La classe AndroidJUnitRunner est un exécuteur de test JUnit qui vous permet d'exécuter des tests JUnit 4 instrumentés sur des appareils Android, y compris ceux qui utilisent les frameworks de test Espresso, UI Automator et Compose.
Le lanceur de test gère le chargement de votre package de test et de l'application testée sur un appareil, l'exécution de vos tests et la création de rapports sur les résultats des tests.
Ce lanceur de tests prend en charge plusieurs tâches de test courantes, y compris les suivantes:
Écrire des tests JUnit
L'extrait de code suivant montre comment écrire un test JUnit 4 instrumenté pour vérifier que l'opération changeText de la classe ChangeTextBehavior fonctionne correctement:
Kotlin
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class) @LargeTest // Optional runner annotation class ChangeTextBehaviorTest { val stringToBeTyped = "Espresso" // ActivityTestRule accesses context through the runner @get:Rule val activityRule = ActivityTestRule(MainActivity::class.java) @Test fun changeText_sameActivity() { // Type text and then press the button. onView(withId(R.id.editTextUserInput)) .perform(typeText(stringToBeTyped), closeSoftKeyboard()) onView(withId(R.id.changeTextBt)).perform(click()) // Check that the text was changed. onView(withId(R.id.textToBeChanged)) .check(matches(withText(stringToBeTyped))) } }
Java
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class) @LargeTest // Optional runner annotation public class ChangeTextBehaviorTest { private static final String stringToBeTyped = "Espresso"; @Rule public ActivityTestRule<MainActivity>; activityRule = new ActivityTestRule<>;(MainActivity.class); @Test public void changeText_sameActivity() { // Type text and then press the button. onView(withId(R.id.editTextUserInput)) .perform(typeText(stringToBeTyped), closeSoftKeyboard()); onView(withId(R.id.changeTextBt)).perform(click()); // Check that the text was changed. onView(withId(R.id.textToBeChanged)) .check(matches(withText(stringToBeTyped))); } }
Accéder au contexte de l'application
Lorsque vous utilisez AndroidJUnitRunner pour exécuter vos tests, vous pouvez accéder au contexte de l'application testée en appelant la méthode statique ApplicationProvider.getApplicationContext(). Si vous avez créé une sous-classe personnalisée de Application dans votre application, cette méthode renvoie le contexte de votre sous-classe personnalisée.
Si vous êtes un implémentateur d'outils, vous pouvez accéder aux API de test de bas niveau à l'aide de la classe InstrumentationRegistry. Cette classe inclut l'objet Instrumentation, l'objet Context de l'application cible, l'objet Context de l'application de test et les arguments de ligne de commande transmis à votre test.
Filtrer les tests
Dans vos tests JUnit 4.x, vous pouvez utiliser des annotations pour configurer l'exécution des tests. Cette fonctionnalité réduit le besoin d'ajouter du code récurrent et conditionnel dans vos tests. En plus des annotations standards compatibles avec JUnit 4, l'exécuteur de test accepte également les annotations spécifiques à Android, y compris les suivantes:
@RequiresDevice: spécifie que le test ne doit s'exécuter que sur des appareils physiques, et non sur des émulateurs.@SdkSuppress: empêche l'exécution du test sur un niveau d'API Android inférieur au niveau donné. Par exemple, pour empêcher l'exécution des tests sur tous les niveaux d'API inférieurs à 23, utilisez l'annotation@SDKSuppress(minSdkVersion=23).@SmallTest,@MediumTestet@LargeTest: classifiez la durée d'exécution d'un test et, par conséquent, la fréquence à laquelle vous pouvez l'exécuter. Vous pouvez utiliser cette annotation pour filtrer les tests à exécuter en définissant la propriétéandroid.testInstrumentationRunnerArguments.size:
-Pandroid.testInstrumentationRunnerArguments.size=small
Tests de fragmentation
Si vous devez paralléliser l'exécution de vos tests, en les partageant sur plusieurs serveurs pour les exécuter plus rapidement, vous pouvez les diviser en groupes ou en fragments. Le lanceur de test permet de diviser une seule suite de tests en plusieurs segments. Vous pouvez ainsi exécuter facilement les tests appartenant au même segment en tant que groupe. Chaque fragment est identifié par un numéro d'index. Lorsque vous exécutez des tests, utilisez l'option -e numShards pour spécifier le nombre de partitions distinctes à créer et l'option -e shardIndex pour spécifier la partition à exécuter.
