在您了解如何处理不同的手表形状之后,需要确定您要使用的 surface。
常见的应用布局包括:
- 单屏(最简单):界面元素可全部显示在一个屏幕中,无需滚动。
- 垂直容器(最常见):内容溢出到屏幕的可见部分之外(在滚动后可以看到)。
- 其他方案:列表、分页或 2D 平移。
以下部分将介绍这些布局类型。如果您需要多个屏幕,可以结合使用不同的布局类型。
注意:对于 activity,请从 ComponentActivity 继承;如果您使用的是 fragment,则从 FragmentActivity 继承。其他 activity 类型使用了移动设备专用的界面元素,Wear OS 不需要这些元素。
单屏
用户无需滚动,即可在单个屏幕中看到所有元素。这也意味着您只能添加少量元素。

图 1. 单屏布局示例。
单屏适合与 BoxInsetLayout 和 ConstraintLayout 组合使用,用以排列您的元素。
垂直容器
垂直容器是最常见的应用类型。某些内容未显示在屏幕上,但可以通过滚动访问。
图 2 展示了一些完整的应用布局,在这些示例中,手表的圆形屏幕上仅会显示部分内容。在这些示例中,主要内容位于容器的顶部,其他关键用户历程 (CUJ) 和设置位于底部。这是适用于内容布局的最佳实践。
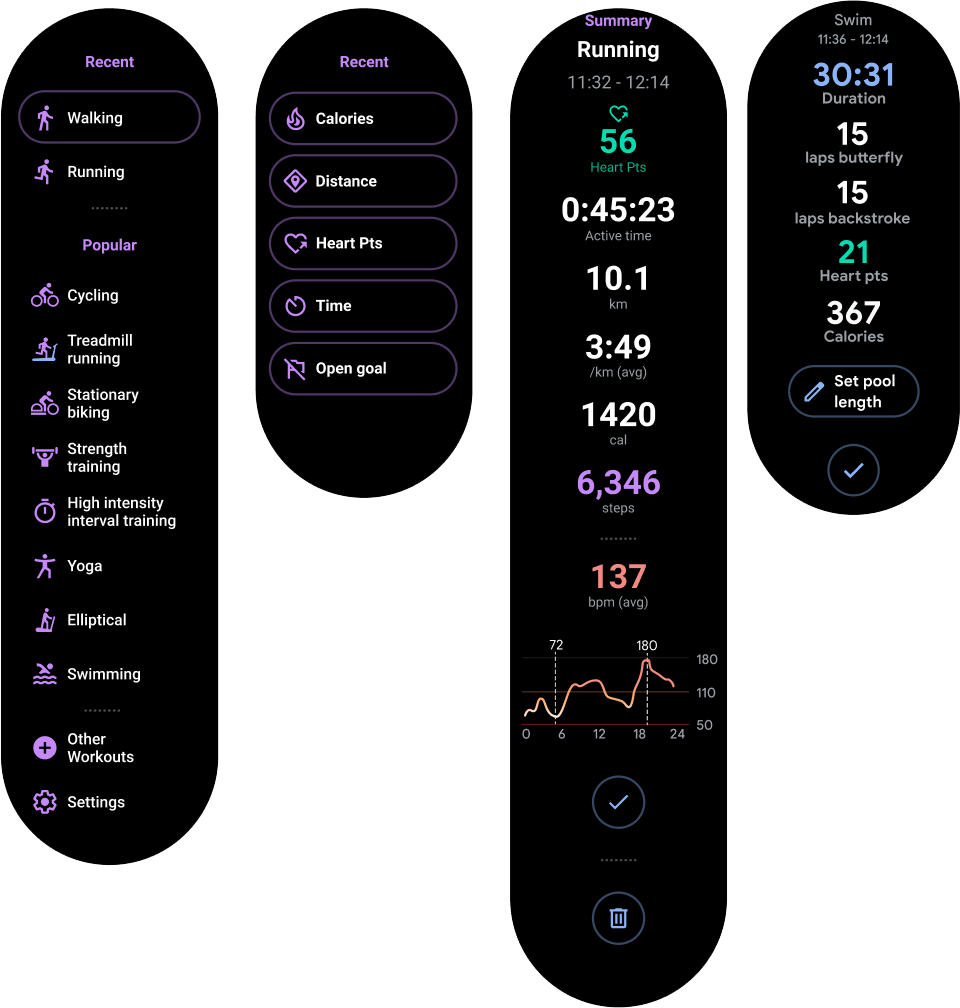
图 2. 垂直容器布局示例。
与单屏应用布局不同,请勿使用 BoxInsetLayout。请改为在 NestedScrollView 中使用 ConstraintLayout。在 ConstraintLayout 中放置最适合您的应用的 widget。如此一来,您就可以利用圆形显示屏侧边的额外空间。
图 3. NestedScrollView 内的 ConstraintLayout 中的内容。
和图 3 中的示例一样,请确保垂直容器顶部和底部的内容足够小,与圆形显示屏的顶部和底部相适应。
注意:请尽可能在 XML 中设置 android:scrollbars="vertical",从而为 NestedScrollView 添加滚动指示器。这不仅有助于用户确认是否有更多内容,还可以让他们了解目前在所有内容中所处的位置。
应用布局的其他方案
-
列表:使用专为穿戴式设备 surface 优化的
WearableRecyclerViewwidget 显示大量数据。如需了解详情,请参阅在 Wear OS 上创建列表。 - 水平分页:对于具有多个同级屏幕的用例,请使用水平滑动。如果您使用水平分页,则必须支持通过在左侧边缘滑动来关闭当前界面。
- 2D 平移:对于地图等用例,用户可以向不同方向拖动平移。如果您的 activity 占据了整个屏幕,请启用滑动即可关闭功能。


