GNSS 간섭은 다음 두 가지 카테고리로 분류할 수 있습니다.
- 잼
- 스푸핑
재밍 공격은 GNSS와 동일한 주파수 범위에서 강력한 무선 신호를 브로드캐스트하여 GNSS 위성에서 브로드캐스트되는 상대적으로 약한 신호를 압도하는 방식으로 이루어집니다. 이로 인해 휴대전화를 비롯한 GNSS 수신기가 위치를 계산하지 못할 수 있습니다.
스푸핑은 실제 GNSS 신호인 척하는 가짜 신호가 브로드캐스트되는 보다 정교한 공격입니다. 이러한 가짜 신호는 GNSS 수신기가 실제와 매우 다른 위치나 시간을 계산하도록 속일 수 있으며, 이는 매핑 및 탐색 앱이 사용자에게 잘못된 정보를 제공하도록 혼동하기에 충분합니다.
GNSS 스푸핑 또는 재밍 정보
신호의 신호 강도 또는 반송파 대 잡음비 (C/N0)와 휴대전화의 GNSS 무선의 자동 게인 제어 (AGC)는 간섭을 나타내는 좋은 지표가 될 수 있습니다.
스푸핑이나 재밍이 관찰되면 AGC가 감소하는 경향이 있습니다. 무선 통신 장치가 강한 전파를 수신하면 수신된 신호의 전력을 조정하기 위해 증폭기의 게인 (AGC)을 낮춥니다.
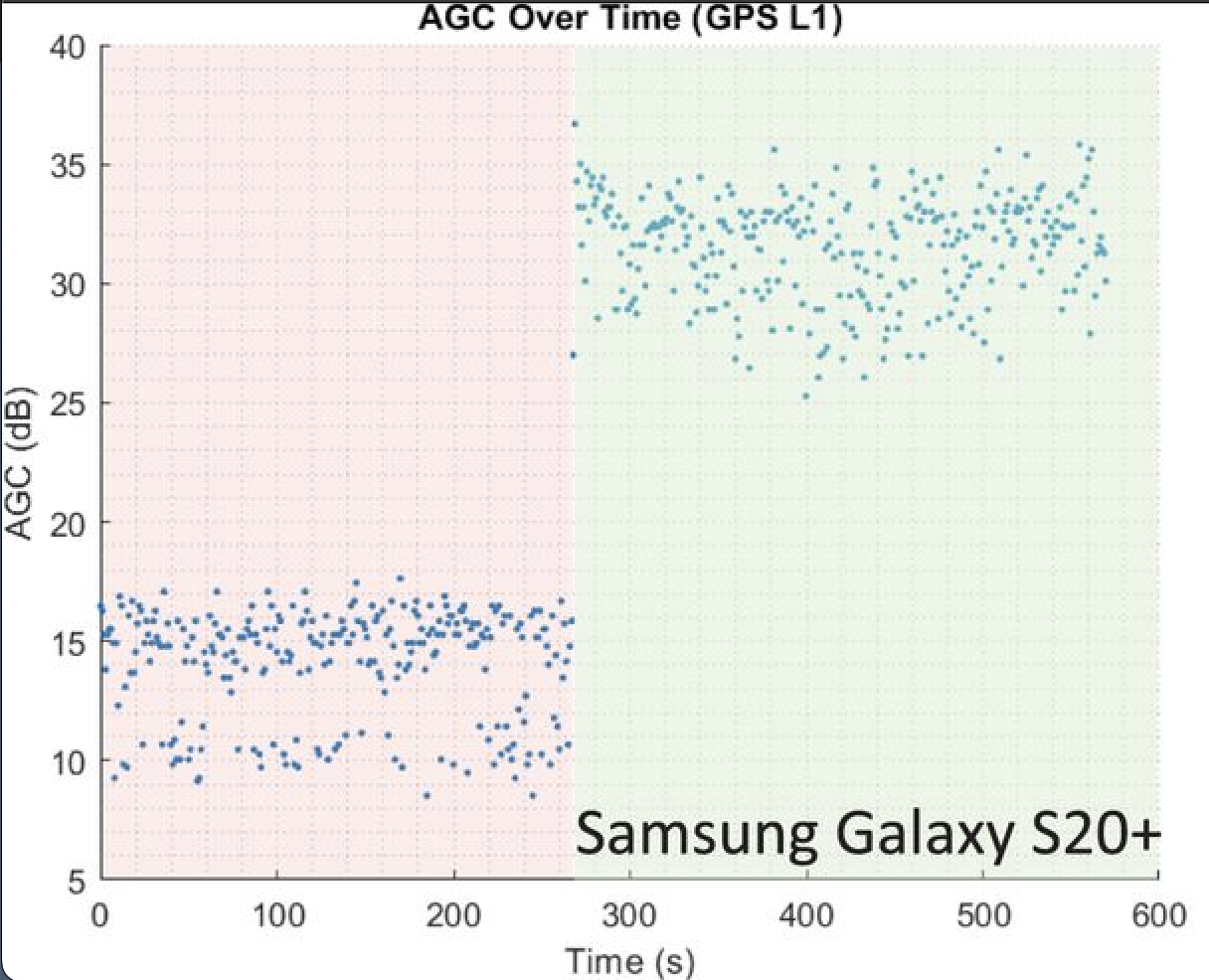
하지만 C/N0의 동작은 재밍과 스푸핑 이벤트 간에 달라집니다. 재밍 이벤트의 경우 라디오에서 관찰되는 노이즈가 평소보다 훨씬 강합니다. 따라서 캐리어 대 노이즈 비율의 분모가 증가하고 C/N0 값이 떨어집니다. 스푸핑의 경우 위성에서 나오는 실제 신호를 압도할 만큼 큰 가짜 신호가 브로드캐스트되므로 전체 신호 강도가 강해져 C/N0가 증가합니다.
GNSS 스푸핑 또는 재밍 확인