Par exemple, pour diviser la suite de tests en 10 fragments et n'exécuter que les tests regroupés dans le deuxième fragment, utilisez la commande adb suivante:
adb shell am instrument -w -e numShards 10 -e shardIndex 2
Utiliser Android Test Orchestrator
Android Test Orchestrator vous permet d'exécuter chacun des tests de votre application dans son propre appel de Instrumentation. Lorsque vous utilisez AndroidJUnitRunner version 1.0 ou ultérieure, vous avez accès à Android Test Orchestrator.
Android Test Orchestrator offre les avantages suivants pour votre environnement de test:
- État partagé minimal:chaque test s'exécute dans sa propre instance
Instrumentation. Par conséquent, si vos tests partagent l'état de l'application, la majeure partie de cet état partagé est supprimée du processeur ou de la mémoire de votre appareil après chaque test. Pour supprimer tout état partagé du processeur et de la mémoire de votre appareil après chaque test, utilisez l'indicateurclearPackageData. Pour obtenir un exemple, consultez la section Activer depuis Gradle. - Les plantages sont isolés:même si un test plante, il ne supprime que sa propre instance de
Instrumentation. Cela signifie que les autres tests de votre suite s'exécutent toujours, ce qui fournit des résultats de test complets.
Cette isolation peut entraîner une augmentation du temps d'exécution des tests, car Android Test Orchestrator redémarre l'application après chaque test.
Android Studio et Firebase Test Lab sont tous deux préinstallés avec Android Test Orchestrator, mais vous devez activer cette fonctionnalité dans Android Studio.
Activer depuis Gradle
Pour activer Android Test Orchestrator à l'aide de l'outil de ligne de commande Gradle, procédez comme suit:
- Étape 1: Modifiez le fichier Gradle. Ajoutez les instructions suivantes au fichier
build.gradlede votre projet:
android {
defaultConfig {
...
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
// The following argument makes the Android Test Orchestrator run its
// "pm clear" command after each test invocation. This command ensures
// that the app's state is completely cleared between tests.
testInstrumentationRunnerArguments clearPackageData: 'true'
}
testOptions {
execution 'ANDROIDX_TEST_ORCHESTRATOR'
}
}
dependencies {
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test:runner:1.1.0'
androidTestUtil 'androidx.test:orchestrator:1.1.0'
}
- Étape 2: Exécutez Android Test Orchestrator en exécutant la commande suivante:
./gradlew connectedCheck
Activer depuis Android Studio
Pour activer Android Test Orchestrator dans Android Studio, ajoutez les instructions indiquées dans Activer depuis Gradle au fichier build.gradle de votre application.
Activer à partir de la ligne de commande
Pour utiliser Android Test Orchestrator sur la ligne de commande, exécutez les commandes suivantes dans une fenêtre de terminal:
DEVICE_API_LEVEL=$(adb shell getprop ro.build.version.sdk)
FORCE_QUERYABLE_OPTION=""
if [[ $DEVICE_API_LEVEL -ge 30 ]]; then
FORCE_QUERYABLE_OPTION="--force-queryable"
fi
# uninstall old versions
adb uninstall androidx.test.services
adb uninstall androidx.test.orchestrator
# Install the test orchestrator.
adb install $FORCE_QUERYABLE_OPTION -r path/to/m2repository/androidx/test/orchestrator/1.4.2/orchestrator-1.4.2.apk
# Install test services.
adb install $FORCE_QUERYABLE_OPTION -r path/to/m2repository/androidx/test/services/test-services/1.4.2/test-services-1.4.2.apk
# Replace "com.example.test" with the name of the package containing your tests.
# Add "-e clearPackageData true" to clear your app's data in between runs.
adb shell 'CLASSPATH=$(pm path androidx.test.services) app_process / \
androidx.test.services.shellexecutor.ShellMain am instrument -w -e \
targetInstrumentation com.example.test/androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner \
androidx.test.orchestrator/.AndroidTestOrchestrator'
Comme le montre la syntaxe de la commande, vous installez Android Test Orchestrator, puis vous l'utilisez directement.
adb shell pm list instrumentation
Utiliser différentes chaînes d'outils
Si vous utilisez une autre chaîne d'outils pour tester votre application, vous pouvez toujours utiliser Android Test Orchestrator en procédant comme suit:
- Incluez les packages nécessaires dans le fichier de compilation de votre application.
- Activez Android Test Orchestrator à partir de la ligne de commande.
