Este documento mostra as etapas básicas de configuração e o fluxo de trabalho da ferramenta Batterystats e do script Battery Historian. Para aprender a usar o Battery Historian para inspecionar padrões de consumo de bateria, consulte Analisar o consumo de energia com o Battery Historian.
O Batterystats é uma ferramenta incluída no framework do Android que coleta dados da
bateria do seu dispositivo. Use o adb para despejar os
dados coletados sobre a bateria na sua máquina de desenvolvimento e criar um relatório que pode
ser analisado usando o Battery Historian. O Battery Historian converte o relatório do
Batterystats em uma visualização HTML que pode ser aberta no navegador.
O Batterystats e o Battery Historian são úteis para:
- mostrar onde e como os processos estão puxando corrente da bateria;
- identificar tarefas do app que podem ser adiadas ou removidas para melhorar a duração da bateria.
Instalar o Battery Historian
Você pode usar o Docker para instalar o Battery Historian. Para conferir métodos de instalação alternativos, incluindo criação com base na origem, consulte o README (em inglês) na página do projeto no GitHub. Para instalar usando o Docker, siga estas etapas:
Instale o Docker seguindo as instruções no site. Qualquer tipo de assinatura funciona, incluindo uma assinatura pessoal gratuita.
Para confirmar se o Docker foi instalado corretamente, abra a linha de comando e digite:
docker run hello-worldSe o Docker estiver instalado corretamente, ele vai mostrar uma saída como esta:
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 78445dd45222: Pull complete Digest: sha256:c5515758d4c5e1e838e9cd307f6c6a0d620b5e07e6f927b07d05f6d12a1ac8d7 Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminalInicie o app Docker Desktop, que é um front-end de GUI para o Docker, antes de executar a imagem do Battery Historian. Isso vai inicializar as ferramentas do Docker. O Battery Historian não é executado até que você faça isso pelo menos uma vez.
Execute o Battery Historian na linha de comando durante a primeira execução. O app Docker Desktop não permite especificar a porta em que o servidor da Web será executado. Você só pode fazer isso na linha de comando. No entanto, depois que você executa o contêiner na linha de comando, é criada uma entrada que permite iniciar o servidor usando a mesma porta do listener do Docker Desktop.
Execute a imagem do Battery Historian usando o seguinte comando:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
O Battery Historian usa a porta que você quiser, conforme o especificado em
port_number.Acesse o Battery Historian no navegador para confirmar se ele está sendo executado. O endereço varia de acordo com o sistema operacional:
- Para Linux e Mac
- O Battery Historian está disponível em
http://localhost:port_number. - Para Windows
- Depois de iniciado, o Docker vai informar o endereço IP da máquina que está
sendo usada. Por exemplo, se o endereço IP for 123.456.78.90, o Battery
Historian vai estar disponível em
http://123.456.78.90:port_number.
Em seguida, na página inicial do Battery Historian, você poderá fazer upload e conferir as estatísticas da bateria.
Figura 1. A página inicial do Battery Historian.
Coletar dados com o Batterystats
Para coletar dados do seu dispositivo usando o Batterystats e abri-los no Battery Historian, faça o seguinte:
Conecte seu dispositivo móvel ao computador.
Em uma janela do terminal, encerre o servidor
adbem execução com o seguinte comando:adb kill-serverReinicie o
adbe confira se há dispositivos conectados com o comando a seguir.adb devicesEle vai listar seu dispositivo, de maneira semelhante ao exemplo de saída a seguir.

Figura 2. Saída de adb devices, mostrando um dispositivo conectado.Se nenhum dispositivo for listado, confira se o smartphone está conectado e se a depuração USB está ativada. Em seguida, encerre e reinicie o
adb.Redefina a coleta de dados da bateria com o seguinte comando:
adb shell dumpsys batterystats --resetO dispositivo está sempre coletando estatísticas sobre a bateria e outras informações de depuração em segundo plano. A redefinição apaga dados de coleta anteriores. Se você não fizer isso, a saída poderá ser muito grande.
Desconecte o dispositivo do computador para que a única corrente em uso seja a da bateria.
Use o app e execute ações para a coleta de dados. Por exemplo, desconecte o Wi-Fi e envie dados para a nuvem.
Reconecte o smartphone.
Confira se o smartphone foi reconhecido e execute o seguinte comando:
adb devicesDescarregue todos os dados da bateria com o comando a seguir. Isso pode demorar um pouco.
adb shell dumpsys batterystats > [path/]batterystats.txt
O arquivo
batterystats.txtserá criado no diretório especificado usando o argumento de caminho opcional. Se você não especificar um caminho, o arquivo será criado no seu diretório inicial.Crie um relatório com base nos dados brutos.
