는 인텐트 추가 항목을 통해 앱에 전달된 인수는
고유하게 식별할 수 있습니다. 이 경우
인수 값을 검색 인수로 사용하고 사용자를 검색으로 이동
확인할 수 있습니다. 적절한 항목을 명확하게 구분하고 선택할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 사용자의 검색어가 '예시 식당에서 주문'이라고 하면
BII ORDER_MENU_ITEM을 사용하는 경우 사용자에게
이름이 "Example Restaurant"과 일치하는 음식점
언어 및 언어 지원
각 앱 작업 BII에서 개발 및 테스트에 지원되는 언어 내장 인텐트 참조에 나열되어 있습니다. 일부 BII에는 개발자 테스트 및 어시스턴트에서 사용자 트리거를 위한 언어 지원
