এই পৃষ্ঠাটি বর্ণনা করে যে কীভাবে ম্যানিফেস্ট মার্জিং কাজ করে এবং কীভাবে আপনি মার্জ দ্বন্দ্বগুলি সমাধান করতে মার্জ পছন্দগুলি প্রয়োগ করতে পারেন৷ অ্যাপ ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলের ভূমিকার জন্য, অ্যাপ ম্যানিফেস্ট ওভারভিউ দেখুন।
একাধিক ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল মার্জ করুন
আপনার APK বা Android App Bundle ফাইলে শুধুমাত্র একটি AndroidManifest.xml ফাইল থাকতে পারে, কিন্তু আপনার Android স্টুডিও প্রোজেক্টে মূল উৎস সেট, বিল্ড ভেরিয়েন্ট এবং আমদানি করা লাইব্রেরি দ্বারা প্রদত্ত বেশ কয়েকটি ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল থাকতে পারে। আপনার অ্যাপ তৈরি করার সময়, গ্রেডল বিল্ড সমস্ত ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলকে আপনার অ্যাপে প্যাকেজ করা একটি একক ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলে একত্রিত করে।
ম্যানিফেস্ট মার্জার টুলটি মার্জ হিউরিস্টিকস অনুসরণ করে এবং আপনি বিশেষ XML অ্যাট্রিবিউটের সাথে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা মার্জ পছন্দগুলি মেনে প্রতিটি ফাইলের সমস্ত XML উপাদানকে একত্রিত করে৷
টিপ: আপনার মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টের ফলাফলগুলির পূর্বরূপ দেখতে এবং দ্বন্দ্ব ত্রুটিগুলি খুঁজে পেতে নিম্নলিখিত বিভাগে বর্ণিত মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ভিউ ব্যবহার করুন৷
অগ্রাধিকার একত্রীকরণ
মার্জার টুলটি প্রতিটি ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলের অগ্রাধিকারের উপর ভিত্তি করে ক্রমানুসারে একটি ফাইলে সমস্ত ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলকে একত্রিত করে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি আপনার তিনটি ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল থাকে, তাহলে সর্বনিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টটি পরবর্তী-সর্বোচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে মার্জ করা হয় এবং তারপর সেটি সর্বোচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে মার্জ করা হয়, যেমন চিত্র 1-এ দেখানো হয়েছে।
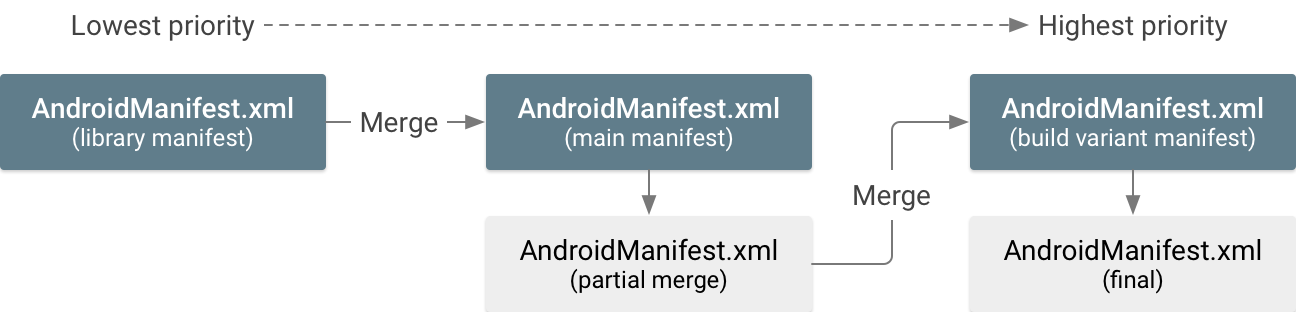
তিনটি মৌলিক ধরণের ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল রয়েছে যেগুলি একে অপরের সাথে মার্জ করা যেতে পারে এবং তাদের মার্জ অগ্রাধিকারগুলি নিম্নরূপ (প্রথমে সর্বোচ্চ অগ্রাধিকার):
- আপনার বিল্ড বৈকল্পিক জন্য ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল
আপনার ভেরিয়েন্টের জন্য একাধিক সোর্স সেট থাকলে, তাদের প্রকাশ্য অগ্রাধিকারগুলি নিম্নরূপ:
- বৈকল্পিক ম্যানিফেস্ট তৈরি করুন (যেমন
src/demoDebug/) - বিল্ড টাইপ ম্যানিফেস্ট (যেমন
src/debug/) - পণ্যের স্বাদ ম্যানিফেস্ট (যেমন
src/demo/)আপনি যদি ফ্লেভার ডাইমেনশন ব্যবহার করেন, তাহলে ম্যানিফেস্ট অগ্রাধিকারগুলি
flavorDimensionsপ্রপার্টিতে (প্রথম হল সর্বোচ্চ অগ্রাধিকার) তালিকাভুক্ত প্রতিটি মাত্রার ক্রম অনুসারে।
- বৈকল্পিক ম্যানিফেস্ট তৈরি করুন (যেমন
- অ্যাপ মডিউলের জন্য প্রধান ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল
- একটি অন্তর্ভুক্ত লাইব্রেরি থেকে ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল
আপনার যদি একাধিক লাইব্রেরি থাকে, তাহলে তাদের ম্যানিফেস্ট অগ্রাধিকারগুলি আপনার Gradle
dependenciesব্লকে প্রদর্শিত ক্রম অনুসারে মেলে।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, একটি লাইব্রেরি ম্যানিফেস্ট প্রধান ম্যানিফেস্টে একত্রিত হয়, তারপর প্রধান ম্যানিফেস্ট বিল্ড ভেরিয়েন্ট ম্যানিফেস্টে একত্রিত হয়। মনে রাখবেন যে এইগুলি সমস্ত উৎস সেটের জন্য একই মার্জ অগ্রাধিকার, যেমনটি বিল্ড উইথ সোর্স সেটে বর্ণিত হয়েছে।
গুরুত্বপূর্ণ: build.gradle ফাইল থেকে বিল্ড কনফিগারেশনগুলি মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলের যেকোনো সংশ্লিষ্ট বৈশিষ্ট্যকে ওভাররাইড করে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, build.gradle বা build.gradle.kts ফাইল থেকে minSdk <uses-sdk> ম্যানিফেস্ট এলিমেন্টে মিলে যাওয়া বৈশিষ্ট্যটিকে ওভাররাইড করে। বিভ্রান্তি এড়াতে, <uses-sdk> উপাদানটি ছেড়ে দিন এবং শুধুমাত্র build.gradle ফাইলে এই বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি সংজ্ঞায়িত করুন। আরো বিস্তারিত জানার জন্য, আপনার বিল্ড কনফিগার করুন দেখুন।
