Android 16에는 개발자를 위한 훌륭한 새로운 기능과 API가 도입되었습니다. 다음 섹션에서는 관련 API를 시작하는 데 도움이 되도록 이러한 기능을 요약합니다.
새로운 API, 수정된 API, 삭제된 API에 관한 자세한 목록은 API 차이점 보고서를 참고하세요. 새로운 API에 관한 자세한 내용은 Android API 참조를 방문하세요. 새로운 API가 강조 표시되어 쉽게 확인 가능합니다.플랫폼 변경사항이 앱에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 영역도 검토해야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 다음 페이지를 참고하세요.
핵심 기능
Android에는 Android 시스템의 핵심 기능을 확장하는 새로운 API가 포함되어 있습니다.
2025년 두 가지 Android API 출시
- 이 미리보기는 2025년 2분기에 출시될 예정인 Android의 다음 주요 버전입니다. 이 버전은 이전의 모든 API 버전과 유사하며, 여기서 targetSdkVersion에 종종 연결된 계획된 동작 변경사항을 적용할 수 있습니다.
- 더 많은 기기에서 Android의 주요 버전을 더 빨리 사용할 수 있도록 생태계 전반의 기기 출시 일정에 더 잘 맞추기 위해 메이저 버전을 3분기에서 2분기로 한 분기 앞당겨 출시할 계획입니다. 2분기에 주요 버전이 출시될 예정이므로 앱이 준비되었는지 확인하기 위해 전년보다 몇 개월 더 일찍 연간 호환성 테스트를 진행해야 합니다.
- 2025년 4분기에 새로운 개발자 API도 포함된 버전을 출시할 계획입니다. 2분기 주요 출시는 2025년에 앱에 영향을 줄 수 있는 계획된 동작 변경사항이 포함된 유일한 출시입니다.
Q4 마이너 출시에서는 새로운 개발자 API 외에도 기능 업데이트, 최적화, 버그 수정이 포함됩니다. 앱에 영향을 미치는 동작 변경사항은 포함되지 않습니다.
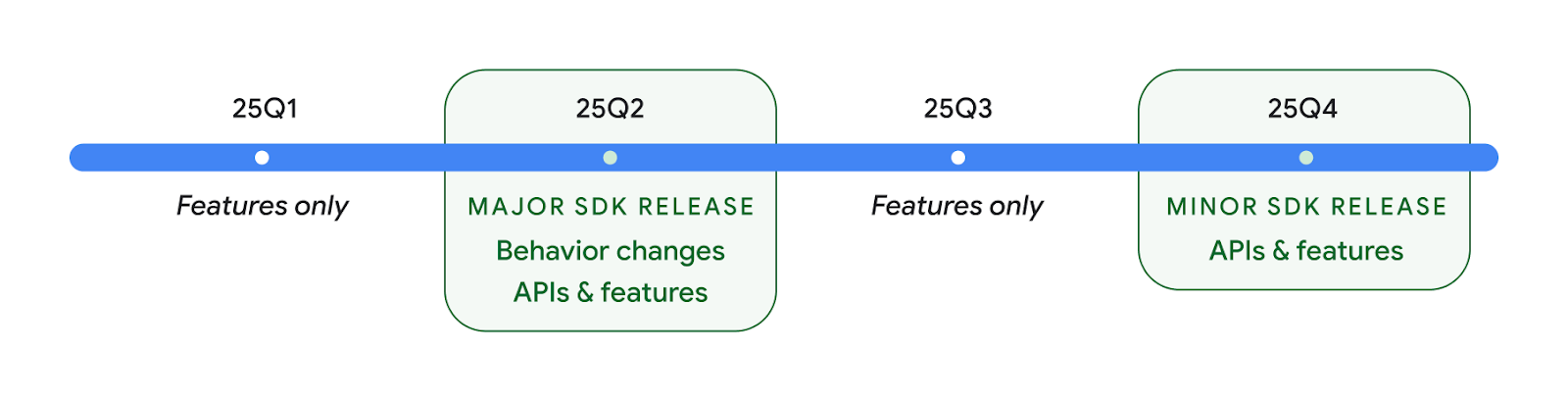
앞으로도 분기별로 Android 버전이 계속 출시될 예정입니다. API 출시 사이의 1분기 및 3분기 업데이트는 지속적인 품질을 보장하는 데 도움이 되는 점진적 업데이트를 제공합니다. Google은 기기 파트너와 적극적으로 협력하여 최대한 많은 기기에 Q2 버전을 제공하기 위해 노력하고 있습니다.