Architecture
L'APK du service Orchestrator est stocké dans un processus distinct de l'APK de test et de l'APK de l'application testée:
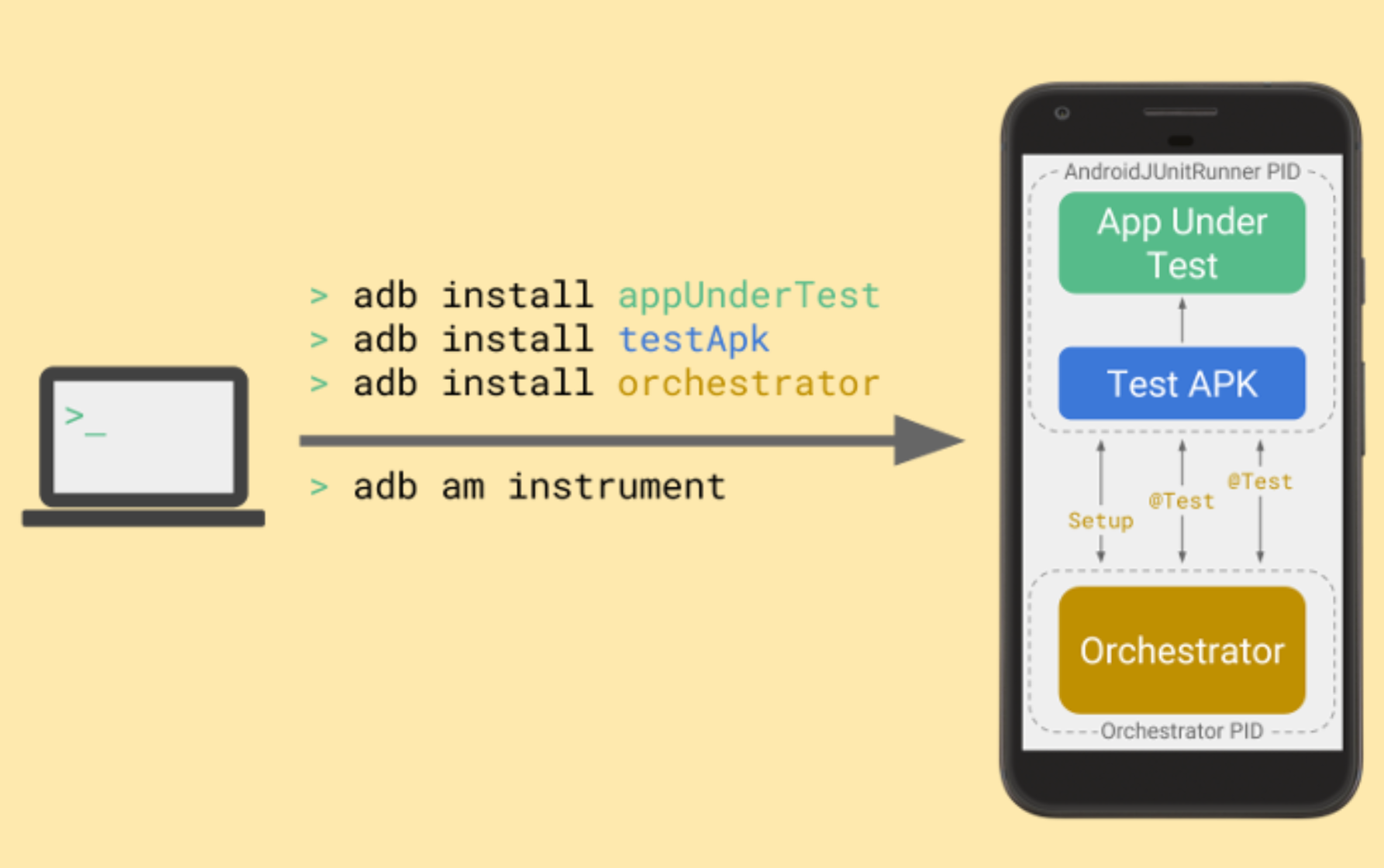
Android Test Orchestrator collecte les tests JUnit au début de l'exécution de votre suite de tests, mais il exécute ensuite chaque test séparément, dans sa propre instance de Instrumentation.
Plus d'informations
Pour en savoir plus sur l'utilisation d'AndroidJUnitRunner, consultez la documentation de référence de l'API.
Ressources supplémentaires
Pour en savoir plus sur l'utilisation de AndroidJUnitRunner, consultez les ressources suivantes.
Exemples
- AndroidJunitRunnerSample: présente les annotations de test, les tests paramétrés et la création de suites de tests.