- Para dispositivos com o Android 7.0 e versões mais recentes:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.zip
- Para dispositivos com o Android 6.0 e anteriores:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.txt
O relatório de bugs pode demorar alguns minutos para ser concluído. Não desconecte o dispositivo nem cancele o processo antes disso.
Esses arquivos são criados no diretório especificado usando o argumento de
pathopcional, assim como obatterystats.txtdescrito acima. Se você não especificar um caminho, eles serão criados no seu diretório inicial.Execute o Battery Historian usando o comando a seguir, caso ele ainda não esteja em execução:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
Para conferir seus dados no Battery Historian, abra-o no navegador. No Mac e Linux, o Battery Historian é executado em
http://localhost:port_number. No Windows, o Battery Historian é executado emhttp://your_IP_address:port_number.Clique em Browse e escolha o arquivo do relatório de bugs criado acima.
Clique em Submit. O Battery Historian vai abrir um gráfico criado com base nos dados do Batterystats.
Conferir dados com gráficos do Battery Historian
Dados relevantes relacionados ao consumo de energia ao longo do tempo são incluídos nos gráficos do Battery Historian.
Cada linha mostra um segmento de barra colorida quando um componente do sistema está ativo e, portanto, puxando corrente da bateria. O gráfico não mostra a quantidade de bateria usada pelo componente, apenas se o app está ativo. Os gráficos são organizados por categoria, sendo uma barra para cada categoria ao longo do tempo, conforme mostrado no eixo X.
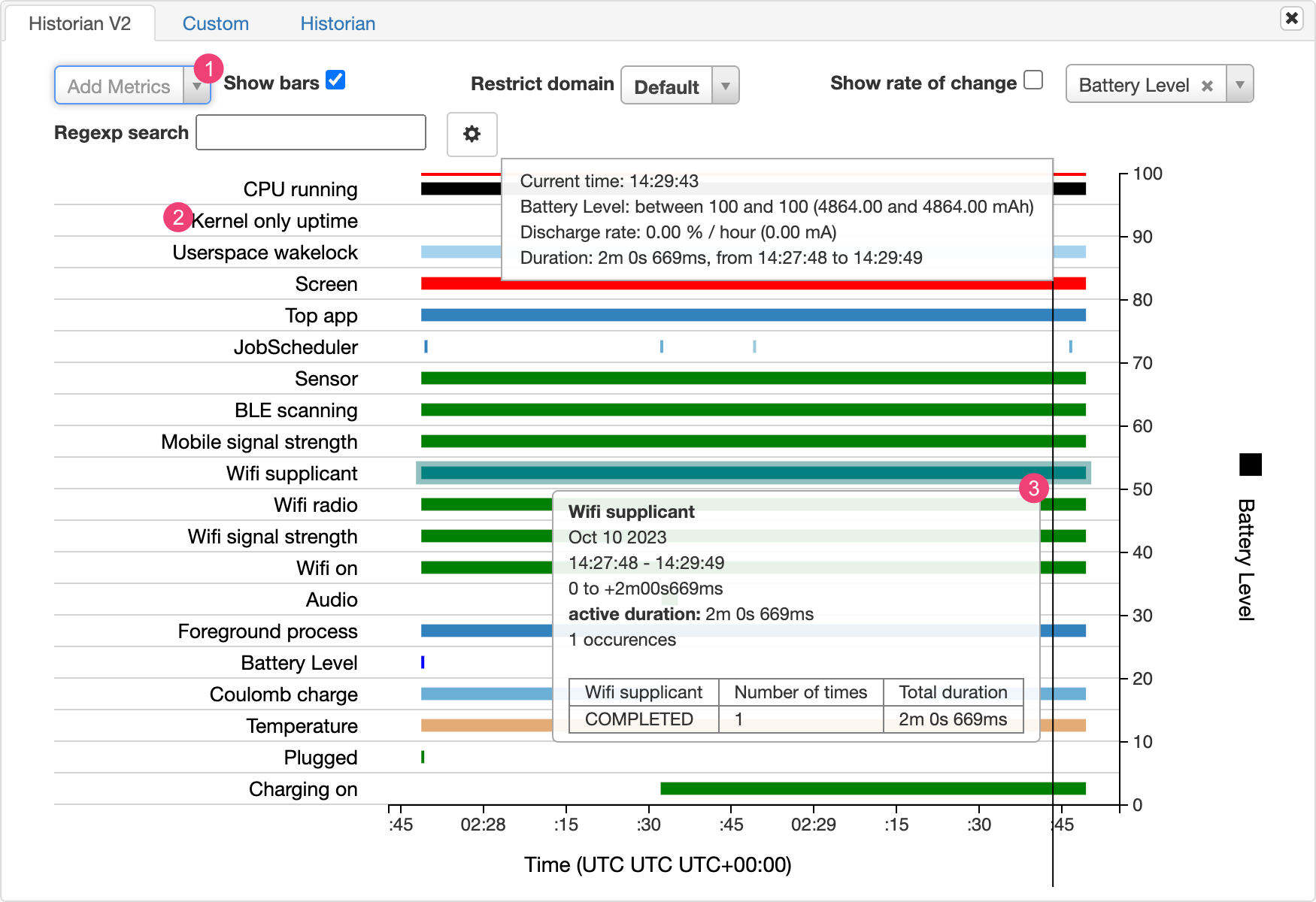
- Adicione outras métricas usando a lista suspensa.
