يتوافق Android مع مجموعة متنوعة من أجهزة USB الطرفية وملحقات USB من Android (الأجهزة التي تتّبع بروتوكول ملحقات Android) من خلال وضعَين: ملحق USB ومضيف USB. في وضع ملحق USB، تعمل أجهزة USB الخارجية كمضيف USB. في ما يلي أمثلة على الملحقات:
- وحدات تحكم في الروبوتات
- محطات مواقف دراجات
- المعدات التشخيصية والموسيقية
- أكشاك
- أجهزة قراءة البطاقات
وغير ذلك الكثير. وهذا يمنح الأجهزة التي تعمل بنظام تشغيل Android ولا تتمتع بإمكانيات المضيف إمكانية التفاعل مع أجهزة USB. يجب تصميم ملحقات USB على Android لتعمل مع الأجهزة التي تعمل بنظام التشغيل Android، ويجب أن تكون متوافقة مع بروتوكول الاتصال بملحقات Android. في وضع مضيف USB، يعمل الجهاز الذي يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android كمضيف. ومن أمثلة الأجهزة الكاميرات الرقمية ولوحات المفاتيح وأجهزة الماوس ووحدات التحكم في الألعاب. لا يزال بإمكان أجهزة USB المصمَّمة لمجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات والبيئات التفاعل مع تطبيقات Android التي يمكنها الاتصال بالجهاز بشكل صحيح.
يوضح الشكل 1 الاختلافات بين الوضعين. عندما يكون الجهاز الذي يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android في وضع المضيف، فإنه يعمل كمضيف USB ويشغِّل الناقل. عندما يكون الجهاز الذي يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android في وضع ملحق USB، تعمل أجهزة USB المتصلة (أحد ملحقات USB من Android في هذه الحالة) كمضيف وتشغّل الناقل.
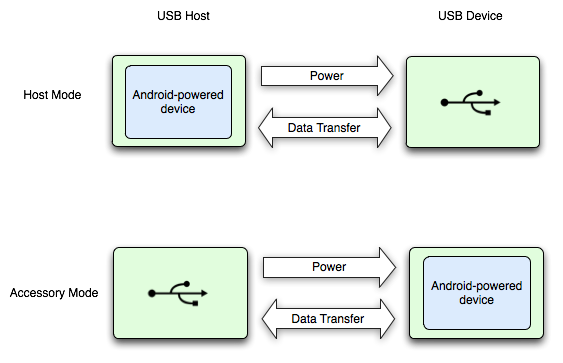
الشكل 1. مضيف USB وأوضاع الملحق
تتوافق أوضاع المضيف وملحقات USB مباشرةً في Android 3.1 (المستوى 12 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الأنظمة الأساسية الأحدث. ويتم أيضًا نقل وضع ملحق USB إلى الإصدار Android 2.3.4 (المستوى 10 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) كمكتبة إضافات لإتاحة مجموعة أكبر من الأجهزة. يمكن للشركات المصنّعة للأجهزة اختيار ما إذا كان سيتم تضمين مكتبة الإضافات في صورة نظام الجهاز أم لا.
ملاحظة: يعتمد دعم أوضاع مضيف USB وملحقاته في الأساس على مكونات الجهاز، بغض النظر عن مستوى النظام الأساسي. يمكنك فلترة الأجهزة
التي تتوافق مع مضيف USB وملحقاته من خلال عنصر
<uses-feature>.
راجِع وثائق ملحق USB والمضيف لمزيد من التفاصيل.
اعتبارات تصحيح الأخطاء
عند تصحيح أخطاء التطبيقات التي تستخدم ملحق USB أو ميزات المضيف، من المرجح أن يكون لديك جهاز USB متصل بجهازك الذي يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android. ويمنعك ذلك من إنشاء اتصال adb بالجهاز الذي يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android
باستخدام USB. ولا يزال بإمكانك الوصول إلى adb عبر الاتصال بالشبكة. لتفعيل ميزة adb
عبر اتصال شبكة:
- عليك توصيل الجهاز الذي يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android باستخدام USB بالكمبيوتر.
- من دليل
platform-tools/لحزمة SDK، أدخِلadb tcpip 5555عند طلب الأمر. - أدخِل
adb connect <device-ip-address>:5555. من المفترض أن تكون متصلاً الآن بالجهاز الذي يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android ويمكنك إصدار أوامرadbالمعتادة، مثلadb logcat. - لضبط جهازك على الاستماع على USB، أدخِل
adb usb.