GnssLogger 앱의 스푸핑/재밍 탭을 사용하여 환경이 C/N0 및 AGC에 미치는 영향을 실시간으로 탐색할 수 있습니다.
실시간 AGC 및 C/N0 플롯
스푸핑/재밍 탭에는 각 GNSS 별자리 및 대역 (예: 'GPS L1' 또는 'G:L1:", 'Galileo E5a' 또는 'E:E5A:").
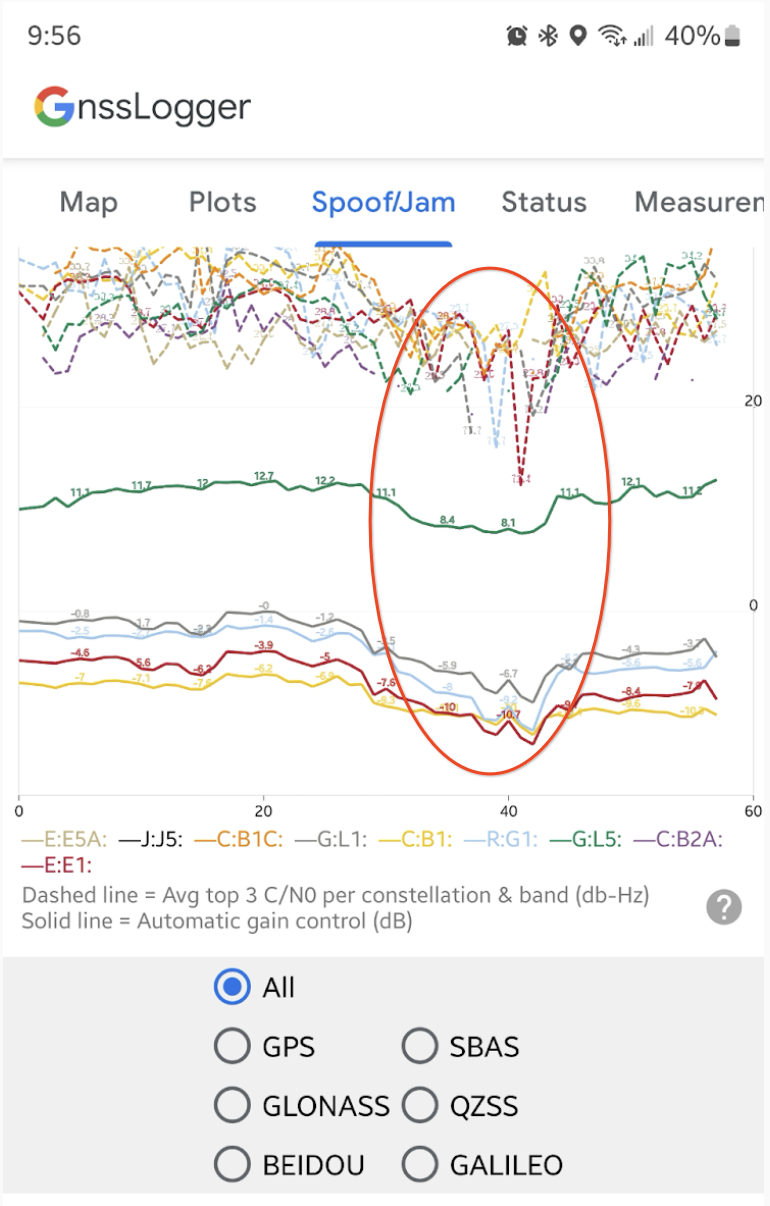
스푸핑 및 재밍에 대한 실시간 검사
AGC 및 C/N0의 실시간 플롯 아래에 앱은 GNSS 간섭과 관련된 조건을 식별하는 일련의 자동 데이터 검사를 표시합니다.
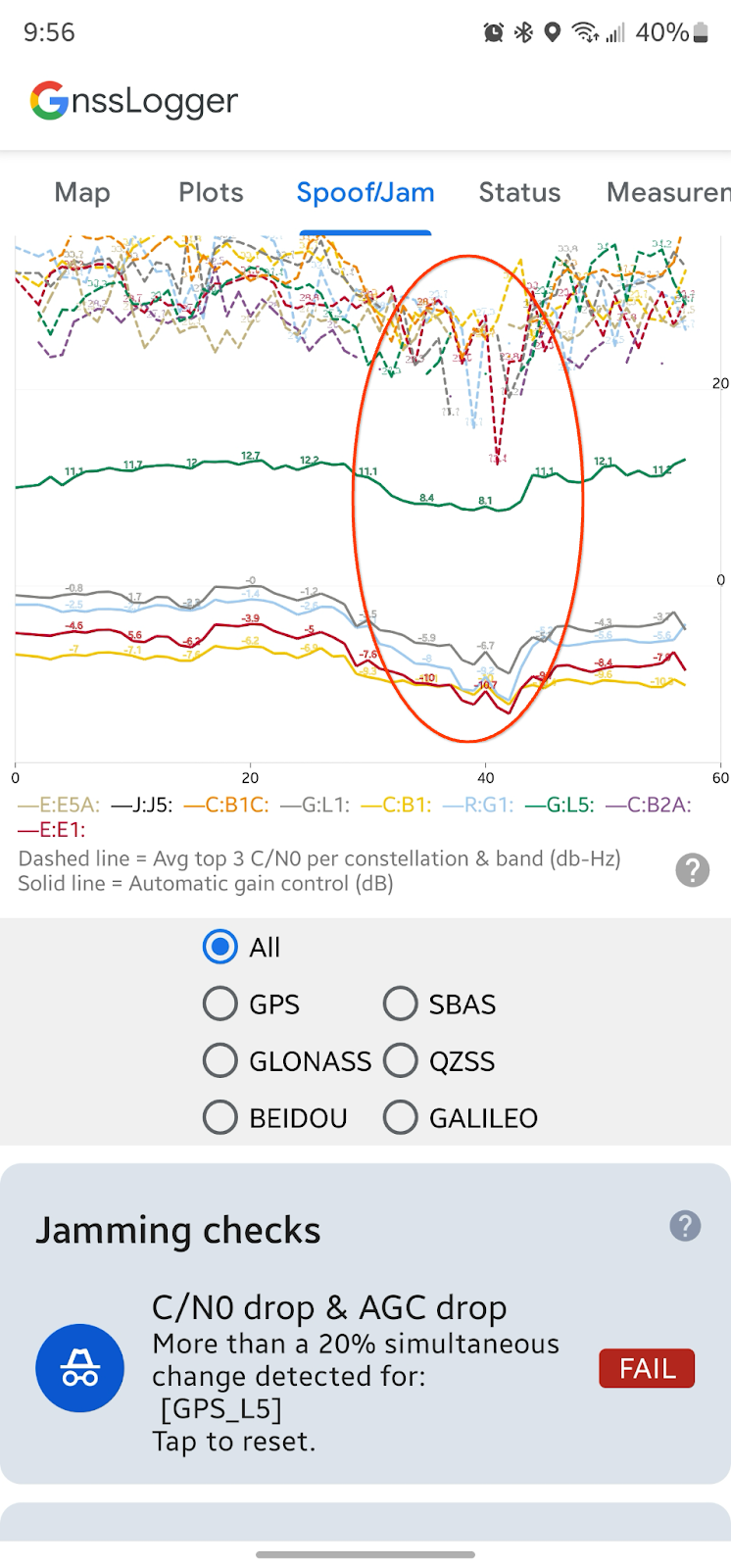
재밍 확인 섹션에서 앱은 최근 10개 에포크의 C/N0 및 AGC 평균이 이전 50개 에포크와 비교하여 변경되었는지 확인합니다. C/N0와 AGC가 동시에 감소하면 GNSS 재밍의 증상일 수 있습니다. 