메인 및 마이너 출시에서 새 API 사용
API 수준 검사를 사용하여 코드 블록을 보호하는 작업은 현재 VERSION_CODES와 함께 SDK_INT 상수를 사용하여 실행됩니다. 이는 주요 Android 출시에서 계속 지원됩니다.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
새 SDK_INT_FULL 상수는 새 VERSION_CODES_FULL 열거형을 사용하여 주 버전과 부 버전 모두에 대한 API 검사에 사용할 수 있습니다.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
Build.getMinorSdkVersion() 메서드를 사용하여 부 SDK 버전만 가져올 수도 있습니다.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
이 API는 아직 최종 결정되지 않았으며 변경될 수 있으므로 우려되는 점이 있으면 의견을 보내주세요.
사용자 환경 및 시스템 UI
Android 16에서는 앱 개발자와 사용자가 필요에 맞게 기기를 구성할 수 있는 제어 기능과 유연성이 향상되었습니다.
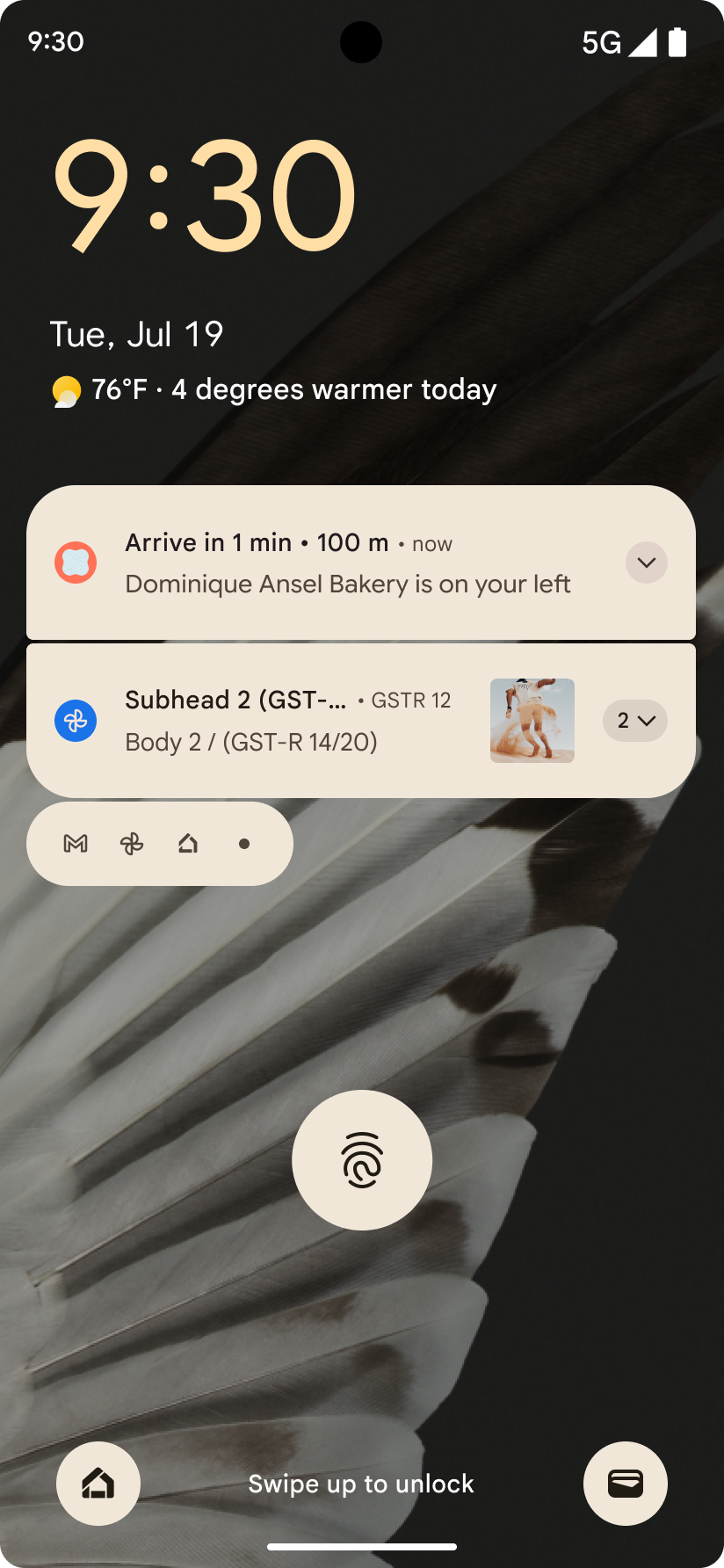
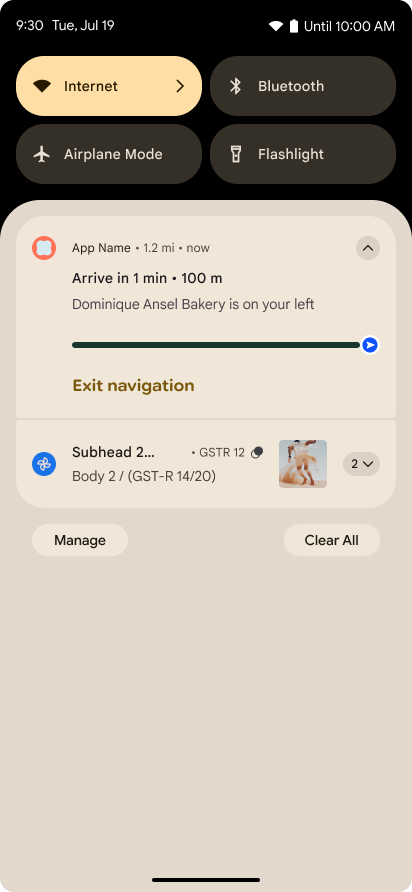
진행 상황 중심 알림
Android 16에서는 사용자가 시작부터 끝까지 사용자 시작 여정을 원활하게 추적할 수 있도록 진행률 중심 알림을 도입합니다.
