Using the BluetoothAdapter,
you can find remote Bluetooth devices either through device discovery or by
querying the list of paired devices.
Make sure you have the appropriate Bluetooth permissions and set up your app for Bluetooth before attempting to find Bluetooth devices.
Device discovery is a scanning procedure that searches the local area for Bluetooth-enabled devices and requests some information about each one. This process is sometimes referred to as discovering, inquiring, or scanning. A nearby Bluetooth device responds to a discovery request only if it is currently accepting information requests by being discoverable. If a device is discoverable, it responds to the discovery request by sharing some information, such as the device's name, its class, and its unique MAC address. Using this information, the device that is performing the discovery process can then choose to initiate a connection to the discovered device.
Because discoverable devices might reveal information about the user's location, the device discovery process requires location access. If your app is being used on a device that runs Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher, consider using the Companion Device Manager API instead. This API performs device discovery on your app's behalf, so your app doesn't need to request location permissions.
Once a connection is made with a remote device for the first time, a pairing request is automatically presented to the user. When a device is paired, the basic information about that device—such as the device's name, class, and MAC address—is saved and can be read using the Bluetooth APIs. Using the known MAC address for a remote device, a connection can be initiated with it at any time without performing discovery, assuming the device is still within range.
Note that there is a difference between being paired and being connected:
- To be paired means that two devices are aware of each other's existence, have a shared link-key that can be used for authentication, and are capable of establishing an encrypted connection with each other.
- To be connected means that the devices currently share an RFCOMM channel and are able to transmit data with each other. The current Bluetooth APIs require devices to be paired before an RFCOMM connection can be established. Pairing is automatically performed when you initiate an encrypted connection with the Bluetooth APIs.
The following sections describe how to find devices that have been paired and how to discover new devices using device discovery.
Query paired devices
Before performing device discovery, it's worth querying the set of paired
devices to see if the desired device is already known. To do so, call
getBondedDevices().
This returns a set of
BluetoothDevice objects
representing paired devices. For example, you can query all paired devices and
get the name and MAC address of each device, as the following code snippet
demonstrates:
Kotlin
val pairedDevices: Set<BluetoothDevice>? = bluetoothAdapter?.bondedDevices pairedDevices?.forEach { device -> val deviceName = device.name val deviceHardwareAddress = device.address // MAC address }
Java
Set<BluetoothDevice> pairedDevices = bluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices(); if (pairedDevices.size() > 0) { // There are paired devices. Get the name and address of each paired device. for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) { String deviceName = device.getName(); String deviceHardwareAddress = device.getAddress(); // MAC address } }
To initiate a connection with a Bluetooth device, all that's needed from the
associated BluetoothDevice object is the MAC address, which you retrieve by
calling
getAddress(). You
can learn more about creating a connection in Connect Bluetooth
devices.
Discover devices
To start discovering devices, call
startDiscovery().
The process is asynchronous and returns a boolean value indicating whether
discovery has successfully started. The discovery process usually involves an
inquiry scan of about 12 seconds, followed by a page scan of each device found
to retrieve its Bluetooth name.
To receive information about each device discovered, your app must register a
BroadcastReceiver
for the
ACTION_FOUND
intent. The system broadcasts this intent for each device. The intent contains
the extra fields
EXTRA_DEVICE and
EXTRA_CLASS, which
in turn contain a BluetoothDevice and a
BluetoothClass, respectively.
The following code snippet shows how you can register to handle the broadcast
when devices are discovered:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { ... // Register for broadcasts when a device is discovered. val filter = IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND) registerReceiver(receiver, filter) } // Create a BroadcastReceiver for ACTION_FOUND. private val receiver = object : BroadcastReceiver() { override fun onReceive(context: Context, intent: Intent) { val action: String = intent.action when(action) { BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND -> { // Discovery has found a device. Get the BluetoothDevice // object and its info from the Intent. val device: BluetoothDevice = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE) val deviceName = device.name val deviceHardwareAddress = device.address // MAC address } } } } override fun onDestroy() { super.onDestroy() ... // Don't forget to unregister the ACTION_FOUND receiver. unregisterReceiver(receiver) }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { ... // Register for broadcasts when a device is discovered. IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND); registerReceiver(receiver, filter); } // Create a BroadcastReceiver for ACTION_FOUND. private final BroadcastReceiver receiver = new BroadcastReceiver() { public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { String action = intent.getAction(); if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) { // Discovery has found a device. Get the BluetoothDevice // object and its info from the Intent. BluetoothDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE); String deviceName = device.getName(); String deviceHardwareAddress = device.getAddress(); // MAC address } } }; @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); ... // Don't forget to unregister the ACTION_FOUND receiver. unregisterReceiver(receiver); }
To initiate a connection with a Bluetooth device, you call getAddress() on the
BluetoothDevice to retrieve the associated MAC address.
Enable discoverability
To make the local device discoverable to other devices, call
startActivityForResult(Intent, int)
with the
ACTION_REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE
intent. This issues a request to enable the system's discoverable mode without
having to navigate to the Settings app, which would stop your own app. By
default, the device becomes discoverable for two minutes. You can define a
different duration, up to five minutes, by adding the
EXTRA_DISCOVERABLE_DURATION
extra.
The following code snippet sets the device to be discoverable for five minutes:
Kotlin
val requestCode = 1; val discoverableIntent: Intent = Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE).apply { putExtra(BluetoothAdapter.EXTRA_DISCOVERABLE_DURATION, 300) } startActivityForResult(discoverableIntent, requestCode)
Java
int requestCode = 1; Intent discoverableIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE); discoverableIntent.putExtra(BluetoothAdapter.EXTRA_DISCOVERABLE_DURATION, 300); startActivityForResult(discoverableIntent, requestCode);
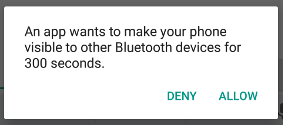
Figure 2: The enabling discoverability dialog.
A dialog is displayed, requesting the user's permission to make the device
discoverable, as shown in figure 2. If the user responds "Allow," then the
device becomes discoverable for the specified amount of time. Your activity then
receives a call to the
onActivityResult()
callback, with the result code equal to the duration that the device is
discoverable. If the user responded "Deny", or if an error occurred, the result
code is RESULT_CANCELED.
The device silently remains in discoverable mode for the allotted time. To be
notified when the discoverable mode has changed, register a BroadcastReceiver
for the
ACTION_SCAN_MODE_CHANGED
intent. This intent contains the extra fields
EXTRA_SCAN_MODE
and
EXTRA_PREVIOUS_SCAN_MODE,
which provide the new and old scan mode, respectively. Possible values for each
extra are as follows:
SCAN_MODE_CONNECTABLE_DISCOVERABLE- The device is in discoverable mode.
SCAN_MODE_CONNECTABLE- The device isn't in discoverable mode but can still receive connections.
SCAN_MODE_NONE- The device isn't in discoverable mode and cannot receive connections.
If you are initiating the connection to a remote device, you don't need to enable device discoverability. Enabling discoverability is only necessary when you want your app to host a server socket that accepts incoming connections, as remote devices must be able to discover other devices before initiating connections to those other devices.