- Mantenha o ponteiro do mouse sobre o nome da métrica para conferir mais informações sobre cada uma delas, incluindo uma legenda para as cores usadas no gráfico.
- Mantenha o ponteiro do mouse sobre uma barra para conferir informações mais detalhadas sobre a métrica e as estatísticas da bateria em um ponto específico da linha do tempo.
Outra saída do Batterystats
Confira mais informações do arquivo batterystats.txt na
seção de estatísticas abaixo do gráfico do Battery Historian.
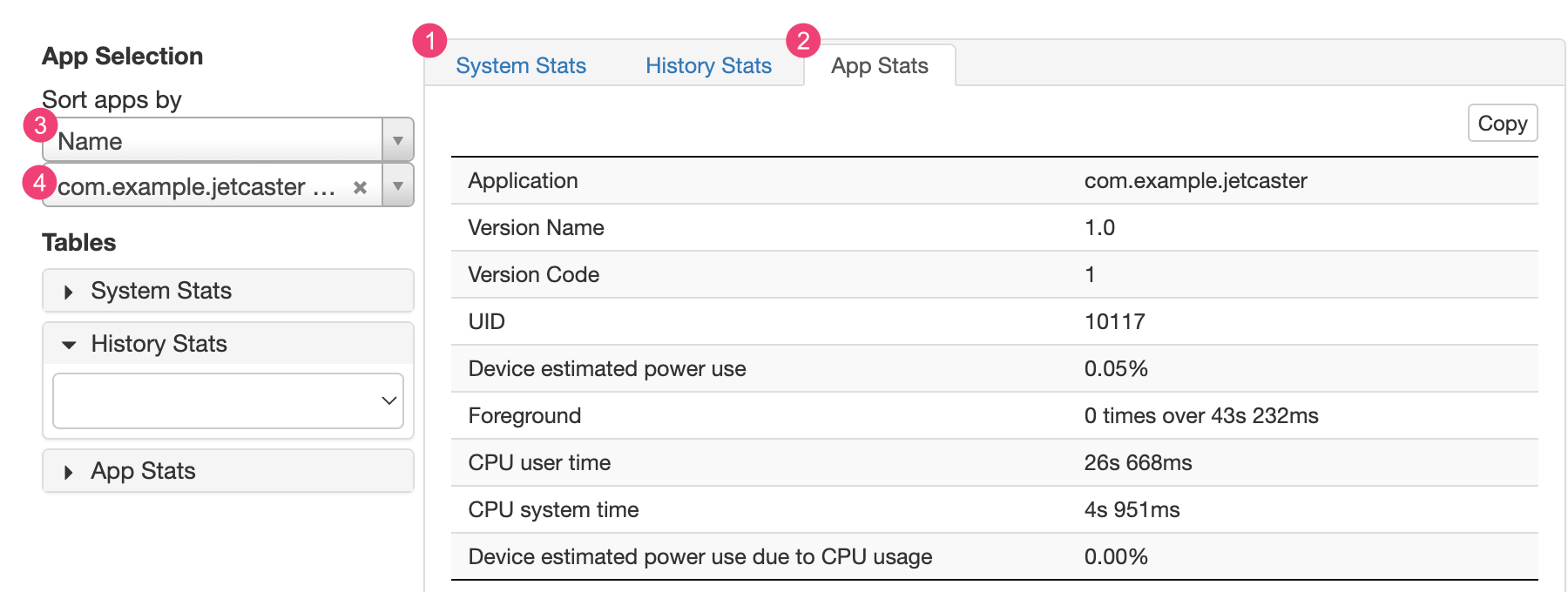
A guia 1 System Stats inclui estatísticas de todo o sistema, como níveis de sinal de celular e brilho da tela. Essas informações fornecem um panorama geral do que está acontecendo no dispositivo. Isso é especialmente útil para garantir que nenhum evento externo está afetando seu teste.
A guia 2 App Stats inclui informações sobre apps específicos. Classifique a lista de apps usando a lista suspensa 3 Sort apps by no painel App Selection. Confira as estatísticas de um app específico usando a lista suspensa 4.