Notification.ProgressStyle는 진행 상황 중심의 알림을 만들 수 있는 새로운 알림 스타일입니다. 주요 사용 사례로는 차량 공유, 배송, 내비게이션이 있습니다. Notification.ProgressStyle 클래스 내에서 포인트 및 세그먼트를 사용하여 사용자 여정의 상태와 마일스톤을 나타낼 수 있습니다.
자세한 내용은 진행률 중심 알림 문서 페이지를 참고하세요.
뒤로 탐색 예측 업데이트
Android 16에서는 홈으로 돌아가기 애니메이션과 같은 동작 탐색에서 뒤로 탐색 예측 시스템 애니메이션을 사용 설정하는 데 도움이 되는 새로운 API를 추가합니다. 새로운 PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER에 onBackInvokedCallback를 등록하면 앱이 일반 뒤로 탐색 흐름에 영향을 주지 않고 시스템이 뒤로 탐색을 처리할 때마다 일반 onBackInvoked 호출을 수신할 수 있습니다.
Android 16에서는 finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() 및 moveTaskToBackCallback도 추가합니다. 이러한 콜백을 OnBackInvokedDispatcher에 등록하면 시스템은 뒤로 동작이 호출될 때 특정 동작을 트리거하고 상응하는 사전 애니메이션을 재생할 수 있습니다.
더 풍부한 햅틱
Android는 처음부터 햅틱 액추에이터 제어를 노출했습니다.
Android 11에서는 기기 정의 시맨틱 프리미티브의 VibrationEffect.Compositions를 통해 고급 액추에이터가 지원할 수 있는 더 복잡한 햅틱 효과에 대한 지원을 추가했습니다.
Android 16에는 앱이 햅틱 효과의 진폭과 주파수 곡선을 정의하면서 기기 기능 간의 차이를 추상화할 수 있는 햅틱 API가 추가되었습니다.
개발자 생산성 및 도구
생산성 향상을 위한 대부분의 작업은 Android 스튜디오, Jetpack Compose, Android Jetpack 라이브러리와 같은 도구를 중심으로 이루어지지만, Google에서는 항상 플랫폼에서 비전을 실현할 수 있는 방법을 모색합니다.
라이브 배경화면 콘텐츠 처리
Android 16에서는 라이브 배경화면 프레임워크에 동적 사용자 중심 배경화면의 문제를 해결하기 위한 새로운 콘텐츠 API가 추가됩니다. 현재 사용자 제공 콘텐츠를 통합하는 라이브 배경화면에는 복잡한 서비스별 구현이 필요합니다. Android 16에서는 WallpaperDescription 및 WallpaperInstance를 도입합니다. WallpaperDescription을 사용하면 동일한 서비스에서 라이브 배경화면의 고유한 인스턴스를 식별할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 홈 화면과 잠금 화면에 인스턴스가 있는 배경화면에는 두 위치 모두 고유한 콘텐츠가 있을 수 있습니다. 배경화면 선택 도구와 WallpaperManager는 이 메타데이터를 사용하여 사용자에게 배경화면을 더 효과적으로 표시함으로써 개발자가 다양한 맞춤형 라이브 배경화면 환경을 만드는 프로세스를 간소화할 수 있습니다.
성능 및 배터리
Android 16에서는 앱에 관한 유용한 정보를 수집하는 데 도움이 되는 API를 도입합니다.
시스템 트리거 프로파일링
ProfilingManager가 Android 15에 추가되어 앱이 현장의 공개 기기에서 Perfetto를 사용하여 프로파일링 데이터 수집을 요청할 수 있습니다.
그러나 이 프로파일링은 앱에서 시작해야 하므로 시작 또는 ANR과 같은 중요한 흐름은 앱에서 캡처하기 어렵거나 불가능합니다.
이를 위해 Android 16에서는 ProfilingManager에 시스템 트리거 프로파일링을 도입합니다. 앱은 콜드 스타트 reportFullyDrawn 또는 ANR과 같은 특정 트리거의 트레이스를 수신하는 데 관심을 등록할 수 있으며, 그러면 시스템이 앱을 대신하여 트레이스를 시작하고 중지합니다. 트레이스가 완료되면 결과가 앱의 데이터 디렉터리에 전송됩니다.