দ্বন্দ্ব হিউরিস্টিকস মার্জ করুন
মার্জার টুল যৌক্তিকভাবে প্রতিটি XML উপাদানকে একটি ম্যানিফেস্ট থেকে অন্য একটি ম্যানিফেস্টের সংশ্লিষ্ট উপাদানের সাথে মেলাতে পারে। মিল কীভাবে কাজ করে সে সম্পর্কে বিশদ বিবরণের জন্য, পূর্ববর্তী বিভাগে মার্জ অগ্রাধিকারগুলি দেখুন।
যদি নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের একটি উপাদান উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের কোনো উপাদানের সাথে মেলে না, তাহলে এটি মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টে যোগ করা হয়। যাইহোক, যদি একটি ম্যাচিং এলিমেন্ট থাকে, তাহলে মার্জার টুলটি প্রত্যেকটি থেকে একই এলিমেন্টে সমস্ত অ্যাট্রিবিউটকে একত্রিত করার চেষ্টা করে। যদি টুলটি দেখতে পায় যে উভয় ম্যানিফেস্টে ভিন্ন মানের সাথে একই বৈশিষ্ট্য রয়েছে, তাহলে একটি মার্জ বিরোধ দেখা দেয়।
সারণি 1 সম্ভাব্য ফলাফলগুলি চিত্রিত করে যখন মার্জার টুল একই উপাদানের মধ্যে সমস্ত বৈশিষ্ট্য একত্রিত করার চেষ্টা করে।
সারণি 1. বৈশিষ্ট্য মানগুলির জন্য ডিফল্ট মার্জ আচরণ
| উচ্চ অগ্রাধিকার বৈশিষ্ট্য | নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার বৈশিষ্ট্য | অ্যাট্রিবিউটের মার্জ ফলাফল |
|---|---|---|
| কোন মূল্য নেই | কোন মূল্য নেই | কোন মান নেই (ডিফল্ট মান ব্যবহার করুন) |
| মান বি | মান বি | |
| মান ক | কোন মূল্য নেই | মান ক |
| মান ক | মান ক | |
| মান বি | দ্বন্দ্ব ত্রুটি — আপনাকে অবশ্যই একটি মার্জ নিয়ম মার্কার যোগ করতে হবে। |
যাইহোক, এমন কিছু পরিস্থিতিতে রয়েছে যেখানে একত্রীকরণ দ্বন্দ্ব এড়াতে মার্জার টুল ভিন্নভাবে আচরণ করে:
-
<manifest>উপাদানের বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি কখনই একত্রিত হয় না; শুধুমাত্র সর্বোচ্চ অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি ব্যবহার করা হয়৷ -
<uses-feature>এবং<uses-library>উপাদানগুলির মধ্যেandroid:requiredবৈশিষ্ট্য একটি OR মার্জ ব্যবহার করে। যদি একটি বিরোধ থাকে,"true"প্রয়োগ করা হয় এবং একটি ম্যানিফেস্টের জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় বৈশিষ্ট্য বা লাইব্রেরি সর্বদা অন্তর্ভুক্ত করা হয়। -
<uses-sdk>উপাদানের বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি সর্বদা উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট থেকে মান ব্যবহার করে, নিম্নলিখিত পরিস্থিতিতে ছাড়া:- যখন নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে একটি
minSdkমান বেশি থাকে, আপনিoverrideLibraryমার্জ নিয়ম প্রয়োগ না করলে একটি ত্রুটি ঘটে। - যখন নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের একটি
targetSdkVersionমান কম থাকে, তখন মার্জার টুল উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের মান ব্যবহার করে এবং এটি আমদানি করা লাইব্রেরি সঠিকভাবে কাজ করা নিশ্চিত করার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় যে কোনও সিস্টেম অনুমতি যোগ করে (যে ক্ষেত্রে উচ্চতর Android সংস্করণে অনুমতি সীমাবদ্ধতা বেড়েছে)। এই আচরণ সম্পর্কে আরও তথ্যের জন্য, অন্তর্নিহিত সিস্টেম অনুমতি সম্পর্কে বিভাগটি দেখুন।
- যখন নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে একটি
-
<intent-filter>উপাদানটি ম্যানিফেস্টের মধ্যে মেলে না। প্রতিটিকে অনন্য হিসাবে বিবেচনা করা হয় এবং মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টে সাধারণ মূল উপাদানে যোগ করা হয়।
বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলির মধ্যে অন্যান্য সমস্ত বিরোধের জন্য, আপনি একটি ত্রুটি পেয়েছেন এবং আপনাকে অবশ্যই উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলে একটি বিশেষ বৈশিষ্ট্য যোগ করে এটিকে কীভাবে সমাধান করতে হবে তা মার্জার টুলকে নির্দেশ দিতে হবে৷ মার্জ রুল মার্কার সম্পর্কে নিম্নলিখিত বিভাগটি দেখুন।
