Komponent Dialog wyświetla wyskakujące okienka lub prosi o wprowadzenie danych przez użytkownika na warstwie nad główną treścią aplikacji. Tworzy ono przerwanie w interfejsie, aby przyciągnąć uwagę użytkownika.
Dostępne przypadki użycia dialogu:
- potwierdzenie działania użytkownika, na przykład usunięcia pliku;
- Proszenie o wprowadzenie danych przez użytkownika, np. w aplikacji do zarządzania listą zadań.
- Wyświetlanie listy opcji do wyboru przez użytkownika, np. wybór kraju w konfiguracji profilu.
W tym temacie opisano następujące implementacje:
Zgodność wersji
Ta implementacja wymaga, aby minimalna wersja pakietu SDK projektu była ustawiona na poziom API 21 lub wyższy.
Zależności
Okno tworzenia alertu
Komponent AlertDialog udostępnia wygodne API do tworzenia dialogów w stylu Material Design. W tym przykładzie w oknie alertu są 2 przyciski: jeden do zamykania okna i drugi do potwierdzania prośby:
Ta implementacja zakłada funkcję kompozytową nadrzędną, która przekazuje argumenty funkcji kompozytowej podrzędnej w ten sposób:
Wyniki
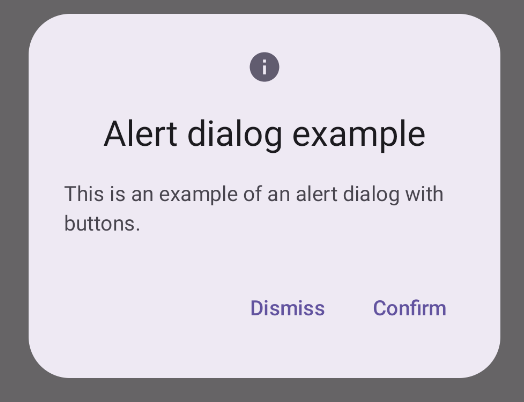
Najważniejsze punkty
AlertDialog ma określone parametry do obsługi poszczególnych elementów dialogu. Należą do nich:
title: tekst, który pojawia się u góry okna dialogowego.text: tekst wyśrodkowany w dialogu.icon: grafika wyświetlana u góry okna.onDismissRequest: funkcja wywoływana, gdy użytkownik zamyka okno, np. przez kliknięcie poza nim.dismissButton: kompozyt służący jako przycisk zamknięcia.confirmButton: komponent służący jako przycisk potwierdzenia.Gdy użytkownik kliknie jeden z przycisków, okno dialogowe się zamknie. Gdy użytkownik kliknie „Potwierdź”, wywołuje funkcję, która również obsługuje potwierdzenie. W tym przykładzie są to funkcje
onDismissRequest()ionConfirmRequest().Jeśli dialog wymaga bardziej złożonego zestawu przycisków, możesz skorzystać z komponentu
Dialogi wypełnić go w bardziej swobodny sposób.
Tworzenie okna
Dialog to podstawowy komponent, który nie zapewnia żadnego stylizowania ani wstępnie zdefiniowanych miejsc na treści. Jest to prosty kontener, który należy wypełnić kontenerem takim jak Card. Oto niektóre z najważniejszych parametrów dialogu:
onDismissRequest: funkcja lambda wywoływana, gdy użytkownik zamknie okno.properties: instancjaDialogProperties, która zapewnia dodatkowe możliwości dostosowywania.
Tworzenie podstawowego dialogu
Ten przykład pokazuje podstawową implementację kompozytu Dialog. Pamiętaj, że jako kontener pomocniczy używa Card. Bez elementu Card element Text wyświetlałby się sam nad główną treścią aplikacji.
Wynik
Pamiętaj, że gdy okno jest otwarte, główna treść aplikacji pod nim jest przyciemniona i wygaszona:

Tworzenie zaawansowanego okna
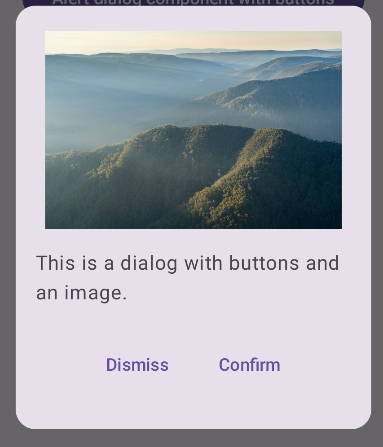
Poniżej przedstawiamy bardziej zaawansowane wdrożenie komponentu Dialog. W tym przypadku komponent ręcznie implementuje interfejs podobny do tego z poprzedniego przykładu.AlertDialog
Wynik
Kolekcje zawierające ten przewodnik
Ten przewodnik należy do tych kolekcji krótkich przewodników, które obejmują szersze zagadnienia związane z tworzeniem aplikacji na Androida:
Tekst wyświetlany

Prośba o dane użytkownika