ApplicationStartInfo에서 구성요소 시작
ApplicationStartInfo는 Android 15에서 추가되어 앱이 프로세스 시작 이유, 시작 유형, 시작 시간, 제한, 기타 유용한 진단 데이터를 볼 수 있습니다. Android 16에서는 시작을 트리거한 구성요소 유형을 구분하는 getStartComponent()를 추가합니다. 이는 앱의 시작 흐름을 최적화하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
작업 인트로스펙션 개선
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API는 작업이 대기 중일 수 있는 이유를 반환합니다. 하지만 작업이 여러 가지 이유로 대기 중일 수 있습니다.
Android 16에서는 개발자가 설정한 명시적 제약 조건과 시스템에서 설정한 암시적 제약 조건으로 인해 작업이 대기 중인 여러 가지 이유를 반환하는 새로운 API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId)를 도입합니다.
또한 최신 제약 조건 변경사항 목록을 반환하는 JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId)도 도입됩니다.
특히 특정 작업의 성공률이 감소하거나 특정 작업 완료 지연과 관련된 버그가 있는 경우 API를 사용하여 작업이 실행되지 않는 이유를 디버그하는 것이 좋습니다. 예를 들어 백그라운드에서 위젯을 업데이트하지 못하거나 앱 시작 전에 미리 가져오기 작업을 호출하지 못했습니다.
이렇게 하면 시스템 정의 제약조건과 명시적으로 설정된 제약조건 중 어느 것이 특정 작업이 완료되지 않는 원인인지 더 잘 파악할 수 있습니다.
자동 조절 새로고침 빈도
Android 15에서 도입된 적응형 새로고침 빈도 (ARR)를 사용하면 지원되는 하드웨어의 디스플레이 새로고침 빈도가 개별 VSync 단계를 사용하여 콘텐츠 프레임 속도에 맞게 조정될 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 전력 소비량이 줄어들고 버벅거림을 유발할 수 있는 모드 전환이 필요하지 않게 됩니다.
Android 16에서는 hasArrSupport() 및 getSuggestedFrameRate(int)을 도입하고 getSupportedRefreshRates()를 복원하여 앱이 ARR을 더 쉽게 활용할 수 있도록 합니다. RecyclerView 1.4는 플링 또는 원활한 스크롤에서 정착할 때 내부적으로 ARR을 지원하며, 더 많은 Jetpack 라이브러리에 ARR 지원을 추가하기 위한 작업을 계속하고 있습니다. 이 프레임 속도 도움말에서는 앱에서 ARR을 직접 사용할 수 있도록 프레임 속도를 설정하는 데 사용할 수 있는 여러 API를 설명합니다.
ADPF의 여유 공간 API
SystemHealthManager에서는 게임 및 리소스 사용량이 많은 앱에 사용 가능한 CPU 및 GPU 리소스의 추정치를 제공하도록 설계된 getCpuHeadroom 및 getGpuHeadroom API를 도입합니다. 이러한 메서드는 특히 열 제한을 감지하는 다른 Android 동적 성능 프레임워크 (ADPF) API와 함께 사용할 때 앱 또는 게임이 시스템 상태를 가장 효과적으로 개선하는 방법을 측정하는 방법을 제공합니다.
지원되는 기기에서 CpuHeadroomParams 및 GpuHeadroomParams를 사용하면 헤드룸을 계산하는 데 사용되는 시간 창을 맞춤설정하고 평균 또는 최소 리소스 가용성 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 CPU 또는 GPU 리소스 사용량을 적절하게 줄여 사용자 환경과 배터리 수명을 개선할 수 있습니다.
접근성
Android 16에는 앱을 모든 사용자에게 제공하는 데 도움이 되는 새로운 접근성 API와 기능이 추가되었습니다.
접근성 API 개선
Android 16에는 TalkBack과 같은 접근성 서비스를 사용하는 사용자의 일관성을 개선하는 데 도움이 되는 UI 시맨틱을 개선하는 API가 추가되었습니다.
텍스트 대비를 극대화하기 위한 텍스트 윤곽선
저시력 사용자는 대비 감도가 낮아서 물체를 배경과 구분하기가 어렵습니다. 이러한 사용자를 지원하기 위해 Android 16에서는 고대비 텍스트를 대체하는 윤곽선 텍스트를 도입했습니다. 윤곽선 텍스트는 텍스트 주위에 더 큰 대비 영역을 그려 가독성을 크게 개선합니다.