ডিফল্ট বৈশিষ্ট্য মান উপর নির্ভর করবেন না. যেহেতু সমস্ত অনন্য বৈশিষ্ট্য একই উপাদানের সাথে একত্রিত করা হয়েছে, তাই এটি অপ্রত্যাশিত ফলাফলের কারণ হতে পারে যদি উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট প্রকৃতপক্ষে একটি অ্যাট্রিবিউট ঘোষণা না করে তার ডিফল্ট মানের উপর নির্ভর করে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট android:launchMode অ্যাট্রিবিউট ঘোষণা না করে, তাহলে এটি "standard" -এর ডিফল্ট মান ব্যবহার করে —কিন্তু যদি নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট এই বৈশিষ্ট্যটিকে একটি ভিন্ন মান দিয়ে ঘোষণা করে, তাহলে সেই মানটি মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টে প্রয়োগ করা হয়, যা ডিফল্ট মানটিকে ওভাররাইড করে। আপনি স্পষ্টভাবে প্রতিটি বৈশিষ্ট্য আপনি এটি হতে চান হিসাবে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা উচিত. প্রতিটি অ্যাট্রিবিউটের জন্য ডিফল্ট মান ম্যানিফেস্ট রেফারেন্সে নথিভুক্ত করা হয়।
নিয়ম মার্কার মার্জ
একটি মার্জ রুল মার্কার হল একটি XML অ্যাট্রিবিউট যা আপনি কীভাবে মার্জ দ্বন্দ্বগুলি সমাধান করবেন বা অবাঞ্ছিত উপাদান এবং বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি সরাতে হবে সে সম্পর্কে আপনার পছন্দ প্রকাশ করতে ব্যবহার করতে পারেন৷ আপনি একটি সম্পূর্ণ উপাদান বা একটি উপাদানের শুধুমাত্র নির্দিষ্ট বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলিতে একটি মার্কার প্রয়োগ করতে পারেন।
দুটি ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল মার্জ করার সময়, মার্জার টুল উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলে এই মার্কারগুলির জন্য সন্ধান করে।
সমস্ত চিহ্নিতকারী Android tools নেমস্পেসের অন্তর্গত, তাই আপনাকে প্রথমে <manifest> উপাদানে এই নামস্থানটি ঘোষণা করতে হবে, যেমনটি এখানে দেখানো হয়েছে:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.myapp" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
নোড মার্কার
একটি সম্পূর্ণ XML উপাদানে একটি মার্জ নিয়ম প্রয়োগ করতে (একটি প্রদত্ত ম্যানিফেস্ট উপাদানের সমস্ত বৈশিষ্ট্য এবং এর সমস্ত চাইল্ড ট্যাগগুলিতে), নিম্নলিখিত বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি ব্যবহার করুন:
-
tools:node="merge" - মার্জ কনফ্লিক্ট হিউরিস্টিকস ব্যবহার করে কোনো দ্বন্দ্ব না থাকলে এই ট্যাগের সমস্ত বৈশিষ্ট্য এবং নেস্টেড উপাদানগুলিকে মার্জ করুন৷ এটি উপাদানগুলির জন্য ডিফল্ট আচরণ।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity>
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait" tools:node="merge"> </activity>
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity>
tools:node="mergeOnlyAttributes"- শুধুমাত্র এই ট্যাগে গুণাবলী মার্জ করুন; নেস্টেড উপাদান একত্রিত করবেন না।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" /> <data android:type="image/*" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity>
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait" tools:node="mergeOnlyAttributes"> </activity>
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged"> </activity>
tools:node="remove"- মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্ট থেকে এই উপাদানটি সরান। যখন আপনি আপনার মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্টে এমন একটি উপাদান আবিষ্কার করেন যেটি আপনার নিয়ন্ত্রণের বাইরে (যেমন একটি আমদানি করা লাইব্রেরি) একটি নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল দ্বারা সরবরাহ করা প্রয়োজন নেই তখন ব্যবহার করা হয়।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> <meta-data android:name="cow" android:value="@string/moo"/> <meta-data android:name="duck" android:value="@string/quack"/> </activity-alias>
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> <meta-data android:name="cow" tools:node="remove"/> </activity-alias>
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> <meta-data android:name="duck" android:value="@string/quack"/> </activity-alias>
-
tools:node="removeAll" -
tools:node="remove"এর মতো, কিন্তু এটি এই উপাদানের প্রকারের সাথে মিলে যাওয়া সমস্ত উপাদানকে সরিয়ে দেয় (একই মূল উপাদানের মধ্যে)।নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> <meta-data android:name="cow" android:value="@string/moo"/> <meta-data android:name="duck" android:value="@string/quack"/> </activity-alias>
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> <meta-data tools:node="removeAll"/> </activity-alias>
