Android 16 플랫폼에는 앱에 영향을 줄 수 있는 동작 변경사항이 있습니다. targetSdkVersion과 관계없이 Android 16에서 실행되는 모든 앱에 적용되는 동작 변경사항은 다음과 같습니다. 이러한 변경사항을 적절히 지원해야 하는 경우 앱을 테스트한 후 필요에 따라 수정해야 합니다.
또한 Android 16을 타겟팅하는 앱에만 영향을 주는 동작 변경사항 목록을 검토해야 합니다.
핵심 기능
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 Android 시스템의 다양한 핵심 기능을 수정하거나 확장하는 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
JobScheduler 할당량 최적화
Starting in Android 16, we're adjusting regular and expedited job execution runtime quota based on the following factors:
- Which app standby bucket the application is in: in Android 16, active standby buckets will start being enforced by a generous runtime quota.
- If the job starts execution while the app is in a top state: in Android 16, Jobs started while the app is visible to the user and continues after the app becomes invisible, will adhere to the job runtime quota.
- If the job is executing while running a Foreground Service: in Android 16, jobs that are executing concurrently with a foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota. If you're leveraging jobs for user initiated data transfer, consider using user initiated data transfer jobs instead.
This change impacts tasks scheduled using WorkManager, JobScheduler, and
DownloadManager. To debug why a job was stopped, we recommend logging why your
job was stopped by calling WorkInfo.getStopReason() (for
JobScheduler jobs, call JobParameters.getStopReason()).
For information about how your app's state affects the resources it can use, see Power management resource limits. For more information on battery-optimal best practices, refer to guidance on optimize battery use for task scheduling APIs.
We also recommend leveraging the new
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API introduced in
Android 16 to understand why a job has not executed.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable override of certain job quota optimizations as long as the app is running on an Android 16 device.
To disable enforcement of "top state will adhere to job runtime quota", run the
following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To disable enforcement of "jobs that are executing while concurrently with a
foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota", run the following
adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To test certain app standby bucket behavior, you can set the app standby bucket
of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
To understand the app standby bucket your app is in, you can get the app standby
bucket of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
비어 있는 작업 중지 이유가 삭제됨
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground 완전히 지원 중단
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) 메서드는 예약 앱이 포그라운드에 있거나 일시적으로 백그라운드 제한사항에서 제외된 경우 작업의 중요도를 나타냅니다.
이 메서드는 Android 12 (API 수준 31)부터 지원 중단되었습니다. Android 16부터는 더 이상 효과적으로 작동하지 않으며 이 메서드를 호출해도 무시됩니다.
이 기능 삭제는 JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground()에도 적용됩니다. Android 16부터 메서드가 호출되면 메서드는 false를 반환합니다.
순서가 지정된 브로드캐스트 우선순위 범위가 더 이상 전역이 아님
Android apps are allowed to define priorities on broadcast receivers to control
the order in which the receivers receive and process the broadcast. For
manifest-declared receivers, apps can use the
android:priority attribute to define the priority and for
context-registered receivers, apps can use the
IntentFilter#setPriority() API to define the priority. When
a broadcast is sent, the system delivers it to receivers in order of their
priority, from highest to lowest.
In Android 16, broadcast delivery order using the android:priority attribute
or IntentFilter#setPriority() across different processes will not be
guaranteed. Broadcast priorities will only be respected within the same
application process rather than across all processes.
Also, broadcast priorities will be automatically confined to the range
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Only system components will be
allowed to set SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY as broadcast
priority.
Your app might be impacted if it does either of the following:
- Your application has declared multiple processes with the same broadcast intent, and has expectations around receiving those intents in a certain order based on the priority.
- Your application process interacts with other processes and has expectations around receiving a broadcast intent in a certain order.
If the processes need to coordinate with each other, they should communicate using other coordination channels.
ART 내부 변경사항
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
16KB 페이지 크기 호환성 모드
Android 15에서는 플랫폼의 성능을 최적화하기 위해 16KB 메모리 페이지 지원을 도입했습니다. Android 16에서는 4KB 메모리 페이지용으로 빌드된 일부 앱이 16KB 메모리 페이지용으로 구성된 기기에서 실행될 수 있도록 하는 호환성 모드를 추가합니다.
앱이 Android 16 이상을 실행하는 기기에서 실행 중일 때 Android에서 앱에 4KB 정렬 메모리 페이지가 있음을 감지하면 자동으로 호환성 모드를 사용하고 사용자에게 알림 대화상자를 표시합니다. AndroidManifest.xml에서 android:pageSizeCompat 속성을 설정하여 이전 버전과의 호환성 모드를 사용 설정하면 앱이 실행될 때 대화상자가 표시되지 않습니다. android:pageSizeCompat 속성을 사용하려면 Android 16 SDK를 사용하여 앱을 컴파일하세요.
최상의 성능, 안정성, 안정성을 위해 앱은 계속 16KB 정렬되어야 합니다. 16KB 메모리 페이지를 지원하도록 앱을 업데이트하는 방법에 관한 최근 블로그 게시물을 참고하세요.
사용자 경험 및 시스템 UI
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 더 일관되고 직관적인 사용자 환경을 만들기 위한 다음 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
방해가 되는 접근성 안내 지원 중단
Android 16 deprecates accessibility announcements, characterized by the use of
announceForAccessibility or the dispatch of
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT accessibility events. These can create
inconsistent user experiences for users of TalkBack and Android's screen reader,
and alternatives better serve a broader range of user needs across a variety of
Android's assistive technologies.