Android 16에는 앱이 이 모드가 사용 설정되어 있는지 확인하거나 리스너를 등록할 수 있는 새로운 AccessibilityManager API가 포함되어 있습니다. 이는 주로 Compose와 같은 UI 도구 키트가 유사한 시각적 환경을 제공하기 위한 것입니다. UI 도구 키트 라이브러리를 유지 관리하거나 앱이 android.text.Layout 클래스를 우회하는 맞춤 텍스트 렌더링을 실행하는 경우 이를 사용하여 윤곽선 텍스트가 사용 설정된 시점을 알 수 있습니다.

TtsSpan에 길이가 추가됨
Android 16은 ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES, ARG_SECONDS으로 구성된 TYPE_DURATION를 사용하여 TtsSpan를 확장합니다. 이를 통해 시간 길이에 직접 주석을 달 수 있으므로 TalkBack과 같은 서비스에서 정확하고 일관된 텍스트 음성 변환 출력을 보장할 수 있습니다.
여러 라벨이 있는 요소 지원
현재 Android에서는 UI 요소가 다른 요소에서 접근성 라벨을 파생할 수 있도록 허용하며, 이제 웹 콘텐츠에서 일반적인 시나리오인 여러 라벨을 연결하는 기능을 제공합니다. AccessibilityNodeInfo 내에 목록 기반 API를 도입하면 Android에서 이러한 다중 라벨 관계를 직접 지원할 수 있습니다. 이번 변경의 일환으로 AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy 및 #getLabeledBy가 #addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy, #getLabeledByList로 대체되었습니다.
확장 가능한 요소 지원 개선
Android 16에는 메뉴 및 확장 가능한 목록과 같은 상호작용 요소의 펼쳐진 상태 또는 접힌 상태를 전달할 수 있는 접근성 API가 추가되었습니다. setExpandedState를 사용하여 펼쳐진 상태를 설정하고 CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED 콘텐츠 변경 유형으로 TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents를 전달하면 TalkBack과 같은 스크린 리더가 상태 변경을 알리도록 할 수 있으므로 더 직관적이고 포용적인 사용자 환경을 제공할 수 있습니다.
미확정 진행률 표시줄
Android 16에는 RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE가 추가되어 결정된 ProgressBar 위젯과 결정되지 않은 ProgressBar 위젯 모두에 RangeInfo를 노출할 수 있는 방법이 제공됩니다. 이를 통해 TalkBack과 같은 서비스가 진행률 표시기에 더 일관되게 의견을 제공할 수 있습니다.
3-state CheckBox
이제 Android 16의 새로운 AccessibilityNodeInfo 메서드 getChecked 및 setChecked(int)는 '선택됨' 및 '선택 해제됨' 외에도 '부분 선택됨' 상태를 지원합니다. 이는 지원 중단된 불리언 isChecked 및 setChecked(boolean)를 대체합니다.
보충 설명
접근성 서비스가 ViewGroup를 설명하면 하위 뷰의 콘텐츠 라벨을 결합합니다. ViewGroup에 contentDescription를 제공하면 접근성 서비스는 포커스를 설정할 수 없는 하위 뷰의 설명도 재정의한다고 가정합니다. 이는 접근성 관련 현재 선택사항 (예: 'Roboto')을 유지하면서 드롭다운 (예: 'Font Family')과 같은 항목에 라벨을 지정하려는 경우 문제가 될 수 있습니다. Android 16에서는 setSupplementalDescription를 추가하여 하위 요소의 정보를 재정의하지 않고도 ViewGroup에 관한 정보를 제공하는 텍스트를 제공할 수 있습니다.
필수 양식 입력란
Android 16에서는 앱이 접근성 서비스에 양식 필드 입력이 필요하다고 알릴 수 있도록 AccessibilityNodeInfo에 setFieldRequired를 추가합니다. 이는 사용자가 필수 약관 체크박스와 같이 간단한 양식부터 다양한 유형의 양식을 작성할 때 중요한 시나리오입니다. 사용자가 필수 입력란을 일관되게 식별하고 빠르게 탐색할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
LEA 보청기를 사용한 음성 통화 시 휴대전화를 마이크 입력으로 사용
Android 16에서는 LE Audio 보청기 사용자가 음성 통화를 위해 보청기의 내장 마이크와 휴대전화의 마이크 간에 전환할 수 있는 기능을 추가합니다. 이는 소음이 심한 환경이나 보청기의 마이크가 제대로 작동하지 않을 수 있는 다른 상황에서 유용할 수 있습니다.
LEA 보청기의 주변 볼륨 제어
Android 16에는 LE Audio 보청기 사용자가 보청기의 마이크에서 수신하는 주변 소음의 볼륨을 조절할 수 있는 기능이 추가되었습니다. 배경 소음이 너무 크거나 너무 조용한 경우에 유용합니다.