이 상황이 감지되면 카드에 실패 메시지와 함께 자세한 정보가 표시됩니다.
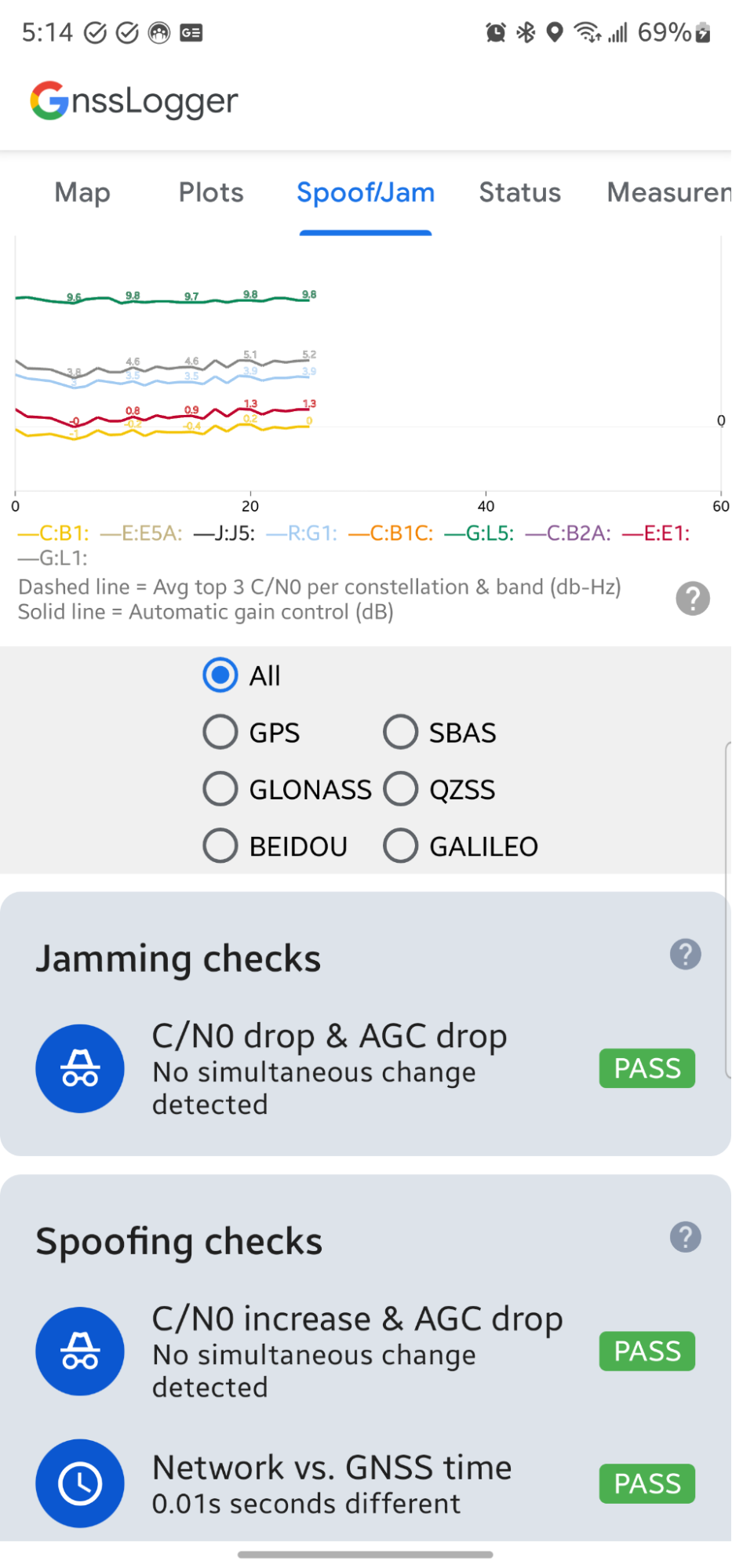
스푸핑 확인 섹션의 첫 번째 카드에서도 C/N0 및 AGC를 확인하지만 C/N0의 증가와 AGC의 감소가 동시에 발생하는지 확인합니다.
두 번째 스푸핑 관련 검사는 기기에서 계산된 GNSS 시간과 인터넷을 통해 네트워크 시간 프로토콜 (NTP) 서버에서 가져온 시간 (네트워크 시간 - GNSS 시간) 간의 1초 이상 차이를 찾습니다. 큰 차이는 계산된 GNSS 시간이 유효하지 않음을 나타낼 수 있습니다.
도움말, 유용한 정보, 주의사항
GnssLogger의 스푸핑/재밍 기능을 사용할 때 유의해야 할 사항은 다음과 같습니다.
- 이는 실험용 기능입니다. 다양한 Android 기기에서 AGC 특성을 자세히 알아볼수록 스푸핑 및 재밍 변경에 사용되는 정확한 알고리즘이 업데이트될 수 있습니다.
- 이 기능은 모든 스푸핑 및 재밍을 포착하지 않습니다. 실시간 그래프와 데이터 확인을 통해 실시간으로 데이터 속성을 더 쉽게 파악할 수 있지만 모든 스푸핑 또는 재밍 사례를 감지할 만큼 강력하지는 않습니다.
- 이 기능은 C/N0 및 AGC의 변화를 감지하도록 설계되었습니다. 스푸핑이나 재밍이 있는 상태에서 앱을 열고 C/N0 및 AGC가 일정하게 유지되면 스푸핑과 재밍이 감지되지 않습니다.
- NTP 서버가 반드시 안전한 것은 아닙니다. 네트워크 시간도 스푸핑될 수 있습니다.
공개 문제 추적기를 사용하여 스푸핑/재밍 기능에 대한 의견을 제공합니다.
