Android 通过 USB 配件和 USB 主机两种模式支持各种 USB 外围设备和 Android USB 配件(实现 Android 配件协议的硬件)。在 USB 配件模式下,外部 USB 硬件充当 USB 主机。配件示例包括:
- 机器人控制器
- 停放点
- 诊断和音乐设备
- 自助服务终端
- 读卡器
等等。这样,不具备主机功能的 Android 设备就能够与 USB 硬件进行交互。Android USB 配件必须设计为与 Android 设备兼容,并且必须遵循 Android 配件通信协议。在 USB 主机模式下,Android 设备充当主机。设备示例包括数码相机、键盘、鼠标和游戏控制器。专为各种应用和环境设计的 USB 设备仍可与能够与设备正确通信的 Android 应用交互。
图 1 展示了这两种模式之间的差异。当 Android 设备处于主机模式时,它会充当 USB 主机并为总线供电。当 Android 设备处于 USB 配件模式时,连接的 USB 硬件(在本例中为 Android USB 配件)将充当主机并为总线供电。
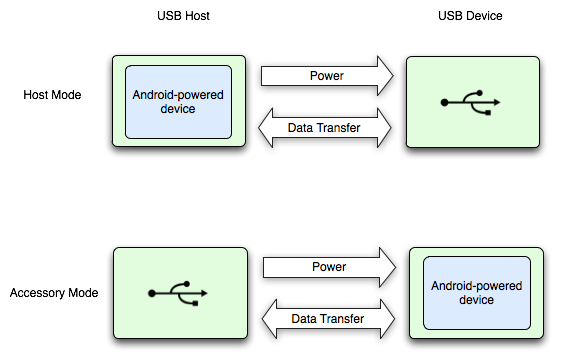
图 1. USB 主机和配件模式
Android 3.1(API 级别 12)或更高版本的平台直接支持 USB 配件和主机模式。USB 配件模式还作为插件库向后移植到 Android 2.3.4(API 级别 10),以支持更广泛的设备。设备制造商可以选择是否在设备的系统映像中包含插件库。
注意:对 USB 主机和配件模式的支持最终取决于设备的硬件,而与平台级别无关。您可以通过 <uses-feature> 元素过滤出支持 USB 主机和配件的设备。如需了解详情,请参阅 USB 配件和主机文档。
调试注意事项
调试使用 USB 配件或主机功能的应用时,您很可能已将 USB 硬件连接到 Android 设备。这样可以阻止您使用 USB 与 Android 设备建立 adb 连接。您仍可通过网络连接访问 adb。如需通过网络连接启用 adb,请执行以下操作:
- 通过 USB 将 Android 设备连接到计算机。
- 在 SDK
platform-tools/目录中,在命令提示符处输入adb tcpip 5555。 - 输入
adb connect <device-ip-address>:5555。您现在应该已连接到 Android 设备,并且可以发出常规的adb命令(如adb logcat)。 - 要设置设备来监听 USB,请输入
adb usb。