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> </activity-alias> -
tools:node="replace" - নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার উপাদান সম্পূর্ণরূপে প্রতিস্থাপন করুন। অর্থাৎ, যদি নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে একটি মিলে যাওয়া উপাদান থাকে, তাহলে তা উপেক্ষা করুন এবং এই ম্যানিফেস্টে যেভাবে দেখা যাচ্ছে ঠিক সেইভাবে এই উপাদানটি ব্যবহার করুন।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> <meta-data android:name="cow" android:value="@string/moo"/> <meta-data android:name="duck" android:value="@string/quack"/> </activity-alias>
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias" tools:node="replace"> <meta-data android:name="fox" android:value="@string/dingeringeding"/> </activity-alias>
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity-alias android:name="com.example.alias"> <meta-data android:name="fox" android:value="@string/dingeringeding"/> </activity-alias>
-
tools:node="strict" - নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের এই উপাদানটি উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের উপাদানের সাথে হুবহু মেলে না (অন্যান্য মার্জ নিয়ম মার্কার দ্বারা সমাধান না হলে) যে কোনো সময় একটি বিল্ড ব্যর্থতা তৈরি করুন। এটি মার্জ দ্বন্দ্ব হিউরিস্টিকসকে ওভাররাইড করে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে একটি অতিরিক্ত বৈশিষ্ট্য অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে, তবে বিল্ড ব্যর্থ হয় (যেখানে ডিফল্ট আচরণ একত্রিত ম্যানিফেস্টে অতিরিক্ত বৈশিষ্ট্য যুক্ত করে)।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity>
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait" tools:node="strict"> </activity>
এটি একটি ম্যানিফেস্ট মার্জ ত্রুটি তৈরি করে। দুটি ম্যানিফেস্ট উপাদান কঠোর মোডে মোটেও আলাদা হতে পারে না। এই পার্থক্যগুলি সমাধান করতে আপনাকে অবশ্যই অন্যান্য মার্জ নিয়ম মার্কারগুলি প্রয়োগ করতে হবে৷ (
tools:node="strict"ব্যতীত, এই দুটি ফাইল ত্রুটি ছাড়াই একসাথে একত্রিত হতে পারে, যেমনtools:node="merge"এর উদাহরণে দেখানো হয়েছে।)
বৈশিষ্ট্য চিহ্নিতকারী
পরিবর্তে একটি ম্যানিফেস্ট ট্যাগের নির্দিষ্ট বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলিতে একটি মার্জ নিয়ম প্রয়োগ করতে, নিম্নলিখিত বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি ব্যবহার করুন৷ প্রতিটি বৈশিষ্ট্য কমা দ্বারা পৃথক করা এক বা একাধিক বৈশিষ্ট্যের নাম (অ্যাট্রিবিউট নেমস্পেস সহ) গ্রহণ করে।
-
tools:remove=" attr, ... " - মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্ট থেকে নির্দিষ্ট বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি সরান৷ যখন নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলে এই বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে এবং আপনি নিশ্চিত করতে চান যে সেগুলি মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টে যাবে না।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged">
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait" tools:remove="android:windowSoftInputMode">
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait">
-
tools:replace=" attr, ... " - নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে নির্দিষ্ট বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলিকে এই ম্যানিফেস্টের সাথে প্রতিস্থাপন করুন৷ অন্য কথায়, সর্বদা উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশের মান রাখুন।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:theme="@oldtheme" android:exported="false" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged">
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:theme="@newtheme" android:exported="true" android:screenOrientation="portrait" tools:replace="android:theme,android:exported">
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:theme="@newtheme" android:exported="true" android:screenOrientation="portrait" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged">