카메라
Android 16에서는 전문가급 카메라 사용자를 위한 지원이 강화되어 정확한 색온도 및 색조 조정과 함께 하이브리드 자동 노출이 가능합니다. 새 야간 모드 표시기를 사용하면 앱이 야간 모드 카메라 세션으로 전환해야 하는 시점을 알 수 있습니다. 새로운 Intent 작업을 통해 모션 사진을 더 쉽게 촬영할 수 있으며, HEIC 인코딩과 ISO 21496-1 초안 표준의 새로운 파라미터를 지원하여 UltraHDR 이미지를 계속 개선하고 있습니다.
하이브리드 자동 노출
Android 16에서는 Camera2에 새로운 하이브리드 자동 노출 모드를 추가하여 노출의 특정 측면을 수동으로 제어하는 동시에 자동 노출 (AE) 알고리즘이 나머지를 처리하도록 할 수 있습니다. ISO + AE 및 노출 시간 + AE를 제어할 수 있으므로 전체 수동 제어 또는 자동 노출에 전적으로 의존하는 기존 접근 방식에 비해 더 큰 유연성을 제공합니다.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
정확한 색상 온도 및 색조 조정
Android 16에서는 전문 동영상 녹화 애플리케이션을 더 효과적으로 지원하기 위해 미세한 색온도 및 색조 조정을 위한 카메라 지원을 추가합니다. 이전 Android 버전에서는 백열, 흐림, 황혼과 같이 사전 설정 목록으로 제한된 옵션이 포함된 CONTROL_AWB_MODE를 통해 화이트 밸런스 설정을 제어할 수 있었습니다. COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT를 사용하면 COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE 및 COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT를 사용하여 상관 색상 온도에 따라 화이트 밸런스를 정확하게 조정할 수 있습니다.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
다음 예는 다양한 색온도 및 색조 조정을 적용한 후의 사진 모습을 보여줍니다.





카메라 야간 모드 장면 감지
앱이 야간 모드 카메라 세션을 전환할 시기를 알 수 있도록 Android 16에는 EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR가 추가되었습니다. 지원되는 경우 Camera2 내 CaptureResult에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
이 API는 Instagram에서 사용자가 멋진 저조도 사진을 찍을 수 있게 된 방법 블로그 게시물에서 곧 제공될 예정이라고 간단히 언급한 API입니다. 이 게시물은 야간 모드를 구현하는 방법에 관한 실용적인 가이드와 함께 인앱 카메라에서 공유되는 사진 수가 증가함에 따라 인앱 야간 모드 사진의 품질이 향상되는 사례를 보여주는 사례 연구를 제공합니다.
모션 사진 캡처 인텐트 작업
Android 16에는 카메라 애플리케이션이 모션 사진을 캡처하고 반환하도록 요청하는 표준 인텐트 작업인 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE 및 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE가 추가되었습니다.
이미지가 쓰여질 위치를 제어하기 위해 추가 EXTRA_OUTPUT를 전달하거나 Intent.setClipData(ClipData)을 통해 Uri를 전달해야 합니다. ClipData를 설정하지 않으면 Context.startActivity(Intent)를 호출할 때 자동으로 복사됩니다.
UltraHDR 이미지 개선

Android 16에서는 울트라 HDR 이미지로 눈부신 이미지 품질을 제공하기 위해 계속 노력하고 있습니다. HEIC 파일 형식의 UltraHDR 이미지 지원을 추가합니다. 이러한 이미지는 ImageFormat 유형 HEIC_ULTRAHDR을 가져오고 기존 UltraHDR JPEG 형식과 유사한 삽입된 게인맵을 포함합니다. UltraHDR에 대한 AVIF 지원도 준비 중입니다.
또한 Android 16은 획득 맵 수학이 적용되어야 하는 색상 공간을 가져오고 설정하는 기능과 SDR 획득 맵이 있는 HDR 인코딩된 기본 이미지 지원을 비롯하여 ISO 21496-1 초안 표준의 추가 매개변수를 UltraHDR에 구현합니다.
그래픽
Android 16에는 AGSL을 사용한 맞춤 그래픽 효과와 같은 최신 그래픽 개선사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
AGSL을 사용한 맞춤 그래픽 효과
Android 16에서는 RuntimeColorFilter 및 RuntimeXfermode를 추가하여 임곗값, 세피아, 색조 채도와 같은 복잡한 효과를 작성하고 그리기 호출에 적용할 수 있습니다. Android 13부터 AGSL을 사용하여 Shader를 확장하는 맞춤 RuntimeShaders를 만들 수 있었습니다. 새 API는 이를 반영하여 ColorFilter를 확장하는 AGSL 기반 RuntimeColorFilter와 소스 및 대상 픽셀 간에 AGSL 기반 맞춤 컴포지션 및 블렌딩을 구현할 수 있는 Xfermode 효과를 추가합니다.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
연결
Android 16은 앱이 최신 통신 및 무선 기술을 이용할 수 있도록 플랫폼을 업데이트합니다.
