Tài liệu này trình bày các bước và quy trình thiết lập cơ bản cho công cụ Batterystats và tập lệnh Battery Historian. Để tìm hiểu cách sử dụng Battery Historian cho việc kiểm tra quy trình tiêu thụ pin, vui lòng đọc bài viết Phân tích mức sử dụng năng lượng bằng Battery Historian.
Batterystats là một công cụ có trong khung Android thu thập dữ liệu pin trên thiết bị của bạn. Bạn có thể sử dụng adb để kết xuất dữ liệu pin đã thu thập vào máy phát triển và tạo một báo cáo mà bạn có thể phân tích bằng cách sử dụng Battery Historian. Battery Historian chuyển đổi báo cáo từ Batterystats thành hình ảnh HTML mà bạn có thể xem trong trình duyệt của mình.
Batterystats và Battery Historian hữu ích cho những trường hợp sau:
- Cho bạn biết vị trí và cách các quy trình đang lấy nguồn điện từ pin.
- Xác định những việc cần làm trong ứng dụng của bạn có thể bị trì hoãn hoặc xoá để cải thiện thời lượng pin.
Cài đặt Battery Historian
Bạn có thể sử dụng Docker để cài đặt Battery Historian. Để biết các phương thức cài đặt thay thế, bao gồm cả tạo từ nguồn, hãy xem tệp README trên trang GitHub của dự án. Để cài đặt bằng Docker, hãy làm như sau:
Cài đặt Docker bằng cách làm theo các hướng dẫn trên trang web Docker. Mọi loại gói thuê bao đều hoạt động, bao gồm cả gói thuê bao Cá nhân miễn phí.
Để xác nhận là Docker được cài đặt chính xác, hãy mở dòng lệnh và nhập lệnh sau:
docker run hello-worldNếu Docker được cài đặt chính xác, bạn sẽ thấy kết quả như sau:
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 78445dd45222: Pull complete Digest: sha256:c5515758d4c5e1e838e9cd307f6c6a0d620b5e07e6f927b07d05f6d12a1ac8d7 Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminalChạy ứng dụng Docker Desktop (là một giao diện người dùng đồ hoạ của Docker) trước khi bạn chạy hình ảnh Battery Historian. Thao tác chạy lệnh này sẽ khởi động các công cụ của Docker. Battery Historian không chạy cho đến khi bạn làm việc này ít nhất một lần.
Chạy công cụ Battery Historian từ dòng lệnh trong lần chạy đầu tiên. Ứng dụng Docker Desktop không cho phép bạn chỉ định cổng để chạy máy chủ web. Bạn chỉ có thể thực hiện việc này từ dòng lệnh. Tuy nhiên, sau khi bạn chạy thành công vùng chứa từ dòng lệnh, một mục nhập sẽ được tạo trong Docker Desktop. Bạn có thể chạy mục nhập đó bằng cùng một cổng trình nghe trên Docker Desktop.
Chạy hình ảnh Battery Historian bằng cách dùng lệnh sau:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Battery Historian sử dụng cổng mà bạn chọn, như đã chỉ định bằng
port_number.Hãy chuyển đến trang Battery Historian trong trình duyệt để xác nhận trang này đang chạy. Địa chỉ khác nhau tuỳ thuộc vào hệ điều hành của bạn:
- Dành cho Linux và Mac
- Battery Historian có tại
http://localhost:port_number. - Dành cho Windows
- Sau khi khởi động Docker, bạn sẽ biết được địa chỉ IP của máy mà Docker đang sử dụng. Ví dụ: nếu địa chỉ IP là 123.456.78.90, thì Battery Historian có tại
http://123.456.78.90:port_number.
Khi đó, trang này sẽ hiển thị trang chủ của Battery Historian, nơi bạn có thể tải lên và xem số liệu thống kê về pin.
Hình 1. Trang chủ của Battery Historian.
Thu thập dữ liệu bằng Batterystats
Để thu thập dữ liệu từ thiết bị bằng Batterystats và mở thiết bị trong Battery Historian, hãy làm như sau:
Kết nối thiết bị di động với máy tính của bạn.