-
tools:strict=" attr, ... " - নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের এই বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টের বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলির সাথে হুবহু মেলে না তখনই একটি বিল্ড ব্যর্থতা তৈরি করুন৷ মার্জ কনফ্লিক্ট হিউরিস্টিকসে বর্ণিত বিশেষ আচরণ ব্যতীত সকল বৈশিষ্ট্যের জন্য এটি ডিফল্ট আচরণ।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="landscape"> </activity>
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:screenOrientation="portrait" tools:strict="android:screenOrientation"> </activity>
এটি একটি ম্যানিফেস্ট মার্জ ত্রুটি তৈরি করে। দ্বন্দ্ব সমাধানের জন্য আপনাকে অবশ্যই অন্যান্য মার্জ নিয়ম মার্কার প্রয়োগ করতে হবে। এটি ডিফল্ট আচরণ, তাই স্পষ্টভাবে
tools:strict="screenOrientation"।
আপনি একটি উপাদানে একাধিক মার্কার প্রয়োগ করতে পারেন, যেমনটি নিম্নলিখিত উদাহরণে দেখানো হয়েছে:
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:theme="@oldtheme" android:exported="false" android:allowTaskReparenting="true" android:windowSoftInputMode="stateUnchanged">
উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার প্রকাশ:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:theme="@newtheme" android:exported="true" android:screenOrientation="portrait" tools:replace="android:theme,android:exported" tools:remove="android:windowSoftInputMode">
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফলাফল:
<activity android:name="com.example.ActivityOne" android:theme="@newtheme" android:exported="true" android:allowTaskReparenting="true" android:screenOrientation="portrait">
মার্কার নির্বাচক
আপনি যদি শুধুমাত্র একটি নির্দিষ্ট আমদানি করা লাইব্রেরিতে মার্জ নিয়ম মার্কার প্রয়োগ করতে চান, তাহলে লাইব্রেরি প্যাকেজ নামের সাথে tools:selector অ্যাট্রিবিউট যোগ করুন।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, নিম্নোক্ত ম্যানিফেস্টের সাথে, remove রিমুভ করার নিয়মটি তখনই প্রয়োগ করা হয় যখন নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলটি com.example.lib1 লাইব্রেরি থেকে হয়:
<permission android:name="permissionOne" tools:node="remove" tools:selector="com.example.lib1">
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট অন্য কোনো উৎস থেকে হলে, মার্জ remove নিয়ম উপেক্ষা করা হয়।
দ্রষ্টব্য: আপনি যদি এটি একটি বৈশিষ্ট্য চিহ্নিতকারীর সাথে ব্যবহার করেন, তাহলে এটি মার্কারে নির্দিষ্ট করা সমস্ত বৈশিষ্ট্যের ক্ষেত্রে প্রযোজ্য।
আমদানি করা লাইব্রেরির জন্য <uses-sdk> ওভাররাইড করুন
ডিফল্টরূপে, প্রধান ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলের চেয়ে বেশি একটি minSdk মান সহ একটি লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করার সময়, একটি ত্রুটি ঘটে এবং লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করা যায় না।
মার্জার টুলটি এই বিরোধকে উপেক্ষা করতে এবং আপনার অ্যাপের নিম্ন minSdk মান রেখে লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করতে, <uses-sdk> ট্যাগে overrideLibrary অ্যাট্রিবিউট যোগ করুন। অ্যাট্রিবিউটের মান এক বা একাধিক লাইব্রেরি প্যাকেজের নাম হতে পারে (কমা দ্বারা পৃথক করা), লাইব্রেরিগুলি নির্দেশ করে যেগুলি প্রধান ম্যানিফেস্টের minSdk ওভাররাইড করতে পারে।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি আপনার অ্যাপের প্রধান ম্যানিফেস্ট overrideLibrary এইভাবে প্রয়োগ করে:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.app" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"> <uses-sdk tools:overrideLibrary="com.example.lib1, com.example.lib2"/> ...
তারপরে <uses-sdk> ট্যাগ সংক্রান্ত কোনো ত্রুটি ছাড়াই নিম্নলিখিত ম্যানিফেস্টকে মার্জ করা যেতে পারে এবং মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্ট অ্যাপ ম্যানিফেস্ট থেকে minSdk="2" রাখে।
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.lib1"> <uses-sdk android:minSdk="4" /> ...