강화된 보안으로 범위 지정
Android 16은 Wi-Fi 6의 802.11az를 지원하는 기기의 Wi-Fi 위치에 강력한 보안 기능 지원을 추가합니다. 이를 통해 앱은 프로토콜의 더 높은 정확도, 확장성, 동적 예약을 AES-256 기반 암호화 및 MITM 공격 방지와 같은 보안 개선사항과 결합할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 노트북이나 차량 도어 잠금 해제와 같은 근접 사용 사례에서 더 안전하게 사용할 수 있습니다. 802.11az는 Wi-Fi 6 표준과 통합되어 인프라와 기능을 활용하여 더 광범위하게 채택하고 더 쉽게 배포할 수 있습니다.
일반 범위 지정 API
Android 16에는 로컬 기기와 원격 기기 간의 지원되는 하드웨어에서 거리와 각도를 결정하는 방법을 제공하는 새로운 RangingManager가 포함되어 있습니다. RangingManager는 BLE 채널 소리 재생, BLE RSSI 기반 측정, 초광대역, Wi-Fi 왕복 시간과 같은 다양한 측정 기술의 사용을 지원합니다.
호환 기기 관리자 기기 감지
Android 16에서는 호환 앱 서비스를 바인딩하기 위한 새로운 API가 도입됩니다. BLE가 범위 내에 있고 블루투스가 연결되어 있으면 서비스가 바인딩되고 BLE가 범위 내에 없거나 블루투스가 연결 해제되면 서비스가 바인딩 해제됩니다. 앱은 다양한 DevicePresenceEvent에 따라 새 'onDevicePresenceEvent()' 콜백을 수신합니다.
자세한 내용은 'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'를 참고하세요.
미디어
Android 16에는 미디어 환경을 개선하는 다양한 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
사진 선택 도구 개선사항
사진 선택 도구는 사용자가 전체 미디어 라이브러리가 아닌 로컬 저장소와 클라우드 저장소의 선택한 이미지 및 동영상에 대한 액세스 권한을 앱에 부여할 수 있는 안전한 내장 방법을 제공합니다. Google 시스템 업데이트 및 Google Play 서비스를 통해 모듈식 시스템 구성요소를 조합하여 사용하면 Android 4.4 (API 수준 19)까지 지원됩니다. 통합하려면 관련 Android Jetpack 라이브러리와 함께 코드 몇 줄만 있으면 됩니다.
Android 16에는 사진 선택 도구가 다음과 같이 개선되었습니다.
- 삽입된 사진 선택 도구: 앱이 사진 선택 도구를 뷰 계층 구조에 삽입할 수 있는 새로운 API입니다. 이렇게 하면 앱이 과도하게 광범위한 권한이 필요하지 않고도 사용자가 미디어를 선택할 수 있는 프로세스 격리를 활용하면서 앱의 더 통합된 부분처럼 느껴질 수 있습니다. 플랫폼 버전 간에 호환성을 극대화하고 통합을 간소화하려면 삽입된 사진 선택 도구를 통합하려는 경우 향후 Android Jetpack 라이브러리를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
- 포토 선택 도구의 Cloud Search: Android 포토 선택 도구의 클라우드 미디어 제공업체에서 검색을 사용 설정하는 새로운 API입니다. 사진 선택 도구의 검색 기능이 곧 제공될 예정입니다.
Advanced Professional Video
Android 16에서는 전문 수준의 고화질 동영상 녹화 및 후반 제작에 사용하도록 설계된 고급 전문 동영상 (APV) 코덱 지원을 도입합니다.
APV 코덱 표준에는 다음과 같은 기능이 있습니다.
- 지각적으로 무손실 동영상 화질 (원시 동영상 화질에 가깝음)
- 편집 워크플로를 더 효과적으로 지원하기 위한 낮은 복잡도와 높은 처리량의 프레임 내부 전용 코딩 (픽셀 도메인 예측 없음)
- 경량 엔트로피 코딩 스킴을 통해 2K, 4K, 8K 해상도 콘텐츠의 최대 몇 Gbps에 이르는 높은 비트 전송률 범위 지원
- 몰입형 콘텐츠를 위한 프레임 타일링 및 병렬 인코딩 및 디코딩 사용
- 다양한 크로마 샘플링 형식 및 비트 깊이 지원
- 심각한 시각적 품질 저하 없이 여러 디코딩 및 재인코딩 지원
- 멀티뷰 동영상 및 깊이, 알파, 미리보기와 같은 보조 동영상 지원
- HDR10/10+ 및 사용자 정의 메타데이터 지원
APV의 참조 구현은 OpenAPV 프로젝트를 통해 제공됩니다. Android 16에서는 10비트 인코딩과 함께 YUV 422 색상 샘플링을 제공하고 최대 2Gbps의 타겟 비트 전송률을 제공하는 APV 422-10 프로필에 대한 지원을 구현합니다.