Từ cửa sổ dòng lệnh, hãy tắt máy chủ
adbđang chạy bằng cách chạy lệnh sau:adb kill-serverKhởi động lại
adbrồi kiểm tra các thiết bị đã kết nối bằng cách chạy lệnh sau.adb devicesLệnh này liệt kê thiết bị của bạn, tương tự như kết quả trong ví dụ sau.

Hình 2. Kết quả về adb devices, cho thấy một thiết bị đã kết nốiNếu lệnh này không liệt kê thiết bị nào, hãy đảm bảo điện thoại của bạn đã được kết nối và bật tính năng Gỡ lỗi qua USB, sau đó dừng và khởi động lại
adb.Đặt lại chế độ thu thập dữ liệu về pin bằng cách chạy lệnh sau:
adb shell dumpsys batterystats --resetThiết bị luôn thu thập Batterystats (số liệu thống kê về pin) và các thông tin gỡ lỗi khác ở chế độ nền. Thao tác đặt lại sẽ xoá dữ liệu về pin thu thập được trước đó. Nếu bạn không đặt lại, kết quả có thể rất lớn.
Ngắt kết nối thiết bị khỏi máy tính để bạn chỉ vẽ dòng điện từ pin của thiết bị.
Dùng ứng dụng của bạn và thực hiện các thao tác mà bạn muốn thu thập dữ liệu. Ví dụ: ngắt kết nối Wi-Fi và gửi dữ liệu lên đám mây.
Kết nối lại điện thoại.
Đảm bảo điện thoại của bạn được nhận dạng rồi chạy lệnh sau:
adb devicesKết xuất tất cả dữ liệu về pin bằng cách chạy lệnh sau. Quá trình này sẽ mất một chút thời gian.
adb shell dumpsys batterystats > [path/]batterystats.txt
Tệp
batterystats.txtđược tạo trong thư mục bạn chỉ định bằng cách sử dụng đối số đường dẫn không bắt buộc. Nếu bạn không chỉ định đường dẫn, tệp này sẽ được tạo trong thư mục gốc của bạn.Tạo báo cáo từ dữ liệu thô.
- Đối với các thiết bị chạy Android 7.0 trở lên:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.zip
- Đối với các thiết bị chạy Android 6.0 trở xuống:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.txt
Có thể mất vài phút để hoàn tất quá trình báo cáo lỗi. Đừng ngắt kết nối thiết bị hoặc huỷ quá trình này cho đến khi hoàn tất.
Cũng giống như với
batterystats.txt, các tệp này được tạo trong thư mục mà bạn chỉ định bằng cách sử dụng đối sốpathkhông bắt buộc. Nếu bạn không chỉ định đường dẫn, các đường dẫn đó sẽ được tạo trong thư mục gốc của bạn.Nếu Battery Historian chưa chạy, hãy chạy công cụ này bằng cách sử dụng lệnh sau:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Để xem dữ liệu của bạn trong Battery Historian, hãy mở công cụ này trong trình duyệt. Đối với Mac và Linux, Battery Historian chạy tại
http://localhost:port_number. Đối với Windows, Battery Historian chạy tạihttp://your_IP_address:port_number.Nhấp vào Browse (Duyệt qua) rồi chọn tệp báo cáo lỗi mà bạn đã tạo ở trên.
Nhấp vào Submit (Gửi). Battery Historian mở một biểu đồ được tạo từ dữ liệu Batterystats của bạn.
Xem dữ liệu bằng biểu đồ Battery Historian
Biểu đồ Battery Historian vẽ đồ thị các sự kiện liên quan đến nguồn điện theo thời gian.
Mỗi hàng hiển thị một phân đoạn thanh màu khi một thành phần hệ thống đang hoạt động và theo đó vẽ dòng điện từ pin. Biểu đồ không cho biết mức sử dụng pin của thành phần đó mà chỉ cho biết liệu ứng dụng có đang hoạt động hay không. Các biểu đồ được sắp xếp theo danh mục, hiển thị một thanh cho từng danh mục theo thời gian, như biểu diễn trên trục x của biểu đồ.