অন্তর্নিহিত সিস্টেম অনুমতি
কিছু অ্যান্ড্রয়েড এপিআই যা একসময় অ্যাপের মাধ্যমে অবাধে অ্যাক্সেসযোগ্য ছিল অ্যান্ড্রয়েডের সাম্প্রতিক সংস্করণে সিস্টেম অনুমতি দ্বারা সীমাবদ্ধ হয়ে গেছে।
এই APIগুলিতে অ্যাক্সেসের আশা করে এমন অ্যাপগুলি ভাঙা এড়াতে, Android এর সাম্প্রতিক সংস্করণগুলি অ্যাপগুলিকে অনুমতি ছাড়াই সেই APIগুলি অ্যাক্সেস করা চালিয়ে যেতে দেয় যদি targetSdkVersion যে সংস্করণটিতে সীমাবদ্ধতা যুক্ত করা হয়েছিল তার চেয়ে কম মান সেট করা থাকে। এই আচরণটি অ্যাপটিকে API-তে অ্যাক্সেসের অনুমতি দেওয়ার জন্য একটি অন্তর্নিহিত অনুমতি দেয়। targetSdkVersion জন্য আলাদা মান আছে এমন মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্ট প্রভাবিত হতে পারে।
যদি নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলের targetSdkVersion জন্য একটি কম মান থাকে যা এটিকে একটি অন্তর্নিহিত অনুমতি প্রদান করে এবং উচ্চ-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্টে একই অন্তর্নিহিত অনুমতি না থাকে (কারণ এর targetSdkVersion যে সংস্করণে সীমাবদ্ধতা যোগ করা হয়েছিল তার সমান বা বেশি), তাহলে মার্জার টুলটি স্পষ্টভাবে সিস্টেমকে যোগ করার অনুমতি দেয়।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি আপনার অ্যাপ targetSdkVersion 4 বা উচ্চতর সেট করে এবং 3 বা তার নিচে সেট করা targetSdkVersion সহ একটি লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করে, মার্জার টুলটি মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টে WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE অনুমতি যোগ করে।
সারণি 2 আপনার মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টে যোগ করা যেতে পারে এমন সমস্ত সম্ভাব্য অনুমতি তালিকাভুক্ত করে:
সারণি 2. একত্রীকরণ সরঞ্জামটি একত্রিত ম্যানিফেস্টে যোগ করতে পারে এমন অনুমতিগুলির তালিকা৷
| নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ঘোষণা করে | মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টে অনুমতি যোগ করা হয়েছে |
|---|---|
targetSdkVersion 3 বা তার কম | WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE , READ_PHONE_STATE |
targetSdkVersion 15 বা তার কম এবং READ_CONTACTS ব্যবহার করছে | READ_CALL_LOG |
targetSdkVersion 15 বা তার কম এবং WRITE_CONTACTS ব্যবহার করছে | WRITE_CALL_LOG |
মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্ট পরিদর্শন করুন এবং দ্বন্দ্ব খুঁজুন
এমনকি আপনি আপনার অ্যাপ তৈরি করার আগে, আপনি আপনার মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্ট কেমন দেখাচ্ছে তার একটি পূর্বরূপ দেখতে পারেন। একটি পূর্বরূপ দেখতে, নিম্নলিখিতগুলি করুন:
- Android স্টুডিওতে, আপনার
AndroidManifest.xmlফাইল খুলুন। - সম্পাদকের নীচে মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ট্যাবে ক্লিক করুন।
মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ভিউ বাম দিকে মার্জ করা ম্যানিফেস্টের ফলাফল এবং ডানদিকে প্রতিটি মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলের তথ্য দেখায়, যেমন চিত্র 2-এ দেখানো হয়েছে।
নিম্ন-অগ্রাধিকার ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলগুলি থেকে যে উপাদানগুলিকে একত্রিত করা হয়েছিল সেগুলি বাম দিকে বিভিন্ন রঙে হাইলাইট করা হয়েছে৷ প্রতিটি রঙের কী ম্যানিফেস্ট সোর্সের অধীনে নির্দিষ্ট করা হয়েছে।
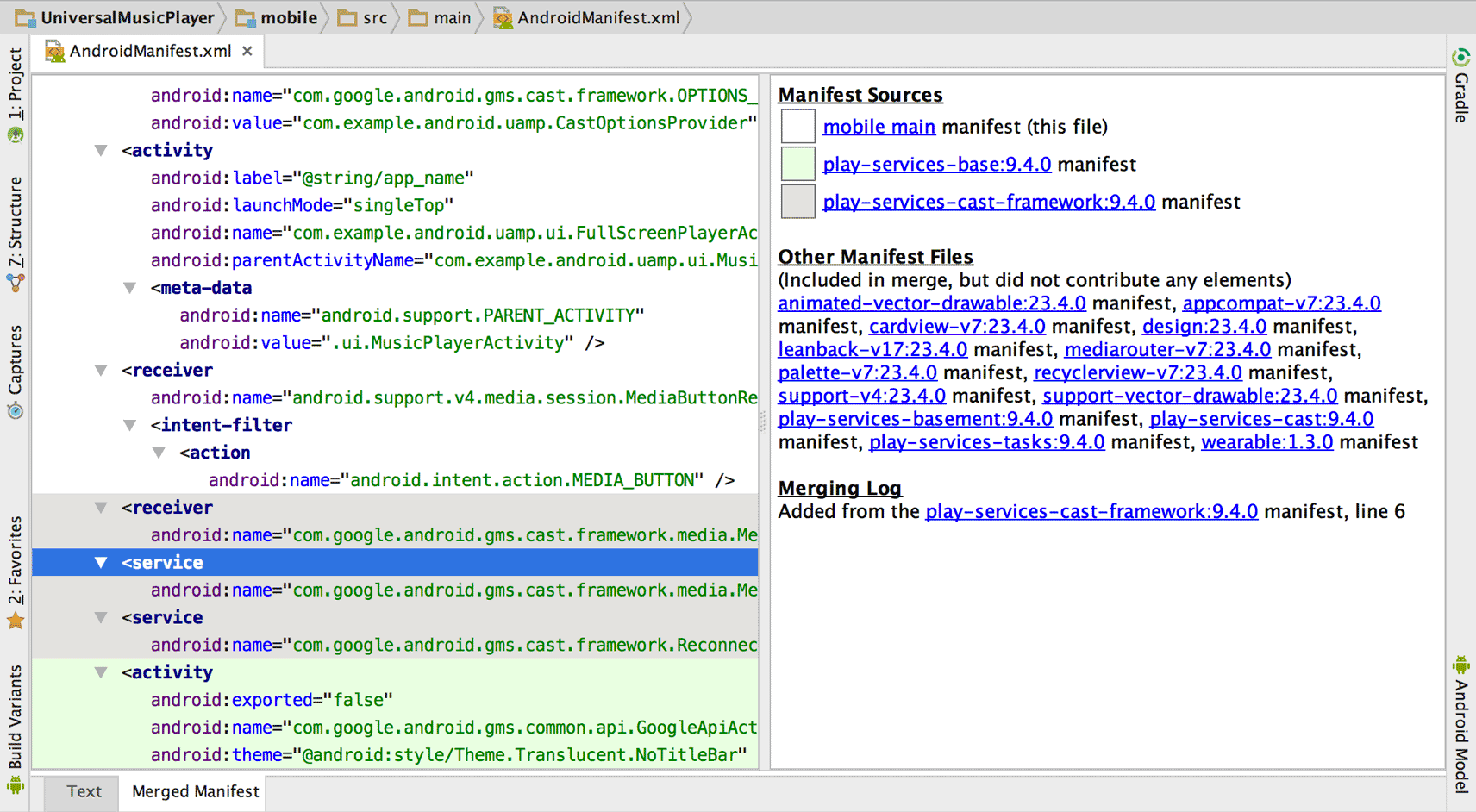
চিত্র 2. মার্জড ম্যানিফেস্ট ভিউ।
ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলগুলি যেগুলি বিল্ডের অংশ ছিল কিন্তু উপাদান বা বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি অবদান রাখে নি অন্য ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলগুলির অধীনে তালিকাভুক্ত করা হয়েছে৷