Examples of alternatives:
- For significant UI changes like window changes, use
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)andsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - To inform the user of changes to critical UI, use
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. These should be used sparingly as they may generate announcements every time a View is updated. - To notify users about errors, send an
AccessibilityEventof typeAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORand setAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), or useTextView#setError(CharSequence).
The reference documentation for the deprecated
announceForAccessibility API includes more details about
suggested alternatives.
3버튼 탐색 지원
Android 16 brings predictive back support to the 3-button navigation for apps that have properly migrated to predictive back. Long-pressing the back button initiates a predictive back animation, giving you a preview of where the back swipe takes you.
This behavior applies across all areas of the system that support predictive back animations, including the system animations (back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity).
자동 테마 앱 아이콘
Beginning with Android 16 QPR 2, Android automatically applies themes to app icons to create a cohesive home screen experience. This occurs if an app does not provide its own themed app icon. Apps can control the design of their themed app icon by including a monochrome layer within their adaptive icon and previewing what their app icon will look like in Android Studio.
기기 폼 팩터
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 가상 기기 소유자가 디스플레이에 투영할 때 앱에 적용되는 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
가상 기기 소유자 재정의
가상 기기 소유자는 가상 기기를 만들고 관리하는 신뢰할 수 있는 앱 또는 권한이 있는 앱입니다. 가상 기기 소유자는 가상 기기에서 앱을 실행한 다음 개인용 컴퓨터, 가상 현실 기기, 자동차 인포테인먼트 시스템과 같은 원격 기기의 디스플레이에 앱을 투영합니다. 가상 기기 소유자는 휴대전화와 같은 로컬 기기에 있습니다.
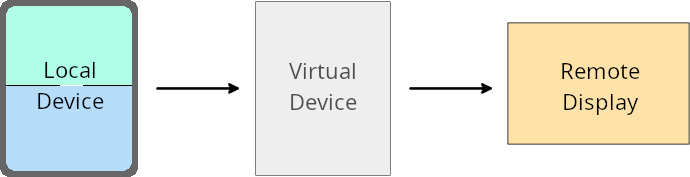
앱별 재정의
Android 16 (API 레벨 36)을 실행하는 기기에서 가상 기기 소유자는 가상 기기 소유자가 관리하는 일부 가상 기기의 앱 설정을 재정의할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 앱 레이아웃을 개선하기 위해 가상 기기 소유자는 앱을 외부 디스플레이에 투영할 때 방향, 가로세로 비율, 크기 조절 제한을 무시할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 주요 변경사항
Android 16 동작은 자동차 디스플레이나 Chromebook과 같은 대형 화면 폼 팩터의 앱 UI에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 특히 세로 방향의 소형 디스플레이용으로 설계된 레이아웃의 경우 더욱 그렇습니다. 모든 기기 폼 팩터에 맞게 앱을 적응형으로 만드는 방법을 알아보려면 적응형 레이아웃 정보를 참고하세요.
참조
보안
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 악성 앱으로부터 앱과 사용자를 보호하는 데 도움이 되는 시스템 보안을 촉진하는 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
인텐트 리디렉션 공격에 대한 보안 개선
Android 16 provides default security against general Intent redirection
attacks, with minimum compatibility and developer changes required.
We are introducing by-default security hardening solutions to Intent
redirection exploits. In most cases, apps that use intents normally won't
experience any compatibility issues; we've gathered metrics throughout our
development process to monitor which apps might experience breakages.
Intent redirection in Android occurs when an attacker can partly or fully control the contents of an intent used to launch a new component in the context of a vulnerable app, while the victim app launches an untrusted sub-level intent in an extras field of an ("top-level") Intent. This can lead to the attacker app launching private components in the context of the victim app, triggering privileged actions, or gaining URI access to sensitive data, potentially leading to data theft and arbitrary code execution.
Opt out of Intent redirection handling
Android 16 introduces a new API that allows apps to opt out of launch security protections. This might be necessary in specific cases where the default security behavior interferes with legitimate app use cases.
For applications compiling against Android 16 (API level 36) SDK or higher
You can directly use the removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method on the Intent
object.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
For applications compiling against Android 15 (API level 35) or lower
While not recommended, you can use reflection to access the
removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
호환 앱에 더 이상 검색 시간 제한 알림이 전송되지 않음
Android 16 introduces a new behavior during
companion device pairing flow to protect the user's location
privacy from malicious apps. All companion apps running on Android 16 are no
longer directly notified of discovery timeout using
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Instead, the user is
notified of timeout events with a visual dialog. When the user dismisses
the dialog, the app is alerted of the association failure with
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
The search duration has also been extended from the original 20 seconds, and the device discovery can be stopped by the user at any point during the search. If at least one device was discovered within the first 20 seconds of starting the search, the CDM stops searching for additional devices.
연결
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 주변기기와의 연결을 개선하기 위해 블루투스 스택에 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
결합 손실 처리 개선
Starting in Android 16, the Bluetooth stack has been updated to improve security and user experience when a remote bond loss is detected. Previously, the system would automatically remove the bond and initiate a new pairing process, which could lead to unintentional re-pairing. We have seen in many instances apps not taking care of the bond loss event in a consistent way.
To unify the experience, Android 16 improved the bond loss handling to the system. If a previously bonded Bluetooth device could not be authenticated upon reconnection, the system will disconnect the link, retain local bond information, and display a system dialog informing users of the bond loss and directing them to re-pair.