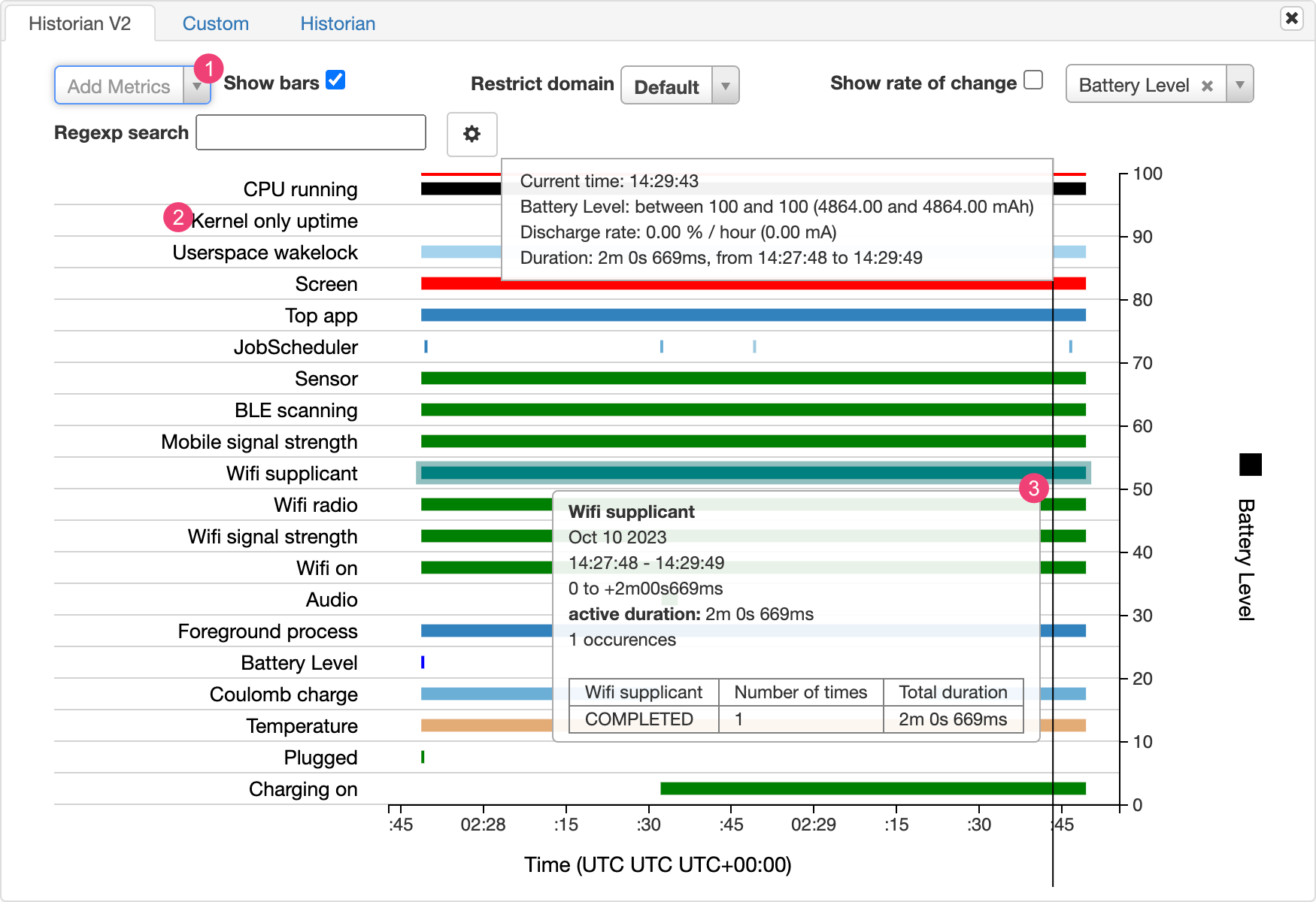
- Thêm các chỉ số khác trong danh sách thả xuống.
- Giữ con trỏ trên tên chỉ số để xem thêm thông tin về từng chỉ số, bao gồm một khoá cho các màu được dùng trong biểu đồ.
- Giữ con trỏ trên một thanh để xem thông tin chi tiết hơn về chỉ số đó và số liệu thống kê về pin tại một thời điểm cụ thể trên dòng thời gian.