개인정보처리방침
Android 16에는 앱 개발자가 사용자 개인 정보를 보호하는 데 도움이 되는 다양한 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
헬스 커넥트 업데이트
헬스 커넥트는 중간 및 고강도 활동에 관한 세계보건기구 가이드라인에 따라 정의된 데이터 유형인 ACTIVITY_INTENSITY를 추가합니다. 각 레코드에는 시작 시간, 종료 시간, 활동 강도가 보통인지 격렬한지 여부가 필요합니다.
헬스 커넥트에는 의료 기록을 지원하는 업데이트된 API도 포함되어 있습니다. 이를 통해 앱은 명시적인 사용자 동의를 얻어 FHIR 형식으로 의료 기록을 읽고 쓸 수 있습니다.
Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스
Android 16에는 사용자가 자신의 개인 정보가 보호된다는 사실을 알 수 있는 기술을 개발하기 위한 Google의 지속적인 노력의 일환으로 Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스의 최신 버전이 통합되어 있습니다. Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스 개발자 베타 프로그램에 대한 자세한 내용은 웹사이트를 참고하세요. SDK가 제공하는 앱과 별도의 전용 런타임 환경에서 실행되도록 허용하여 사용자 데이터 수집 및 공유를 더 강력하게 보호하는 SDK 런타임을 확인하세요.
보안
Android 16에는 앱의 보안을 강화하고 앱의 데이터를 보호하는 데 도움이 되는 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
키 공유 API
Android 16에는 Android 키 저장소 키에 대한 액세스 권한을 다른 앱과 공유하는 것을 지원하는 API가 추가되었습니다. 새 KeyStoreManager 클래스는 앱 uid의 키에 대한 액세스 권한 부여 및 취소를 지원하며 앱이 공유 키에 액세스할 수 있는 API를 포함합니다.
기기 폼 팩터
Android 16은 앱이 Android의 폼 팩터를 최대한 활용할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
TV용 표준화된 사진 및 오디오 품질 프레임워크
Android 16의 새로운 MediaQuality 패키지는 오디오 및 사진 프로필, 하드웨어 관련 설정에 액세스하기 위한 표준화된 API 모음을 노출합니다. 이를 통해 스트리밍 앱은 프로필을 쿼리하고 미디어에 동적으로 적용할 수 있습니다.
- 더 넓은 다이나믹 레인지로 마스터링된 영화는 어두운 부분의 미묘한 디테일을 확인하고 주변광에 맞게 조정하려면 더 높은 색상 정확도가 필요하므로 밝기보다 색상 정확도를 선호하는 프로필이 적합할 수 있습니다.
- 라이브 스포츠 이벤트는 종종 협소한 다이내믹 레인지로 마스터링되지만, 햇빛이 비치는 낮에 시청되는 경우가 많으므로 색상 정확성보다 밝기를 선호하는 프로필을 사용하면 더 나은 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
- 완전히 양방향인 콘텐츠는 지연 시간을 줄이기 위해 최소한의 처리가 필요하고 프레임 속도가 더 높아야 하므로 많은 TV에 게임 프로필이 제공됩니다.
이 API를 사용하면 앱이 프로필 간에 전환하고 사용자는 지원되는 TV를 콘텐츠에 가장 적합하게 조정할 수 있습니다.
다국어 지원
Android 16에서는 기기가 여러 언어로 사용될 때 사용자 환경을 보완하는 기능이 추가되었습니다.
세로 텍스트
Android 16은 텍스트를 세로로 렌더링하고 측정하기 위한 하위 수준 지원을 추가하여 라이브러리 개발자를 위한 기본적인 세로 쓰기 지원을 제공합니다. 이는 일반적으로 세로 쓰기 시스템을 사용하는 일본어와 같은 언어에 특히 유용합니다. Paint 클래스에 새로운 플래그인 VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG가 추가되었습니다. 이 플래그가 Paint.setFlags를 사용하여 설정되면 Paint의 텍스트 측정 API는 가로 진행 대신 세로 진행을 보고하고 Canvas는 텍스트를 세로로 그립니다.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
측정 시스템 맞춤설정
이제 사용자는 설정의 지역 설정에서 측정 시스템을 맞춤설정할 수 있습니다. 사용자 환경설정은 언어 코드의 일부로 포함되므로 ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED에 BroadcastReceiver를 등록하여 지역 설정이 변경될 때 언어 구성 변경을 처리할 수 있습니다.
형식 지정자를 사용하면 로컬 환경에 맞게 조정할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 영어 (미국)로 '0.5인치'는 휴대전화를 영어 (덴마크)로 설정했거나 측정 시스템 환경설정으로 미터법을 사용하는 영어 (미국)로 휴대전화를 사용하는 사용자에게는 '12,7mm'입니다.
이러한 설정을 찾으려면 설정 앱을 열고 시스템 > 언어 및 지역으로 이동하세요.