একটি উপাদান কোথা থেকে এসেছে সে সম্পর্কে তথ্য দেখতে, বাম ফলকে এটিতে ক্লিক করুন এবং মার্জিং লগের অধীনে বিশদটি প্রদর্শিত হবে।
যদি কোনো দ্বন্দ্ব দেখা দেয়, তাহলে মার্জ রুল মার্কার ব্যবহার করে কীভাবে দ্বন্দ্ব সমাধান করা যায় তার জন্য সুপারিশ সহ মার্জিং ত্রুটির অধীনে দেখা যায়।
ইভেন্ট লগ উইন্ডোতেও ত্রুটিগুলি মুদ্রিত হয়। সেগুলি দেখতে, দেখুন > টুল উইন্ডোজ > ইভেন্ট লগ নির্বাচন করুন।
মার্জিং ডিসিশন ট্রির সম্পূর্ণ লগ দেখতে, আপনি আপনার মডিউলের build/outputs/logs/ ডিরেক্টরিতে লগ ফাইলটি খুঁজে পেতে পারেন, যার নাম manifest-merger- buildVariant -report.txt ।
নীতিগুলি একত্রিত করুন
ম্যানিফেস্ট মার্জার টুল যৌক্তিকভাবে প্রতিটি XML উপাদানকে একটি ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইল থেকে অন্য ফাইলের সংশ্লিষ্ট উপাদানের সাথে মেলাতে পারে। একত্রীকরণ একটি ম্যাচ কী ব্যবহার করে প্রতিটি উপাদানের সাথে মেলে, হয় একটি অনন্য বৈশিষ্ট্য মান (যেমন android:name ) অথবা ট্যাগের স্বতন্ত্রতা (উদাহরণস্বরূপ, শুধুমাত্র একটি <supports-screen> উপাদান থাকতে পারে)।
যদি দুটি ম্যানিফেস্টে একই XML উপাদান থাকে, তাহলে টুলটি তিনটি মার্জ নীতির একটি ব্যবহার করে দুটি উপাদানকে একত্রিত করে:
- একত্রিত করুন
- একই ট্যাগে সমস্ত অ-বিরোধী বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলিকে একত্রিত করুন এবং তাদের নিজ নিজ মার্জিং নীতি অনুসারে চাইল্ড উপাদানগুলিকে একত্রিত করুন৷ যদি কোনো বৈশিষ্ট্য একে অপরের সাথে বিরোধিতা করে, তাহলে মার্জ নিয়ম মার্কারগুলির সাথে একত্রিত করুন।
- শুধুমাত্র শিশুদের একত্রীকরণ
- বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলিকে একত্রিত বা মার্জ করবেন না (শুধুমাত্র সর্বোচ্চ অগ্রাধিকার মেনিফেস্ট ফাইল দ্বারা প্রদত্ত বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি রাখুন) এবং তাদের মার্জিং নীতি অনুসারে চাইল্ড উপাদানগুলিকে একত্রিত করুন৷
- রাখা
- উপাদানটিকে যেমন আছে-তাই রেখে দিন এবং মার্জ করা ফাইলের সাধারণ প্যারেন্ট এলিমেন্টে যোগ করুন। এটি শুধুমাত্র তখনই ব্যবহৃত হয় যখন একই উপাদানের একাধিক ঘোষণার জন্য এটি গ্রহণযোগ্য হয়।
সারণি 3 প্রতিটি উপাদানের ধরন, ব্যবহার করা একত্রীকরণ নীতির ধরন এবং দুটি ম্যানিফেস্টের মধ্যে একটি উপাদান মিল নির্ধারণ করতে ব্যবহৃত কী তালিকাভুক্ত করে:
সারণি 3. ম্যানিফেস্ট এলিমেন্ট মার্জ পলিসি এবং ম্যাচ কী
| উপাদান | মার্জ নীতি | ম্যাচ কী |
|---|---|---|
<action> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<activity> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<application> | একত্রিত করুন | প্রতি <manifest> শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে. |
<category> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<data> | একত্রিত করুন | প্রতি <intent-filter> শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে। |
<grant-uri-permission> | একত্রিত করুন | প্রতি <provider> শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে. |
<instrumentation> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<intent-filter> | রাখা | কোন মিল নেই; মূল উপাদানের মধ্যে বেশ কয়েকটি ঘোষণা অনুমোদিত। |
<manifest> | শুধুমাত্র শিশুদের একত্রীকরণ | ফাইল প্রতি শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে. |
<meta-data> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<path-permission> | একত্রিত করুন | প্রতি <provider> শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে. |