Kết quả thống kê bổ sung về pin
Bạn có thể xem thêm thông tin từ tệp batterystats.txt trong phần số liệu thống kê bên dưới biểu đồ Battery Historian.
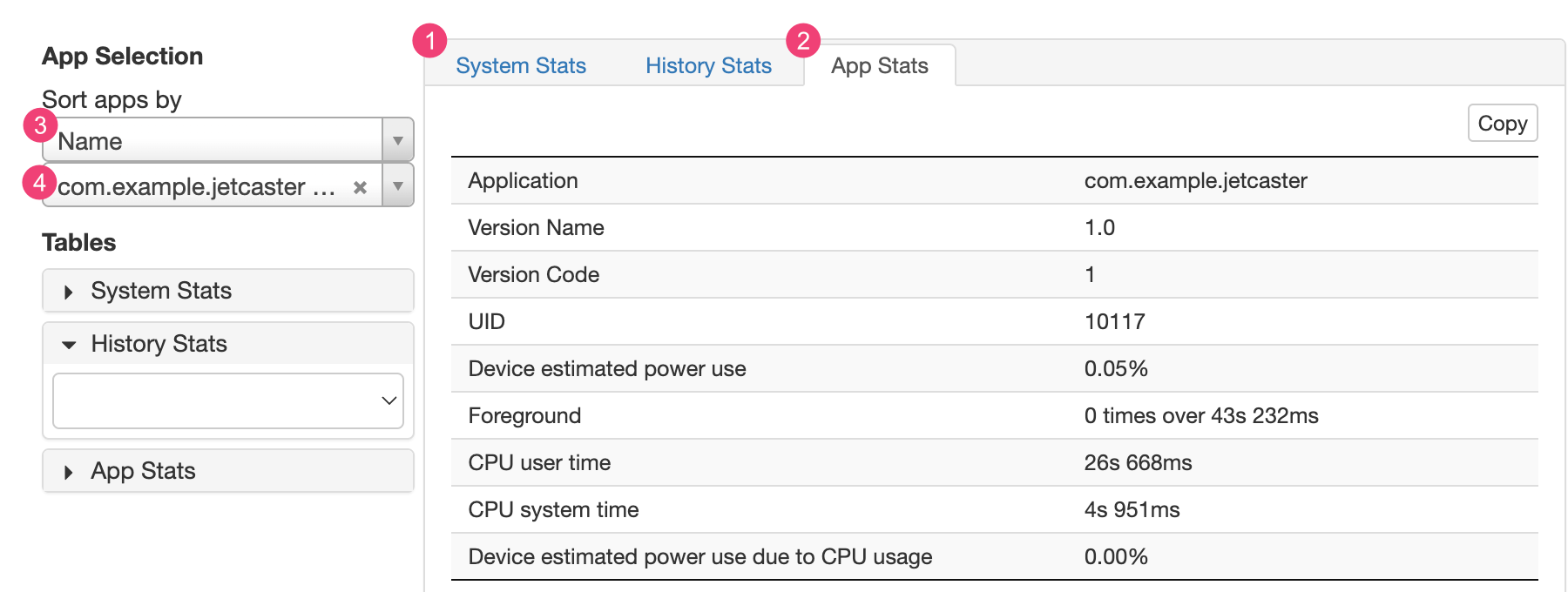
Thẻ 1 Thống kê hệ thống bao gồm số liệu thống kê trên toàn hệ thống, chẳng hạn như mức tín hiệu di động và độ sáng màn hình. Thông tin này cung cấp thông tin tổng quan về những gì đang xảy ra với thiết bị. Điều này đặc biệt hữu ích khi đảm bảo không có sự kiện bên ngoài nào đang ảnh hưởng đến thử nghiệm của bạn.
Thẻ 2 Thống kê ứng dụng bao gồm thông tin về các ứng dụng cụ thể. Sắp xếp danh sách ứng dụng bằng các dùng danh sách thả xuống 3Sắp xếp ứng dụng theo trong ngăn Lựa chọn ứng dụng. Bạn có thể chọn một ứng dụng cụ thể để xem số liệu thống kê bằng cách dùng 4 danh sách thả xuống ứng dụng.