<permission-group> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<permission> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<permission-tree> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<provider> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<receiver> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<screen> | একত্রিত করুন | android:screenSize বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<service> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<supports-gl-texture> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<supports-screen> | একত্রিত করুন | প্রতি <manifest> শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে. |
<uses-configuration> | একত্রিত করুন | প্রতি <manifest> শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে. |
<uses-feature> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name অ্যাট্রিবিউট (যদি উপস্থিত না থাকে, তাহলে android:glEsVersion অ্যাট্রিবিউট) |
<uses-library> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<uses-permission> | একত্রিত করুন | android:name বৈশিষ্ট্য |
<uses-sdk> | একত্রিত করুন | প্রতি <manifest> শুধুমাত্র একটি আছে. |
| কাস্টম উপাদান | একত্রিত করুন | কোন মিল নেই; এগুলি মার্জার টুলের কাছে অজানা এবং সর্বদা একত্রিত ম্যানিফেস্টে অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে। |
ম্যানিফেস্টে বিল্ড ভেরিয়েবল ইনজেক্ট করুন
আপনি যদি আপনার AndroidManifest.xml ফাইলে ভেরিয়েবল সন্নিবেশ করতে চান যা আপনার build.gradle ফাইলে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয়েছে, আপনি manifestPlaceholders সম্পত্তির সাথে তা করতে পারেন। এই বৈশিষ্ট্যটি কী-মানের জোড়াগুলির একটি মানচিত্র নেয়, যেমনটি এখানে দেখানো হয়েছে:
গ্রোভি
android { defaultConfig { manifestPlaceholders = [hostName:"www.example.com"] } ... }
কোটলিন
android { defaultConfig { manifestPlaceholders["hostName"] = "www.example.com" } ... }
তারপরে আপনি একটি অ্যাট্রিবিউট মান হিসাবে ম্যানিফেস্ট ফাইলে স্থানধারকগুলির মধ্যে একটি সন্নিবেশ করতে পারেন:
<intent-filter ... >
<data android:scheme="https" android:host="${hostName}" ... />
...
</intent-filter>
ডিফল্টরূপে, বিল্ড টুলগুলি ${applicationId} প্লেসহোল্ডারে আপনার অ্যাপের অ্যাপ্লিকেশন আইডিও প্রদান করে। মান সর্বদা বর্তমান বিল্ডের জন্য চূড়ান্ত অ্যাপ্লিকেশন আইডির সাথে মেলে, বিল্ড ভেরিয়েন্টের পরিবর্তন সহ। এটি উপযোগী যখন আপনি শনাক্তকারীর জন্য একটি অনন্য নামস্থান ব্যবহার করতে চান যেমন একটি অভিপ্রায় ক্রিয়া, এমনকি আপনার বিল্ড ভেরিয়েন্টের মধ্যেও।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি আপনার build.gradle ফাইলটি এরকম দেখায়:
গ্রোভি
android { defaultConfig { applicationId "com.example.myapp" } flavorDimensions "type" productFlavors { free { applicationIdSuffix ".free" dimension "type" } pro { applicationIdSuffix ".pro" dimension "type" } } }
কোটলিন
android { defaultConfig { applicationId = "com.example.myapp" } flavorDimensions += "type" productFlavors { create("free") { applicationIdSuffix = ".free" dimension = "type" } create("pro") { applicationIdSuffix = ".pro" dimension = "type" } } }
তারপরে আপনি এইভাবে আপনার ম্যানিফেস্টে অ্যাপ্লিকেশন আইডি সন্নিবেশ করতে পারেন:
<intent-filter ... >
<action android:name="${applicationId}.TRANSMOGRIFY" />
...
</intent-filter>
এবং আপনি যখন "ফ্রি" পণ্যের স্বাদ তৈরি করেন তখন স্পষ্ট ফলাফল হল:
<intent-filter ... >
<action android:name="com.example.myapp.free.TRANSMOGRIFY" />
...
</intent-filter>
আরও তথ্যের জন্য, আবেদন আইডি সেট করুন পড়ুন।

